Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Metal in Acid Solution Lab-Activity Report Siti Ashri Sahidahlisdiani 0902124 International Program On Science Education
Uploaded by
Shinichi D. Kudo MaschupilarealOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Metal in Acid Solution Lab-Activity Report Siti Ashri Sahidahlisdiani 0902124 International Program On Science Education
Uploaded by
Shinichi D. Kudo MaschupilarealCopyright:
Available Formats
qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwerty uiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasd fghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzx cvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmq Metal in Acid Solution Lab-Activity Report Siti Ashri SahidahLisdiani wertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyui 0902124 International
Program on science opasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfg Education hjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxc vbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmq wertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyui opasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfg hjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxc vbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmq wertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyui opasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfg hjklzxcvbnmrtyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbn mqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwert yuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopas
I.
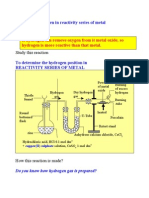
Title Metals in Acid Reaction
II.
Objective To identify the reaction between metals in acidic solution
III.
Basic Theory A metal is a chemical element that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat and forms cations and ionic bonds with non-metals.In chemistry, a metal (from Greek "" mtallon, "mine") is an element, compound, or alloy characterized by high electrical conductivity. In a metal, atoms readily lose electrons to form positive ions (cations). Those ions are surrounded by delocalized electrons, which are responsible for the conductivity. The solid thus produced is held by electrostatic interactions between the ions and the electron cloud, which are called metallic bonds. Reaction between metal and acid solution Acids react with most metals and a salt is produced. But unlike the reaction between acids and bases we don't get any water. Instead we get hydrogen gas. This is the general word equation for the reaction: metal + acid salt + hydrogen The salt produced depends upon the metal and the acid. Here are two examples: zinc + sulfuric acid zinc sulfate + hydrogen magnesium + hydrochloric acid magnesium chloride + hydrogen It doesn't matter which metal or acid is used, if there is a reaction we always get hydrogen gas as well as the salt
IV.
Apparatus and Substance a. Apparatus 1 Test tube
Pipette
Spatulla
b. Substance 1 HCl
H2SO4
Zn
Cu
Fe
Mg
Zn (powder)
Fe (powder)
V.
Procedures
VI.
Experiment Result a. Zn (II)
Observation Result Reaction in HCl -There were reaction -Much bubbles were produced
Picture
Reaction H2SO4
-There were reaction -Much bubbles were produced
b. Cu (II) Observation Result Reaction in HCl No reaction occured Picture
Reaction H2SO4
No reaction occured
c. Fe (II) Observation Result Reaction in HCl -There were reaction -Much bubbles were produced Picture
Reaction H2SO4
-There were reaction -Much bubbles were produced
d. Mg (II) Observation Result Reaction in HCl -There were reaction -Much bubbles were produced Picture
Reaction H2SO4
-There were reaction -Little bubbles were produced
e. Zn (powder) Observation Result Reaction in HCl -There were reaction Picture
-Small precipitation
Reaction H2SO4
-There were reaction -Long precipitation
f.
Fe (powder) Observation Result Reaction in HCl -There were reaction -Small precipitation Picture
Reaction H2SO4
-There were reaction -Long precipitation
VII.
