Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BJT Transistor Modeling
Uploaded by
Monique Elago CagatinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BJT Transistor Modeling
Uploaded by
Monique Elago CagatinCopyright:
Available Formats
ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS ANALYSIS AND DESIGN
BJT Transistor Modeling
BJT Transistor Modeling
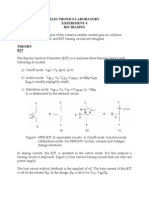
Objectives: 1. To use the superposition theorem to draw the dc and ac equivalent circuits 2. To determine the important parameters of a two-port system for analysis and design of an amplifier 3. To identify the two models commonly used in the small-signal ac analysis of transistor networks
BJT Transistor Modeling
Biasing
The DC voltages applied to a transistor in order to turn it on so that it can amplify the AC signal
BJT Transistor Modeling
Operating Point
The DC input establishes an establishes an operating or quiescent point called the Q-point
BJT Transistor Modeling
Three Stages of Operation
Active or Linear Region Operation BaseEmitter junction is forward biased BaseCollector junction is reverse biased Cutoff Region Operation BaseEmitter junction is reverse biased Saturation Region Operation BaseEmitter junction is forward biased BaseCollector junction is forward biased
BJT Transistor Modeling
BJT Transistor Modeling
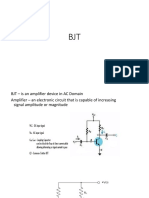
A model is an equivalent circuit that represents the AC characteristics of the transistor. A model uses circuit elements that approximate the behavior of the transistor. There are two models commonly used in small signal AC analysis of a transistor: re model Hybrid equivalent model
BJT Transistor Modeling
When introducing the ac model for a BJT: 1. All dc sources are set to zero and replaced by a short-circuit connection to ground. 2. All capacitors are replaced by a short-circuit equivalent. 3. All elements in parallel with an introduced short-circuit equivalent should be removed from the network. 4. The network should be redrawn as often as possible.
BJT Transistor Modeling
BJT Transistor Modeling
BJT Transistor Modeling
BJT Transistor Modeling
Important Parameters: Zi, Z0, Av, Ai
BJT Transistor Modeling
Input Impedance, Zi
The input impedance of a BJT transistor amplifier is purely resistive in nature, and depending on the manner in which the transistor is employed, can vary from a few ohms to megaohms.
BJT Transistor Modeling
Output Impedance, Zo
The output impedance is determined at the output terminals looking back into the system with the applied signal set to zero. It is resistive in nature and can vary from a few ohms to a level that can exceed 2 M .
BJT Transistor Modeling
Voltage Gain, Av
Depending on the configuration, the magnitude of the voltage gain for a loaded single-stage amplifier typically ranges from just less than 1 to a few hundred. A multistage system, however, can have a voltage gain in the thousands.
BJT Transistor Modeling
Current Gain, Ai
For BJT amplifiers, the current gain typically ranges from a level just less than 1 to a level that may exceed 100.
BJT Transistor Modeling
Phase Relationship
For the typical transistor amplifier at frequencies that permit ignoring the effects of the reactive elements, the input and output signals are either 1800 out of phase or in phase.
BJT Transistor Modeling
Comparison Between the Three-Transistor Configurations
BJT Transistor Modeling
The re Transistor Model
BJTs are basically current-controlled devices; therefore the re model uses a diode and a current source to duplicate the behavior of the transistor. One disadvantage to this model is its sensitivity to the DC level. This model is designed for specific circuit conditions.
