Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FIN470 Exam1 Key Solutions
Uploaded by
rquadros21Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FIN470 Exam1 Key Solutions
Uploaded by
rquadros21Copyright:
Available Formats
Exam1 FIN470 Spring 2009 Key
1. A bond which is issued without recording of the owner's name and for which payments are made to whomever has physical possession of the bond is said to be in: A. registered form. B. bearer form. C. collateral status. D. new-issue condition. E. debenture status.
Ross - Chapter 007 #9 SECTION: 7.2 TOPIC: BEARER FORM TYPE: DEFINITIONS
2. Your _____ tax rate is the amount of tax payable on the next taxable dollar you earn. A. total B. mean C. residual D. marginal E. average
Ross - Chapter 002 #9 SECTION: 2.3 TOPIC: MARGINAL TAX RATES TYPE: DEFINITIONS
3. Frank invests $2,500 in an account that pays 6 percent simple interest. How much money will he have at the end of four years? A. $3,163 B. $3,100 C. $2,650 D. $10,600 E. $3,156 Ending value = $2,500 + ($2,500 .06 4) = $3,100.00
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 005 #16 SECTION: 5.1 TOPIC: SIMPLE INTEREST TYPE: PROBLEMS
4. The Smith Co., which is currently operating at full capacity, has sales of $3,000, current assets of $800, current liabilities of $400, net fixed assets of $1,900, and a 6 percent profit margin. The firm has no long-term debt and does not plan on acquiring any. The firm does not pay any dividends. Sales are expected to increase by 9 percent next year. If all assets, liabilities, and costs vary directly with sales, how much additional equity financing is required for next year? A. $10.80 B. $196.20 C. $103.50 D. $40.00 E. $207.00 Projected assets = ($800 + $1,900) 1.09 = $2,943 Projected liabilities = $400 1.09 = $436 Current equity = $800 + $1,900 $400 = $2,300 Projected increase in retained earnings = $3,000 .06 1.09 = $196.20 Equity funding need = $2,943 $436 $2,300 $196.20 = $10.80
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 004 #45 SECTION: 4.2 TOPIC: PRO FORMA STATEMENTS TYPE: PROBLEMS
5. Which one of the following statements concerning the annual percentage rate is correct? A. The effective annual rate is lower than the annual percentage rate when an interest rate is compounded quarterly. B. When firms advertise the annual percentage rate they are violating U.S. truth-in-lending laws. C. The annual percentage rate considers interest on interest. D. The rate of interest you actually pay on a loan is called the annual percentage rate. E. The annual percentage rate equals the effective annual rate when the rate on an account is designated as simple interest.
Ross - Chapter 006 #17 SECTION: 6.3 TOPIC: ANNUAL PERCENTAGE RATE TYPE: CONCEPTS
6. A loan where the borrower pays interest each period, and repays some or all of the principal of the loan over time is called a(n) _____ loan. A. balloon B. continuous C. amortized D. interest-only E. pure discount
Ross - Chapter 006 #11 SECTION: 6.4 TOPIC: AMORTIZED LOAN TYPE: DEFINITIONS
7. Gerald's Manufacturing is operating at 78 percent of its fixed asset capacity and has current sales of $575,000. How fast can the firm grow before any new fixed assets are needed? A. 44.00 percent B. 31.16 percent C. 28.21 percent D. 22.00 percent E. 37.00 percent Full-capacity sales = $575,000 / .78 = $737,179.49; Maximum growth without additional assets = ($737,179.49 / $575,000) 1 = .28205 = 28.21 percent
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 004 #51 SECTION: 4.3 TOPIC: FULL CAPACITY SALES AND FIXED ASSETS TYPE: PROBLEMS
8. When constructing a pro forma statement, net working capital generally: A. varies only if the firm is producing at less than full capacity. B. remains fixed. C. varies only if the firm maintains a fixed debt-equity ratio. D. varies proportionately with sales. E. varies only when the firm is producing at full capacity.
Ross - Chapter 004 #18 SECTION: 4.3 TOPIC: PRO FORMA STATEMENTS TYPE: CONCEPTS
9. An unsecured debt of a firm with a maturity of less than 10 years is called a(n): A. debenture. B. blanket bond. C. unfunded liability. D. note. E. sinking fund.
Ross - Chapter 007 #11 SECTION: 7.2 TOPIC: NOTE TYPE: DEFINITIONS
10. A business entity which taxes it owners like partners while providing those owners with limited liability is called a: A. general partnership. B. limited proprietorship. C. corporation. D. sole proprietorship. E. limited liability company.
Ross - Chapter 001 #13 SECTION: 1.2 TOPIC: LIMITED LIABILITY COMPANY TYPE: DEFINITIONS
11. Which one of the following is a use of cash? A. payment received from a customer on his or her account B. decrease in the cash balance C. payment to a supplier D. sale of common stock E. sale of inventory to a cash customer
Ross - Chapter 003 #39 SECTION: 3.1 TOPIC: USES OF CASH TYPE: CONCEPTS
12. The discount rate that makes the net present value of an investment exactly equal to zero is called the: A. external rate of return. B. profitability index. C. internal rate of return. D. equalizer. E. average accounting return.
