Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IEEE 802.16 Broadband Wireless Access Working Group OFDM Frame Structure 2002-01-11
Uploaded by
Chien Pham HuyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IEEE 802.16 Broadband Wireless Access Working Group OFDM Frame Structure 2002-01-11
Uploaded by
Chien Pham HuyCopyright:
Available Formats
2002-01-11
IEEE 802.16a-02/16
Project
IEEE 802.16 Broadband Wireless Access Working Group <http://ieee802.org/16> OFDM Frame Structure 2002-01-11 Lei Wang Brian Gieschen Wi-LAN Inc. 2891 Sunridge Way, NE Calgary, AB, Canada, T1Y 7K7 Voice: (403)273-9133 Fax: (403)273-5100 Email: LeiW@wi-lan.com; BrianG@wi-lan.com;
Title Date Submitted Source(s)
Re: Abstract
This is a contribution to IEEE 802.16 TGa. This contribution combines two subsections for the OFDM Frame Structure in 802.16a/D1 document and provides an improved description. To Enhance the OFDM Frame Structure definition and description in 802.16a/D1.
This document has been prepared to assist IEEE 802.16. It is offered as a basis for discussion and is not binding on the contributing individual(s) or organization(s). The material in this document is subject to change in form and content after further study. The contributor(s) reserve(s) the right to add, amend or withdraw material contained herein. The contributor grants a free, irrevocable license to the IEEE to incorporate text contained in this contribution, and any modifications thereof, in the creation of an IEEE Standards publication; to copyright in the IEEE's name any IEEE Standards publication even though it may include portions of this contribution; and at the IEEE's sole discretion to permit others to reproduce in whole or in part the resulting IEEE Standards publication. The contributor also acknowledges and accepts that this contribution may be made public by IEEE 802.16. The contributor is familiar with the IEEE 802.16 Patent Policy and Procedures (Version 1.0) <http://ieee802.org/16/ipr/patents/policy.html>, including the statement IEEE standards may include the known use of patent(s), including patent applications, if there is technical justification in the opinion of the standards-developing committee and provided the IEEE receives assurance from the patent holder that it will license applicants under reasonable terms and conditions for the purpose of implementing the standard. Early disclosure to the Working Group of patent information that might be relevant to the standard is essential to reduce the possibility for delays in the development process and increase the likelihood that the draft publication will be approved for publication. Please notify the Chair <mailto:r.b.marks@ieee.org> as early as possible, in written or electronic form, of any patents (granted or under application) that may cover technology that is under consideration by or has been approved by IEEE 802.16. The Chair will disclose this notification via the IEEE 802.16 web site <http://ieee802.org/16/ipr/patents/notices>.
Purpose
Notice
Release
Patent Policy and Procedures
2002-01-11
IEEE 802.16a-02/16
Acknowledgements
The following people have contributed to this document: Shawn Taylor Gordon Antonello Shane Rogers
ii
2002-01-11
IEEE 802.16a-02/16
Introduction
This document combines the two Frame Structure subsections of Mode AL OFDM in 802.16a/D1 document. Also, an improved description is provided.
Reference
IEEE P802.16/D5 - 2001.
[TG1/D5]
[TG3&4/D1] IEEE 802.16a/D1 - 2001.
Suggested Text for Section 8.3.5.3.3.1
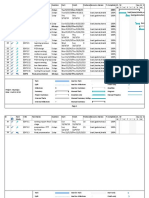
8.3.3.3.3.1 OFDM Frame Structure The OFDM PHY supports a frame-based transmission. The frame length is encoded in the Frame Duration Code in the PHY Synchronization Field (see 8.3.5.3.3.4.1) of a DL-MAP or DL-UL-MAP message. The frame duration code is defined in Table 176. The frame interval contains both transmissions (PHY PDUs) of BS and SSs and guard intervals. Figure 210 and Figure 211 show the frame structures for the OFDM PHY with TDD and FDD, respectively.
2002-01-11
IEEE 802.16a-02/16
Time
Frame n-1
Frame n
Frame n+1
Frame n+2
DL Sub-frame
D L PH Y PDU
UL Sub-frame
Contenti on sl ot for initi al ranging Contention slot for BW Req. UL PHY PDU from SS#1
......
UL PHY PDU from SS#K
o ne or multiple DL bursts; each has d ifferent modulation/coding, transmitted i n order of decreasing robustness. Pre amble FCH DL Burst 1 D L Bu rst 2
......
DL Burst M
Preamble
UL Burst
o ne UL burst per U L PHY PHY PD U, transmitted i n the modulation/ co ding specific to the source SS.
one OFDM symbol with the well-konw modulation/coding {QPSK, (3 2, 24, 4)}
MAC Msg 1 (MAC PDU-1)
......
MAC Msg N (MAC PDU-N )
Pad MAC Msg 1 (MAC PDU-1 )
......