BJT Transistor Modeling
Common Base Configuration
BJT Transistor Modeling
BJT Transistor Modeling
BJT Transistor Modeling
Common Emitter Configuration
BJT Transistor Modeling
BJT Transistor Modeling
BJT Transistor Modeling
The Hybrid Equivalent Model
BJT Transistor Modeling
BJT Transistor Modeling
Short-circuit input impedance parameter
Open-circuit reverse transfer voltage ratio parameter
BJT Transistor Modeling
Hybrid input equivalent circuit
BJT Transistor Modeling
Short-circuit forward transfer current ratio parameter
Open-circuit output admittance parameter
BJT Transistor Modeling
Hybrid output equivalent circuit
BJT Transistor Modeling
Complete Hybrid Equivalent Circuit
BJT Transistor Modeling
BJT Transistor Modeling
Typical values of h-parameters
BJT Transistor Modeling
Approximate Hybrid Equivalent Circuit
BJT Transistor Modeling
Hybrid versus re model
Common-base configuration
BJT Transistor Modeling
Hybrid versus re model
Common-emitter configuration
BJT Transistor Modeling
Hybrid versus re model
Common-collector configuration
BJT Transistor Modeling
QUESTIONS
You might also like
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument1 pageBipolar Junction TransistorRoker boyNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument47 pagesTransistorsAmiey MahleNo ratings yet
- Lec 05Document38 pagesLec 05నాంగిరి సురేష్No ratings yet
- Electronics 2Document69 pagesElectronics 2joeNo ratings yet
- Small Signal AnalysisDocument24 pagesSmall Signal AnalysisLyell Claire Mendoza100% (1)
- Electronic SwitchesDocument24 pagesElectronic Switchesرغد كنعانNo ratings yet
- 09 ExperimentDocument4 pages09 ExperimentMuhammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Power BJTDocument19 pagesPower BJTSamay GoenkaNo ratings yet
- Power Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument27 pagesPower Bipolar Junction TransistorNikhil Kushwaha50% (2)
- Unit 6. Introduction To Bi-Polar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document9 pagesUnit 6. Introduction To Bi-Polar Junction Transistor (BJT)Gunjan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Study of BJT operating modes and characteristicsDocument31 pagesStudy of BJT operating modes and characteristicsHarsh DeshwalNo ratings yet
- EEE 312 Lecture1Document11 pagesEEE 312 Lecture1Zeynal Abidin ŞabaşNo ratings yet
- EEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Experiment 4 - BJT BiasingDocument4 pagesEEM328 Electronics Laboratory - Experiment 4 - BJT Biasingdonatello84100% (1)
- BJT AS AmplifierDocument6 pagesBJT AS AmplifierMuhammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document46 pagesUnit 2Manan JainNo ratings yet
- Trans Switch AmplDocument47 pagesTrans Switch AmplNugie TyoNo ratings yet
- 3.bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document44 pages3.bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)luis_sergio_barrosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BJTDocument20 pagesIntroduction To BJTLutfiza Fajri AfriliyaniNo ratings yet
- BJT Fundamentals ExplainedDocument58 pagesBJT Fundamentals ExplainedMiyuki NakiriNo ratings yet
- Electric Actuation SystemsDocument55 pagesElectric Actuation SystemsOmar HishamNo ratings yet
- BJT PDFDocument49 pagesBJT PDFJai GicangaoNo ratings yet
- BJT MosfetDocument31 pagesBJT MosfetDheerLakhotiaNo ratings yet
- Power TransistorDocument37 pagesPower Transistorsaikarthick023No ratings yet
- Transistor Biasing2Document17 pagesTransistor Biasing2Anant UpadhiyayNo ratings yet
- 53 - 36765 - ME593 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 1 - DC Motors PDFDocument56 pages53 - 36765 - ME593 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 1 - DC Motors PDFDora TengNo ratings yet
