Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sec 3e Chem My 09 p2 (Ans)
Uploaded by
martynchekycOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sec 3e Chem My 09 p2 (Ans)
Uploaded by
martynchekycCopyright:
Available Formats
SA1: SPA Chemistry Paper 2 (2009) Name: _______________________ ( Section A: [ 50marks ] Answer all the questions in the spaces
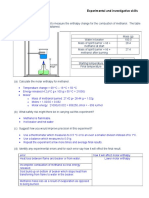
provided. 1 The table below lists the melting and boiling points of some elements. element aluminium argon bromine caesium gallium lithium mercury potassium symbol Al Ar Br Cs Ga Li Hg K m.p. /C 660 -189 -7 29 30 180 -39 64 b.p. /C 2470 -186 59 690 2400 1330 357 774 ) Date: ________________
Use the data in the table to answer the following. (a) Which element exists as a liquid over the largest range of temperature ? Galium [1] (b) Which elements are liquids at room temperature (25 C) ? Mercury, bromine [1] (c) Which of the element named in (b) changes from a liquid to a solid when placed in a freezer at -15 C ? Bromine [1] (d) Which elements would melt when heated from room temperature to body temperature (37 C) ? Caesium, gallium [1] (e) Describe how the arrangement and movement of particles in aluminium change as the temperature rises from 659 C to 661 C. Particles remain close together but are not orderly arranged. [1] Particles can slide over one another in the liquid. [1]
Ammonia (Mr = 17) and hydrogen chloride (Mr = 36.5) are both gases. When these two gases react together, white fumes of ammonium chloride is formed. A student set up the apparatus shown below to study the reaction.
A X
(a) (i)
After a few minutes, white fumes of ammonium chloride were seen at point A in the tube. Name the process which causes the gases to move along the tube. Diffusion [1]
(ii)
Use the kinetic particle theory to explain this observation. Particles of ammonia and hydrogen chloride diffuse/evaporate from the cotton wool. Hydrogen chloride is heavier/denser than ammonia. It diffuses at a slower rate causing the white fumes to form at A. [3]
(b)
Similar white fumes are formed when methylamine, CH3NH2 (Mr = 31), reacts with hydrogen chloride. Place a cross (X) on the tube to show where the white fumes will be seen when the student repeated the experiment using methylamine, in place of the aqueous ammonia.
[1]
The apparatus below was used to separate a mixture of two liquids called octane (boiling point 125 C) and decane (boiling point 175 C). thermometer
water out X
Y water in
(a)
What is this method of separation called ? Fractional distillation [1]
(b)
What feature must the two liquids have to be separated by this method ? They must have different boiling point [1]
(c)
Name the piece of apparatus labelled X: condenser [1] Y: fractionating column [1]
(d)
Which liquid appears in the beaker first ? Explain your answer. Octane. It has lower boiling point. [2]
(e)
What observation, during the experiment, will tell you that the liquid collected is pure ? The thermometer shows a constant temperature [1]
(f)
Using the axis provided, sketch a graph to show how the total volume of distillate collected in the beaker changes with the temperature shown on the thermometer.
1 mark for correct shape 1 mark for showing change of volume at 125 C and 175 C [2] 4 A powder consists of a mixture of the four substances given in the table. action of water on substance insoluble insoluble insoluble insoluble action of hot dilute sulfuric acid on substance does not react dissolves to give a blue solution dissolves to give a green solution dissolves to give a green solution
substance copper copper(II) oxide nickel nickel oxide
Suggest how a dry sample of copper powder can be obtained from this mixture. Dissolve mixture in hot dilute sulfuric acid. [1] Filter mixture. [1] Rinse/Wash residue(copper) with water. [1] Dry residue. [1]
5 (a) (i)
Substances can be classified as elements or compounds or mixtures. Oxygen is an element. Water is a compound. Sea water is a mixture. Use these substances to illustrate one difference between the composition of an element and the composition of a compound. Oxygen is an element made up of only oxygen atoms [1] while water is a compound made up of oxygen and hydrogen atoms chemically combined. [1]
(ii)
one difference between the composition of a mixture and the composition of a compound. Water is made up of oxygen and hydrogen atoms chemically combined in a fixed ratio. [1] Sea water does not have a fixed composition of dissolved substances in water. [1]
(b)
The seasoning used in a packet of instant noodle contains the folllowing ingredients: salt, soy sauce powder, sugar, curry spices, monosodium glutamate and a permitted colouring.
