Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AC Voltage & Frequency
Uploaded by
Jatinder SinghOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AC Voltage & Frequency
Uploaded by
Jatinder SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
AC Motor Specifications
AC Voltage & Frequency: Your choices are... 115 / 120V 60 Hz 208-230 / 240V 60 Hz 460 / 480V 60 Hz 575 / 600V 60 Hz 50 Hz / Internation al Power 400 Hz / Aerospace Other Search Logic: 115 / 120V is standard residential or commercial voltage for 60Hz power (North America). These are for 60Hz power (North America).
These are for 60Hz power (North America).
These are for 60Hz power (North America).
International voltage levels, such as those common in Asia and Europe, and includes all 50Hz power.
Motors and other components using 400Hz power are primarily used for aerospace applications. Unlisted voltage / frequency motor. All products with ANY of the selected attributes will be returned as matches. Leaving all boxes unchecked will not limit the search criteria for this question; products with all attribute options will be returned as matches.
Phase Your choices are... Singlephase Threephase Standard commercial and residential power is single-phase, meaning one sinusoidal or other alternating voltage pattern. Three-phase power contains three simultaneous sinusoidal or other alternating voltage patterns, typically 120 out of phase with each other. Higher power efficiency and smoothness of operation is possible with three-phase operation. Three-phase power is most typically used for industrial or high power motors. All products with ANY of the selected attributes will be returned as matches. Leaving all boxes unchecked will not limit the search criteria for this question; products with all attribute options will be returned as matches.
Search Logic:
Shaft Speed: Search Logic:
Shaft speed refers to no-load rotational speed of output shaft at rated terminal voltage. User may specify either, both, or neither of the "At Least" and "No More Than" values. Products returned as matches will meet all specified criteria.
Continuous Output Power: Search Logic:
Mechanical power provided by the motor output.
User may specify either, both, or neither of the "At Least" and "No More Than" values. Products returned as matches will meet all specified criteria.
Continuous Torque: Search Logic:
Output torque capability of the motor is under constant running conditions.
User may specify either, both, or neither of the "At Least" and "No More Than" values. Products returned as matches will meet all specified criteria.
AC Motor Type
Motor Type: Your choices are... Inductio Induction motors derive their name from the fact that current is induced into the rotor n windings without any physical connection with the stator windings (which are directly connected to an AC power supply). Induction motors are adaptable to many different environments and capable of providing considerable power as well as variable speed control. Typically there is "slip," or loss of exact speed tracking with induction motors. Synchro Synchronous motors operate at constant speed up to full load. The rotor speed is equal nous to the speed of the rotating magnetic field of the stator; there is no slip. Reluctance and permanent magnet are the two major types of synchronous motors. A synchronous motor is often used where the exact speed of a motor must be maintained. AC Servom otors Univers al Other Search Logic: AC servomotors are typically permanent magnet, synchronous motors that can often have low torque-to-inertia ratios for high acceleration ratings.
Universal motors can operate at approximately the same speed and output on either DC or single-phase AC power. Universal motors are also known as an AC/DC motors. Unlisted or specialized AC motor construction. All products with ANY of the selected attributes will be returned as matches. Leaving all boxes unchecked will not limit the search criteria for this question; products with all attribute options will be returned as matches.
Multi-
Motor speed can be continuously adjusted or set at discrete speeds within the operating
speed? Search Logic:
range. "Required" and "Must Not Have" criteria limit returned matches as specified. Products with optional attributes will be returned for either choice.
Reversi ble? Search Logic:
Motor can be run in both clockwise and counterclockwise directions with approximately the same operating characteristics. "Required" and "Must Not Have" criteria limit returned matches as specified. Products with optional attributes will be returned for either choice.
Gearmotor / Gearhead Options
Motor Configurat ion: Your choices are... Motor Only The motor does not have a gearbox of any kind.
Gearmotor This category includes units with single integral gearheads, or replaceable / interchangeable gearhead options. Search Logic: All products with ANY of the selected attributes will be returned as matches. Leaving all boxes unchecked will not limit the search criteria for this question; products with all attribute options will be returned as matches.
