Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Part A - Questions & Answers: Input Processing Output
Uploaded by
Parthiban SOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Part A - Questions & Answers: Input Processing Output
Uploaded by
Parthiban SCopyright:
Available Formats
PART A - QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
1. What is Data? Data are a collection of: a. Facts b. Measurements c. Statistics
2. Compare information & data. Data consists of facts and figures that are relatively meaningless to the user. (e.g., number of hours worked by an employee) Information is processed data or meaningful data. (e.g., multiplying the hours worked by the hourly rate to get each employees gross earnings).
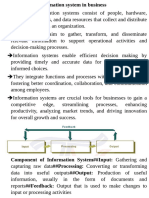
3. Explain the concept of system. A system may be defined as a set of elements which are joined together to achieve a common objective. The set of elements for a system may be understood as Input, Process and output. A system has one or more multiple inputs; these inputs are processed through a transformation process to convert these inputs into outputs.
INPUT
PROCESSING
OUTPUT
FEEDBACK/CONTROL
4. Information Technology
Information technology is the use of computers and software to manage information. IT consists of hardware, software, telecommunications, database management and other information processing technologies used in computer based information system.
5. Artificial Intelligence.
AI is an application that enables the computer system to perform some of the same logical reasoning tasks as humans.
The ability of a computer or other machine to perform those activities that are normally thought to require intelligence.
6. What is an Information System? Information system is an integrated set of components for collecting, storing, processing, and communicating information. Business firms, other organizations, and individuals rely on information systems to manage their operations, compete in the marketplace, supply services, and augment personal lives.
7. What are the different kinds of Information System based on hierarchy? Information systems support different types of decisions at different levels of the organizational hierarchy. Major types of Information systems are:
Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) Management Information Systems (MIS) Decision Support Systems (DSS) Executive Support Systems (ESS) Office Automation system (OAS) Business Expert System (BES)
Relation of information systems to levels of organization 8. List out the role of System analyst. Systems analysts act as the principal liaison between the information systems groups and the rest of the organization. It is the systems analyst's job to translate business problems and requirements into information requirements and systems. The System analyst has various tasks to perform.
Communication: The Analyst should examine the communication structure in the organization and where necessary set up formal structures to ensure that users have information about the system as it develops.
Education: At all stages of the project, the analyst should concentrate on educating individuals at all levels.
Participation: Both formal and informal structures should be used to allow people to contribute ideas on the old systems and new systems.
Training: Training sessions should be used to impart skills and to build up user confidence.
Job design: In designing new jobs, major aim should be to retain the satisfactory ones of the old job and to remove the unsatisfactory ones.
9. Define MIS. According to G.B.Davis, Management Information System is defined as an integrated man/machine system for providing information to support the operations, management and decision making functions in an organization.
10. What are the characteristics of MIS?
The main characteristics of MIS are:
MIS is comprehensive in nature. MIS is centrally coordinated to ensure that its data processing, office automation, decision support system are developed and operated in a planned and coordinated way.
MIS is rationally integrated. MIS transforms data into information. MIS enhances productivity in several ways. MIS should provide relevant information. It should provide feedback about its own efficiency and effectiveness.
It must be designed to be easily modified.
11. List out the functions of MIS. The MIS must perform the following functions in order to meet its objectives. Data Capturing Processing of data Storage of information Retrieval of information Dissemination of management information
12. List out the basic requirements of MIS. The basic requirements of a computer based MIS are:
Hardware: It refers to Physical computer and other associated devices. Software: It means the instructions or programs that direct the operation of hardware.
Database: The database contains all data utilized by the application software. Operations Personnel: It includes Computer Operators , system analysts, Programmers etc.,
Procedures. UNIT II
13. What is SDLC? SDLC stands for Software Development Life Cycle. SDLC is the process of developing information systems through investigation, analysis, design, implementation and maintenance. SDLC is also known as information systems development or application development. SDLC is a systems approach to problem solving. 14. List out the various stages of SDLC. 1. Preliminary Investigation 2. Feasibility Study 3. Analysis 4. Design 5. Coding 6. Testing 7. Maintenance & Review.