Discussion In this experiment,there were many reactions of metals that were react with acid solution.In general equation,the reaction between metals and acid reaction should be Metals + Acid solution Salt from metal ion + Hydrogen From the general reaction that is shown upper,can be described that the reaction between metals and as acid solution will pruduce salt and Hydrogen. The salt itself commonly presence as ionic solution which is dissolve in the solution and hard to solve in the solution and hard to distinguish.Meanwhile the presence of hydrogen can be seen from the presence bubble in the reaction. Here are the reaction which were occured during the experiment 1. Zinc (II) In solution of H2SO4 Zn (s) + H2SO4 (aq) ZnSO (aq) + H2 (g) In solution of HCl Zn + HCl (aq) ZnCl2 (aq) + H2(g) 2. Cu (II) In solution of H2SO4 Cu (II) (s)+ H2SO4 (aq) In solution of HCl Cu (II) (s)+ HCl (aq) 3. Fe (II) In solution of H2SO4 Fe (II) (s) + H2SO4 (aq) FeSO4 (aq) + H2 (g) In solution of HCl Fe(II) (s) + HCl (aq) FeCl2 (aq) + H2 (g) 4. Mg (II)
In solution of H2SO4 Mg(II) (s) + H2SO4 (aq) MgSO4 (aq) + H2 (g)
In solution of HCl Mg(II) (s) + HCl (aq) MgCl (aq) + H2 (g)
5. Zn (powder) In solution of H2SO4 Zn (s) + H2SO4 (aq) ZnSO (aq) + H2 (g) In solution of HCl Zn (s) + 2 HCl (aq) ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g) 6. Fe (powder) In solution of H2SO4
Fe (s) + H2SO4 (aq) FeSO4 (aq) + H2 (g)
In solution of HCl Fe (s) + HCl (aq) FeCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
VIII.
Conclussion 1. The reaction of metal and acid always produce hydrogen as the result. 2. Not all the metal can be reacted with Acid and produced salt and H2. 3. The salt which is produced is hard to be distinguished because it present in ionic form.
IX.
Suggestion 1. Be careful in taking metal compound,use gloves to avoid the dangerous. 2. Dont use same metal substance for each solution.
X.
Refference http://www.suite101.com/content/preparation-of-soluble-metal-salts-in-the-laba187813 (accesed on:April,20th 2011) http://www.docbrown.info/page04/Y11revQs/acidreactionequationsFHanswers.ht m (accesed on:April,20th 2011)
Pre-lab 1. What is the properties of metals? Chemical Metals are usually inclined to form cations through electron loss\ reacting with oxygen in the air to form oxides over changing timescales (iron rusts over years, while potassium burns in seconds). Examples: 4 Na + O2 2 Na2O (sodium oxide) The transition metals (such as iron, copper, zinc, and nickel) take much longer to oxidize. Others, like palladium, platinum and gold, do not react with the atmosphere at all. Some metals form a barrier layer of oxide on their surface which cannot be penetrated by further oxygen molecules and thus retain their shiny appearance and good conductivity for many decades (like aluminium, magnesium, some steels, and titanium). The oxides of metals are generally basic, as opposed to those of nonmetals, which are acidic. Painting, anodizing or plating metals are good ways to prevent their corrosion. However, a more reactive metal in the electrochemical series must be chosen for coating, especially when chipping of the coating is expected. Water and the two metals form an electrochemical cell, and if the coating is less reactive than the coatee, the coating actually promotes corrosion. Physical Metals in general have high electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, luster and density, and the ability to be deformed under stress without cleaving.While there are several metals that have low density, hardness, and melting points, these (the alkali and alkaline earth metals) are extremely reactive, and are rarely encountered in their elemental, metallic form. Optically speaking, metals are opaque, shiny and lustrous. This is because visible lightwaves are not readily transmitted through the bulk of their microstructure. The large number of free electrons in any typical metallic solid (element or alloy) is responsible for the fact that they can never be categorized as transparent materials.The majority of metals have higher densities than the majority of nonmetals.