Ross - Chapter 009 #6 SECTION: 9.5 TOPIC: INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN TYPE: DEFINITIONS
13. Which one of the following will increase the net present value of a project? A. an increase in the discount rate B. increasing the amount of the initial cash outflow C. decreasing the required rate of return D. having all incoming cash flows occur in the final year of a project rather than periodically over a five-year period E. decreasing the amount of each cash inflow
Ross - Chapter 009 #12 SECTION: 9.1 TOPIC: NET PRESENT VALUE TYPE: CONCEPTS
14. An annuity is a(n): A. level stream of perpetual cash flows. B. decreasing stream of cash flows occurring for a fixed period of time. C. increasing stream of cash flows occurring for a fixed period of time. D. increasing stream of perpetual cash flows. E. level stream of cash flows occurring for a fixed period of time.
Ross - Chapter 006 #1 SECTION: 6.2 TOPIC: ANNUITY TYPE: DEFINITIONS
15. Which one of the following is a source of cash? A. an increase in accounts payable B. a purchase of inventory C. an increase in cash D. a credit sale to a customer E. the payoff of a loan
Ross - Chapter 003 #37 SECTION: 3.1 TOPIC: SOURCES OF CASH TYPE: CONCEPTS
16. The underlying assumption of the dividend growth model is that a stock is worth: A. an amount computed as the next annual dividend divided by the market rate of return. B. the present value of the future cash flows which it generates. C. the same amount as any other stock that pays the same current dividend and has the same required rate of return. D. the same amount to every investor regardless of the investor's desired rate of return. E. an amount computed as the next annual dividend divided by the required rate of return.
Ross - Chapter 008 #29 SECTION: 8.1 TOPIC: DIVIDEND GROWTH MODEL TYPE: CONCEPTS
17. Raoul has $800 today. Which one of the following statements is correct if he invests this money at a positive rate of interest for ten years? Assume the interest is compounded annually. A. If Raoul can earn 7 percent, he will have to wait about six years to have $1,600 total. B. The higher the interest rate, the longer he has to wait for his money to grow to $2,000 in value. C. At 7.2 percent interest, Raoul should expect to have about $1,600 in his account at the end of the ten years. D. At the end of the ten years, Raoul will have less money if he invests at 9 percent rather than at 8 percent. E. The higher the interest rate he earns, the less money he will have in the future.
Ross - Chapter 005 #15 SECTION: 5.1 TOPIC: RULE OF 72 TYPE: CONCEPTS
18. You just settled an insurance claim. The settlement calls for increasing payments over a 5-year period. The first payment will be paid one year from now in the amount of $30,000. The following payments will increase by 6 percent annually. What is the value of this settlement to you today if you can earn 8.5 percent on your investments? A. $141,414.14 B. $152,008.16 C. $126,408.28 D. $132,023.05 E. $129,417.11
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 006 #64 SECTION: 6.2 TOPIC: GROWING ANNUITY PRESENT VALUE TYPE: PROBLEMS
19. The higher the degree of financial leverage employed by a firm, the: A. lower the balance in accounts payable. B. higher the number of outstanding shares of stock. C. lower the amount of debt incurred. D. less debt a firm has per dollar of total assets. E. higher the probability that the firm will encounter financial distress.
Ross - Chapter 002 #31 SECTION: 2.1 TOPIC: FINANCIAL LEVERAGE TYPE: CONCEPTS
20. A business formed by two or more individuals who each have unlimited liability for all of the firm's business debts is called a: A. corporation. B. limited liability company. C. sole proprietorship. D. limited partnership. E. general partnership.
Ross - Chapter 001 #7 SECTION: 1.2 TOPIC: GENERAL PARTNERSHIP TYPE: DEFINITIONS
21. Six years ago, Thompson Distributors purchased a mailing machine at a cost of $368,000. This equipment is currently valued at $172,200 on today's balance sheet but could actually be sold for $211,400. This is the only fixed asset the firm owns. Net working capital is $121,000 and long-term debt is $82,500. What is the book value of shareholders' equity? A. $89,700 B. $406,500 C. $249,900 D. $211,400 E. $210,700 Book value of shareholders' equity = $172,200 + $121,000 $82,500 = $210,700
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 002 #53 SECTION: 2.1 TOPIC: BOOK VALUE TYPE: PROBLEMS
22. A 7 percent preferred stock pays a total of _____ a year in dividends per share. Assume dividends are paid quarterly. A. $21.00 B. $3.50 C. $28.00 D. $7.00 E. $14.00
Ross - Chapter 008 #46 SECTION: 8.2 TOPIC: PREFERRED STOCK TYPE: CONCEPTS
23. The difference between a firm's current assets and its current liabilities is called: A. net working capital. B. operating cash flow. C. capital spending. D. cash flow from assets. E. cash flow to creditors.
Ross - Chapter 002 #13 SECTION: 2.1 TOPIC: NET WORKING CAPITAL TYPE: DEFINITIONS
24. The price a dealer is willing to pay for a security is called the: A. bid price. B. asked price. C. auction price. D. equilibrium price. E. bid-ask spread.
