Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Teks - Science
Uploaded by
funderrOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Teks - Science
Uploaded by
funderrCopyright:
Available Formats
TEKS
Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) in science addressed by the activities in this curriculum are listed by number near the beginning of each activity. The following is a list of the full text of the TEKS addressed by the curriculum as a reference for teachers. Only the TEKS addressed by the activities in this curriculum are included in this listing. These TEKS will help teachers see how the concepts and process skills of each grade level are related and build over the grade levels becoming more complex with each year. RELATED TEKS Kindergarten K.1 Scientific Processes. The student participates in classroom and field investigations following home and school safety procedures. The student is expected to: (A) demonstrate safe practices during classroom and field investigations; and (B) learn how to use and conserve resources. K.2 Scientific Processes. The student develops abilities necessary to do scientific inquiry in the field and the classroom. The student is expected to: (A) ask questions about organisms, objects, and events; (B) plan and conduct simple descriptive investigations; (C) gather information using simple equipment and tools to extend the senses; (D) construct reasonable explanations using information; and (E) communicate findings about simple investigations. K.3 Scientific Processes. The student knows that information and critical thinking are used in making decisions. The student is expected to: (A) make decisions using information; (B) discuss and justify the merits of decisions; and (C) explain a problem in his/her own words and propose a solution. K.4 Scientific Processes. The student uses age-appropriate tools and models to verify that organisms and objects and part of organisms and objects can be observed, described and measured. The student is expected to: (A) identify and use senses as tools of observation; and (B) make observations using tools including hand lenses, balances, cups, bowls, and computers. K.5 Science Concepts. The student knows that organisms, objects and events have properties and patterns. The student is expected to: (A) describe properties of objects and characteristics of organisms; (C) recognize and copy patterns seen in charts and graphs.
K.6 Science Concepts. The student knows that systems have parts and are composed of organisms and objects. The student is expected to: (A) sort organisms and objects into groups according to their parts and describe how the groups are formed; (B) record observations about parts of plants including leaves, roots, stems, and flowers; (C) record observations about parts of animals including wings, feet, heads, and tails; (D) identify parts that, when separated from the whole, may result in the part or the whole not working, such as cars without wheels and plants without roots; (E) manipulate parts of objects such as toys, vehicles, or construction sets that, when put together, can do things they cannot do by themselves. K.7 Science Concepts. The student knows that many types of change occur. The student is expected to: (A) observe, describe, and record changes in size, mass, color, position, quantity, time, temperature, sound, and movement; (D) observe and record stages in the life cycle of organisms in their natural environment. K.8 Science Concepts. The student knows the difference between living organisms and nonliving objects. The student is expected to: (A) identify a particular organism or object as living or nonliving; (B) group organisms and objects as living and nonliving. K.9 Science Concepts. The student knows that living organisms have basic needs. The student is expected to: (A) identify basic needs of living organisms; (B) give examples of how living organisms depend on each other; and (C) identify ways that the Earth can provide resources for life. K.10 Science Concepts. The student knows that the natural world includes rocks, soil, and water. The student is expected to: (A) observe and describe properties of rocks, soil, and water; and (B) give examples of ways that rocks, soil, and water are useful.