2. What is the properties of HCl?
Molecular weight : 36.461 g/mol
Liquid phase
Liquid density (1.013 bar at boiling point) : 1191 kg/m3 Liquid/gas equivalent (1.013 bar and 15 C (59 F)) : 772 vol/vol Boiling point (1.013 bar) : -85.1 C Latent heat of vaporization (1.013 bar at boiling point) : 443.38 kJ/kg Vapor pressure (at 20 C or 68 F) : 42.6 bar Solubility in water (1.013 bar and 0 C (32 F)) : 506 vol/vol
3. What is the properties of H2SO4? Appearance: colorless viscous liquid Melting point: -2 C Boiling point: 327C Density: 1.84g/mL Reacts violently with water Water soluble in all proportions Extremely corrosive and causes severe burns Harmful if inhaled, ingested, or skin contact
Post-lab 1.What is the indicator that metal react with acid? there are bubble, precipitation. 2.What happens when you mix hydrochloric acid with zinc metal? The hydrochloric acid decomposes or breaks down the zinc metal causing a bubbling reaction and creating hydrogen
You might also like
- KVS Class X Science Study Material SummaryDocument147 pagesKVS Class X Science Study Material SummaryritujalanNo ratings yet
- Sci 10Document134 pagesSci 10Pirated VirusNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Official ReportDocument26 pagesHydrogen Official Reportfirdausynuzula47No ratings yet
- Activity 1.1 The Law of Conservation of Mass: Information and AdviceDocument3 pagesActivity 1.1 The Law of Conservation of Mass: Information and Advice11223366wcNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ClassX Resource MaterialDocument10 pagesChemistry ClassX Resource MaterialÂåřøhī MāhåjáňNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report SolubilityDocument5 pagesLaboratory Report SolubilityIndraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Copper Post LabDocument3 pagesChemistry of Copper Post LabFerid HacizadeNo ratings yet
- Final CL 10 Science Most Repeated Previous Year QuestionsDocument19 pagesFinal CL 10 Science Most Repeated Previous Year QuestionsAditi Pandya100% (1)
- Class10 Science Notes Chapter1 PDFDocument6 pagesClass10 Science Notes Chapter1 PDFdineshhissarNo ratings yet
- Language of Chemistry: CH5 STD:7Document44 pagesLanguage of Chemistry: CH5 STD:7Aatman GargNo ratings yet
- Ques Ans Chem X Apr 28, 2021Document5 pagesQues Ans Chem X Apr 28, 2021Atif AnsariNo ratings yet
- From Copper To Copper LabDocument8 pagesFrom Copper To Copper LabShakilMirza100% (9)
- Acids Bases Salts Board Exam RevisionDocument69 pagesAcids Bases Salts Board Exam RevisionManu GoelNo ratings yet
- Activity-1.4: Materials Required ProcedureDocument10 pagesActivity-1.4: Materials Required ProcedureShreyansNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 10Document8 pagesChemistry Class 10Ruchika RastogiNo ratings yet
- Cycle of Copper Reactions LabDocument6 pagesCycle of Copper Reactions LabbigfoottedNo ratings yet
- Lab.4 QMC 23Document19 pagesLab.4 QMC 23Brayan Gutierrez CartagenaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Rxns F16Document13 pagesChemical Rxns F16Kenn EvangelioNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemistry-Experi. 1Document13 pagesDepartment of Chemistry-Experi. 1ThabisoNo ratings yet
- Minerals 09 00661 v2Document17 pagesMinerals 09 00661 v2Ryan PermanaNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Copper: Percent YieldDocument20 pagesReactions of Copper: Percent Yieldwann711100% (1)
- Instructions for Writing a Chemistry RecordDocument8 pagesInstructions for Writing a Chemistry Recordpr,moNo ratings yet
- Xam Idea Science Standard Class 10 Term 1 MCQ - 211011 - 094103Document183 pagesXam Idea Science Standard Class 10 Term 1 MCQ - 211011 - 094103Shreya Ajith100% (5)
- Chemistry Class 10 CDFDocument11 pagesChemistry Class 10 CDFPuppala VardhanNo ratings yet
- Solution 1:: Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument9 pagesSolution 1:: Chemical Reactions and EquationsOjasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument9 pagesChemistry Projectmgarg2004No ratings yet
