Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gout Drugs
Uploaded by
Michael BrownOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gout Drugs
Uploaded by
Michael BrownCopyright:
Available Formats
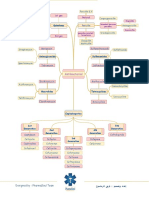
Drug
Anti-Gout
Allopurinol
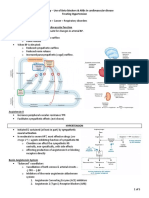
Mechanism Intra-articular crystals (gout = monosodium urate monohydrate; pseudogout = calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate, & basic calcium phosphates); Urate tends to crystallize in colder & more acidic conditions. Neutrophils ingesting crystals secrete inflammatory mediators that lower pH & lead to further urate precipitation Analog of hypoxanthine metabolized to active oxypurinol. Both agents uric acid production & purine excretion via inhibition of xanthine oxidase (at low doses: competitive; at high doses & any dose of oxypurinol: non-competitive) Arrests mitosis in metaphase by binding to tubulin & prevents mitotic spindle formation in granulocytes & other motile cells. Inhibits migration of granylocytes into inflamed areas & their metabolic & phagocytic activities. Prevents elaboration of urate-induced glycoprotein in joints Intra-articular steroids (methylprednisolone), systemic (oral prednisone) or IM triamcinolone, hexacetonide, & corticotrophin Anti-inflammatory via inhibition of COX (mainly PGE2, which plays a major role in crystal induced inflammation, & acts synergistically w/other mediators (bradykinin, LTB4) to enhance dilatation, pain sn, & neutrophil chemotaxis)
Activity/Use Prompt commencement impt
Side Effects/Toxicities Recurrent attacks usual
Other Cautions
For hyperuricemia, gout, prevention of hyperuricemia in pts. receiving antineoplastic drugs Prevention & tx of gout. No analgesia. Give within 24 hrs. Best when neither NSAIDs or colchicine are recommended (elderly w/renal or hepatic dz, cardiac failure, PUD, hypersn) Non-salicylate NSAIDs are DOC for acute crystal induced arthritis
Hypersn rxn, rash if w/ampicillin; risk of bone marrow suppression if w/cyclophosphamide GI upset from chronic exposure to drug & its metabolites due to enterohepatic circulation ( turnover of jejunal mucosal cells), diarrhea. Short duration of tx & rare side effects
t1/2 for probenecid & enhances its uricosuric effect (probenecid clearance of oxypurinol); levels of mercaptopurine & theophylline Long-term use: hair loss, bone marrow depression, peripheral neuritis, myopathy ( CPK) Avoid if joint sepsis not excluded & in those prone to hypoglycemia
Colchicine
Steroids
NSAIDs
NSAIDS: nonselective = Naproxen, Sulindac, Indomethacin; selective for COX2 = Rofecoxib, Celecoxib Avoid in pts. w/nephrolithiasis or w/overproduction of uric acid. Also inhibits tubular secretion of other drugs like methotrexate & NSAIDs Mostly excreted unchanged in urine, but To avoid precipitating an early attack 10% eliminated as N-p-hydroxyphenyl of gout, give w/colchicine. Risk of GI metabolite which has potent uricosuric irritation, hypersn, hematopoeisis, effects. May induce hypoglycemia inhibition of platelet aggregation, (inhibits metabolism of sulfonylurea oral renal stones ( fluid intake) hypoglycemic agents) Methemoglobinemia, acute renal failure, anaphylaxis Renal urate stones ( fluid intake to avoid). Mild GI irritation & acute gouty arthritis attack possible (give NSAIDs & colchicine)
Probenecid
Used to tx gout & also to inhibit the Inhibits uric acid reabsorption (via competition for the anion exchanger) active secretion of PCN G in pts. where in the proximal tubule, resulting in secretion or uric acid (action is PCN resistance is an issue or in pts. tx blunted by salicylates). Also moderately analgesic & anti-inflammatory w/neurosyphilis or gonorrhea infection Inhibits uric acid reabsorption in the proximal tubule. Small doses inhibit uric acid secretion.
Sulfinpyrazone
For chronic gout
Rasburicase
Benzbromarone
A recombinant urate-oxidase that catalyzes the enzymatic oxidation of uric acid into the soluble & inactive metabolite allantoin Potent uricosuric agent used in Europe TNF- plays a central role in the immune response seen in rheumatoid arthritis Recombinant human anti-TNF monoclonal Ab that complexes w/soluble TNF- & prevents its interaction w/p55 & p75 cell surface receptors. Macrophage & T cell fxn are downregulated.
