Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson Plan 2 - Integers
Uploaded by
dionnesartinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson Plan 2 - Integers
Uploaded by
dionnesartinCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson Plan Title: Integers Concept/Topic to Teach: Adding and Subtracting Integers Standards Addressed: 7.
1 Demonstrate computational fluency with addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of integers. Specific Objectives: The students will be able to add and subtract integers. Required Materials: Graph paper, pencil, colored pencils, 2 sticks of different colored base ten blocks for each group, Teacher Tube Video to introduce Integer Rules at:
http://www.teachertube.com/viewVideo.php? title=Integers&video_id=121930
Anticipatory Set (Lead-In): Introductory video on teachertube that introduces Integers and goes over the rules for adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing integers. Step-By-Step Procedures for Teaching the Lesson: Ok so do those rules seem like they will be hard to remember? Yes, I agree they do so to help us better understand the rules which will make them easier to remember we are going to be playing with blocks today. (Give every group 2 sticks of base ten blocks.) Alright, look at the blocks you have. Does any group have all of the same color? Right, each group should have two different colors. Before we can play with the blocks we have to understand one concept. A negative and a positive are called opposites and opposites make zero. So if you have a positive 5 and a negative 5 and you combine them you get zero because you have the same amount (5) and one of the 5s is positive and one of the 5s is negative. So lets see if you guys understand what I am talking about. (Proceed to ask several simple opposites questions such as: -1+1, -2+2, 1-1, 1+-1, 2-2, 2+-2 All the answers should be zero.)
Ok good now lets illustrate this concept with your blocks. Break one block of each color off of your stick of blocks. One color represents positive and the other color represents negative. So if I have 1 orange block and 1 blue block what integer problem does that represent? Yes -1+1. And what is the answer to that problem we just made out of blocks? Yes 0. Ok so now lets try something a little harder. Break off 3 positive blocks and 5 negative blocks. First what problem does this represent? Yes 3+ (5). Using what we learned earlier about opposites what can we do to figure out the answer to this problem? Yes, pair the blocks up using 1 of each color. Ok so pair up your blocks, one of each color. How many pairs do you have? Yes, 3. How many blocks do you have left over that are not in a pair? Yes, 2. Are there two positive blocks or two negative blocks? Yes, two negative blocks. So the answer to our problem 3+ (-5) is negative 2. Now, in your groups I want you to build, write down, answer, and make a drawing on your graph paper of 10 integer problems. First, build a math problem out of your blocks. Next, make a drawing on your graph paper of the blocks that you have. Then, pair your blocks up. Circle on your drawing which blocks are left over. Finally, write down what problem the blocks represent and the answer to the problem. After the students have had 25 minutes to finish the assignment, each member of the group will come up and draw one problem on the Promethean Board that their group wrote and write down the problem that it illustrates. After everyone in the classroom has had time to come put one problem up on the Promethean Board we will go over all of the problems and discuss them as a class. Guided Practice/Monitoring: As the students are working on their problems I will be walking around the room making sure that the students are 1) modeling their problems with
the blocks, 2)drawing a picture of their blocks, 3)write down the representative problem and the answer to the problem, 4)circled the remaining blocks after being paired up. While walking around I will also make sure that the students are getting the correct answers to the problems they are making and if they are not I will use questioning techniques to guide them to the correct answer. Closure (Reflect Anticipatory Set): After the problems have been reviewed whole group, we will discuss the integer rules again and discuss how the blocks make the rules easier. Assessment Based on Objectives: At the end of class, students will be able to add and subtract integers with the usage of base ten blocks with 85% accuracy. Adaptations (For Students With Special Needs): An SLD student with a disability in math can use a calculator to subtract or add. Extensions (For Advanced Students): Advanced students can solve the integer problems without the blocks or make problems consisting of 3 and 4 numbers. Possible Connections to Other Subjects: After covering temperatures in Science class this lesson can reinforce temperatures dropping and rising. Reflection: This lesson reinforced my belief that math is learned best through hands on activities. When students can learn through real life situations and apply what they have learned they retain the knowledge with a higher success rate.
Sample Technology Product Illustrating Integer Problems using Promethean Software 1. Open the Promethean software. 2. Use the drawing tool to draw your blocks. 3. Color each block according to your base ten blocks using the fill tool. 4. Pair the blocks up by using the select tool. 5. Circle the ones that are left over by using the pen tool. 6. Using the pen tool write the math problem associated with the illustration.