Ross - Chapter 007 #19 SECTION: 7.5 TOPIC: BID PRICE TYPE: DEFINITIONS
25. Tracie deposits $5,000 into an account that pays 3 percent interest compounded annually. Chris deposits $5,000 into an account that pays 3 percent simple interest. Both deposits were made this morning. Which of the following statements are true concerning these two accounts? I. At the end of one year, both Tracie and Chris will have the same amount in their accounts. II. At the end of five years, Tracie will have more money in her account than Chris has in his. III. Chris will never earn any interest on interest. IV. All else equal, Chris made the better investment. A. I, III, and IV only B. III and IV only C. II, III, and IV only D. I, II, and III only E. I and II only
Ross - Chapter 005 #13 SECTION: 5.1 TOPIC: SIMPLE VERSUS COMPOUND INTEREST TYPE: CONCEPTS
26. The primary market is the market in which: A. a particular security tends to trade the most frequently. B. trades occur on the floor of the NYSE only. C. all securities which are included in the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) must trade. D. newly issued securities are offered for sale. E. shareholders who are also company officers offer their securities for sale.
Ross - Chapter 001 #17 SECTION: 1.5 TOPIC: PRIMARY MARKET TYPE: DEFINITIONS
27. A firm has sales of $1,640, net income of $135, net fixed assets of $1,200, and current assets of $530. The firm has $280 in inventory. What is the common-size statement value of inventory? A. 30.42 percent B. 16.18 percent C. 15.68 percent D. 15.01 percent E. 52.83 percent Common-size inventory = $280 ($1,200 + $530) = .1618497 = 16.18 percent
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 003 #75 SECTION: 3.2 TOPIC: COMMON-SIZE STATEMENTS TYPE: PROBLEMS
28. What is the future value of $3,497 invested for 15 years at 7.5 percent compounded annually? A. $10,347.19 B. $14,911.08 C. $7,431.13 D. $14,289.16 E. $15,267.21 Future value = $3,497 (1 + .075)15 = $10,347.19
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 005 #20 SECTION: 5.1 TOPIC: FUTURE VALUE TYPE: PROBLEMS
29. Baker's Men's Wear has a 5.5 percent, semiannual coupon bond outstanding with a current market price of $978.90. The bond has a par value of $1,000 and a yield to maturity of 5.76 percent. How many years is it until this bond matures? A. 27.21 years B. 22.19 years C. 11.10 years D. 12.27 years E. 44.38 years
; It's easiest to solve this problem is using financial calculator. You can then use the calculator answer as the time period in the formula just to verify that your answer is correct.
The number of six-month periods is 22.191. The number of years is 11.0955 = 11.10 years.
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 007 #90 SECTION: 7.1 TOPIC: TIME TO MATURITY OF COUPON BOND TYPE: PROBLEMS
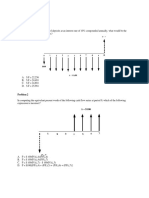
30. Flagler Stores is analyzing a project with the following cash flows. Should this project be accepted based on the discounting approach to the modified internal rate of return if the discount rate is 12 percent? Why or why not?
A. No; The MIRR is 13.48 percent. B. Yes; The MIRR is 23.67 percent. C. No; The MIRR is 11.92 percent. D. Yes; The MIRR is 13.48 percent. E. Yes: The MIRR is 18.77 percent. The modified cash flows will be:
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 009 #66 SECTION: 9.5 TOPIC: MODIFIED INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN TYPE: PROBLEMS
31. As the discount rate increases, the present value of $2,000 to be received four years from now: A. also increases. B. becomes negative. C. will vary but the direction of the change is unknown. D. remains constant. E. decreases.
Ross - Chapter 005 #11 SECTION: 5.2 TOPIC: PRESENT VALUE AND DISCOUNT RATE TYPE: CONCEPTS
32. According to the statement of cash flows, an increase in accounts receivable will _____ the cash flow from _____ activities. A. increase; operating B. increase; investment C. decrease; operating D. decrease; financing E. increase; financing
Ross - Chapter 003 #41 SECTION: 3.1 TOPIC: STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS TYPE: CONCEPTS
33. A bond that pays interest annually yields a 6.875 percent rate of return. The inflation rate for the same period is 4.35 percent. What is the real rate of return on this bond? A. 2.64 percent B. 2.42 percent C. 2.61 percent D. 2.53 percent E. 2.38 percent
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 007 #107 SECTION: 7.6 TOPIC: FISHER EFFECT TYPE: PROBLEMS
34. Peter owns The Train Store which he is trying to sell so that he can retire and travel. The Train Store owns the building in which it is located. This building was built at a cost of $427,000 and is currently appraised at $575,000. The display counters and fixtures originally cost $87,000 and are currently valued at $49,000. The inventory is valued on the balance sheet at $289,000 and has a retail market value equal to 1.4 times its cost. Peter expects the store to collect 97 percent of the $48,041 in accounts receivable. The firm has $11,200 in cash and has total debt of $167,400. What is the market value of this firm? A. $907,800 B. $957,000 C. $945,800 D. $771,000 E. $919,000 Market value of firm = $575,000 + $49,000 + 1.4($289,000) + .97($48,041) + $11,200 $167,400 = $919,000
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 002 #54 SECTION: 2.1 TOPIC: MARKET VALUE TYPE: PROBLEMS
35. The tax rates are as shown. California Surfin' currently has taxable income of $86,750. How much additional tax will the firm owe if taxable income increases by $16,500?