Gearing (if applicable) :
Your choices are... Spur Spur gear heads include one or more sets of pinion-gear sets, in which one pinion drives one gear. These sets can be stacked or cascaded to achieve higher reduction ratios. Planetary gear heads involve several gears per stage rather than one pinion-gear set. A "sun gear" drives multiple planet or satellite gears, which then mesh on the inside of an internal or annular gear to provide relatively high torque and power transmission ratings. Harmonic drives are extremely precise speed reduction systems, which transmit power via a rotating elliptical element that engages a flexible cup that then engages an internal gear, typically fixed. This power transmission delivers precise angular position in very high input-to-output ratio (50:1 & up) applications. Worm gearing uses right-angled drives in which a worm drives a wheel coupled to the output shaft or shafts. This arrangement is used for high reduction and compact right-angle power transmission. Bevel gear sets have intersecting axes that are commonly, but not always, perpendicular. They mate via teeth on angled edges. Unlisted or specialized gearing arrangement. All products with ANY of the selected attributes will be returned as matches. Leaving all boxes unchecked will not limit the search criteria for this question; products with all attribute options will be returned as matches.
Planetary
Harmonic
Worm
Bevel
Other Search Logic:
Gearbox Ratio: Search Logic:
Gearbox ratio is the ratio of input speed to output speed. A ratio greater than one indicates speed reduction, while a ratio less than one indicates speed increase. User may specify either, both, or neither of the "At Least" and "No More Than" values. Products returned as matches will meet all specified criteria.
Gearbox Efficiency:
Efficiency is the percentage of power or torque that is transferred through the gearbox. Losses occur due to factors such as friction and slippage inside the gearbox. User may specify either, both, or neither of the "At Least" and "No More Than" values. Products returned as matches will meet all specified criteria.
Search Logic:
Feedback
Feedbac k Your choices are... Integral Integral encoders are attached for angular position signal. These encoders may include Encoder absolute or incremental encoders and a number of different encoder signal types. Integral Integral resolvers indicate angular position. Resolvers often rely on magnetic fields Resolver and are typically very robust; they are sometimes specified for harsh environments. Integral Tachom eter Other Search Logic: Tachometers produce an output indicating rotational speed of motor.
Unlisted or specialized feedback signal. All products with ANY of the selected attributes will be returned as matches. Leaving all boxes unchecked will not limit the search criteria for this question; products with all attribute options will be returned as matches.
AC Motor Shaft Options
Orientat ion / Type Your choices are... In-line Offset / Parallel Right Angle Hollow Output shaft axis is in-line with axis of motor rotation. Output shaft is parallel with, but not concentric to, the axis of motor rotation.
Output shaft axis is perpendicular to motor rotation axis, intersecting or nonintersecting. Hollow output shafts have a hole or bore that can accept a shaft. Outputs with collets for tool bits are one example. Unlisted shaft angle or configuration. All products with ANY of the selected attributes will be returned as matches. Leaving all boxes unchecked will not limit the search criteria for this question; products with all attribute options will be returned as matches.
Other Search Logic:
Number of Shafts Your choices are... Singleended Doubleended One, single-ended output shaft.
Two output shafts. This may be one coming out the front and one coming out the back, or two coming out from a transverse gearbox.
Search Logic:
All products with ANY of the selected attributes will be returned as matches. Leaving all boxes unchecked will not limit the search criteria for this question; products with all attribute options will be returned as matches.
AC Motor Housing
Design Units: Your choices are... English
Refers to the base units for specifications such as diameter, length, and threading. Combinations are possible and this information is not known for some products.
Base units such as inches or fractions of an inch for primary dimensions as the shaft size, mounting geometry, etc. Metric units such as millimeters or centimeters are used for primary dimensions as the shaft size, mounting geometry, etc. All products with ANY of the selected attributes will be returned as matches. Leaving all boxes unchecked will not limit the search criteria for this question; products with all attribute options will be returned as matches.
Metric
Search Logic:
Motor Shape: Your choices are... Cylindric al Body Square Cylindrical motor body cross-sections are round.
Square motor bodies have a square or rectangular shape.
Body Search Logic: All products with ANY of the selected attributes will be returned as matches. Leaving all boxes unchecked will not limit the search criteria for this question; products with all attribute options will be returned as matches.
Diameter / Width: Search Logic:
Diameter of cylindrical motors or width / height of square motors. This is for the motor body only and does not include flanges. User may specify either, both, or neither of the "At Least" and "No More Than" values. Products returned as matches will meet all specified criteria.