Lowers urate levels more effectively than allopurinol - initial mgmt in peds pts. Efficacy by production of Abs w/leukemia, lymphoma & solid tumor against drug. Hemolysis in G6PDmalignancies on chemo (tumor lysis deficient syndrome) Effective in pts. w/renal dz
Anti-Rheumatic
TNF- Blocking Agents Adalimumab Infliximab Get PPD before tx!! Used to decrease rate of formation of new erosions in RA Risk of macrophage-dept. infections (i.e.: TB or other opportunistic infections)
Chimeric (25% mouse, 75% human) monoclonal Ab that binds to Used to tx RA & ulcerative colitis in combo Infusion rxns, development of Abs to soluble & membrane-bound TNF- - similar mechanism to adalimumab w/methotrexate drug, infections Fusion protein of two soluble TNFp75 receptor moieties linked to Fc portion of human IgG1. Binds TNF- molecules & also inhibits lymphotoxin- Converted in plasma & intestines to active agent A77-1726. Inhibits dihydroorotate dehydrogenase leading to a in ribonucleotide synthesis & arrest of stimulated cells in G1 phase of cell growth. Inhibits T cell proliferation & B cell production of auto-Abs Recombinant humanized anti-CD11a monoclonal Ab that inhibits the interaction of LFA-1 on all lymphocytes w/ICAM-1, thereby inhibiting adhesion, activation, & migration of lymphocytes into skin Active agent is metabolite 6-thioguanine, which suppresses the synthesis of inosinic acid, B & T cell fxn, Ig production, & IL-2 secretion Suppress T lymphocytes' response to mitogens, leukocyte chemotaxis, stabilize lysosomal enzymes, inhibit DNA & RNA Metabolite of PCN & analog of cystine Agents include Auranofin, Gold sodium thiomalate, Aurothioglucose. Probable mechanism: alter morphology & fxn of macrophages & inhibit IL-8, IL-1, & VEGF. Auranofin inhibits release of PGE2 & LB4. Metabolized to phenylacetic acid mustard which cross-links DNA & prevents cell replication Active metabolite is phosphoramide mustard which inhibits cells repln by cross-linking DNA. Suppresses T & B cell fxn. Active vs. RA (only oral, not if IV). Useful for SLE, vasculitis, wegener's granulomatosis Used for joint pains of SLE & Sjogren's syndrome (dryness of mucus membrane, D isomer used to tx RA Slows radiologic progression of RA. Also used for Sjogren's & juvenile RA Retinal damage, dyspepsia, N/V, abd pain, rashes, nightmares Rarely used due to toxicity Chrysiasis (gray-blue skin pigmentation) of GI tract mucus membranes & skin, exfoliative dermatitis, renal damage, thrombocytopenia Dose-dept. bone marrow suppression, infertility w/azoospermia & amenorrhea Dose-related infertility in men/women, bone marrow suppression, alopecia Used to tx RA, juvenile chronic arthritis, Risk of activation of latent TB & psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis. opportunistic infections, also injection rate of formation of new erosions but site rxns ineffective for ulcerative colitis! As effective as methotrexate in tx RA Approved for tx of adult pts. w/severe psoriasis Diarrhea & elevation in liver enzymes are main side effects. Also mild alopecia, weight gain, HTN Excretion & clearance enhanced by colestyramine
Etanercept
Leflunomide
Efalizumab others Azathioprine Chloroquine Hydroxychloroquine d-Penicillamine Gold Salts
Contraindicated w/renal/hepatic dz, infectious hepatitis, hematologic disorders High risk of leukemia after 3 yrs of use! Hemorrhagic cystitis, rare bladder carcinoma, pulmonary fibrosis
Chlorambucil Cyclophosphamide
Methotrexate
Cyclosporine
Mycophenolate mofetil
Sulfasalazine