- Slide 4 - Electronics (Transistors)Document48 pagesSlide 4 - Electronics (Transistors)Priyatharshan ViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document16 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)mikko intalNo ratings yet
- Lab - Vi: Name - Kushagra Sagar ROLL NUMBER - 2021BCS0105Document10 pagesLab - Vi: Name - Kushagra Sagar ROLL NUMBER - 2021BCS0105Kushagra SagarNo ratings yet
- BJT Biotech 106Document16 pagesBJT Biotech 106Sehaj MannNo ratings yet
- Nguyentuan 31102Document62 pagesNguyentuan 31102Tuấn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- DEVICE EXP 5 STUDENT MANUAL NewDocument6 pagesDEVICE EXP 5 STUDENT MANUAL NewPial Hassan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Module 2-18EE53Document59 pagesModule 2-18EE53AshwiniNo ratings yet
- IGBTDocument22 pagesIGBTumeshgangwar100% (1)
- الكترونيك نموذجيDocument10 pagesالكترونيك نموذجيMohammed KasimNo ratings yet
- 8- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument38 pages8- Bipolar Junction TransistorShahnail MemonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - BJTDocument24 pagesChapter 6 - BJTNuyu HasyimieNo ratings yet
- LectureDocument20 pagesLectureعمر الحكيميNo ratings yet
- BJT 1sdsdsaDocument59 pagesBJT 1sdsdsamoganraj8munusamyNo ratings yet
- DET40073 Topic 1Document54 pagesDET40073 Topic 1HAAVINESHNo ratings yet
- AbcDocument8 pagesAbcFasil TareNo ratings yet
- BJT Characteristics: CE, CB, CC ConfigurationsDocument26 pagesBJT Characteristics: CE, CB, CC Configurationsgirishkumardarisi254No ratings yet
- Chapter 2. TransistorsDocument69 pagesChapter 2. TransistorsAnh Ha Duy AnhNo ratings yet
- 4 - BJT TransistorsDocument48 pages4 - BJT Transistorsangelo rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Elektronik 1 Sunum 5 9736Document210 pagesElektronik 1 Sunum 5 9736inamullahNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument38 pagesUnit 4 - Bipolar Junction TransistorCel LuviaNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lec4.Document13 pagesPower Electronics Lec4.Fahmeed Ali MeoNo ratings yet
- 03 Handout 1Document6 pages03 Handout 1Abigail ResneraNo ratings yet
- BJT Fundamentals ExplainedDocument20 pagesBJT Fundamentals ExplainedNur NajmiNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Devices FinalDocument35 pagesPower Electronics Devices FinalmcclottryNo ratings yet
- Microwave Semiconductor Devices and Transistor Surface GeometriesDocument21 pagesMicrowave Semiconductor Devices and Transistor Surface GeometriesjohnmechanjiNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics & SCRDocument55 pagesPower Electronics & SCRsoumyaranjan_kar34No ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lec.Document10 pagesPower Electronics Lec.Fahmeed Ali MeoNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Modern Power Electronics Components and SystemsDocument16 pagesIntroduction to Modern Power Electronics Components and SystemsdanimannyNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor: Unit 3Document56 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor: Unit 3adamwaizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ElectronicsDocument78 pagesChapter 1 ElectronicsBenjaminNo ratings yet
- Transistor Basics: BJTs and FETsDocument45 pagesTransistor Basics: BJTs and FETsMohammad Gulam AhamadNo ratings yet
- Electronics - 1 Lecture 13Document37 pagesElectronics - 1 Lecture 13rizwanspirit11No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Critique PaperDocument3 pagesCritique PaperMonique Elago CagatinNo ratings yet
- Cogongrass Invasion in AlabamaDocument2 pagesCogongrass Invasion in AlabamaMonique Elago CagatinNo ratings yet