Housing Length: Search Logic:
Housing length is the length of the motor body, not including shaft.
User may specify either, both, or neither of the "At Least" and "No More Than" values. Products returned as matches will meet all specified criteria.
NEMA Frame Size: Search Logic:
NEMA frame sizes conform to a standard size and mounting configuration identified by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA). Only numerical sizes are searchable in this field. User may specify either, both, or neither of the "At Least" and "No More Than" values. Products returned as matches will meet all specified criteria.
Enclosure Options Your choices are... Open Open-frame of frameless enclosures have minimal or frame-like support, but no Frame / overall casing. Frameless
Search Logic:
All products with ANY of the selected attributes will be returned as matches. Leaving all boxes unchecked will not limit the search criteria for this question; products with all attribute options will be returned as matches.
AC Motor Options
Integral Driver Electronics? Search Logic:
Integral driver electronics are on-board or attached drivers or amplifier electronics.
"Required" and "Must Not Have" criteria limit returned matches as specified. Products with optional attributes will be returned for either choice.
Integral Brake? Search Logic:
Integral brake can be mechanical or electronic.
"Required" and "Must Not Have" criteria limit returned matches as specified. Products with optional attributes will be returned for either choice.
Integral Clutch? Search Logic:
Integral clutches engage and disengage the motor.
"Required" and "Must Not Have" criteria limit returned matches as specified. Products with optional attributes will be returned for either choice.
Brake / Integral combination of brake and clutch. Clutch Combination? Search Logic: "Required" and "Must Not Have" criteria limit returned matches as specified. Products with optional attributes will be returned for either choice.
Environment Full required ranged of ambient operating temperature.
Operating Full required range of operating temperature. Temperature : Search Logic: User may specify either, both, or neither of the limits in a "From - To" range; when both are specified, matching products will cover entire range. Products returned as matches will meet all specified criteria.
Shock Rating: Search Logic:
Shock rating is the maximum shock the motor can withstand and still meet operating specifications. All matching products will have a value greater than or equal to the specified value.
Vibration Rating: Search Logic:
Vibrating rating is the maximum vibration the motor can withstand and still meet operating specifications. All matching products will have a value greater than or equal to the specified value.
Totally Enclosed
Totally enclosed motors have an enclosure that prevents free exchange of air between the inside and the outside of the enclosure. Common ratings are TEFC (fan-cooled) and TENV (non-ventilated); this is not an airtight rating. These motors are most frequently used in potentially contaminated environments. "Required" and "Must Not Have" criteria limit returned matches as specified. Products with optional attributes will be returned for either choice.
Search Logic:
Dust-proof
Dust-proof motors protect against dust infiltration with features such as total enclosure and labyrinth seals for shafts.
The IP (Ingress Protection) rating for dust-proof motors is IP6x. Search Logic: "Required" and "Must Not Have" criteria limit returned matches as specified. Products with optional attributes will be returned for either choice.
Drip-proof
Drip-proof motors contain ventilation openings that are designed so that drops of liquid or solid particles falling from any angle within 15 degrees of vertical cannot enter the motor. Motors with an IP rating of IPx1 through IPx9 are considered drip-proof.
Search Logic:
"Required" and "Must Not Have" criteria limit returned matches as specified. Products with optional attributes will be returned for either choice.
Waterproof
There are several degrees of waterproofing applicable to motors and they are reflected in the IP rating for the motor: IPx1: Protection against vertically falling drops of water (drip-proof). IPx2: Protection against direct sprays of water up to 15 degrees from vertical. IPx3: Protection against direct sprays of water up to 60 degrees from vertical. IPx4: Protection against water sprayed from all directions. IPx5: Protected against low pressure jets of water from all directions. IPx6: Protected against high pressure jets of water from all directions. IPx7: Protected against the effects of immersion up to 1 meter. IPx8: Protected against long periods of immersion under pressure.
Search Logic:
"Required" and "Must Not Have" criteria limit returned matches as specified. Products with optional attributes will be returned for either choice.