At low doses used to tx RA, anti-inflammatory mechanisms Nausea, mucosal ulcers, dose-dept. predominate rather than the anti-proliferative ones. MTX inhibits 5hepatotoxicity & rare lung hypersn. Reabsorption in proximal jejunum, aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR) Contraindicated in pregnancy, enters cells via active (folate receptors formylotransferase resulting in accumulation of adenosine which DMARD of choice to tx RA alcoholism, liver/kidney dz, untreated &), passive & facilitated diffusion. binds to A2 receptors to cAMP, which then secretion of TNF, IFNfolate deficiency, pancytopenia, Polyglutamate metabolites stored in , IL-12, IL-6, & inhibits phagocytosis. Also induces apoptosis, immunodeficiency, concurrent liver & RBCs for a long time suppresses neutrophil chemotaxis, ICAM & VCAM in synovial tissue, trimethoprim tx inhibits dihydrofolate reductase, etc. Inhibits calcineurin, a phosphatase that normally dephosphorylates the cytoplasmic subunit of nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) allowing NFAT to translocate to the nucleus & augment tcr of several Significant nephrotoxicity made worse Drug retards the appearance of new Hyperkalemia, HTN, hepatotoxicity, cytokines. In T cells, calcineurin inhibition blocks IL-2 gene tcr & by other meds that inhibit CYP3A. bony erosions in RA gingival hyperplasia, hirsutism release, & ultimately inhibits T cell activation. Also inhibits macrophageGrapefruit juice bioavailability 62%. T cell interactions & T cell responsiveness; affects T cell-dept. B cell fxn. Active agent is mycophenolic acid which inhibits enzyme inosine monophosphatase dehydrogenase (IMPDH), w/resultant depletion of guanosine nucleotides needed for DNA & RNA synthesis. 5x more potent inhibitor of IMPDH type II isoform found in B- & T-cells, thus GI intolerance, bone marrow Used to tx renal dz due to SLE specifically inhibits lymphocyte activation & proliferation. May also suppression, hepatotoxicity enhance apoptosis. Inhibits E-selectin, P-selectin, & intercellular adhesion molecule 1, thereby interfering w/leukocyte adhesion to endothelial cells Metabolized to sulfapyridine & 5-aminosalicylic acid. rate of Hemolytic anemia, appearance of new joint damage. Inhibits IgA & IgM rheumatoid Sulfapyridine is active moiety when tx RA methemoglobinemia, N/V, headache factor production
You might also like
- Drug ClassDocument13 pagesDrug ClassEdfren Salazar Colon100% (1)
- Pharmacology Drug ChartDocument50 pagesPharmacology Drug ChartEssentialForLivingNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of HypertensionDocument4 pagesPharmacology of HypertensionFlower100% (1)
- Pharmacology A - NSAIDSDocument14 pagesPharmacology A - NSAIDSselflessdoctorNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting on Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument72 pagesDrugs Acting on Autonomic Nervous SystemDebashis ParidaNo ratings yet
- NSAIDDocument1 pageNSAIDShubhangiNo ratings yet
- (CV2) Pharmacology of AnticoagulantsDocument6 pages(CV2) Pharmacology of AnticoagulantsHanifa Shereen B. AliNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology TableDocument9 pagesPharmacology TableMaryam KhushbakhatNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action For Each Class of AntiDocument146 pagesMechanism of Action For Each Class of AntiReynaldo RiveraNo ratings yet
- Drug class prefixes and suffixesDocument5 pagesDrug class prefixes and suffixesPj MontecilloNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology FirecrackerDocument37 pagesPharmacology FirecrackerRehan Usman100% (1)
- UWorld - Psych Review Charts (From Questions)Document47 pagesUWorld - Psych Review Charts (From Questions)uowhywxuuiragjadchNo ratings yet
- Renal Guide and Charts: AlbuminDocument16 pagesRenal Guide and Charts: AlbuminYaima JimenezNo ratings yet
- Mu 002Document10 pagesMu 002chandanNo ratings yet
- Sedative-Hypnotic and Antipsychotic Drugs GuideDocument17 pagesSedative-Hypnotic and Antipsychotic Drugs GuideBijay Kumar MahatoNo ratings yet
- 3 Treatment of HypertensionDocument7 pages3 Treatment of HypertensiontiaraNo ratings yet
- PCOL Maps PDFDocument11 pagesPCOL Maps PDFZinc YuloNo ratings yet
- Immunopharmacology: GlucocorticoidsDocument9 pagesImmunopharmacology: GlucocorticoidsCas BuNo ratings yet
- NERVOUS MnemonicsDocument4 pagesNERVOUS MnemonicsHimNo ratings yet
- Pharmayield: Must Know Pharmacology NotesDocument2 pagesPharmayield: Must Know Pharmacology NotesBianca Desiree VergaraNo ratings yet
- Chart Antibacterial Drugs PDFDocument1 pageChart Antibacterial Drugs PDFMunaf AlsumaryNo ratings yet