- Class X NCERT Solutions Chemistry by NTSE GuruDocument5 pagesClass X NCERT Solutions Chemistry by NTSE GuruNTSE GuruNo ratings yet
- 10 Ch-1Document24 pages10 Ch-1egtuhin581No ratings yet
- Textbook Ref & Notes - Chem-Describing Reactions PDFDocument29 pagesTextbook Ref & Notes - Chem-Describing Reactions PDFVenuNo ratings yet
- Determine Hydrogen's Position in the Reactivity SeriesDocument5 pagesDetermine Hydrogen's Position in the Reactivity SeriesYulia PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Changes in MatterDocument29 pagesChanges in MatterThisari GunasingheNo ratings yet
- 2020 2021 Class X Chemistry Part 1 AWDocument135 pages2020 2021 Class X Chemistry Part 1 AWThanveer Ahmad100% (1)
- IB Chem IA Bleach PDFDocument17 pagesIB Chem IA Bleach PDFsushma111No ratings yet
- MAMALUBA - Assignment For Chem Lab 401Document2 pagesMAMALUBA - Assignment For Chem Lab 401Sophia Indirah MamalubaNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 Class 10Document5 pagesChem 1 Class 10InkspireNo ratings yet
- ActivitiesDocument12 pagesActivitiesArchita MundharaNo ratings yet
- H2 Chemistry SummaryDocument16 pagesH2 Chemistry SummarySherman HoNo ratings yet
- To Analuyse Different Samples of AlloysDocument13 pagesTo Analuyse Different Samples of AlloysmukulNo ratings yet
- AMPLOP PEskam-dikonversiDocument29 pagesAMPLOP PEskam-dikonversiahlan habibiNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY ASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONDocument3 pagesCHEMISTRY ASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONAmogh ChavanNo ratings yet
- P. Joy: Inorganic PaperDocument64 pagesP. Joy: Inorganic PaperbhartiyaanujNo ratings yet
- Kvs Ro, Jaipur: Class:-XDocument24 pagesKvs Ro, Jaipur: Class:-XVedant DuaNo ratings yet
- Cation SeparationDocument22 pagesCation SeparationDiane Angeles50% (2)
- Corrosion Course Work 2Document6 pagesCorrosion Course Work 2Charles NtaNo ratings yet
- Class X Chap 1 2016Document2 pagesClass X Chap 1 2016Kanishk AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Praktikum Anorganik Hydrogen and OxygenDocument25 pagesPraktikum Anorganik Hydrogen and Oxygenqurrota ainynNo ratings yet
- Shobhit ScienceDocument126 pagesShobhit ScienceMack TripathiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Booklet - Shobhit NirwanDocument21 pagesChemical Reactions Booklet - Shobhit NirwanOWAIS AHMED75% (8)
- Worksheet-1 (Chemical Reaction)Document6 pagesWorksheet-1 (Chemical Reaction)Sachin Garg100% (1)
- All InorganicDocument125 pagesAll InorganicMarco WongNo ratings yet
- Sulfur Impact On BuildingDocument28 pagesSulfur Impact On BuildingAdianMuhammadRidhoNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen and its compounds: key properties and reactionsDocument5 pagesHydrogen and its compounds: key properties and reactionsGagan NdNo ratings yet
- Fiveless ChemistryDocument16 pagesFiveless ChemistryhelamahjoubmounirdmoNo ratings yet
- Karski 2003Document5 pagesKarski 2003farah al-sudaniNo ratings yet
- SS2 2ND TERM NewDocument59 pagesSS2 2ND TERM Newpalmer okiemuteNo ratings yet
- A System of Instruction in the Practical Use of the BlowpipeFrom EverandA System of Instruction in the Practical Use of the BlowpipeNo ratings yet
- A System of Instruction in the Practical Use of the Blowpipe: Being A Graduated Course Of Analysis For The Use Of Students And All Those Engaged In The Examination Of Metallic CombinationsFrom EverandA System of Instruction in the Practical Use of the Blowpipe: Being A Graduated Course Of Analysis For The Use Of Students And All Those Engaged In The Examination Of Metallic CombinationsNo ratings yet
- Water Gas Shift Reaction: Research Developments and ApplicationsFrom EverandWater Gas Shift Reaction: Research Developments and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Modern Carbonylation MethodsFrom EverandModern Carbonylation MethodsLászló KollárNo ratings yet