Special / Extreme Environment
s Your choices are... Clean Room Use Clean rooms are classified by particulate size and density in the ambient air. One such rating method classifies rooms according to number of particles larger than 0.5 micron in one cubic foot of air. There are various governmental, metric, and international standards. Motors rated for suitability in a clean room will identify the particular standard for which they are rated. Motors with a cryogenic rating are constructed for extremely low ambient temperatures such as 20 K and below. Explosion-proof motors have totally enclosed housings that are constructed to withstand internal explosion of a specified gas, vapor, or dust. Should such an explosion occur, the enclosure would prevent the ignition or explosion of the gas or vapor surrounding the motor enclosure. Several explosion-proof ratings are governed by Underwriter's Laboratories (UL). Radiation-hardened motors are constructed of materials designed to withstand high-energy gamma radiation. Ratings are expressed in units such as permissible RADs in total accumulated dose (TAD). Vacuum-rated motors incorporate features such as lubricant vapor pressure below rated ambient vacuum and construction techniques. All products with ANY of the selected attributes will be returned as matches. Leaving all boxes unchecked will not limit the search criteria for this question; products with all attribute options will be returned as matches
Cryogenic Use Explosionproof
Radiationhardened
Vacuum Use
Search Logic:
Understanding Induction Motor Nameplate Information
May 1, 2004 12:00 PM, By Ed Cowern, P.E., Baldor Electric Co. 12 Comments | Related ContentShareThis187 Keeping the language common among manufacturers is critical to making motors interchangeable
The U.S. motor industry has worked on a standardized basis for more than three-quarters of a century. The standardization agency National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) was established in 1926 to promote the standardization of electrical apparatus and supplies. As a result of this group's efforts, you can expect standard motors from different manufacturers to meet or exceed minimum performance parameters and, for the most part, be about the same size. A critical part of making motors interchangeable is ensuring that nameplate information is common among manufacturers. The common language of the motor nameplate enables installation and maintenance personnel to quickly understand and recognize exactly what type of motor they're dealing with during a new installation or replacement procedure. The NEC states that the motor nameplate must show the following information: Rated voltage or voltages Rated full-load amps for each voltage level Frequency Phase Rated full-load speed Insulation class and rated ambient temperature Rated horsepower Time rating Locked-rotor code letter Manufacturer's name and address
In addition to this required information, motor nameplates may also include data like frame size, NEMA design letter, service factor, full-load efficiency, and power factor. Finally, some nameplates may even include data like bearing identification numbers, certification code, manufacturer serial number, and symbols and logos. Basic nameplate data. In order to fully understand the details presented on motor nameplates we'll examine each of these items more closely and explain its importance. Rated voltage Motors are designed to yield optimal performance when operating at a specific voltage level, or a combination of voltage levels in the case of dual-voltage or trivoltage motors. This value is known as the nameplate voltage. In recognition of the fact that voltage changes on your power distribution system occur due to changing load conditions within your facility and on the utility supply that feeds your facility, motors are designed with a 10% tolerance for voltage above and below the rated nameplate value. Thus, a motor with a rated nameplate voltage of 460V should be expected to
operate successfully between 414V and 506V. Rated full-load amperage As the torque load on a motor increases, the amperage required to power the motor also increases. When the full-load torque and horsepower is reached, the corresponding amperage is known as the full-load amperage (FLA). This value is determined by laboratory tests; the value is usually rounded up slightly and recorded as the nameplate value. Rounding up allows for manufacturing variations that can occur and some normal voltage variations that might increase the full-load amps of the motor. The nameplate FLA is used to select the correct wire size, motor starter, and overload protection devices necessary to serve and protect the motor. Frequency To operate successfully, the motor frequency must match the power system (supply) frequency. In North America, this frequency is 60 Hz (cycles). In other parts of the world, the frequency may be 50 or 60 Hz. Phase This concept is fairly simple in the United States. You either have a singlephase or 3-phase motor. Rated full-load speed This is the motor's approximate speed under full-load conditions, when voltage and frequency are at the rated values. A somewhat lower value than the actual laboratory test result figures is usually stamped