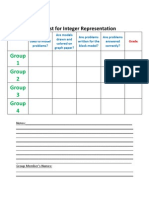
Checklist for Integer Representation
Are Are Are blocks models problems used to drawn and written for model colored on the block problems? graph model? paper? Are problems answered correctly? Grade
Grou p1 Grou p2 Grou p3 Grou p4
You might also like
- Edtpa Lesson Plan 1 ElemmathDocument4 pagesEdtpa Lesson Plan 1 Elemmathapi-24281405889% (9)
- Constructivist Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesConstructivist Lesson Planapi-35614029167% (3)
- Lesson Plan For GerundsDocument3 pagesLesson Plan For GerundsMary Jill Sumiguin Caber80% (51)
- Grade 3 (MUSIC 4th Quarter)Document37 pagesGrade 3 (MUSIC 4th Quarter)anon_3805127483% (18)
- Addition Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesAddition Lesson Planapi-252145631100% (1)
- NCERT Lesson Plans Class 6th A Pact With Sun by Vijay Kumar HeerDocument23 pagesNCERT Lesson Plans Class 6th A Pact With Sun by Vijay Kumar HeerVIJAY KUMAR HEER75% (12)
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofDocument8 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding ofSolarEclipp CandelansaNo ratings yet
- Indirect Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesIndirect Lesson Planapi-295821640No ratings yet
- Annotated-Math 205e 20lesson 20planning 20template 20spring 202021 281 29 20 287 29-1Document6 pagesAnnotated-Math 205e 20lesson 20planning 20template 20spring 202021 281 29 20 287 29-1api-644779880No ratings yet
- Educ 2108 Lesson Plan - WebsiteDocument4 pagesEduc 2108 Lesson Plan - Websiteapi-723369108No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2Document3 pagesLesson Plan 2api-278725808No ratings yet
- Adding and Subtracting Whole NumbersDocument7 pagesAdding and Subtracting Whole Numbersapi-234983083No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 11 7math Katelyn SheridanDocument5 pagesLesson Plan 11 7math Katelyn Sheridanapi-253725168No ratings yet
- Grade4 PatternsoftherainbowDocument5 pagesGrade4 Patternsoftherainbowapi-532462704No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Mastery 1Document4 pagesUnit 5 Mastery 1api-609653871No ratings yet
- Differentiation Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesDifferentiation Lesson Planapi-639293682No ratings yet
- Pa 10-27Document8 pagesPa 10-27api-252186515No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Lesson Title and Class/Duration: Topic: TEK(s)Document2 pagesLesson Plan: Lesson Title and Class/Duration: Topic: TEK(s)api-548172707No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Tennessee Curriculum Subject: Mathematics Level: 4 Standard: Standard 2 - Number and OperationsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan: Tennessee Curriculum Subject: Mathematics Level: 4 Standard: Standard 2 - Number and Operationsapi-325339089No ratings yet
- Maed 3224 LP Task 4 SherrillDocument5 pagesMaed 3224 LP Task 4 Sherrillapi-381776945No ratings yet
- Indirect Instruction Lesson Plan - Math: PerformanceDocument8 pagesIndirect Instruction Lesson Plan - Math: Performanceapi-336817618No ratings yet
- Name: Grade Level: Day: CCSS Standards: 5NFD9.1-Solve Word Problems Involving Addition and Subtraction of FractionsDocument6 pagesName: Grade Level: Day: CCSS Standards: 5NFD9.1-Solve Word Problems Involving Addition and Subtraction of Fractionsapi-300499643No ratings yet
- Observation 2 11 10 16Document6 pagesObservation 2 11 10 16api-306923856No ratings yet
- Revised Imb Math 3224Document11 pagesRevised Imb Math 3224api-336823793No ratings yet
- Activity Name: Math Modeling Unit and Activities: Indiana State StandardsDocument11 pagesActivity Name: Math Modeling Unit and Activities: Indiana State StandardsAmin Ur Rahman KhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesLesson Planapi-336569593No ratings yet
- Part B Lesson Plans For Learning SegmentDocument12 pagesPart B Lesson Plans For Learning Segmentapi-205136734No ratings yet