- REKAP - TPP - XLSX - Filename - UTF-8''REKAP TPP-1Document32 pagesREKAP - TPP - XLSX - Filename - UTF-8''REKAP TPP-1Rini AnggraenieNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument2 pagesUnit 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenespavankumar3905syNo ratings yet
- Product Catalog 2017 1Document35 pagesProduct Catalog 2017 1Wah Wah SoeNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: CHEMISTRY 5070/21Document20 pagesCambridge O Level: CHEMISTRY 5070/21Fasih RazaNo ratings yet
- FPS Product List 2Document2 pagesFPS Product List 2Calvin XuNo ratings yet
- Foaming Capacity of Soaps (Ameen Rasool)Document18 pagesFoaming Capacity of Soaps (Ameen Rasool)Ameen RasoolNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Activity 7 - Notes TypedDocument3 pagesUnit 1 Activity 7 - Notes TypedSijie LiNo ratings yet
- URINE PRESERVATIVES: PROPER HANDLING & STORAGEDocument23 pagesURINE PRESERVATIVES: PROPER HANDLING & STORAGEHEMAMALINI RAMASESHANNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Compounds and Benzene StructureDocument5 pagesAromatic Compounds and Benzene StructureAbigail P. ARANGGANo ratings yet
- Chemical Methode ManualDocument211 pagesChemical Methode ManualThufeil Tufi Yunindika100% (1)
- Mechanism of 2-methylbut-2-ene formationDocument88 pagesMechanism of 2-methylbut-2-ene formation22S48 SUNDARAM RAMASUBBU RAKSHANo ratings yet
- Eco-MPE: Multi-Purpose Epoxy For Use As A Primer, Broadcast or Build CoatDocument2 pagesEco-MPE: Multi-Purpose Epoxy For Use As A Primer, Broadcast or Build CoatServandoNo ratings yet
- Identification of Aldehydes and KetonesDocument6 pagesIdentification of Aldehydes and Ketonesعلاوي البرشلونيNo ratings yet
- O-Ring Compound Data SheetDocument3 pagesO-Ring Compound Data SheetScarlet BlancoNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesCarbohydratesDanluidQMalintadNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument34 pagesNomenclature of Organic Compoundstapas kunduNo ratings yet
- Desulphurization of Lead Cake by Sodium CarbonateDocument6 pagesDesulphurization of Lead Cake by Sodium CarbonateVic Tres DosNo ratings yet
- Tub & Tile Cleaners - 031Document2 pagesTub & Tile Cleaners - 031mndmattNo ratings yet
- Ionic Polymerization: Dr. Saima Shabbir, MS&EDocument19 pagesIonic Polymerization: Dr. Saima Shabbir, MS&ETayyab AhsanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9Document6 pagesExperiment 9clairedemotica100% (1)
- Salting-out effect explained using Le Chatelier's principleDocument1 pageSalting-out effect explained using Le Chatelier's principlesnowblindedNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Test For CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesQualitative Test For CarbohydratesmegmayorNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical Reactions Detailed Worksheet Extra EditedDocument5 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions Detailed Worksheet Extra EditedBayot KuhNo ratings yet
- FentanylDocument2 pagesFentanylMulayam Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- Inhibitors of Cerebroside MetabolismDocument12 pagesInhibitors of Cerebroside MetabolismMaarten van GinkelNo ratings yet
- Biodiesel Production Methods and Fuel Properties ReviewDocument13 pagesBiodiesel Production Methods and Fuel Properties ReviewKa HinaNo ratings yet
- Module 62 Rate of Reaction Concentration Effect - DwiDocument2 pagesModule 62 Rate of Reaction Concentration Effect - Dwirudi_zNo ratings yet
- Fe HbedDocument6 pagesFe HbedMuhammad Iqbal ChandioNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds Question Paper For JEE Advanced 2019Document6 pagesCarbonyl Compounds Question Paper For JEE Advanced 2019misostudyNo ratings yet
- United States Patent Office: Patented June 16, 1964Document3 pagesUnited States Patent Office: Patented June 16, 1964Vansala GanesanNo ratings yet