on the nameplate because this value can change slightly due to factors like manufacturing tolerances, motor temperature, and voltage variations. On standard induction motors, the full-load speed is typically 96% to 99% of the no-load speed. Insulation class and rated ambient temperature A critical element in motor life is the maximum temperature that occurs at the hottest spot in the motor. The temperature that occurs at that spot is a combination of motor design (temperature rise) and the ambient (surrounding) temperature. The standard way of indicating these components is by showing the allowable maximum ambient temperature, usually 40C (104F), and the class of insulation used in the design of the motor. Available classes are B, F, and H. Rated horsepower Horsepower is the measure of how much work a motor can be expected to do. This value is based on the motor's full-load torque and full-load speed ratings and is calculated as follows: Horsepower (hp)=[Motor SpeedTorque (lb-ft)]5,250 The standardized NEMA table of motor horsepower ratings runs from 1 hp to 450 hp. If a load's actual horsepower requirement falls between two standard horsepower ratings, you should generally select the larger size motor for your application. Time rating Standard motors are rated for continuous duty (24/7) at their rated load and maximum ambient temperature. Specialized motors can be designed for short-time requirements where intermittent duty is all that's needed. These motors can carry a shorttime rating from 5 minutes to 60 minutes. The NEMA definition for short-time motors is as follows: All short-time ratings are based upon corresponding short-time load tests, which shall commence only when the windings and other parts of the motor are within 5C of the ambient temperature at the time of the test. By using short-time ratings, it's
possible to reduce the size, weight, and cost of the motor required for certain applications. For example, you may choose to install an induction motor with a 15minute rating to power a pre-operation oil pump used to pre-lube a gas turbine unit because it would be unusual for this type of motor to be operated for more than 15 minutes at a time. Locked-rotor code letter When AC motors are started with full voltage applied, they create an inrush current that's usually many times greater than the value of the full-load current. The value of this high current can be important on some installations because it can cause a voltage dip that might affect other equipment. There are two ways to find the value of this current: Look it up in the motor performance data sheets as provided by the manufacturer. It will be noted as the locked-rotor current. Use the locked-rotor code letter that defines an inrush current a motor requires when starting it.
Manufacturer's name and address Most manufacturers include their name and address on the motor nameplate. Optional nameplate data. In addition to the required items noted above, more information is typically included on a motor nameplate. Frame size Under the NEMA system, most motor dimensions are standardized and categorized by a frame size number and letter designation. In fractional horsepower motors the frame sizes are two digits and represent the shaft height of the motor from the bottom of the base in sixteenths of an inch. For example, a 56-frame motor would have a shaft height (D dimension) of 56/16 of an inch, or 3.5 inches. On larger 3-digit frame size motors, 143T through 449T, a slightly different system is used where the first two digits represent the shaft height in quarters of an inch. For example, a 326T frame would have a D dimension of 32 one-quarter inches, or 8 inches. Although no direct inch measurement relates to it, the third digit of three-digit frame sizes, in this case a 6, is an indication of the motor body's length. The longer the motor body, the longer the distance between mounting bolt holes in the base (i.e. greater F dimension). For example, a 145T frame has a larger F dimension than does a 143T frame. When working with metric motors (IEC type), the concept is the same as noted above with one exception the shaft height above the base is now noted in millimeters rather than inches. The frame size is the shaft height in millimeters. NEMA design letter Certain types of machinery may require motors with specialized performance characteristics. For example, cranes and hoists that have to start with full loads imposed may require motors with operating characteristics much different from what is required for pumps and blowers. Motor performance characteristics can be altered by design changes in lamination, winding, rotor, or any combination of these three items.
Most standard motors for general-purpose applications meet or exceed the values specified for Design B motors in NEMA MG-1, Standard for Motors and Generators. Design A motors are sometimes used on applications that require high breakdown (pullout) torque, such as injection molding machines. Design C motors are selected for applications that require high starting (locked-rotor) torque, such as inclined conveyors. Design D motors, also called high slip motors, are sometimes used to power hoists and cycling loads, such as oil well pump jacks and low-speed punch presses.
