Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Electricity
Uploaded by
Rowena ChavezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Electricity
Uploaded by
Rowena ChavezCopyright:
Available Formats
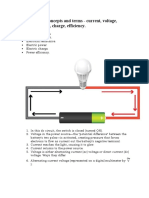
What is electricity? Electricity is a form of energy. Electricity is the flow of electrons.
All matter is made up of atoms, and an atom has a center, called a nucleus. The nucleus contains positively charged particles called protons and uncharged particles called neutrons. The nucleus of an atom is surrounded by negatively charged particles called electrons. The negative charge of an electron is equal to the positive charge of a proton, and the number of electrons in an atom is usually equal to the number of protons. When the balancing force between protons and electrons is upset by an outside force, an atom may gain or lose an electron. When electrons are "lost" from an atom, the free movement of these electrons constitutes an electric current. How does
A thermocouple is a junction between two different metals that produces a voltage related to a temperature difference. Thermocouples are a widely used type of temperature sensor for measurement and control[1] and can also be used to convert heat into electric power. They are inexpensive[2] and interchangeable, are supplied fitted with standard connectors, and can measure a wide range of temperatures. The main limitation is accuracy: system errors of less than one degree Celsius (C) can be difficult to achieve.[3]Any junction of dissimilar metals will produce an electric potential related to temperature. Thermocouples for practical measurement of temperature are junctions of specific alloys which have a predictable and repeatable relationship between temperature and voltage. Photo voltage cell- Reports the development of a new technology for the electrolytic deposition of a metal on a solar cell, without employing an external electric bias field, but by using the internal photo-induced voltage of the solar cell itself. The experimental details of depositing silver over the existing metalized contact structure of the cell and a transparent conducting oxide coating over the entire solar cell front surface are discussed. The proposed technique reduces the consumption of the processing materials and makes the fabrication procedure less expensive and simpler. In electricity generation, an electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. The reverse conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy is done by a motor; motors and generators have many similarities. A generator forces electrons in the windings to flow through the external electrical circuit. It is somewhat analogous to a water pump, which creates a flow of water but does not create the water inside. The source of mechanical energy may be a reciprocating or turbine steam engine, water falling through a turbine or waterwheel, an internal combustion engine, a wind turbine, a hand crank, compressed air or any other source of mechanical energy. An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy.[1] Since the invention of the first battery (or "voltaic pile") in 1800 by Alessandro Volta, batteries have become a common power source for many household and industrial applications. According to a 2005 estimate, the worldwide battery industry generates US$48 billion in sales each year,[2] with 6% annual growth.[3]
There are two types of batteries: primary batteries (disposable batteries), which are designed to be used once and discarded when they are exhausted, and secondary batteries (rechargeable batteries), which are designed to be recharged and used multiple times. Miniature cells are used to power devices such as hearing aids and wristwatches; larger batteries provide standby power for telephone exchanges or computer data centers.
You might also like
- Battery 22Document4 pagesBattery 22abdul ali munderNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument14 pagesPower Plant Engineeringاحمد الربيعيNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electricity and ElectronicsDocument71 pagesFundamentals of Electricity and ElectronicsJude SedaNo ratings yet
- Electric BatteryDocument17 pagesElectric Batterymohan yadavNo ratings yet
- Battery - Energy EducationDocument2 pagesBattery - Energy Educationsam labineNo ratings yet
- ZZZ Battter yDocument12 pagesZZZ Battter yPokemon GoNo ratings yet
- Electric Battery - WikipediaDocument20 pagesElectric Battery - WikipediaCentral LabNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between AC Batteries & DC BatteriesDocument8 pagesThe Difference Between AC Batteries & DC BatteriesabyNo ratings yet