First Grade 1.1 Scientific Processes. The student conducts classroom and field investigations following home and school safety procedures. The student is expected to:
(A) demonstrate safe practices during classroom and field investigations; and (B) learn how to use and conserve resources and materials. 1.2 Scientific Processes. The student develops abilities necessary to do scientific inquiry in the field and in the classroom. The student is expected to: (A) ask questions about organisms, objects, and events; (B) plan and conduct simple descriptive investigations; (C) gather information using simple equipment and tools to extend the senses; (D) construct reasonable explanations and draw conclusions; and (E) communicate explanations about investigations. 1.3 Scientific Processes. The student knows that information and critical thinking are used in making decisions. The student is expected to: (A) make decisions using information; (B) discuss and justify the merits of decisions; and (C) explain a problem in his/her own words and identify a task and solution related to the problem. 1.4 Scientific Processes. The student uses age-appropriate tools and models to verify that organisms and objects and parts of organisms and objects can be observed, described, and measured. The student is expected to: (A) collect information using tools including hand lenses, clocks, computers, thermometers, and balances; (B) record and compare collected information; 1.5 Science Concepts. The student knows that organisms, objects, and events have properties and patterns. The student is expected to: (B) identify, predict, and create, patterns including those seen in charts, graphs, and numbers; 1.6 Science Concepts. The student knows that systems have parts and are composed of organisms and objects. The student is expected to: (A) sort organisms and objects according to their parts and characteristics; (B) observe and describe the parts of plants and animals; (C) manipulate objects such as toys, vehicles, or construction sets so that the parts are separated from the whole which may result in the part or the whole not working; and (D) identify parts that, when put together, can do things they cannot do by themselves, such as a working camera with film, a car moving with a motor, and an airplane flying with fuel. 1.7 Science Concept. The student knows that many types of change occur. The student is expected to: (A) observe, measure, and record changes in size, mass, color, position, quantity,
sound and movement. (D) observe and record changes in the life cycle of organisms. 1.8 Science Concept. The student distinguishes between living organisms and nonliving objects. The student is expected to: (A) group living organisms and nonliving objects; and (B) compare living organisms and nonliving objects. 1.9 Science Concept. The student knows that living organisms have basic needs. The student is expected to: (A) identify characteristics of living organisms that allow their basic needs to be met; and (B) compare and give examples of the ways living organisms depend on each other for their basic needs. 1.10 Science Concepts. The student knows that the natural world includes rocks, soil, and water. (B) observe and describe differences in rocks and soil samples; and (C) identify how rocks, soil, and water can be recycled.
Second Grade 2.1 Scientific Processes. The student conducts classroom and field investigations following home and school safety procedures. The student is expected to: (A) demonstrate safe practices during classroom and field investigations; and (B) learn how to use and conserve resources and dispose of materials. 2.2 Scientific Processes. The student develops abilities necessary to do scientific inquiry in field and classroom. (A) ask questions about organisms, objects, and events; (B) plan and conduct simple descriptive investigations; (C) compare results of investigations with what students and scientists know about the world; (D) gather information using simple equipment and tools to extend the senses; (E) construct reasonable explanations and draw conclusions using information and prior knowledge; and (F) communicate explanations about investigations. 2.3 Scientific Processes. The student knows that information and critical thinking are used in making decisions. The student is expected to: (A) make decisions using information; (B) discuss and justify the merits of decisions; and (C) explain a problem in his/her own words and identify a task and solution related to the problem. 2.4 Scientific Processes. The student uses age-appropriate tools and models to verify that organisms and objects and parts of organisms and objects can be observed, described, and measured. The student is expected to: (A) collect information using tools including rulers, meter sticks, measuring cups, clocks, hand lenses, computers, thermometers, and balances; and (B) measure and compare organisms and objects and parts of organisms and objects, using standard and non-standard units. 2.5 Science Concept. The student knows that organisms, objects and events have properties and patterns. The student is expected to: (A) classify and sequence organisms, objects, and events based on properties and patterns; and (B) identify, predict, replicate, and crate patterns including those seen in charts, graphs, and numbers. 2.6 Science Concept. The student knows that systems have parts and are composed of organisms and objects. The student is expected to: (A) manipulate, predict, and identify parts that, when separated from the whole, may result in the part or the whole not working, such as flashlights without batteries and plants without leaves;
(B) manipulate, predict, and identify parts that, when put together, can do things they cannot do by themselves, such as a guitar and guitar strings; (D) observe and record the functions of animal parts. 2.7 Science Concept. The student knows that many types of change occur. The student is expected to: (A) observe, measure, record, analyze, predict, and illustrate changes in size, mass, temperature, color, position, quantity, sound, and movement. 2.8 Science Concept. The student distinguishes between living organisms and nonliving objects. The student is expected to: (A) identify characteristics of living organisms; and (B) identify characteristics of nonliving objects. 2.9 Science Concept. The student knows that living organisms have basic needs. The student is expected to: (A) identify the external characteristics of different kinds of plants and animals that allow their needs to be met; and (B) compare and give examples of the ways living organisms depend on each other and on their environments. 2.10 Science Concept. The student knows that the natural world includes rocks, soil, water, and gases of the atmosphere. (B) identify uses of natural resources.