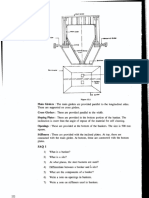
This is a typical torque-speed curve for a standard AC induction motor. It's important to understand some details of motor performance as shown by a typical Torque-Speed curve in the Figure to the right. The plot shows what happens in terms of output torque and motor speed when a motor is started with full voltage applied. The motor is initially at zero speed and develops locked-rotor torque (Point A). As the motor accelerates, some motor designs produce a slight dip in torque. If they do, the lowest point on this curve is called the pull-in or pull-up torque (Point B). As the speed increases further, the torque generally increases to the highest point on the curve (Point C), which is called the pullout or breakdown torque. Finally, when the motor is loaded to its full-load torque, the motor speed stabilizes (Point D). If the motor isn't driving anything, its speed goes up to its no-load speed or synchronous speed (Point E). For example, on a four-pole motor operating at 60 Hz, the no-load speed might be 1,799 RPM and synchronous speed would be 1,800 RPM. Each of these points (A, B, C, and D) has absolute values (usually expressed in poundfeet). However, they're frequently given in terms of a percentage of the full-load torque. For example, a 20-hp, 60-Hz, four-pole motor could have a full-load torque of 59.5 pound-feet and a locked-rotor torque of 116 pound-feet. This is shown as: (11659.5)100=195%
Similarly, the breakdown torque of 199 pound-feet could be shown as: (19959.5)100=334%
You might also like
- RBE Series Motors Brochure en-US 2003 1Document44 pagesRBE Series Motors Brochure en-US 2003 1Animesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- Oriental MotorDocument23 pagesOriental MotorSameer SangvikarNo ratings yet
- RBE (H) Series Motors: Data PublicationDocument44 pagesRBE (H) Series Motors: Data PublicationKOMATSU SHOVELNo ratings yet
- RBE Series Motors Brochure en-US 2003Document44 pagesRBE Series Motors Brochure en-US 2003derribo78No ratings yet
- Kaizen - Motor Selection GuideDocument11 pagesKaizen - Motor Selection GuideAmory Sabri AsmaroNo ratings yet
- DCMotorsDocument19 pagesDCMotorsAndrew BuckleyNo ratings yet
- Kaizen - Motor Selection GuideDocument10 pagesKaizen - Motor Selection GuideKarrar HussainNo ratings yet
- Motor&Drive BasicsDocument35 pagesMotor&Drive Basicsmathankumar1980No ratings yet
- Ac MotorsDocument273 pagesAc Motorschompink6900100% (1)
- Synchronous Motors Selection Guide KM - SG - 000183 - en-USDocument24 pagesSynchronous Motors Selection Guide KM - SG - 000183 - en-USJuan Francisco Marin MendiolaNo ratings yet
- Motors: Ratings and SpecificationsDocument8 pagesMotors: Ratings and SpecificationsSoumen BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Es Catalogue enDocument16 pagesEs Catalogue enLiêm HiếuNo ratings yet
- AC MotorsDocument52 pagesAC Motorsjennybunnyomg50% (6)
- Chapter 19 - Dynamic ModelsDocument141 pagesChapter 19 - Dynamic Modelswoldemariam workuNo ratings yet
- Choosing A Motor and Gearing CombinationDocument4 pagesChoosing A Motor and Gearing CombinationqeddyNo ratings yet
- Stepper Motor PDFDocument9 pagesStepper Motor PDFΓιώργος ΔήμαςNo ratings yet
- SRD-vehicle Traction Applications PDFDocument20 pagesSRD-vehicle Traction Applications PDFEduardo BittencourtNo ratings yet
- VFDDocument13 pagesVFDvenumechNo ratings yet
- Mott Chapter 21Document29 pagesMott Chapter 21kundayi shavaNo ratings yet
- Permanent Magnet Motors GB 05-2004Document72 pagesPermanent Magnet Motors GB 05-2004David Lopez Rebollo100% (1)
- Induction and Synchronous Motor FundamentalsDocument10 pagesInduction and Synchronous Motor Fundamentalshozipek5599100% (1)
- Project Electric BikeDocument28 pagesProject Electric Bikeachint9100% (1)