(i)
Monosodium glutamate has the chemical formula COOH(CH2)2CH(NH2)COONa. How many elements and atoms are there in one unit of monosodium glutamate ? no. of elements:5 [1] no. of atoms: 19 [1]
(ii)
Name three compounds found in the seasoning. salt, sugar, monosodium glutamate [2] Name two mixtures found in the seasoning. soy sauce powder, curry spices, permitted colouring [2]
(iii)
The structure of an ion formed by an isotope of element Q is shown below.
(a)
Name the subatomic particles A, B and C. A: electrons [1] B: neutrons [1] C: protons [1]
(b) (c)
What is the nucleon (mass) number of this isotope ? 7[1] Would another isotope of element Q has the same nucleon number ? Explain your answer. No. [1] Isotopes of the same element have different no. of neutrons. [1]
(d) (i)
Element Q reacts with oxygen to form a compound. Write down the chemical formula of this compound. Q2O [1]
(ii)
Draw a dot and cross diagram to show the bonding in this compound. Your drawing should show outer electrons only.
____________________________________________________________ [2] 6
In recent years scientists have made tube-shaped structures of carbon called nanotubes.
(a)
State two differences between the structure of a carbon nanotube and the structure of diamond. In carbon nanotubes, each C atom is joined to 3 others on a flat layer. [1] In diamond, each C atom is joined to 4 others in a tetrahedral arrangement. [1] Carbon nanotubes are fifty times stronger than iron. Suggest why these nanotubes are so strong based on their structure and bonding. It has a macromolecular structure made up of C atoms joined together by strong covalent bonds [2] Compare the electrical conductivity of carbon nanotubes and diamond. Explain your answer. Carbon nanotubes conduct electricity but diamond does not. Carbon nanotubes contain free electrons as each C atom uses only 3 of its valency electrons for bonding. Diamond does not contain free electrons as all the C valency electrons are used for bonding. [3]
(b)
(c)
Section B: [ 30 marks ] Answer three questions from this section. The last question is in the form of an either/or and only one of the alternatives should be attempted. 8 The graph shows the electronegativity of elements in the third row of the Periodic Table. The electronegativity is the tendency of an atom, in a molecule, to attract electrons to itself.
(a)
Describe the trend in electronegativity across the third row of the Periodic Table. Suggest an explanation for the trend you have given. The electronegativity increases across the row. Increasing number of protons across the row results in greater attractive force from the atom to attract electrons. [2]
(b) (i) (ii) (c)
In which group of the Periodic Table would you expect to find the most electronegative elements: group VII [1] the least electronegative elements: group 1[1] Do you expect electronegative elements to be metals or non-metals ? Explain your answer. Non-metals. They need to gain electrons to fill up their outermost shell/ achieve a noble gas configuration. [2]
(d) (i)
Argon is the last element found in the third row of the Periodic Table. Draw a diagram to show the full electronic structure of an argon atom. Use (X) to represent an electron.
Drawing shows a configuration of 2.8.8
____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ [2] (ii) Explain why the electronegativity of argon is missing from the graph. Atoms of argon have a completely filled outermost shell and do not exist as molecules. [1]
The metal tungsten, symbol W, is used to make wire filaments in light bulb. The wire glows when electricity passes through it. tungsten filament
(a)
Draw a diagram to show the metallic bonding in pure tungsten.
____________________________________________________________ [2] 9
(b)
Using your diagram in (a), explain why metals such as tungsten are good conductors of electricity. Has free moving electrons [1]
(c)
In a light bulb, the tungsten wire may get so hot that it melts and breaks. This graph shows the heating curve for tungsten.
(i)
Use the graph to give the boiling point of tungsten. 5600oC [1]
(ii)
Predict the temperature when tungsten wire breaks. 3400oC [1]
(iii)
Complete the diagram to show the arrangement of tungsten atoms when the tungsten wire breaks.
Show particles that are close together but not orderly arranged.
_________________________ [1]
10
(d)
The table shows some information about the compounds of tungsten.
name of compound tungsten(VI) oxide tungsten(III) oxide tungsten(IV) sulfide
____________ (i) (ii)
chemical formula WO3 W2O3 WS2
Complete the table by filling in the three empty boxes.