Third Grade 3.1 Scientific Processes. The student conducts field and laboratory investigations following home and school safety procedures and environmentally appropriate and ethical practices. The Student is expected to: (A) demonstrate safe practices during field and laboratory investigations; and (B) make wise choices in the use and conservation of resources and the disposal or recycling of materials. 3.2 Scientific Processes. The student uses scientific inquiry methods during field and laboratory investigations. The student is expected to: (A) plan and implement descriptive investigations including asking well defined questions, formulating testable hypotheses, and selecting and using equipment and technology; (B) collect information by observing and measuring; C) analyze and interpret information to construct reasonable explanations from direct and indirect evidence; (D) communicate valid conclusions; and (E) construct simple graphs, tables, maps, and charts to organize, examine and evaluate information. 3.3 Scientific Processes. The student knows that information, critical thinking, and scientific problem solving are used in making decisions. The student is expected to: (A) analyze, review, and critique scientific explanations, including hypotheses and theories, as to their strengths and weaknesses using scientific evidence and information; (B) draw inferences based on information related to promotional materials for products and services; (C) represent the natural world using models and identify their limitations. (D) evaluate the impact of research on scientific thought, society, and the environment; and (E) connect Grade 3 science concept with the history of science and contributions of scientists. 3.4 Scientific Processes. The student knows how to use a variety of tools and methods to conduct science inquiry. The student is expected to: (A) collect and analyze information using tools including calculators, microscopes, cameras, safety goggles, sound recorders, clocks, computers, thermometers, hand lenses, meter sticks, rulers, balances, magnets, and compasses; and (B) demonstrate that repeated investigations may increase the reliability of results. 3.5 Science Concepts. The student knows that systems exist in the world. The student is expected to:
(A) observe and identify simple systems such as a sprouted seed and a wooden toy car; and (B) observe a simple system and describe the role of various parts such as a yo-yo and string. 3.6 Science Concepts. The student knows that forces cause change. (A) measure and record changes in the position and direction of the motion of an object to which a force such as a push or pull has been applied. 3.8 Science Concepts. The student knows that living organisms need food, water, light, air, a way to dispose of waste, and an environment in which to live. The student is expected to: (A) observe and describe the habitats of organisms within an ecosystem; (B) observe and identify organisms with similar needs that compete with one another for resources such as oxygen, water, food, or space; (C) describe environmental changes in which some organisms would thrive, become ill, or perish; and (D) describe how living organisms modify their physical environment to meet their needs such as beavers building a dam or humans building a home. 3.9 Science Concept. The student knows that species have different adaptations that help them survive and reproduce in their environment. The student is expected to: (A) observe and identify characteristics among species that allow each to survive and reproduce; and (B) analyze how adaptive characteristics help individuals within a species to survive and reproduce. 3.10 Science Concepts. The student knows that many likenesses between offspring and parents are inherited from the parents. (A) identify some inherited traits of plants; and (B) identify some inherited traits of animals. 3.11 Science Concepts. The student knows that the natural world includes earth materials and objects in the sky. (A) identify and describe the importance of earth materials including rocks, soil, water, and gases of the atmosphere in the local area and classify them as renewable, nonrenewable, or inexhaustible resources; (D) describe the characteristics of the Sun.
Fourth Grade 4.1 Scientific Processes. The student conducts field and laboratory investigations following home and school safety procedures and environmentally appropriate and ethical practices. The Student is expected to: (A) demonstrate safe practices during field and laboratory investigations; and (B) make wise choices in the use and conservation of resources and the disposal or recycling of materials. 4.2 Scientific Processes. The student uses scientific inquiry methods during field and laboratory investigations. The student is expected to: (A) plan and implement descriptive investigations including asking well defined questions, formulating testable hypotheses, and selecting and using equipment and technology; (B) collect information by observing and measuring; C) analyze and interpret information to construct reasonable explanations from direct and indirect evidence; (D) communicate valid conclusions; and (E) construct simple graphs, tables, maps, and charts to organize, examine and evaluate information. 