15. Define system analysis. System analysis is a process of collecting and interpreting facts, identifying problems and using the information to recommend improvements in the system.
16. List out the strategies/tools for requirement determination. Interview Questionnaire Record review Observation
17. List out the various Software life cycle models. Waterfall life cycle model. Incremental Life cycle model.
Spiral Life cycle model. WIN WIN spiral model. Object oriented model.
18. DFD Data Flow Diagram (DFD) is a graphical representation of the logical flow of data. It helps in expressing the systems requirements in a simple and understandable form. It is also known as bubble chart.
19. What are the various symbols used in DFD? There are four main symbols used in DFD. Square: It represents Source/ destination of system data.
Circle/Bubble: It represents process that transforms incoming data into outgoing data flow.
Arrow: It is a pipeline through which data flows.
Open rectangle: it represents data store.
20. What do you mean by ER?
An entity-relationship (ER) diagram is a specialized graphic that illustrates the interrelationships between entities in a database.
21. What are the various symbols used in ER? ER diagrams often use symbols to represent three different types of information.
Boxes are commonly used to represent entities. Diamonds are normally used to represent relationships and Eclipse or ovals are used to represent attributes.
22. DBMS. Database Management System (DBMS) is a set of computer programs that controls and allows the creation, maintenance, storage, modification and extraction of information from a database by the end users. It consists of collection of interrelated data and a set of programs to access the data.
23. RDBMS. In Relational Database Management System (RDBMS), data is organized into tables called relations, each of which is implemented as a file.
24. What do you mean by Tuple and attribute in a relation. In relational terminology, a row in a relation is called a tuple and it represents a record or an entity. A column in a relation represents field or an attribute.
25. What is system design? System design starts after the system analysis phase is over. The output of system analysis becomes an input in the design phase. Data requirements are worked out on the basis of user requirement estimates.
26. List out the various feasibility study. The feasibility of a proposed system can be assessed in terms of: Organizational Feasibility Economic Feasibility Technical Feasibility Operational Feasibility
27. What are the objectives of system design? A system is designed with the following objectives:
o
Practicality: The system should be designed in such a way that it may be learnt and operated with ease by the users.
o o o
Flexibility: A system must be responsive to the change. Efficiency: A system should perform jobs within their specified time. Security: This relates to detection and prevention of fraud and abuse of data.
UNIT III
28. Differentiate between MIS and DSS
S.NO. MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEM 1. 2. Information form of a MIS is periodic. Information form of DSS is interactive. information formats are adhoc, DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM
Information formats are pre-specified DSS and fixed.
flexible and adaptable. information about the It provides information to confront specific problems or opportunities. supports the semi-structured and
3.
It
provides
performance of the organization. 4.
It supports structured decisions for It control.
operational and tactical planning and unstructured decisions for technical and strategic planning and control.
5.
It provides indirect support to many It provides direct support tailored to the managers. decision managers. making styles of individual
29. Differentiate between DSS and EIS S.NO. EXECUTIVE INFORMATION SYSTEM 1. It directly supports the value added work It provides information, models or tools for in the organization. 2. It provides tools, information decision making. or It provides tools for analyzing data and building models and help in analyzing the alternatives. 3. Features are:(i) User friendly interface Features are: (i) user controlled interaction (ii) user friendly methods of analyzing with computers (ii) use of models and data. data. DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM
structured methods for making decisions.
30. Define EIS.
Executive Information System (EIS) are management information systems which are designed to meet the strategic information needs of top management. They provide selected and summarized information for senior executives.
31. Where are Expert Systems used? Expert systems are designed and created to facilitate tasks in the fields of
Accounting Medicine Process control Financial service Production Human resources etc.