A. $5,773 B. $6,212 C. $5,811 D. $6,435 E. $6,120 Additional tax = .34($100,000 $86,750) + .39($86,750 + $16,500 $100,000) = $5,772.50 = $5,773
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 002 #58 SECTION: 2.3 TOPIC: TAXES TYPE: PROBLEMS
36. The voting procedure where a shareholder grants authority to another individual to vote his or her shares is called _____ voting. A. proxy B. democratic C. straight D. deferred E. cumulative
Ross - Chapter 008 #7 SECTION: 8.2 TOPIC: PROXY TYPE: DEFINITIONS
37. What is the net present value of a project that has an initial cash outflow of $18,900 and the following cash inflows? The required return is 13.25 percent.
A. $3,109.16 B. -$4,847.47 C. -$2,636.21 D. $4,052.53 E. -$3,840.60
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 009 #58 SECTION: 9.1 TOPIC: NET PRESENT VALUE TYPE: PROBLEMS
38. Which one of the following is a capital budgeting decision? A. deciding whether or not a newly invented product should be produced B. ascertaining the minimum amount of cash which should be kept on hand C. determining the optimal level of inventory to be maintained D. deciding whether a bank loan should be secured or if bonds should be issued E. determining how many bonds versus how many shares of stock should be issued
Ross - Chapter 009 #11 SECTION: CHAPTER 9 INTRODUCTION TOPIC: CAPITAL BUDGETING DECISIONS TYPE: CONCEPTS
39. The dividends paid by a corporation: I. to an individual become taxable income of that individual. II. reduce the taxable income of the corporation. III. are declared by the chief financial officer of the corporation. IV. to another corporation receive preferential tax treatment. A. I and IV only B. I only C. I, II, and IV only D. I, III, and IV only E. II and III only
Ross - Chapter 008 #44 SECTION: 8.2 TOPIC: DIVIDENDS TYPE: CONCEPTS
40. J&J Exporters paid a $1.80 per share annual dividend last month. The company is planning on paying $2.00, $2.50, $2.75, and $3.00 a share over the next four years, respectively. After that the dividend will be constant at $3.20 per share per year. What is the market price of this stock if the market rate of return is 13 percent? A. $7.47 B. $15.96 C. $24.37 D. $22.57 E. $20.73
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 008 #82 SECTION: 8.1 TOPIC: SUPERNORMAL GROWTH TYPE: PROBLEMS
41. The sustainable growth rate of a firm is best described as the: A. maximum growth rate achievable without any limits on the level of debt financing. B. maximum growth rate achievable without external financing of any kind. C. minimum growth rate achievable if the firm maintains a constant equity multiplier. D. maximum growth rate achievable without using any external equity financing while maintaining a constant debt-equity ratio. E. minimum growth rate achievable if the firm does not pay out any cash dividends.
Ross - Chapter 004 #8 SECTION: 4.4 TOPIC: SUSTAINABLE GROWTH RATE TYPE: DEFINITIONS
42. Which one of the following statements concerning a sole proprietorship is correct? A. The profits of a sole proprietorship are taxed twice. B. A sole proprietorship is often structured as a limited liability company. C. The owners of a sole proprietorship share profits as established by the partnership agreement. D. The owner of a sole proprietorship may be forced to sell his or her personal assets to pay company debts. E. A sole proprietorship is designed to protect the personal assets of the owner.
Ross - Chapter 001 #30 SECTION: 1.2 TOPIC: SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP TYPE: CONCEPTS
43. Priestly Engineers wants to save $145,000 to buy some new equipment two years from now. The plan is to set aside an equal amount of money on the first day of each quarter starting today. The firm can earn a 5.5 percent rate of return. How much does the firm have to save each quarter to achieve their goal? A. $17,084.43 B. $17,270.60 C. $17,036.35 D. $17,421.18 E. $17,308.67
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 006 #51 SECTION: 6.2 TOPIC: ANNUITY DUE PAYMENTS AND FUTURE VALUE TYPE: PROBLEMS
44. You just received $278,000 from an insurance settlement. You have decided to set this money aside and invest it for your retirement. Currently, your goal is to retire 38 years from today. How much more will you have in your account on the day you retire if you can earn an average return of 9.5 percent rather than just 9.0 percent? A. $1,818,342 B. $1,611,408 C. $2,033,333 D. $1,396,036 E. $794,014 Future value = $278,000 (1 + .095)38 = $8,745,433.15; Future value = $278,000 $7,349,397.17; Difference = $8,745,433.15 $7,349,397.17 = $1,396,036 (1 + .09)38 =
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 005 #41 SECTION: 5.1 AND 5.3 TOPIC: FUTURE VALUE AND RATE CHANGES TYPE: PROBLEMS
45. A firm generated net income of $624. The depreciation expense was $58 and dividends were paid in the amount of $72. Accounts payables decreased by $28, accounts receivables increased by $16, inventory increased by $41, and net fixed assets increased by $28. What was the net cash flow from operating activity? A. $597 B. $641 C. $608 D. $553 E. $497 Net cash from operating activities = $624 + $58 $28 $16 $41 = $597
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 003 #74 SECTION: 3.1 TOPIC: SOURCES AND USES OF CASH TYPE: PROBLEMS
46. The financial planning method in which accounts vary depending on a firm's predicted sales level is called the _____ approach. A. common-size B. sales reconciliation C. percentage of sales D. time-trend E. sales dilution
Ross - Chapter 004 #3 SECTION: 4.3 TOPIC: PERCENTAGE OF SALES APPROACH TYPE: DEFINITIONS
47. Monika's Gift Barn has cash of $316, accounts receivable of $687, accounts payable of $709, and inventory of $2,108. What is the value of the quick ratio? A. 4.38 B. .71 C. 1.41 D. .23 E. .45 Quick ratio = ($316 + $687) $709 = 1.41
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 003 #78 SECTION: 3.3 TOPIC: LIQUIDITY RATIOS TYPE: PROBLEMS
48. A market where brokers and agents match buyers with sellers is called a(n): A. OTC market. B. liquidation market. C. primary market. D. auction market. E. dealer market.