- Grade 1 Math Addition Within 20 Word ProblemsDocument7 pagesGrade 1 Math Addition Within 20 Word Problemsapi-273170523No ratings yet
- Educ Tech Lesson Plan RotoloDocument4 pagesEduc Tech Lesson Plan RotoloBridget RotoloNo ratings yet
- Division 2 Math Lesson Plan Mon 30th OctDocument4 pagesDivision 2 Math Lesson Plan Mon 30th Octapi-300499643No ratings yet
- Pop Cycle 2 MathDocument6 pagesPop Cycle 2 Mathapi-645158234No ratings yet
- Siop Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesSiop Lesson Planapi-445759249No ratings yet
- Fraction Math Lesson - Observation 2Document6 pagesFraction Math Lesson - Observation 2api-224842598No ratings yet
- Untitled Document 2Document3 pagesUntitled Document 2api-611136518No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 5Document2 pagesLesson Plan 5api-315856092No ratings yet
- Video LessonDocument9 pagesVideo Lessonapi-297505250No ratings yet
- Educ 2220-Educational Technology Lesson Plan Template Ipad MultiplicationDocument5 pagesEduc 2220-Educational Technology Lesson Plan Template Ipad MultiplicationLauren WilhelmNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan With RubricDocument3 pagesLesson Plan With Rubricapi-317228431No ratings yet
- Repeated Subtraction gr3 Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesRepeated Subtraction gr3 Lesson Planapi-356065858No ratings yet
- A Lesson Plan in ElementaryDocument24 pagesA Lesson Plan in ElementaryRhoyet Peralta Braganza IIINo ratings yet
- Blended Learning Lesson Plan Jared Lininger Lesson Title: Math PracticeDocument3 pagesBlended Learning Lesson Plan Jared Lininger Lesson Title: Math Practiceapi-458888827No ratings yet
- Updated Math Lesson 10Document8 pagesUpdated Math Lesson 10api-435713825No ratings yet
- Math 1Document7 pagesMath 1api-546259772No ratings yet
- MylessonplanDocument3 pagesMylessonplanapi-313400286No ratings yet
- Directed Numbers - Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesDirected Numbers - Lesson PlanAteef HatifaNo ratings yet
- Word Problem LessonDocument7 pagesWord Problem Lessonapi-301858309No ratings yet
- Task 4 Erica WilliamsDocument13 pagesTask 4 Erica Williamsapi-333303076No ratings yet
- Teacher Candidate Date/Time of Scheduled Visit Name/Address of School Age/Grade Level Cooperating TeacherDocument6 pagesTeacher Candidate Date/Time of Scheduled Visit Name/Address of School Age/Grade Level Cooperating Teacherapi-318002880No ratings yet
- Ed Tpa 1 2022 MathDocument10 pagesEd Tpa 1 2022 Mathapi-589146946No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Part 1Document4 pagesLesson Plan Part 1Asho GediNo ratings yet
- Math LessonDocument7 pagesMath Lessonapi-380761542No ratings yet
- Formal Lesson Plan Math Lesson 25Document4 pagesFormal Lesson Plan Math Lesson 25api-303421137100% (1)
- Sample Lesson Plan WeeblyDocument7 pagesSample Lesson Plan Weeblyapi-295143259No ratings yet
- Word Problems With 3 Addends RationaleDocument7 pagesWord Problems With 3 Addends Rationaleapi-272902100No ratings yet
- Unit Lesson Plan: Standards That Bridge The Entire UnitDocument5 pagesUnit Lesson Plan: Standards That Bridge The Entire UnitKalinda HarrisNo ratings yet
- Creating and Solving Money Problems: Common Core StandardsDocument5 pagesCreating and Solving Money Problems: Common Core StandardsVIctoria BrumfieldNo ratings yet
- Math Lesson Plan 3-18-21Document2 pagesMath Lesson Plan 3-18-21api-539364921No ratings yet
- Math Fo3 sp16Document4 pagesMath Fo3 sp16api-302793695No ratings yet
- Edtpa Lesson Plan Template : Activity Description of Activities and Setting TimeDocument3 pagesEdtpa Lesson Plan Template : Activity Description of Activities and Setting Timeapi-298532630No ratings yet
- EDUC 2220-Educational Technology Lesson Plan Template: Common Core StandardsDocument3 pagesEDUC 2220-Educational Technology Lesson Plan Template: Common Core StandardsCassidy WenzelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Maryam AlblooshiDocument4 pagesLesson 4 Maryam Alblooshiapi-314477483No ratings yet