32. What is KM?
Knowledge Management (KM) is a process that helps organizations identify, select, organize, disseminate, and transfer important information and expertise that are part of the organizations memory.
33. What is GIS? Geographic information system (GIS) is a special category of DSS that integrate computer graphics and geographic databases with other DSS features. A GIS combines different pieces or layers of information so that more knowledge is gained about a particular location.
34. What are the benefits of GIS? GIS can be used when natural disasters occur. GIS helps banks in the identification of suitable locations for installing new branches or ATM terminals.
GIS can be used to support decisions that require knowledge about the geographic distribution of people or other resources in scientific research. UNIT IV
35. Software Testing Software Testing is a set of activities conducted with the intent of finding errors in software. It is the process of verifying that a program functions properly. 36. Concurrency control Concurrency control provides rules, methods, and design methodologies to maintain the consistency of modules operating concurrently while interacting, and thus the consistency of the whole system. 37. List out the parameters that define software Engineering quality. Software quality measures how well software is designed and how well the software conforms to that design. Some of the parameters measure software quality are : Scalability Correctness Completeness Absence of bugs Fault-tolerance
38. Error detection
Error handling refers to the anticipation, detection, and resolution of programming, application, and communications errors. Specialized programs, called error handlers, are available for some applications.
UNIT V 1. What is pervasive computing? Pervasive computing can be defined as access to information and software applications anytime and anywhere. This form of computing is highly dynamic and disaggregated. Pervasive computing aims at availability and invisibility.
2. What is SCM? Supply chain management (SCM) is the management of a network of interconnected businesses involved in the ultimate provision of product and service packages required by end customers .Supply Chain Management spans all movement and storage of raw materials , work-in-process inventory, and finished goods from point of origin to point of consumption (supply chain).
3. Data warehousing. Data warehousing is defined as a process of centralized data management and retrieval. Data warehousing represents an ideal vision of maintaining a central repository of all organizational data. Centralization of data is needed to maximize user access and analysis.
4. Data Mining. Data mining is the process of extracting patterns from data. Data mining is becoming an increasingly important tool to transform this data into information. It is commonly used in a wide range of profiling practices, such as marketing, surveillance, fraud detection and scientific discovery.
5. What is CMM? CMM (Capability Maturity Model) is a model of process maturity for software development - an evolutionary model of the progress of a companys abilities to develop software.
6. List out the CMM models.
7. e-governance
It is the use of a range of modern Information and Communication Technologies such as Internet, Local Area Networks, mobiles etc. by Government to improve the effectiveness, efficiency, service delivery and to promote democracy.
You might also like
- MBA Anna University-Management Information System 2 MarksDocument24 pagesMBA Anna University-Management Information System 2 Markspadma_abivarshini92% (12)
- Is 217 - Deployment Maintenance & ServicesDocument18 pagesIs 217 - Deployment Maintenance & ServicesAllan IgbuhayNo ratings yet