Ross - Chapter 001 #20 SECTION: 1.5 TOPIC: AUCTION MARKET TYPE: DEFINITIONS
49. Your firm currently has $1,800 in sales and is operating at 60 percent of the firm's capacity. What is the full capacity level of sales? A. $720 B. $4,500 C. $1,080 D. $2,880 E. $3,000 Full-capacity sales = $1,800 / .60 = $3,000
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 004 #47 SECTION: 4.3 TOPIC: FULL CAPACITY SALES LEVEL TYPE: PROBLEMS
50. The process of identifying projects which will produce positive cash flows is called: A. capital structure. B. agency cost analysis. C. financial depreciation. D. working capital management. E. capital budgeting.
Ross - Chapter 001 #3 SECTION: 1.1 TOPIC: CAPITAL BUDGETING TYPE: DEFINITIONS
51. What is the internal rate of return on an investment with the following cash flows?
A. 12.23 percent B. 6.00 percent C. 12.00 percent D. 12.70 percent E. 6.93 percent
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 009 #62 SECTION: 9.5 TOPIC: INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN TYPE: PROBLEMS
52. A 15-year, 6 percent coupon bond pays interest annually. The bond has a face value of $1,000. What is the change in the price of this bond if the market yield to maturity rises to 6.5 percent from the current rate of 6.25 percent? A. 2.50 percent decrease B. 2.43 percent increase C. 2.37 percent increase D. 2.37 percent decrease E. 2.43 percent decrease
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 007 #94 SECTION: 7.1 TOPIC: INTEREST RATE RISK TYPE: PROBLEMS
53. Shares of common stock of the Windy Farms offer an expected total return of 13.8 percent. The dividend is increasing at a constant 4.2 percent per year. What is the dividend yield? A. 8.70 percent B. 9.60 percent C. 18.0 percent D. 12.2 percent E. 15.5 percent Dividend yield = .138 .042 = 9.6 percent
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 008 #69 SECTION: 8.1 TOPIC: DIVIDEND YIELD TYPE: PROBLEMS
54. Your parents are giving you $500 a month for five years while you attend college to earn both a bachelor's and a master's degree. At a 7 percent discount rate, what are these payments worth to you when you first enter college? A. $25,251.00 B. $27,209.17 C. $24,601.18 D. $30,000.00 E. $22,681.13
AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 006 #24 SECTION: 6.2 TOPIC: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUE TYPE: PROBLEMS
Exam1 FIN470 Spring 2009 Summary
Category AACSB TOPIC: ANALYTIC Ross - Chapter 001 Ross - Chapter 002 Ross - Chapter 003 Ross - Chapter 004 Ross - Chapter 005 Ross - Chapter 006 Ross - Chapter 007 Ross - Chapter 008 Ross - Chapter 009 SECTION: 1.1 SECTION: 1.2 SECTION: 1.5 SECTION: 2.1 SECTION: 2.3 SECTION: 3.1 SECTION: 3.2 SECTION: 3.3 SECTION: 4.2 SECTION: 4.3 SECTION: 4.4 SECTION: 5.1 SECTION: 5.1 AND 5.3 SECTION: 5.2 SECTION: 6.2 SECTION: 6.3 SECTION: 6.4 SECTION: 7.1 SECTION: 7.2 SECTION: 7.5 SECTION: 7.6 SECTION: 8.1 SECTION: 8.2 SECTION: 9.1 SECTION: 9.5 SECTION: CHAPTER 9 INTRODUCTION TOPIC: AMORTIZED LOAN TOPIC: ANNUAL PERCENTAGE RATE TOPIC: ANNUITY TOPIC: ANNUITY DUE PAYMENTS AND FUTURE VALUE TOPIC: AUCTION MARKET TOPIC: BEARER FORM TOPIC: BID PRICE TOPIC: BOOK VALUE TOPIC: CAPITAL BUDGETING # of Questions 23 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 6 1 3 2 4 2 4 1 1 1 4 1 4 1 1 4 1 1 2 2 1 1 3 3 2 3 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
TOPIC: CAPITAL BUDGETING DECISIONS TOPIC: COMMON-SIZE STATEMENTS TOPIC: DIVIDEND GROWTH MODEL TOPIC: DIVIDEND YIELD TOPIC: DIVIDENDS TOPIC: FINANCIAL LEVERAGE TOPIC: FISHER EFFECT TOPIC: FULL CAPACITY SALES AND FIXED ASSETS TOPIC: FULL CAPACITY SALES LEVEL TOPIC: FUTURE VALUE TOPIC: FUTURE VALUE AND RATE CHANGES TOPIC: GENERAL PARTNERSHIP TOPIC: GROWING ANNUITY PRESENT VALUE TOPIC: INTEREST RATE RISK TOPIC: INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN TOPIC: LIMITED LIABILITY COMPANY TOPIC: LIQUIDITY RATIOS TOPIC: MARGINAL TAX RATES TOPIC: MARKET VALUE TOPIC: MODIFIED INTERNAL RATE OF RETURN