[3]
Draw a dot and cross diagram to show the electronic structure of a sulfide ion. Your drawing should show the charge on the ion and the outer electrons only.
____________________________________________________________ [2]
11
EITHER 10 Ephedrine and insulin are both drugs that are banned for use by athletes. One way that athletes can be tested for the banned drugs is by chromatography of urine samples. The diagram below shows a chromatogram for ephedrine and insulin and the urine samples from four athletes.
(a)
What does the chromatogram show about the solubility of the two banned drugs in the solvent used ? Insulin is more soluble in the solvent [1]
(b)
Which athletes are tested positive for using drugs that are banned ? Athelete 1 & 3 [1]
(c)
A similar test was carried out on the urine of a fifth athlete. This diagram shows the chromatogram for the fifth athlete.
12
Show, by using Rf values, which one of the banned drugs this athlete has used. Rf of ephedrine = 2 / 5 = 0.4 [1] Rf of insulin = 3/ 5 = 0.6 [1] Rf of spot from 5th athlete = 1.3/ 3.2 = 0.41[1] The athlete used the ban drug ephedrine. Minus 1 mark for not identifying the ban drug used. (d) Describe, with the help of a diagram, how to set up and carry out the chromatography.
(e)
What is the advantage of using a locating agent in the analysis ? Locating agent helps to make colourless spots appear on the chromatogram. [1]
13
20
OR 10 The diagram below shows the arrangement of valency electrons in a molecule of ethanoic acid.
(a) (b) (c)
What is the molecular formula of ethanoic acid ? C2H4O2 [1] Name the type of bonding found in ethanoic acid. covalent bonding [1] Complete the diagram above by showing the arrangement of valency electrons on the carbon, oxygen and hydrogen atoms. Use (X), (O) and () to represent electrons from the carbon, oxygen and hydrogen atoms respectively. [4]
(d)
Would you expect ethanoic acid to have a low or high boiling point ? Explain your reasoning. Low boiling point. Weak forces of attraction between molecules can be easily overcome. [2]
(e)
Predict the electrical conductivity of ethanoic acid when it is a solid. Explain your answer. It will not conduct electricity. No free ions/ free electrons. [2]
14
You might also like
- 2012 OLevel Pure Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and AnswersDocument13 pages2012 OLevel Pure Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and AnswersMethodology OfStudies100% (6)
- 8.acids, Bases and Salts PDFDocument20 pages8.acids, Bases and Salts PDFHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- 2012 OLevel Science Chemistry Paper 3 Questions and AnswersDocument10 pages2012 OLevel Science Chemistry Paper 3 Questions and AnswersMethodology OfStudies100% (1)
- 2015 Combined Chem O Level 5078/03 AnswersDocument8 pages2015 Combined Chem O Level 5078/03 AnswersMethodology OfStudies100% (1)
- Experimental Techniques (TOPIC 2)Document17 pagesExperimental Techniques (TOPIC 2)ChaudhryAbdullahNo ratings yet
- SA1 Chemistry MCQ PracticeDocument2 pagesSA1 Chemistry MCQ Practicechong56No ratings yet
- S 495160Document4 pagesS 495160Khondokar Tarakky0% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE Past PaperDocument4 pagesCambridge IGCSE Past PaperAliceChung50No ratings yet
- June 1999 Paper 1Document16 pagesJune 1999 Paper 1YasirNo ratings yet
- Particles and States of Matter QuestionsDocument19 pagesParticles and States of Matter QuestionsAnand Kumar ShuklaNo ratings yet
- KS3 Chem 7G Practice Questions about Solids, liquids and gasesDocument14 pagesKS3 Chem 7G Practice Questions about Solids, liquids and gasesRumeysaNo ratings yet
- Igcse Chemistry Section 4 Lesson 4Document48 pagesIgcse Chemistry Section 4 Lesson 4alanoud obeidatNo ratings yet
- Chemical Calculations Workbook IgcseDocument29 pagesChemical Calculations Workbook IgcsehannahNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and Salts: Factual QuestionsDocument17 pagesAcids, Bases and Salts: Factual QuestionsRahul RajNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 4 Lesson 2Document79 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Section 4 Lesson 2Phillip TranNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Tests For Cations and AnionsDocument1 pageIGCSE Tests For Cations and AnionsCoolman Poon100% (2)