- Motor Control Centers-Low Voltage Section 12Document22 pagesMotor Control Centers-Low Voltage Section 12victor_omoniyiNo ratings yet
- Theory AC ServmDocument2 pagesTheory AC ServmKaustubh DesaiNo ratings yet
- DC Motors InformationDocument9 pagesDC Motors InformationCarlosNo ratings yet
- 6271 enDocument8 pages6271 enranjithkpvcNo ratings yet
- 3G3JXDocument8 pages3G3JXrwciriloNo ratings yet
- Hypo NicDocument198 pagesHypo NiclptorreNo ratings yet
- BLDC Technology OverviewDocument10 pagesBLDC Technology OverviewMohit Bhatnagar100% (1)
- SP600 AC Drive Dynamic Braking Selection Guide: Instruction Manual D2-3489Document36 pagesSP600 AC Drive Dynamic Braking Selection Guide: Instruction Manual D2-3489roviijoNo ratings yet
- 5 Phase New Pent Bipolar DriverDocument11 pages5 Phase New Pent Bipolar DriverMurat YenerNo ratings yet
- 25:1 Metal Gearmotor 20Dx44L MM: Pendulo InvertidoDocument13 pages25:1 Metal Gearmotor 20Dx44L MM: Pendulo InvertidoGeanpiero Touzet MálagaNo ratings yet
- DC Servomotors Assignment 02Document5 pagesDC Servomotors Assignment 02Saad BhattiNo ratings yet
- Motor Passo A Passo InfoDocument37 pagesMotor Passo A Passo InfojpncorreiaNo ratings yet
- Zero Max DrivesDocument14 pagesZero Max DrivesRanjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Yaskawa A1000 Catalog PDFDocument66 pagesYaskawa A1000 Catalog PDFLê PhụngNo ratings yet
- LV DriveDocument16 pagesLV Driveharshad_soni7912No ratings yet
- Automotive GoniometerDocument6 pagesAutomotive GoniometerifofanahNo ratings yet
- Using A DC Motor As A TachometerDocument5 pagesUsing A DC Motor As A Tachometerumer_0101No ratings yet
- Electric Motor TerminologyDocument26 pagesElectric Motor TerminologyGeorge MarkasNo ratings yet
- A1000catalog enDocument66 pagesA1000catalog enAnonymous b3NKZUbNo ratings yet
- A1000 Catalogue (Overview)Document17 pagesA1000 Catalogue (Overview)pcg_liveNo ratings yet
- Motores YaskawaDocument56 pagesMotores YaskawaLisa GarciaNo ratings yet
- Types of Motor Motor TypesDocument17 pagesTypes of Motor Motor TypesGokulThalaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Motion Control Technology: EngineeringDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Motion Control Technology: EngineeringKhadija RvNo ratings yet
- Z40 Service Training 139240 RevP1Document98 pagesZ40 Service Training 139240 RevP1DANIEL100% (1)
- Stepper Motor Basics: Applicationnote001Document13 pagesStepper Motor Basics: Applicationnote001shark seas100% (1)
- Eceg-5401 2Document37 pagesEceg-5401 2Kide Bay0% (1)
- Selection of MotorsDocument51 pagesSelection of MotorsGohar GujjarNo ratings yet
- Industrial SR BrochureDocument4 pagesIndustrial SR BrochureArinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Mini AllDocument562 pagesMini Allkevin_lim90100% (1)
- AC MotorDocument18 pagesAC MotorCathy IsraelNo ratings yet
- Motor Sizing CalculationsDocument1 pageMotor Sizing CalculationsAarij HanifNo ratings yet
- Kaizen - Motor Selection GuideDocument11 pagesKaizen - Motor Selection Guideneerajkumar101No ratings yet
- Joystick Control of Stepper Motor Using ArduinoDocument7 pagesJoystick Control of Stepper Motor Using ArduinoDany Mathew100% (2)
- EPG 04106e PsDocument4 pagesEPG 04106e PsalbertooliveiraNo ratings yet
- 开关磁阻电机的ANSOFT建模方法Document28 pages开关磁阻电机的ANSOFT建模方法Nuwantha FernandoNo ratings yet
- Speed Changers, Drives & Gears World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryFrom EverandSpeed Changers, Drives & Gears World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNo ratings yet
- VW Transporter T4 (Petrol and Diesel - 1990-1995) Workshop Manual: Owners Edition (Owners' Workshop Manuals)From EverandVW Transporter T4 (Petrol and Diesel - 1990-1995) Workshop Manual: Owners Edition (Owners' Workshop Manuals)No ratings yet