TOPIC: NET PRESENT VALUE TOPIC: NET WORKING CAPITAL TOPIC: NOTE TOPIC: ORDINARY ANNUITY AND PRESENT VALUE TOPIC: PERCENTAGE OF SALES APPROACH TOPIC: PREFERRED STOCK TOPIC: PRESENT VALUE AND DISCOUNT RATE TOPIC: PRIMARY MARKET TOPIC: PRO FORMA STATEMENTS TOPIC: PROXY TOPIC: RULE OF 72 TOPIC: SIMPLE INTEREST TOPIC: SIMPLE VERSUS COMPOUND INTEREST TOPIC: SOLE PROPRIETORSHIP TOPIC: SOURCES AND USES OF CASH TOPIC: SOURCES OF CASH TOPIC: STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS TOPIC: SUPERNORMAL GROWTH TOPIC: SUSTAINABLE GROWTH RATE TOPIC: TAXES TOPIC: TIME TO MATURITY OF COUPON BOND TOPIC: USES OF CASH TYPE: CONCEPTS TYPE: DEFINITIONS TYPE: PROBLEMS
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 15 16 23
You might also like
- Finance Exam Questions #2Document21 pagesFinance Exam Questions #2Cody Chivas100% (1)
- Quiz Week 1 QnsDocument7 pagesQuiz Week 1 Qnsesraa karamNo ratings yet
- Fin Exam ADocument14 pagesFin Exam AtahaalkibsiNo ratings yet
- Managerial Final ExampleDocument8 pagesManagerial Final ExamplemgiraldovNo ratings yet
- Midterm 3 AnswersDocument7 pagesMidterm 3 AnswersDuc TranNo ratings yet
- Prior Exam 3Document9 pagesPrior Exam 3Brian WangNo ratings yet
- FIN350 in Class Work No. 1 First Name - Last NameDocument8 pagesFIN350 in Class Work No. 1 First Name - Last Nameh1ph9pNo ratings yet
- q4 1Document7 pagesq4 1JimmyChaoNo ratings yet
- Finance 300 Exam ReviewDocument9 pagesFinance 300 Exam ReviewAnaliza ArrofoNo ratings yet
- Sample Questions Midterm 1213Document18 pagesSample Questions Midterm 1213Mei-e Loh0% (1)
- Accounting For Liabilities: Learning ObjectivesDocument39 pagesAccounting For Liabilities: Learning ObjectivesJune KooNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE FINAL EXAM KEYDocument8 pagesPRACTICE FINAL EXAM KEYrahulgattooNo ratings yet
- Review For Exam 1Document18 pagesReview For Exam 1Alva CaldwellNo ratings yet
- 50 Multiple Choice, T/F, & Essay QuestionsDocument24 pages50 Multiple Choice, T/F, & Essay QuestionsManal Elkhoshkhany100% (1)
- Corporate Finance Exam GuideDocument8 pagesCorporate Finance Exam Guideneilpatrel31No ratings yet
- HIGGINS Chapter 7 Financial EvaluationDocument6 pagesHIGGINS Chapter 7 Financial EvaluationParul BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Fin 455 Fall 2017 FinalDocument10 pagesFin 455 Fall 2017 FinaldasfNo ratings yet
- Practice questions for corporate finance examDocument8 pagesPractice questions for corporate finance examSadi0% (1)
- Ebook Corporate Finance 9Th Edition Ross Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Corporate Finance 9Th Edition Ross Test Bank Full Chapter PDFquachhaitpit100% (9)
- Set 1 Problem Solving with Compound Interest CalculationsDocument37 pagesSet 1 Problem Solving with Compound Interest CalculationsSummer Wynn DacwagNo ratings yet
- Winter 2010 Midterm With SolutionsDocument11 pagesWinter 2010 Midterm With Solutionsupload55No ratings yet
- 2102 Practice Exam 1 Fall07Document9 pages2102 Practice Exam 1 Fall07John ShinNo ratings yet
- Finance101 Sample Questions 3a08Document19 pagesFinance101 Sample Questions 3a08Eve LNo ratings yet
- Mul MidtermDocument26 pagesMul Midtermthuylinhdo6624No ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting Tables and ProblemsDocument30 pagesCapital Budgeting Tables and ProblemssofikhdyNo ratings yet
- Fin 3403 Review 2 (ch5,6,7)Document20 pagesFin 3403 Review 2 (ch5,6,7)MichaelFraserNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument31 pagesCapital BudgetingKarlovy Dalin100% (2)
- Practice Qs 2Document24 pagesPractice Qs 2SANCHITA PATINo ratings yet
- TCCB REVISIONDocument44 pagesTCCB REVISION21070119No ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 SolutionsDocument13 pagesProblem Set 1 SolutionsVictor100% (1)
- Ebersoll Manufacturing CoDocument5 pagesEbersoll Manufacturing CoShemu PlcNo ratings yet
- IE 360 Engineering Economic Analysis Sample TestDocument11 pagesIE 360 Engineering Economic Analysis Sample TestjohnhenryyambaoNo ratings yet