- Data Flow Diagrams Processes: Name: Amit Pathak ROLL NO: 1302016570Document6 pagesData Flow Diagrams Processes: Name: Amit Pathak ROLL NO: 1302016570pkm7929No ratings yet
- DSS & Mis Unit-4Document11 pagesDSS & Mis Unit-4Kommineni Ravie KumarNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Information Systems ChapterDocument10 pagesSupply Chain Information Systems ChapterAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem MIS MB0047Document9 pages2nd Sem MIS MB0047pandey_hariom12No ratings yet
- MisDocument41 pagesMisinnocentevilshahidNo ratings yet
- CBISDocument6 pagesCBISNida HassanNo ratings yet
- A System Is A Set of Related Components That Produces Specific ResultsDocument5 pagesA System Is A Set of Related Components That Produces Specific ResultsCici JavierNo ratings yet
- Management Information Systems and Dss Unit-Iv: Disha Technical CampusDocument17 pagesManagement Information Systems and Dss Unit-Iv: Disha Technical CampusBiplab BiswasNo ratings yet
- Saeed Peyman Essay Questions: Tutorial 1Document3 pagesSaeed Peyman Essay Questions: Tutorial 1Keanu ReevsNo ratings yet
- Information System and System Development Life CycleDocument18 pagesInformation System and System Development Life CycleNomiNo ratings yet
- CBIS (Computer Based Information System) : DataDocument7 pagesCBIS (Computer Based Information System) : Dataخالد ناهض نايف نجمNo ratings yet
- CS - PPT 1 1Document63 pagesCS - PPT 1 1noreply.myworkspaceNo ratings yet
- Introduction to System Analysis and DesignDocument54 pagesIntroduction to System Analysis and DesignDaliElah RosLiNo ratings yet
- The State Railway System': Information InformationDocument13 pagesThe State Railway System': Information InformationKhondoker Razzakul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Bab 1Document57 pagesBab 1SYED AHMAD SHAUQI BIN SYED SHUHAIMINo ratings yet
- Information Systems: Definitions and ComponentsDocument20 pagesInformation Systems: Definitions and Componentssubhash221103No ratings yet
- MIS Chapter SummaryDocument7 pagesMIS Chapter SummaryHaseeb MujeebNo ratings yet
- Introduction to System Analysis and Design (40chDocument21 pagesIntroduction to System Analysis and Design (40chEmma Mary FuertesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Decision Support SystemsDocument10 pagesUnit 1-Decision Support SystemsDisha Verma KalraNo ratings yet
- IT Systems PDFDocument7 pagesIT Systems PDFDix BrosNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information System An Overview: Unit - 2Document8 pagesAccounting Information System An Overview: Unit - 2naseer ahmedNo ratings yet
- Mis NotesDocument5 pagesMis Notesmayank barsenaNo ratings yet
- Session - 01 - Introduction To MISDocument29 pagesSession - 01 - Introduction To MISMohamed Ahmed AbdiNo ratings yet
- Session 1 and 2 CompleteDocument72 pagesSession 1 and 2 Completedavid nduatiNo ratings yet
- MIS Types and Importance in BusinessDocument10 pagesMIS Types and Importance in BusinessUmema FatimaNo ratings yet
- MIS Lecture 3Document10 pagesMIS Lecture 3dayas1979No ratings yet
- Information SystemsDocument33 pagesInformation Systemsslishanadata100% (11)
- System Analysis & Design: Chapter One: Systems Planning and SelectionDocument230 pagesSystem Analysis & Design: Chapter One: Systems Planning and Selectionbeletesendek16No ratings yet
- MIS Final2Document57 pagesMIS Final2Alok JainNo ratings yet
- MICS Boost Note For CAP III Printable FormDocument53 pagesMICS Boost Note For CAP III Printable FormPratik TimsinaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1) Mis NotesDocument14 pagesTopic 1) Mis NotesDhruvil ShahNo ratings yet
- AIS Chapter 3Document38 pagesAIS Chapter 3bisrattesfaye100% (1)
- Chapter One Introduction To SADDocument26 pagesChapter One Introduction To SADCali Cali100% (1)
- Chapter 01cDocument26 pagesChapter 01csubiramwansasu7No ratings yet
- MC0076 (C)Document19 pagesMC0076 (C)akibond999No ratings yet