- Division of Fractions Grade Level: 5Document6 pagesDivision of Fractions Grade Level: 5api-401808299No ratings yet
- EDUC2220 Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesEDUC2220 Lesson Planrebekah mcmanawayNo ratings yet
- New Concept Mathematics: An Interactive approach to learning Basic MathematicsFrom EverandNew Concept Mathematics: An Interactive approach to learning Basic MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Google Reader AssignmentDocument1 pageGoogle Reader AssignmentdionnesartinNo ratings yet
- Digital Citizenship: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument35 pagesDigital Citizenship: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyledionnesartinNo ratings yet
- Assessment Tool 2Document1 pageAssessment Tool 2dionnesartinNo ratings yet
- Digital Citizenship ProjectDocument1 pageDigital Citizenship ProjectdionnesartinNo ratings yet
- Assessment ToolDocument1 pageAssessment TooldionnesartinNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1 - Introduction To SlopeDocument4 pagesLesson Plan 1 - Introduction To Slopedionnesartin67% (3)
- Lesson Plan 1 - Introduction To SlopeDocument4 pagesLesson Plan 1 - Introduction To Slopedionnesartin67% (3)
- Incusive Education Case StudyDocument10 pagesIncusive Education Case Studyapi-332062674No ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan 22Document1 pageDaily Lesson Plan 22Subashini LetchumananNo ratings yet
- Halo Halo 2Document2 pagesHalo Halo 2Olim Zurc100% (1)
- All About Buying Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesAll About Buying Lesson Planapi-314360876100% (1)
- Learning Delivery Modalities Course 2: Reflection ADocument23 pagesLearning Delivery Modalities Course 2: Reflection AMithz SuNe YahNo ratings yet
- Interim ReportDocument2 pagesInterim Reportapi-524639831No ratings yet
- Proiect Didactic CLOTHESDocument4 pagesProiect Didactic CLOTHESMaricela TopaleaNo ratings yet
- Story Wheel Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesStory Wheel Lesson PlanJackie SnowNo ratings yet
- KSSR Year 3 - Yearly Lesson PlanDocument20 pagesKSSR Year 3 - Yearly Lesson PlanNoraini Awang100% (1)
- DLP in English 2Document14 pagesDLP in English 2kayNo ratings yet
- Halloween Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesHalloween Lesson Planapi-272828057No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Guide for TeachersDocument13 pagesLesson Plan Guide for TeachersSwastika ThapaNo ratings yet
- MicroteachDocument3 pagesMicroteachapi-383946447No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 4Document7 pagesLesson Plan 4api-241193898No ratings yet
- 5 Rules Lesson Plan 1Document4 pages5 Rules Lesson Plan 1api-540021999No ratings yet
- LDM Course 2 For TeachersDocument16 pagesLDM Course 2 For TeachersMarcus Andronicus SchopenhauerNo ratings yet
- Bean Lesson Plan 2Document5 pagesBean Lesson Plan 2api-346205571No ratings yet
- BACNOTAN NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL RPMS e-PortfolioDocument109 pagesBACNOTAN NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL RPMS e-PortfolioMariz Louie DG Kiat-ongNo ratings yet
- Persepolis Lesson PlansDocument6 pagesPersepolis Lesson Plansapi-280869491No ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument5 pagesProbabilityNanieta NacarNo ratings yet
- HBEC4606 Practicum Guide BECE CAug13Document39 pagesHBEC4606 Practicum Guide BECE CAug13tlsaras0% (1)
- Cover Page ModulesDocument46 pagesCover Page ModulesRose May OmbidNo ratings yet
- Q4 English Week 1 Lesson 28 Day 3Document3 pagesQ4 English Week 1 Lesson 28 Day 3Joviner Yabres LactamNo ratings yet
- Eng G9 Q2 W3 D2Document2 pagesEng G9 Q2 W3 D2Nabor Brígh100% (1)
- DLP FormatDocument2 pagesDLP Formatraymond Oliva100% (1)
- WorkthingDocument42 pagesWorkthingNicole BorinNo ratings yet