- Dr. A. Samy TAG Bone Diseases - 1Document2 pagesDr. A. Samy TAG Bone Diseases - 1Herato MenaNo ratings yet
- Pharm C Exam 10 Drug ListDocument2 pagesPharm C Exam 10 Drug ListVokdadaNo ratings yet
- A To Z Diseases LISTS For NEETPGDocument5 pagesA To Z Diseases LISTS For NEETPGQworldNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AgentsDocument45 pagesAdrenergic AgentsAmit ShahNo ratings yet
- Antimycobacterial Drugs PDFDocument3 pagesAntimycobacterial Drugs PDFCas BuNo ratings yet
- AntiemeticsDocument25 pagesAntiemeticsPridho GaziansyahNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism Application Side Effects Contraindication Drug-Drug InteractionsDocument3 pagesDrug Name Mechanism Application Side Effects Contraindication Drug-Drug Interactionsazhar hussinNo ratings yet
- Common Medications UsedDocument3 pagesCommon Medications UsedRay Michael CasupananNo ratings yet
- Pharma ChartsDocument33 pagesPharma ChartsNooreen Hussain100% (1)
- Ultimate Pharm GuideDocument41 pagesUltimate Pharm GuideeanguyenNo ratings yet
- CANCER CHEMOTHERAPY REGIMENS AND THEIR TOXICITIESDocument13 pagesCANCER CHEMOTHERAPY REGIMENS AND THEIR TOXICITIESVaibhav Bharat100% (1)
- Pharma MnemonicsDocument10 pagesPharma MnemonicsMuhammad Ali Aziz100% (4)
- Drugs in Blood DisordersDocument1 pageDrugs in Blood DisordersSantosh patelNo ratings yet
- Approximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMDocument8 pagesApproximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMakane ryuNo ratings yet
- Micro Chart #3 - Italics OnlyDocument27 pagesMicro Chart #3 - Italics Onlyapi-26938624100% (1)
- Week 10 - Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, ArrhythmiaDocument14 pagesWeek 10 - Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, Arrhythmiashivani patel100% (1)
- Antibiotics that inhibit bacterial metabolism and DNA synthesisDocument1 pageAntibiotics that inhibit bacterial metabolism and DNA synthesisjuan esteban MonroyNo ratings yet
- Northern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016Document48 pagesNorthern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016dreneavalentinstefanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDocument5 pagesPharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDana20SNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Reference RangesDocument12 pagesLaboratory Reference RangesPrashanth Raju100% (1)
- Mnemonic PharmaDocument13 pagesMnemonic Pharmamanoj kumarNo ratings yet
- Antihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DDocument28 pagesAntihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of EthanolDocument5 pagesPharmacology of EthanolJoshua RemonNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Disorder Background: Hypomania Has The Same Symptoms of Mania Without Psychotic SymptomsDocument2 pagesBipolar Disorder Background: Hypomania Has The Same Symptoms of Mania Without Psychotic SymptomshumdingerNo ratings yet
- Drug TerminologyDocument5 pagesDrug Terminologyimdaking123No ratings yet
- PHARMA SupertableDocument2 pagesPHARMA SupertablelpanatalioNo ratings yet
- Antiviral - Classification and ImagesDocument2 pagesAntiviral - Classification and ImagesNuwaira Baloch100% (2)
- Review Handouts For Medical Pharmacology: Terriann Crisp, PH.DDocument28 pagesReview Handouts For Medical Pharmacology: Terriann Crisp, PH.Dmus zaharaNo ratings yet
- First Aid Pharmacology AntimicrobialsDocument23 pagesFirst Aid Pharmacology AntimicrobialsLaura Lopez RocaNo ratings yet
- Master Pharm Drug ListDocument1 pageMaster Pharm Drug ListMichelle StramNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The AnsDocument57 pagesDrugs Acting On The AnsAnonymous iG0DCOfNo ratings yet
- Semester 2 Drug ListDocument7 pagesSemester 2 Drug ListNam_Pham_6481No ratings yet
- Pharmacology Important Things To RememberDocument5 pagesPharmacology Important Things To RememberHydie100% (1)
- Anticancer Drugs GuideDocument69 pagesAnticancer Drugs GuideMarlindah SNo ratings yet