- Covalent Bonding NotesDocument1 pageCovalent Bonding Noteschongkee56100% (1)
- Experimental Skills Questions and AnswersDocument4 pagesExperimental Skills Questions and AnswersAbdelmoneim Elmansy IgcseNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Unit Test ReviewDocument7 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Unit Test ReviewKasunDilshan100% (1)
- The Reactivity SeriesDocument25 pagesThe Reactivity SeriesFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Sec 3 Chemistry Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesSec 3 Chemistry Practice Questionschong56100% (1)
- Electricity & Chemistry (Multiple Choice) QPDocument29 pagesElectricity & Chemistry (Multiple Choice) QPGunay OmarovaNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Papers H2 Chemistry 2013Document1,601 pagesPreliminary Papers H2 Chemistry 2013Willy Tan50% (2)
- ESWS 7E ChemistrysamplechapterDocument16 pagesESWS 7E ChemistrysamplechapterAFuentesCaballeroNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 2 Lesson 1Document66 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Section 2 Lesson 1Antonia Putri Sri Nova YolandhaNo ratings yet
- Pure Substances MixturesDocument4 pagesPure Substances MixturesAngela Francisca Bajamundi-Veloso100% (1)
- Calculating Moles and Mass in Chemical ReactionsDocument3 pagesCalculating Moles and Mass in Chemical ReactionsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 7.1Document2 pagesWorksheet 7.1markusNo ratings yet
- Reacting MassesDocument2 pagesReacting MassesTsz Wai WONGNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAS Bonding 1Document14 pagesEdexcel IAS Bonding 1mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 10.1Document2 pagesWorksheet 10.1SavithaBroonanNo ratings yet
- Identification of Ions and GasesDocument5 pagesIdentification of Ions and GasesJobelle Aleli Perez EhinaNo ratings yet
- Homeworks 1 eDocument8 pagesHomeworks 1 eSumi VjNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument5 pagesRespiratoryKrisdiansah PurnawidjajaNo ratings yet
- Sec 4 Chemistry PracticeDocument4 pagesSec 4 Chemistry Practicechong56No ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Oxygen Hydrogen and Carbon DioxideDocument15 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Oxygen Hydrogen and Carbon DioxideS M AkashNo ratings yet
- Energetics Revision Exam QuestionsDocument13 pagesEnergetics Revision Exam QuestionsDulshan JayNo ratings yet
- HalogensDocument15 pagesHalogenskmoiz427No ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 5 Lesson 4Document66 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Section 5 Lesson 4Minh MeoNo ratings yet
- Force Field Questions: Name Ghadeer Hussain Al-Khayat Class Date 1Document2 pagesForce Field Questions: Name Ghadeer Hussain Al-Khayat Class Date 1ghadeer alkhayatNo ratings yet
- Metal and Acids Lessons Year 8Document13 pagesMetal and Acids Lessons Year 8Sara KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Air Around Us Science Form 1Document5 pagesChapter 5 The Air Around Us Science Form 1Angie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Practice Worksheet of Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesPractice Worksheet of Chemical Bondingch khakanNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of Copper ChlorideDocument1 pageElectrolysis of Copper ChlorideSeptina R Nurhalimah100% (1)
- Science (Chemistry) SA PracticeDocument4 pagesScience (Chemistry) SA Practicechong56No ratings yet
- Chapter 8: SaltsDocument23 pagesChapter 8: SaltsWong Wai LunNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle Theory WorksheetDocument2 pagesKinetic Particle Theory WorksheetFandy ArdyNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry Practice ProblemsDocument5 pagesStoichiometry Practice ProblemsDwayneNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Practice TestDocument3 pagesChemical Reactions Practice TestShemy RajNo ratings yet
- Biology: PAPER 1 Multiple ChoiceDocument20 pagesBiology: PAPER 1 Multiple ChoiceAdnan AshrafNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis RevisionDocument15 pagesElectrolysis RevisionPunitha PanchaNo ratings yet