- Electrical Components, Types of Current and CellDocument15 pagesElectrical Components, Types of Current and Cellhk3575568No ratings yet
- K Na Ca MG Al ZN Fe Ni Ti HydroDocument51 pagesK Na Ca MG Al ZN Fe Ni Ti HydroAayush AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Electricity: ElectromagnetismDocument18 pagesElectricity: ElectromagnetismShajara Anglacer AnacanNo ratings yet
- Electronics in Daily LifeDocument40 pagesElectronics in Daily LifeBlind LuvNo ratings yet
- Batteries Electricity Though Chemical ReactionsDocument6 pagesBatteries Electricity Though Chemical ReactionsMuhammad Umar SalmanNo ratings yet
- Electric BatteryDocument20 pagesElectric BatteryANUSHA SINGH V HNo ratings yet
- Generator Are Used To Describe A Device Which Uses Energy From TheDocument5 pagesGenerator Are Used To Describe A Device Which Uses Energy From TheUdayKiranNo ratings yet
- Batteries 2.007 Notes v3Document27 pagesBatteries 2.007 Notes v3jordan JuliusNo ratings yet
- Las Q 1 Week 1 Ste9Document6 pagesLas Q 1 Week 1 Ste9KimmmiNo ratings yet
- Nuclear BatteryDocument26 pagesNuclear BatteryAnanta PatilNo ratings yet
- Transformers & BatteriesDocument8 pagesTransformers & BatteriesUriahs Victor100% (1)
- Electricity Research (Hady G9B)Document4 pagesElectricity Research (Hady G9B)Hady SalehNo ratings yet
- Warren 2Document1 pageWarren 2Leo Ejay Suriaga EjudoNo ratings yet
- BatteryDocument3 pagesBatteryANUSHA SINGH V HNo ratings yet
- GP ProjectDocument19 pagesGP ProjectdhurgeshmalothNo ratings yet
- RW 0004PhotovoltaicsRev5Document4 pagesRW 0004PhotovoltaicsRev5Olawale John AdeotiNo ratings yet
- Research Work - Building Utilities - ElectricalDocument3 pagesResearch Work - Building Utilities - ElectricalKobe AquinoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic and Kinetic Aspects: Electrochemistry: Electrochemical CellDocument23 pagesThermodynamic and Kinetic Aspects: Electrochemistry: Electrochemical CellBasetsana MohlalaNo ratings yet
- Utilities 1 ReviewerDocument11 pagesUtilities 1 ReviewerESCARO, JOSHUA G.No ratings yet
- Half-Cells Anions Anode Cations Cathode Redox Electrolyte: Luigi Galvani Leyden JarDocument3 pagesHalf-Cells Anions Anode Cations Cathode Redox Electrolyte: Luigi Galvani Leyden JarKirstie ImeldaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electricity & Electrical Systems: Prelim Learning ResourcesDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Electricity & Electrical Systems: Prelim Learning ResourcesKib-anne Miguel PasikanNo ratings yet
- Radioisotope Generator: Chain ReactionDocument25 pagesRadioisotope Generator: Chain ReactionDivyanshu nagarNo ratings yet
- U L A B T e yDocument26 pagesU L A B T e yDivyanshu nagarNo ratings yet
- WWW - Seminar: U L A B T E YDocument26 pagesWWW - Seminar: U L A B T E YpankajNo ratings yet
- Areola, ELECTRODocument7 pagesAreola, ELECTROsimeon tayawaNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectricityDocument11 pagesBasic ElectricityFrancess Mae AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Engineering UtilitiesDocument14 pagesEngineering UtilitiesLeo Tocmo TubayNo ratings yet
- Learn Electronics BasicsDocument5 pagesLearn Electronics BasicsstockebrandsolertjNo ratings yet
- Notes EnergyDocument7 pagesNotes EnergyRasha GhabbounNo ratings yet
- Guía 1Document8 pagesGuía 1AlejandroDuranNo ratings yet
- BatteryDocument12 pagesBatteryvinesh6No ratings yet
- Electrical Principles & Technologies: ElectricityDocument50 pagesElectrical Principles & Technologies: ElectricityDorin SumalanNo ratings yet
- Nature of ElectricityDocument64 pagesNature of ElectricityVei AdoptanteNo ratings yet
- Well Come To Session On Basic Electrical Theory: Prolific Systems and Technologies PVT LTDDocument103 pagesWell Come To Session On Basic Electrical Theory: Prolific Systems and Technologies PVT LTDsiddharth1996No ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Concepts and TermsDocument18 pagesBasic Electrical Concepts and TermsMark Jerwin SacapañoNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument161 pagesElectricityamanNo ratings yet
- Battery: Batteries Are Basically Classified Into 2 TypesDocument5 pagesBattery: Batteries Are Basically Classified Into 2 TypesSaurabh ChougaleNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ElectricityDocument86 pagesFundamentals of ElectricityHersal fae Gerardo100% (1)
- Solar Refrigeration Using Peltier EffectDocument15 pagesSolar Refrigeration Using Peltier EffectSyko GamingNo ratings yet
- Battery Wps OfficeDocument5 pagesBattery Wps OfficeTrisha TraigoNo ratings yet