- 02-Building Cooling LoadsDocument3 pages02-Building Cooling LoadspratheeshNo ratings yet
- Math AA SL P 1 Marks SchemeDocument6 pagesMath AA SL P 1 Marks SchemeMrin GhoshNo ratings yet
- Main Girders: CrossDocument3 pagesMain Girders: Crossmn4webNo ratings yet
- Mahindra & MahindraDocument13 pagesMahindra & MahindraAbhishek DharmadhikariNo ratings yet
- Worlds Apart: A Story of Three Possible Warmer WorldsDocument1 pageWorlds Apart: A Story of Three Possible Warmer WorldsJuan Jose SossaNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Solar Mobile Charger: Submitted To: Submitted byDocument16 pagesSeminar On Solar Mobile Charger: Submitted To: Submitted byAkhila GottemukkulaNo ratings yet
- Dawn of Solar PV CookingDocument5 pagesDawn of Solar PV CookingAbhinav AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Awakened Citizen Programme-Report-class VII-2014Document4 pagesAwakened Citizen Programme-Report-class VII-2014bhsgeneral r m saraswathi50% (4)
- Electrowetting - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesElectrowetting - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDwane AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Runyankore-Rukiga Dictionary Launch: President Yoweri Museveni's SpeechDocument28 pagesRunyankore-Rukiga Dictionary Launch: President Yoweri Museveni's SpeechThe New Vision50% (2)
- Column, Slab, Footing and Wall Footing Foundations: Class A MixingDocument47 pagesColumn, Slab, Footing and Wall Footing Foundations: Class A MixingGioharry Nul PanambulanNo ratings yet
- June 2021 QP - Paper 1 (H) Edexcel Chemistry GCSEDocument28 pagesJune 2021 QP - Paper 1 (H) Edexcel Chemistry GCSEmiapoppycollinsNo ratings yet
- 300 PSI CTS (MP-1115) Operation Manual Rev1.3Document18 pages300 PSI CTS (MP-1115) Operation Manual Rev1.3Juan Manuel VizosoNo ratings yet
- Murata High Voltage CeramicDocument38 pagesMurata High Voltage CeramictycristinaNo ratings yet
- Cisco 2500 Series RoutersDocument16 pagesCisco 2500 Series RoutersJull Quintero DazaNo ratings yet
- Shawal 1431 AH Prayer ScheduleDocument2 pagesShawal 1431 AH Prayer SchedulemasjidibrahimNo ratings yet
- 3200AMMe - Part 4Document207 pages3200AMMe - Part 4Tanja Kesic100% (1)
- Twilight PrincessDocument49 pagesTwilight PrincessHikari DiegoNo ratings yet
- Grade - 2 Subject - Mathematics Unit - Geometry Topic - Geometrical Shapes School - Army School Roorkee Prepared by Mrs. RanjanaDocument25 pagesGrade - 2 Subject - Mathematics Unit - Geometry Topic - Geometrical Shapes School - Army School Roorkee Prepared by Mrs. RanjanaPenke Mejado BelenNo ratings yet
- Shandong Baoshida Cable Co, LTD.: Technical ParameterDocument3 pagesShandong Baoshida Cable Co, LTD.: Technical ParameterkmiqdNo ratings yet
- Updated G10 Class Routine Effective From 12 January 2023Document1 pageUpdated G10 Class Routine Effective From 12 January 2023NiloyNo ratings yet
- TNM History Updated June2017Document2 pagesTNM History Updated June2017Lucas AndreoNo ratings yet
- Electric ScootorDocument40 pagesElectric Scootor01fe19bme079No ratings yet
- Material Specification - 077154C-000-JSS-1700-009 - DDocument13 pagesMaterial Specification - 077154C-000-JSS-1700-009 - DStructures ProductionNo ratings yet
- FYP ProposalDocument11 pagesFYP ProposalArslan SamNo ratings yet
- Safe Lorry Loader Crane OperationsDocument4 pagesSafe Lorry Loader Crane Operationsjdmultimodal sdn bhdNo ratings yet
- World's Standard Model G6A!: Low Signal RelayDocument9 pagesWorld's Standard Model G6A!: Low Signal RelayEgiNo ratings yet
- Gemh 108Document20 pagesGemh 108YuvrajNo ratings yet
- Immigrant Italian Stone CarversDocument56 pagesImmigrant Italian Stone Carversglis7100% (2)
- PPT DIARHEA IN CHILDRENDocument31 pagesPPT DIARHEA IN CHILDRENRifka AnisaNo ratings yet