4.3 Scientific Processes. The student knows that information, critical thinking, and scientific problem solving are used in making decisions. The student is expected to: (A) analyze, review, and critique scientific explanations, including hypotheses and theories, as to their strengths and weaknesses using scientific evidence and information; (B) draw inferences based on information related to promotional materials for products and services. (C) represent the natural world using models and identify their limitations. (D) evaluate the impact of research on scientific thought, society, and the environment; and (E) connect Grade 4 science concepts with the history of science and contributions of scientists. 4.4 Scientific Processes. The student knows how to use a variety of tools and methods to conduct science inquiry. The student is expected to: (A) collect and analyze information using tools including calculators, safety goggles, microscopes, cameras, sound recorders, computers, hand lenses, thermometers, rulers, meter sticks, timing devices, balances, and compasses; and (B) demonstrate that repeated investigations may increase the reliability of results. 4.5 Science Concepts. The student knows that complex systems may not work if some parts are removed The student is expected to:
(A) identify and describe the roles of some organisms in living systems such as plants in a schoolyard and parts in nonliving systems such as a light bulb in a circuit; and (B) predict and draw conclusions about what happens when part of a system is removed. 4.6 Science Concepts. The student knows that change can create recognizable patterns. The student is expected to: (C) use reflections to verify that a natural object has symmetry. 4.8 Science Concepts. The student knows that adaptations may increase the survival of members of a species. The student is expected to: (A) identify characteristics that allow members within a species to survive and reproduce. (B) compare adaptive characteristics of various species; (C) identify the kinds of species that lived in the past and compare them to existing species. 4.9 Science Concepts. The student knows that many likenesses between offspring and parents are inherited or learned. The student is expected to: (A) distinguish between inherited traits and learned characteristics; and (B) identify and provide examples of inherited traits and learned characteristics. 4.10 Science Concept. The student knows that certain past events affect present and future events. The student is expected to: (A) identify and observe effects of events that require time for changes to be noticeable including growth. 4.11 Science Concept. The student knows that the natural world includes earth materials and objects in the sky. The student is expected to: (C) identify the Sun as the major source of energy for the Earth and understand its role in the growth of plants.
Fifth Grade 5.1 Scientific Processes. The student conducts field and laboratory investigations following home and school safety procedures and environmentally appropriate and ethical practices. The Student is expected to:
(A) demonstrate safe practices during field and laboratory investigations; and (B) make wise choices in the use and conservation of resources and the disposal or recycling of materials. 5.2 Scientific Processes. The student uses scientific inquiry methods during field and laboratory investigations. The student is expected to: (A) plan and implement descriptive investigations including asking well defined questions, formulating testable hypotheses, and selecting and using equipment and technology; (B) collect information by observing and measuring; (C) analyze and interpret information to construct reasonable explanations from direct and indirect evidence; (D) communicate valid conclusions; and (E) construct simple graphs, tables, maps, and charts using tools including computers to organize, examine and evaluate information. 5.3 Scientific Processes. The student knows that information, critical thinking, and scientific problem solving are used in making decisions. The student is expected to: (A) analyze, review, and critique scientific explanations, including hypotheses and theories, as to their strengths and weaknesses using scientific evidence and information; (B) draw inferences based on information related to promotional materials for products and services; (C) represent the natural world using models and identify their limitations; 5.4 Scientific Processes. The student knows how to use a variety of tools and methods to conduct science inquiry. The student is expected to: (A) collect and analyze information using tools including calculators, microscopes, cameras, sound recorders, computers, hand lenses, rulers, thermometers, compasses, balances, hot plates, meter sticks, timing devices, magnets, collecting nets and safety goggles; and (B) demonstrate that repeated investigations may increase the reliability of results. 5.5 Science Concepts. The student knows that a system is a collection of cycles, structures, and processes that interact. The student is expected to: (A) describe some cycles, structures, and processes that are found in a simple system; and (B) describe some interactions that occur in a simple system. 5.6 Science Concepts. The student knows that some change occurs in cycles. The student is expected to: (C) describe and compare the life cycles of plants and animals. 5.8 Science Concepts. The student knows that energy occurs in many forms. The student is expected to:
(B) identify and demonstrate everyday examples of how light is reflected, such as from tinted windows, and refracted, such as in cameras; 5.9 Science Concept. The student knows that adaptations may increase the survival of members of a species. The student is expected to: (A) compare the adaptive characteristics of species that improve their ability to survive and reproduce in an ecosystem; (B) analyze and describe adaptive characteristics that result in an organisms unique niche in an ecosystem: and (C) predict some adaptive characteristics required for survival and reproduction by an organism in an ecosystem. 5.10 Science Concepts. The student knows that likenesses between offspring and parents can be inherited or learned. (A) identify traits that are inherited from parent to offspring in plants and animals; and (B) give examples of learned characteristics that result from the influence of the environment. 5.11 Science Concept. The student knows that certain past events affect present and future events. The student is expected to: (A) identify and observe actions that require time for changes to be measurable including growth.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- USDA Forest Service Tree Seed ManualDocument162 pagesUSDA Forest Service Tree Seed ManualJulio Mora CastilloNo ratings yet
- The GryphonDocument14 pagesThe GryphonLauraHensonNo ratings yet
- CELLULAR REPRODUCTION: A CONCISE GUIDEDocument35 pagesCELLULAR REPRODUCTION: A CONCISE GUIDEcath bugayongNo ratings yet
- Biology Today and Tomorrow With Physiology 5Th Edition Starr Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument45 pagesBiology Today and Tomorrow With Physiology 5Th Edition Starr Test Bank Full Chapter PDFshelleyrandolphikeaxjqwcr100% (12)
- Module 12 - Human Reproduction Health PDFDocument137 pagesModule 12 - Human Reproduction Health PDFvarunNo ratings yet
- The Menstrual CycleDocument8 pagesThe Menstrual Cyclemarc7victor7sales100% (1)
- Adaptive - Radiation - Activity - Finches. Sabrine AnswersDocument4 pagesAdaptive - Radiation - Activity - Finches. Sabrine AnswersSabrine Benzakour25% (4)
- Male InfertilityDocument14 pagesMale InfertilityDavid TurnerNo ratings yet
- Science: The Menstrual CycleDocument4 pagesScience: The Menstrual CycleLena Beth Tapawan YapNo ratings yet
- Principles of Ecology Study Guide Test 3 Temple UnivDocument8 pagesPrinciples of Ecology Study Guide Test 3 Temple UnivChris VelasquezNo ratings yet
- NCMA 217 Lec Performance Task # 3 Responsible ParenthoodDocument2 pagesNCMA 217 Lec Performance Task # 3 Responsible ParenthoodByren PacpacoNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Rate and Mouse MilkDocument6 pagesMetabolic Rate and Mouse MilkCasey PhilipsNo ratings yet
- The Polygamous Sex - Esther VilarDocument205 pagesThe Polygamous Sex - Esther VilarFederico Deambrosi Algorta100% (1)
- (Monographs On Theoretical and Applied Genetics 2) Pollination Mechanisms, Reproduction andDocument293 pages(Monographs On Theoretical and Applied Genetics 2) Pollination Mechanisms, Reproduction andMaher Gaber Issac AbrahamNo ratings yet
- (Bioethics 2) 2.02 - Chua-Chan - S AIDS - Health Care (Pat G)Document13 pages(Bioethics 2) 2.02 - Chua-Chan - S AIDS - Health Care (Pat G)Mikee MeladNo ratings yet
- Functions of PlacentaDocument18 pagesFunctions of PlacentaMohammad NabeelNo ratings yet
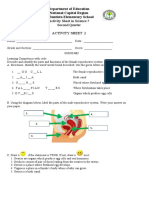
- Activity Sheet in Science 5 Second Quarter Activity Sheet 2Document4 pagesActivity Sheet in Science 5 Second Quarter Activity Sheet 2dinnes masubay100% (3)
- How To Eat A Woman OutDocument14 pagesHow To Eat A Woman OutVlad Bl100% (2)
- Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument5 pagesGestational Trophoblastic DiseaseWarshak NathNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants QuestionsDocument10 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Questionssonika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Perpetuation of Life 1Document8 pagesEarth and Life Science Perpetuation of Life 1Sayno, Samantha Jade C.No ratings yet
- General Biology 2 PowerPointDocument49 pagesGeneral Biology 2 PowerPointRob MaraviveNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesFemale Reproductive Systemkristel ludangcoNo ratings yet
- Female Sex Hormones: Natural Estrogens And ProgestinsDocument30 pagesFemale Sex Hormones: Natural Estrogens And ProgestinsMagdy El-GammalNo ratings yet
- Multiple PregnancyDocument26 pagesMultiple PregnancyRaj PatelNo ratings yet
- Instruction On Respect For Human LifeDocument21 pagesInstruction On Respect For Human LifeJBSfanNo ratings yet
- Biology 1234Document4 pagesBiology 1234Anup Singh TanwarNo ratings yet
- Seed Science and Technology1Document25 pagesSeed Science and Technology1DYCENo ratings yet
- The Population Bomb by Paul R. Ehrlich PDFDocument242 pagesThe Population Bomb by Paul R. Ehrlich PDFPuja Prakoso100% (3)
- Maternal Notes 1Document34 pagesMaternal Notes 1Mica Campoy CabinongNo ratings yet