- FFL SMU Finance For Law .Sample Exam With SolutionDocument7 pagesFFL SMU Finance For Law .Sample Exam With SolutionAaron Goh100% (1)
- I Pledge That I Will Work On The Examination Without Collaborating With Any Other Individuals. SignatureDocument7 pagesI Pledge That I Will Work On The Examination Without Collaborating With Any Other Individuals. SignaturesameraNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Chapter ReviewDocument11 pagesFinancial Management Chapter ReviewkarynNo ratings yet
- Bond Price and Yield RelationshipDocument13 pagesBond Price and Yield Relationshipdscgool1232No ratings yet
- Principles of FinanceDocument5 pagesPrinciples of FinanceELgün F. QurbanovNo ratings yet
- Finance CHapter 1-7 & 12-13sample Mid TermDocument7 pagesFinance CHapter 1-7 & 12-13sample Mid TermsljdhfdlkjsfNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Trial Questions 2Document11 pagesCorporate Finance Trial Questions 2Sylvia Nana Ama DurowaaNo ratings yet
- Chap002 2019 Fall Assignment 2Document6 pagesChap002 2019 Fall Assignment 2Taranom BakhtiaryNo ratings yet
- Exam AnswersDocument5 pagesExam AnswersKelly Smith100% (2)
- Decentralized Organization GoalsDocument45 pagesDecentralized Organization Goalsdaylicious88No ratings yet
- FIN370 Final ExamDocument9 pagesFIN370 Final ExamWellThisIsDifferentNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting: Complete This Problem.) When These Tables Are Insufficient For CompletionDocument30 pagesCapital Budgeting: Complete This Problem.) When These Tables Are Insufficient For CompletionJane Michelle EmanNo ratings yet
- The Following Questions Are Worth 3 Points Each. Provide The Single Best ResponseDocument9 pagesThe Following Questions Are Worth 3 Points Each. Provide The Single Best ResponsePaul Anthony AspuriaNo ratings yet
- TVM Practice Questions Fall 2018Document4 pagesTVM Practice Questions Fall 2018ZarakKhanNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting A Critical Approach CANADIAN Canadian 4th Edition John Friedlan Test Bank DownloadDocument71 pagesFinancial Accounting A Critical Approach CANADIAN Canadian 4th Edition John Friedlan Test Bank DownloadSandra Joyce100% (28)
- Financial MGT Question ExamDocument4 pagesFinancial MGT Question Exambadhasagezali670No ratings yet
- Fin622 McqsDocument25 pagesFin622 McqsIshtiaq JatoiNo ratings yet
- Quiz Week 3 SolnsDocument7 pagesQuiz Week 3 SolnsRiri FahraniNo ratings yet
- Finals Answer KeyDocument13 pagesFinals Answer Keymarx marolinaNo ratings yet
- Calculating Bond Values and Stock PricesDocument8 pagesCalculating Bond Values and Stock Pricesjangrapa100% (1)
- Acelec 331 Summative1 Set ADocument5 pagesAcelec 331 Summative1 Set ALost AlienNo ratings yet
- Chapter13.Investment Centers and Transfer PricingDocument37 pagesChapter13.Investment Centers and Transfer PricingIam Laine100% (15)
- CFP Exam Calculation Workbook: 400+ Calculations to Prepare for the CFP Exam (2018 Edition)From EverandCFP Exam Calculation Workbook: 400+ Calculations to Prepare for the CFP Exam (2018 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CFA Level 1 Calculation Workbook: 300 Calculations to Prepare for the CFA Level 1 Exam (2023 Edition)From EverandCFA Level 1 Calculation Workbook: 300 Calculations to Prepare for the CFA Level 1 Exam (2023 Edition)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Make Money With Dividends Investing, With Less Risk And Higher ReturnsFrom EverandMake Money With Dividends Investing, With Less Risk And Higher ReturnsNo ratings yet
- CFP Certification Exam Practice Question Workbook: 1,000 Comprehensive Practice Questions (2018 Edition)From EverandCFP Certification Exam Practice Question Workbook: 1,000 Comprehensive Practice Questions (2018 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Economic & Budget Forecast Workbook: Economic workbook with worksheetFrom EverandEconomic & Budget Forecast Workbook: Economic workbook with worksheetNo ratings yet