- 2105 - Previous Solution of 16th BatchDocument64 pages2105 - Previous Solution of 16th BatchSheikh AslamNo ratings yet
- Course Content: Computer Science TOTAL: 100: SystemDocument24 pagesCourse Content: Computer Science TOTAL: 100: SystemMac TavishNo ratings yet
- SSADDocument6 pagesSSADraunak19100% (1)
- Difference Between Mis and DssDocument16 pagesDifference Between Mis and DssKelly BaileyNo ratings yet
- Unit-I 2 Mark QuestionsDocument22 pagesUnit-I 2 Mark QuestionsLords PorseenaNo ratings yet
- Xaviers Institute Management Information Systems CourseDocument13 pagesXaviers Institute Management Information Systems Coursesyed tanseerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Systems Analysis and DesignDocument43 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Systems Analysis and Designphongdi2003No ratings yet
- Acc 156 Sas - 23Document5 pagesAcc 156 Sas - 23Severus HadesNo ratings yet
- Introdution of MISDocument39 pagesIntrodution of MISBilal Choudhary100% (1)
- Management Information SystemDocument9 pagesManagement Information SystemAyush SinglaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Systems Analysis and DesignDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Systems Analysis and DesignDev RahaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introducation To MISDocument28 pagesLecture 1 - Introducation To MISahmed haneefNo ratings yet
- Bhopal School of Social Sciences MIS Subject CCE IIDocument9 pagesBhopal School of Social Sciences MIS Subject CCE IILinda BrownNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Chapter 2. ISADDocument21 pagesAssignment On Chapter 2. ISAD20220737No ratings yet
- MIS Lab ManualDocument19 pagesMIS Lab ManualRamesh Chandra Joshi86% (7)
- Managment Information SystemDocument64 pagesManagment Information SystemTech ProffesorNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Information SystemsDocument24 pagesIntroduction to Information SystemsLords PorseenaNo ratings yet
- 4 CbisDocument29 pages4 CbisSheikh ObaidNo ratings yet
- MIS Unit 1Document23 pagesMIS Unit 1Rohit prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Zero To Mastery In Cybersecurity- Become Zero To Hero In Cybersecurity, This Cybersecurity Book Covers A-Z Cybersecurity Concepts, 2022 Latest EditionFrom EverandZero To Mastery In Cybersecurity- Become Zero To Hero In Cybersecurity, This Cybersecurity Book Covers A-Z Cybersecurity Concepts, 2022 Latest EditionNo ratings yet
- Management Information systems - MIS: Business strategy books, #4From EverandManagement Information systems - MIS: Business strategy books, #4No ratings yet
- Knight's Microsoft Business Intelligence 24-Hour Trainer: Leveraging Microsoft SQL Server Integration, Analysis, and Reporting Services with Excel and SharePointFrom EverandKnight's Microsoft Business Intelligence 24-Hour Trainer: Leveraging Microsoft SQL Server Integration, Analysis, and Reporting Services with Excel and SharePointRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- WWW - Modelexam.in: Study Notes For Nism - Certified Personal Financial Advisor Exam (Cpfa)Document28 pagesWWW - Modelexam.in: Study Notes For Nism - Certified Personal Financial Advisor Exam (Cpfa)Parthiban SNo ratings yet
- Solved Practice Question Set On Reasoning For Ibps Po Exam 2012 Set 1Document15 pagesSolved Practice Question Set On Reasoning For Ibps Po Exam 2012 Set 1Md IntshamuddinNo ratings yet
- CWE Mock TestDocument18 pagesCWE Mock TestAnoo RadhaNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Module OverviewDocument30 pagesFinancial Management Module OverviewKamlesh Kumar KhiyataniNo ratings yet
- Eye Exercises And Relaxation For Improving VisionDocument19 pagesEye Exercises And Relaxation For Improving VisionParthiban SNo ratings yet