- Antineoplastic BrizoDocument14 pagesAntineoplastic BrizoMariel Deanne Santos BrizoNo ratings yet
- Immunomodulators: Dr. Kaushik Mukhopadhyay Assistant Professor, Dept. of Pharmacology Esi-PgimsrDocument31 pagesImmunomodulators: Dr. Kaushik Mukhopadhyay Assistant Professor, Dept. of Pharmacology Esi-PgimsrsyarintaadeninaNo ratings yet
- AntidotesDocument2 pagesAntidotesYemaya84No ratings yet
- Drug ReviewDocument3 pagesDrug Reviewapi-493355126No ratings yet
- Fusion Tech ActDocument74 pagesFusion Tech ActrahulrsinghNo ratings yet
- Christian Storytelling EvaluationDocument3 pagesChristian Storytelling Evaluationerika paduaNo ratings yet
- Think Like An EconomistDocument34 pagesThink Like An EconomistDiv-yuh BothraNo ratings yet
- The Meaning of Al FatihaDocument11 pagesThe Meaning of Al Fatihammhoward20No ratings yet
- TOS and CID FORM-TLE 8 ANIMATIONDocument80 pagesTOS and CID FORM-TLE 8 ANIMATIONAriel AntaboNo ratings yet
- Performance AppraisalsDocument73 pagesPerformance AppraisalsSaif HassanNo ratings yet
- Discuss in Details With Appropriate Examples What Factors Could Lead To Sympatric and Allopatric SpeciationDocument5 pagesDiscuss in Details With Appropriate Examples What Factors Could Lead To Sympatric and Allopatric SpeciationKhairul ShahmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 HandoutDocument18 pagesChapter 10 HandoutChad FerninNo ratings yet
- Primer To Using Stampplot® Pro Standard User LicensedDocument21 pagesPrimer To Using Stampplot® Pro Standard User LicensedSandy Rachman AdrianNo ratings yet
- Literature - Part I: Group InterventionsDocument14 pagesLiterature - Part I: Group InterventionsDanielNo ratings yet
- ViscosityDocument7 pagesViscositykiran2381No ratings yet
- 6 Strategies For Effective Financial Management Trends in K12 SchoolsDocument16 pages6 Strategies For Effective Financial Management Trends in K12 SchoolsRainiel Victor M. CrisologoNo ratings yet
- Policy Guidelines On Classroom Assessment K12Document88 pagesPolicy Guidelines On Classroom Assessment K12Jardo de la PeñaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 MafinDocument36 pagesChapter 9 MafinReymilyn SanchezNo ratings yet
- Ash ContentDocument2 pagesAsh Contentvikasbnsl1No ratings yet
- Wjec Gcse English Literature Coursework Mark SchemeDocument6 pagesWjec Gcse English Literature Coursework Mark Schemef6a5mww8100% (2)
- Life and Works of Jose RizalDocument5 pagesLife and Works of Jose Rizalnjdc1402No ratings yet
- Design of Efficient Serial Divider Using HAN CARLSON AdderDocument3 pagesDesign of Efficient Serial Divider Using HAN CARLSON AdderInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Quiz Corrections ADocument4 pagesChapter 5 Quiz Corrections Aapi-244140508No ratings yet
- 59-33 ATO Implementation Journal KSA 100Document18 pages59-33 ATO Implementation Journal KSA 100nicolas valentinNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 5090/61 October/November 2017Document6 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Biology 5090/61 October/November 2017Zarish NoorNo ratings yet
- Test Unit 3Document2 pagesTest Unit 3RAMONA SECUNo ratings yet
- Blaise PascalDocument8 pagesBlaise PascalBosko GuberinicNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 (91 Slides)Document91 pagesLecture 15 (91 Slides)Hasnain GoharNo ratings yet
- The Art of Woodworking Shaker FurnitureDocument147 pagesThe Art of Woodworking Shaker Furnituremalefikus100% (2)
- Readingdev 7Document2 pagesReadingdev 7api-190328610No ratings yet
- SEO-optimized title for practice test documentDocument4 pagesSEO-optimized title for practice test documentThu GiangNo ratings yet
- Crossing To The Dark Side:: Examining Creators, Outcomes, and Inhibitors of TechnostressDocument9 pagesCrossing To The Dark Side:: Examining Creators, Outcomes, and Inhibitors of TechnostressVentas FalcónNo ratings yet
- Hospital Registration Orientation 3 - EQRs With Operating ManualDocument33 pagesHospital Registration Orientation 3 - EQRs With Operating ManualElshaimaa AbdelfatahNo ratings yet
- Mansabdari SystemDocument10 pagesMansabdari SystemSania Mariam100% (8)