- Building Wealth on a Dime: Finding your Financial FreedomFrom EverandBuilding Wealth on a Dime: Finding your Financial FreedomNo ratings yet
- Sagar Kailas Salunke Primary Account Holder Name: Your A/C StatusDocument3 pagesSagar Kailas Salunke Primary Account Holder Name: Your A/C Statussagar_salunkeNo ratings yet
- Innovation & Entrepreneursh IP: The $100 Startup Book Review Presented by Naveen RajDocument19 pagesInnovation & Entrepreneursh IP: The $100 Startup Book Review Presented by Naveen RajNaveen RajNo ratings yet
- Marxist Theory of Citizenship - Anthony GiddensDocument4 pagesMarxist Theory of Citizenship - Anthony GiddensRamita UdayashankarNo ratings yet
- Amgen Inc. v. F. Hoffmann-LaRoche LTD Et Al - Document No. 496Document3 pagesAmgen Inc. v. F. Hoffmann-LaRoche LTD Et Al - Document No. 496Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Question Bank of Sem - 1 To Sem-9 of Faculty of Law PDFDocument203 pagesQuestion Bank of Sem - 1 To Sem-9 of Faculty of Law PDFHasnain Qaiyumi0% (1)
- 14 Virgines Calvo v. UCPBDocument1 page14 Virgines Calvo v. UCPBEloise Coleen Sulla PerezNo ratings yet
- Nimia Production Contract TemplateDocument4 pagesNimia Production Contract TemplateWolf BorstNo ratings yet
- Accreditation of NGOs To BBIsDocument26 pagesAccreditation of NGOs To BBIsMelanieParaynoDaban100% (1)
- CASE BRIEF Switzerland v. Nigeria San Pedro Pio Case PDFDocument3 pagesCASE BRIEF Switzerland v. Nigeria San Pedro Pio Case PDFDILG STA MARIANo ratings yet
- Gridplus Efl Ver No 4 Basic 12 - CNP - English - 05.08.2019Document1 pageGridplus Efl Ver No 4 Basic 12 - CNP - English - 05.08.2019Mayur PatelNo ratings yet
- Ibn Mujahid and Seven Established Reading of The Quran PDFDocument19 pagesIbn Mujahid and Seven Established Reading of The Quran PDFMoNo ratings yet
- X-000009-1603383942652-50963-BBE - Assignment 01Document66 pagesX-000009-1603383942652-50963-BBE - Assignment 01PeuJp75% (4)
- Godisnjak PFSA 2018 Za WebDocument390 pagesGodisnjak PFSA 2018 Za WebAida HamidovicNo ratings yet
- Chair BillDocument1 pageChair BillRakesh S RNo ratings yet
- AsfsadfasdDocument22 pagesAsfsadfasdJonathan BautistaNo ratings yet
- A Study On The Role and Importance of Treasury Management SystemDocument6 pagesA Study On The Role and Importance of Treasury Management SystemPAVAN KumarNo ratings yet
- CIS Union Access Update 2021Document6 pagesCIS Union Access Update 2021Fernando Manholér100% (3)
- Educations of Students With DisabilitiesDocument6 pagesEducations of Students With Disabilitiesapi-510584254No ratings yet
- Austerity Doesn't Work - Vote For A Real Alternative: YoungerDocument1 pageAusterity Doesn't Work - Vote For A Real Alternative: YoungerpastetableNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 Exercises - Investments - BodieDocument2 pagesChapter 14 Exercises - Investments - BodieNguyệtt HươnggNo ratings yet
- LWPYA2 Slide Deck Week 1Document38 pagesLWPYA2 Slide Deck Week 1Thowbaan LucasNo ratings yet
- Rules for Classification of Naval Ships Machinery Systems and Fire ProtectionDocument254 pagesRules for Classification of Naval Ships Machinery Systems and Fire ProtectionMarlon Alejandro Arboleda TapiaNo ratings yet
- Your Electronic Ticket-EMD ReceiptDocument2 pagesYour Electronic Ticket-EMD Receiptazeaq100% (1)
- Assignment 2 SolutionDocument4 pagesAssignment 2 SolutionSobhia Kamal100% (1)
- Acre v. Yuttiki, GR 153029Document3 pagesAcre v. Yuttiki, GR 153029MiguelNo ratings yet
- Smart Parking BusinessDocument19 pagesSmart Parking Businessjonathan allisonNo ratings yet
- AttachmentDocument60 pagesAttachmentTahseen banuNo ratings yet
- A Project Report ON Practice SchoolDocument31 pagesA Project Report ON Practice SchoolSiddharth DevnaniNo ratings yet
- Extra Reading Comprehension Exercises (Unit 7, Page 80) Comprehension QuestionsDocument2 pagesExtra Reading Comprehension Exercises (Unit 7, Page 80) Comprehension Questionsroberto perezNo ratings yet
- McCurdy FR 6-15-18Document12 pagesMcCurdy FR 6-15-18David FritzNo ratings yet