- Balancing EquationsDocument1 pageBalancing Equationschong56No ratings yet
- Social Studies Content PageDocument1 pageSocial Studies Content PagemartynchekycNo ratings yet
- Green Club ScriptDocument2 pagesGreen Club ScriptmartynchekycNo ratings yet
- Instructions To E-Learning Step 1: Login On To ACE-Learning at HTTP://WWW - AceDocument2 pagesInstructions To E-Learning Step 1: Login On To ACE-Learning at HTTP://WWW - AcemartynchekycNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument2 pagesChapter 1 - Kinetic Particle TheorymartynchekycNo ratings yet
- 6 VseprDocument9 pages6 VseprRamadhani Wulan DhariNo ratings yet
- Week 3: Lewis StructureDocument49 pagesWeek 3: Lewis StructureYay SandovalNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry PDFDocument181 pagesOrganic Chemistry PDFShyam Yadav100% (1)
- Gr10 Via Afrika Physical Science Gr10 Study Guide LRDocument159 pagesGr10 Via Afrika Physical Science Gr10 Study Guide LRSimphiwe NyandeniNo ratings yet
- CH 301 Unit 2 Exam-SolutionsDocument9 pagesCH 301 Unit 2 Exam-SolutionsbrunosipodNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Resonance StructureDocument4 pagesTutorial Resonance StructureTirthankar GhoshNo ratings yet
- Homework: Covalent Bonding Diagrams and Practice QuestionsDocument41 pagesHomework: Covalent Bonding Diagrams and Practice QuestionsRXNOFCHMNo ratings yet
- Homework Problems: Structure, Bonding & Hybridization 1. The Molecule Shown Below Is Griseofulvin, An Antifungal CompoundDocument8 pagesHomework Problems: Structure, Bonding & Hybridization 1. The Molecule Shown Below Is Griseofulvin, An Antifungal CompoundPrachi KaushikNo ratings yet
- CHE 101 Out Line-Lecture Schedule 2020-21Document2 pagesCHE 101 Out Line-Lecture Schedule 2020-21AG STXLEZNo ratings yet
- Corriculum Guide Gen Chem 1Document10 pagesCorriculum Guide Gen Chem 1Yuri PaderesNo ratings yet
- Regents Chemistry: Note PacketDocument27 pagesRegents Chemistry: Note PacketEdric HernandezNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry Topic 4 BondingDocument103 pagesIB Chemistry Topic 4 Bondingzarna nirmal rawalNo ratings yet
- Molecular ShapesDocument76 pagesMolecular ShapesLaica BlazaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Quantum Number & Magnetic PropertyDocument39 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Quantum Number & Magnetic PropertyGlyza MacabentaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Questions and AnswersDocument8 pagesChapter 9 Questions and AnswersFausto SalazarNo ratings yet
- Molecules and Ions ConfigurationsDocument44 pagesMolecules and Ions Configurations김은우No ratings yet
- Chemistry course sequence and lesson plansDocument80 pagesChemistry course sequence and lesson plansJoric MagusaraNo ratings yet
- SEM 1 OVERALL (Summary)Document16 pagesSEM 1 OVERALL (Summary)Peh ZeroxNo ratings yet
- Electronic Theory of Valency &bondingDocument12 pagesElectronic Theory of Valency &bondingshivakafle039No ratings yet
- Condensed Structure and Line Structure ExamplesDocument7 pagesCondensed Structure and Line Structure ExamplesYuri DryzgaNo ratings yet
- Markscheme HL Paper1Document23 pagesMarkscheme HL Paper1shanethomasツNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument5 pagesChemistryAmar KumarNo ratings yet
- Bonding Test Review TCDocument4 pagesBonding Test Review TCDessere SosasNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Lecture - 1Document13 pagesInorganic Chemistry Lecture - 1Wanderson Alves PortoNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Chemistry Atoms First 2nd Edition Julia Burdge DownloadDocument7 pagesTest Bank For Chemistry Atoms First 2nd Edition Julia Burdge DownloadPedro Chun97% (34)
- Study Guide For Periodic Table TESTDocument19 pagesStudy Guide For Periodic Table TESTHarani ThillainathanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MixDocument102 pagesChemistry MixAyanda MwambetaniaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Exam Review Grade 11Document28 pagesChemistry Exam Review Grade 11Michael Chiu100% (2)
- Covalent Dative Covalent BondingDocument52 pagesCovalent Dative Covalent BondingDearbhla HubbardNo ratings yet
- Chp10, Mol Geom and HybridizDocument5 pagesChp10, Mol Geom and HybridizMelvin CabonegroNo ratings yet