- S.Parthiban VMM NO:688 Reg NO: 1029195 Vel Tech Multi Tech DR - Rangarajan DR - Sakunthala Engineering CollegeDocument15 pagesS.Parthiban VMM NO:688 Reg NO: 1029195 Vel Tech Multi Tech DR - Rangarajan DR - Sakunthala Engineering CollegeParthiban SNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument30 pagesChapter ILorenzoAgramon100% (2)
- Semester 1 FinalDocument29 pagesSemester 1 FinalBudi NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Research Paper: EuthanasiaDocument10 pagesResearch Paper: Euthanasiahaha198502No ratings yet
- Integ Equ Phys571 T131Document19 pagesInteg Equ Phys571 T131raoni_jampaNo ratings yet
- Final InternshipDocument64 pagesFinal Internshippradeep100% (2)
- TPADocument9 pagesTPAAli ShahNo ratings yet
- Assignment Histogram and Frequency DistributionDocument6 pagesAssignment Histogram and Frequency DistributionFitria Rakhmawati RakhmawatiNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory NOV-DeC 2014Document12 pagesCircuit Theory NOV-DeC 2014sunil1237No ratings yet
- Unified Field Theory - WikipediaDocument24 pagesUnified Field Theory - WikipediaSaw MyatNo ratings yet
- ETH305V Multicultural Education TutorialDocument31 pagesETH305V Multicultural Education TutorialNkosazanaNo ratings yet
- Yoga Poses For Back Pain ReliefDocument11 pagesYoga Poses For Back Pain Reliefshiv yoga100% (2)
- BVRT PDFDocument8 pagesBVRT PDFAleena Zaidi100% (1)
- MarketingDocument3 pagesMarketingAli KhanNo ratings yet
- Urology: Hydronephrosis and Kidney StonesDocument13 pagesUrology: Hydronephrosis and Kidney StonesendiNo ratings yet
- 10, Services Marketing: 6, Segmentation and Targeting of ServicesDocument9 pages10, Services Marketing: 6, Segmentation and Targeting of ServicesPreeti KachhawaNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Karman in The AbhidharmasamuccayaDocument498 pagesThe Theory of Karman in The AbhidharmasamuccayaGuhyaprajñāmitra3100% (5)
- Pastors Sunday MessageDocument4 pagesPastors Sunday MessageDiana Janica Magalong100% (1)
- Medical Missionary and The Final Crisis MainDocument256 pagesMedical Missionary and The Final Crisis MainHarold Wong100% (2)
- Employee Engagement Study: Cone CommunicationsDocument16 pagesEmployee Engagement Study: Cone CommunicationsAndrei CristianNo ratings yet
- Futura.: Design by Zoey RugelDocument2 pagesFutura.: Design by Zoey RugelZoey RugelNo ratings yet
- Fear of Allah-HW Assignment by TahiyaDocument10 pagesFear of Allah-HW Assignment by TahiyashafaqkaziNo ratings yet
- Ayckbourn Absurd Person SingularDocument28 pagesAyckbourn Absurd Person SingularSaheli Gupta0% (1)
- Literary Criticism ExamDocument1 pageLiterary Criticism ExamSusan MigueNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDocument71 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society and PoliticsAl Cheeno AnonuevoNo ratings yet
- Cultural Identity and Diaspora in Jhumpa Lahiri's The NamesakeDocument10 pagesCultural Identity and Diaspora in Jhumpa Lahiri's The NamesakeOlivia DennisNo ratings yet
- THE PHILIPPINE JUDICIAL SYSTEM: PRE-SPANISH AND SPANISH PERIODDocument17 pagesTHE PHILIPPINE JUDICIAL SYSTEM: PRE-SPANISH AND SPANISH PERIODFranchesca Revello100% (1)
- FREE Soroban Abacus Mental Math Learning - BasicDocument74 pagesFREE Soroban Abacus Mental Math Learning - BasicTatyana Sukhomlinova100% (3)
- Bio1227 Microbiology and Parasitology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityDocument16 pagesBio1227 Microbiology and Parasitology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityDannielle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- 2015 International Qualifications UCA RecognitionDocument103 pages2015 International Qualifications UCA RecognitionRodica Ioana BandilaNo ratings yet
- Math 226 Differential Equation: Edgar B. Manubag, Ce, PHDDocument18 pagesMath 226 Differential Equation: Edgar B. Manubag, Ce, PHDJosh T CONLUNo ratings yet