- CulturesDocument3 pagesCulturesMonique Elago CagatinNo ratings yet
- Class ScheduleDocument1 pageClass ScheduleMonique Elago CagatinNo ratings yet
- NEC Sizing ConductorsDocument18 pagesNEC Sizing ConductorsAriel DimacaliNo ratings yet
- TLIAN DT Connector T6 10L - v1.0 - ENDocument2 pagesTLIAN DT Connector T6 10L - v1.0 - ENJoão Pedro Alemonge HonoratoNo ratings yet
- ENG DS OMI 2 Pole Series Relay Data Sheet E 0411Document3 pagesENG DS OMI 2 Pole Series Relay Data Sheet E 0411letterniNo ratings yet
- 1 - Safety in Use of Electricity - Part IIDocument143 pages1 - Safety in Use of Electricity - Part IIMaharajaNo ratings yet
- ps3 FatDocument29 pagesps3 FatRogeriotabiraNo ratings yet
- R.M.K. College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument7 pagesR.M.K. College of Engineering and TechnologyvlkumashankardeekshithNo ratings yet
- ABB Price Book 737Document1 pageABB Price Book 737EliasNo ratings yet
- Ti 20221115 Sg320hx and Sg350hx System Diagram v2 enDocument2 pagesTi 20221115 Sg320hx and Sg350hx System Diagram v2 en2D EngenhariaNo ratings yet
- Split System Air Conditioners Daikin Inverter RZP-DDocument255 pagesSplit System Air Conditioners Daikin Inverter RZP-Djoko riyantoNo ratings yet
- AC Induction Motors vs. Permanent Magnet Synchronous MotorsDocument5 pagesAC Induction Motors vs. Permanent Magnet Synchronous MotorsAhmed GhreebNo ratings yet
- TOEPC71061774Document4 pagesTOEPC71061774bejaouiNo ratings yet
- Macintosh MC275 Service ManualDocument12 pagesMacintosh MC275 Service Manualozzy123No ratings yet
- Liquid Level Control Device: SSR 02 SSR 03 SSR 04Document2 pagesLiquid Level Control Device: SSR 02 SSR 03 SSR 04ahmedNo ratings yet
- A Regenerative Braking Model Using BrushDocument9 pagesA Regenerative Braking Model Using Brushpraveen kumarNo ratings yet
- Module 2 (B) Thyristor Commutation TechniquesDocument42 pagesModule 2 (B) Thyristor Commutation TechniquesK N DEEPSHINo ratings yet
- RB1 Service InformationDocument3 pagesRB1 Service InformationDiego LimaNo ratings yet
- Listening BugDocument14 pagesListening BugNaelah SurtiNo ratings yet
- Multi Cam ModernizationDocument6 pagesMulti Cam ModernizationEngineer ElectronicNo ratings yet
- Bca 121 Basic Electronics Circuits SyllabusDocument7 pagesBca 121 Basic Electronics Circuits SyllabusGlenn GyudNo ratings yet
- Title: Model Ut50A/B/C: Operating ManualDocument33 pagesTitle: Model Ut50A/B/C: Operating ManualEibar016No ratings yet
- Substation Switching SchemesDocument7 pagesSubstation Switching Schemeskukos setosariNo ratings yet
- MADHEPURADocument1 pageMADHEPURAdeepu kumarNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicle Conductive Charging System: Indian StandardDocument54 pagesElectric Vehicle Conductive Charging System: Indian Standardamit singhNo ratings yet
- DC Generators PPT 3974378 (Rujuk)Document93 pagesDC Generators PPT 3974378 (Rujuk)Mahesvaran SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of MOSFET and IGBT For High Repetitive Pulsed Power ModulatorsDocument8 pagesComparative Study of MOSFET and IGBT For High Repetitive Pulsed Power ModulatorsTainá tainlerschyahoo.com.brNo ratings yet
- Earth Batteries PDFDocument0 pagesEarth Batteries PDFMarìa Angélica Guerreiro0% (1)
- ABB concept bs switches and sockets catalogueDocument20 pagesABB concept bs switches and sockets catalogueFahmi FahriNo ratings yet
- Switch FamilyDocument252 pagesSwitch Familybakien-canNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument10 pagesLab ReportAr YanNo ratings yet
- Infineon Tle4729g Ds v01 00 enDocument29 pagesInfineon Tle4729g Ds v01 00 enMbon100% (1)