- Intelligent BuildingsDocument11 pagesIntelligent BuildingsJumeirahlyn TutaanNo ratings yet
- Battery Introduction PDFDocument17 pagesBattery Introduction PDFlavanyaNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Clean Energy Storage and Conversion Devices NotesDocument25 pagesUnit-2 Clean Energy Storage and Conversion Devices NotespvnchemNo ratings yet
- Работа №1 Переведите: The Concept of Electrical CurrentDocument5 pagesРабота №1 Переведите: The Concept of Electrical CurrentлюдмилаNo ratings yet
- CE115 Electrical Part ADocument45 pagesCE115 Electrical Part AMrSamspartNo ratings yet
- Engineering Utilities 1 Module 1Document13 pagesEngineering Utilities 1 Module 1Fra KENo ratings yet
- Nuclear Battery: Ajay Mahato, Ajay Kumar Pal, Dr. Bhagwan Shree Ram (Prof.), Mr. Basavareddy (Prof.)Document6 pagesNuclear Battery: Ajay Mahato, Ajay Kumar Pal, Dr. Bhagwan Shree Ram (Prof.), Mr. Basavareddy (Prof.)santhosh kumarNo ratings yet
- Basic Electric Safty: Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Kukatpally, HyderabadDocument74 pagesBasic Electric Safty: Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Kukatpally, HyderabadVimal KumarNo ratings yet
- Subatomic Paricles PracticeDocument3 pagesSubatomic Paricles PracticeRusherNo ratings yet
- Answers To Selected End-of-Chapter Questions and ProblemsDocument83 pagesAnswers To Selected End-of-Chapter Questions and ProblemsBunny SmithNo ratings yet
- Isotopes and Atomic Mass LabDocument4 pagesIsotopes and Atomic Mass LabjustinNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory WorksheetDocument3 pagesAtomic Theory WorksheetSamiha TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Success in Science P2Document103 pagesSuccess in Science P2Nelson Muchindikeniko Phiri80% (5)
- Magnetic Field-H.C.V-1Document3 pagesMagnetic Field-H.C.V-1Kaustubh PurohitNo ratings yet
- Radiologic Science For Technologists Physics Biology and Protection 11th Edition Bushong Test BankDocument26 pagesRadiologic Science For Technologists Physics Biology and Protection 11th Edition Bushong Test Bankcostardrivel.4vwhu100% (11)
- Ether VibrationsDocument67 pagesEther Vibrationsmira003No ratings yet
- The Whys of Subnuclear Physics - Zichichi (Ed)Document1,238 pagesThe Whys of Subnuclear Physics - Zichichi (Ed)marcos.brum1176No ratings yet
- Chapter 2, 3Document35 pagesChapter 2, 3silvanyangelliong2No ratings yet
- BTL CHLTDocument9 pagesBTL CHLTBùi Hữu ĐứcNo ratings yet
- B17CA Student Guide v3Document186 pagesB17CA Student Guide v3Elcan AlmammadovNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 8 GCSEDocument4 pagesWorksheet 8 GCSEMAHJABEEN NASEEMNo ratings yet
- Electricity and-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesElectricity and-WPS OfficeMarionne KrisnahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Midterm 1 Practice With AnswersDocument5 pagesChemistry Midterm 1 Practice With Answerskashaf93No ratings yet
- Chemistry Bridging Course Lecture NotesDocument3 pagesChemistry Bridging Course Lecture NotesNNo ratings yet
- ESE Module 1Document1 pageESE Module 1bruneeNo ratings yet
- Emission of ElectronsDocument8 pagesEmission of ElectronsNivashini VindhyaNo ratings yet
- Richard Modern Physics Solved QuestionsDocument33 pagesRichard Modern Physics Solved Questionsmurugan_kribhcoNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules and IonsDocument27 pagesAtoms, Molecules and IonsRechellu ZamboangnonNo ratings yet
- Sec 2 Term 1 - 1 NotesDocument35 pagesSec 2 Term 1 - 1 NotesWolfie Saraswathi Santhosham100% (1)
- Science Class Ix Term 2Document62 pagesScience Class Ix Term 2Jayashree Krishnakumar PillaiNo ratings yet
- NAT Reviewer ScienceDocument3 pagesNAT Reviewer ScienceRandy100% (1)
- Grade 12 Physics Module5Document75 pagesGrade 12 Physics Module5Epay Castañares LascuñaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Radiologic Science For Technologists 12th Edition by BushongDocument51 pagesTest Bank For Radiologic Science For Technologists 12th Edition by Bushongmarcuskenyatta275No ratings yet
- Gauss Lab 03Document2 pagesGauss Lab 03Diego Giraldo BoteroNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 A Notes PDFDocument67 pagesChemistry Form 4 A Notes PDFCabdicasiis Maxamuud Guuleed95% (20)
- 5070 Chemistry ECR v1.1 080316Document153 pages5070 Chemistry ECR v1.1 080316warisNo ratings yet
- Serway Physics For Scientists EngineersDocument1,540 pagesSerway Physics For Scientists Engineerstobago528100% (3)
- Preparing For PUPCET Some of The FollowiDocument12 pagesPreparing For PUPCET Some of The Followibry yyy100% (2)