MAC Msg N (MAC PDU-N)
Pad
DL Fr Prefix
DCD, UCD (optinal)
padding (o ptional) MAC Header (6 bytes) MAC Msg Pa yload (optional) C RC (o ptional) MAC Header (6 bytes) MAC Msg Payl oad (optional) CRC (optional)
Rate ID (4 bits)
llength (12 bits)
H CS (8 bits)
FIGURE 210 Frame Structure for the OFDM PHY with TDD A frame consists of a DL sub-frame and an UL sub-frame. A DL sub-frame consists of only one DL PHY PDU. An UL sub-frame consists of contention intervals scheduled for initial ranging and bandwidth request purposes and one or multiple UL PHY PDUs, each transmitted from a different SS. A UL PHY PDU consists of only one burst, which is made up of a preamble and an integer number of OFDM symbols. The burst PHY parameters of an UL PHY PDU are specified by a 4-bit UIUC (Uplink Interval Usage Code) in the UL-MAP. The UIUC encoding is defined in the UCD(Uplink Channel Descriptor) messages. A DL PHY PDU starts from a preamble, which is used for PHY synchronization. The preamble is followed by a FCH (Frame Control Header) burst. The FCH burst is one OFDM symbol long and is transmitted in a well-known modulation/coding: {QPSK, (32,24,4)}. The FCH is followed by one or multiple DL bursts, each transmitted with different PHY parameters and therefore different level of transmission robustness. If there are multiple DL bursts in a DL PHY PDU, they are transmitted in order of decreasing robustness. Each DL burst consists of an integer number of OFDM symbols, and its burst profiles (PHY parameters) are specified by a 4-bit DIUC (Downlink Interval Usage Code) in the DL-MAP. The DIUC encoding is defined in the DCD (Downlink Channel Descriptor) messages.
2002-01-11
IEEE 802.16a-02/16
Time
Frame n-1
Frame n
Frame n+1
Frame n+2
DL Sub-frame
DL PHY PDU
one or multiple DL bursts; if multiple, each has different modulati on/coding, transmitted in o rder of decreasing robustness.
Preamble
FCH
DL Burst 1
DL Bu rst 2
......
D L Burst M
o ne OFDM symbol with the well-konw modulation/coding {QPSK, (32, 24, 4)}
MAC Msg 1 (MAC PDU-1)
......
MAC Msg N (MAC PDU-N)
Pad
DL Fr Prefix
D CD, UCD (optinal)
p adding (optional) MAC Header (6 bytes) MAC Msg Pa yload (optional) C RC (optional)
R ate ID (4 bits)
l length (12 bits)
HCS (8 bits)
UL Sub-frame
Contention slot for initial ranging Contenti on slot for BW R eq.
UL PH Y PD U from SS# 1
......
UL PH Y PDU from SS#K
Preamble
UL Burst
one UL burst per UL PHY PHY PDU, transmitted in the modulation/coding specific to the source SS.
MAC Msg 1 (MAC PDU-1)
......
MAC Msg N (MAC PDU-N)
Pa d
MAC Header (6 bytes)
MAC Msg Pa yload (opti onal)
C RC (optional)
FIGURE 211 Frame Structure for the OFDM PHY with FDD In a DL PHY PDU, a special PHY burst, FCH (Frame Control Header), is used to specify the burst profiles and length of the DL burst-1, that is, the DL burst immediately following the FCH. The FCH is one OFDM symbol long and transmitted with a well-known burst profiles, i.e., {QPSK, (32,24,4)}. The FCH uses the 4-bit Rate_ID to specify the burst profiles of the DL burst-1. The Rate_ID encoding is defined in Table 197. The difference between the Rate_ID and DIUC is whether or not the encoding can be dynamically
2002-01-11
IEEE 802.16a-02/16
changed. The Rate_ID encoding is static and cannot be changed during system operation, while the DIUC encoding can be dynamically changed by the DCD messages. The FCH burst may also contain short MAC control messages, such as, DCD and/or UCD. However, the FCH burst is not able to contain any MAP messages, because of their sizes (for the OFDM PHY, the DL-MAP has at least 24 bytes, and the UL-MAP has at least 23 bytes). Therefore, the MAP messages are transmitted in the DL burst-1. Although the DL burst-1 contains broadcast MAC control messages, it is not necessary to use the most robust well-know modulation/coding. A more efficient modulation/coding may be used if it is supported and applicable to all the SSs of a BS. With the OFDM PHY, a PHY burst, either a DL PHY burst or an UL PHY burst, consists of an integer number of OFDM symbols, carrying MAC messages, i.e., MAC PDUs. To form an integer number of OFDM symbols, a burst payload may be padded by the bytes 0xFF. Then the payload should be scrambled, encoded, and modulated using the burst PHY parameters specified by this standard.
You might also like
- WIMAX Performance EvaluationDocument4 pagesWIMAX Performance EvaluationNikos BizNo ratings yet
- Wimax Overview and System Performance: Fan Wang, Amitava Ghosh, Chandy Sankaran and Phil FlemingDocument5 pagesWimax Overview and System Performance: Fan Wang, Amitava Ghosh, Chandy Sankaran and Phil Flemingitalian_angelNo ratings yet
- RFC 4326Document42 pagesRFC 4326Bhuvanachandran ANo ratings yet
- Raw Data RateDocument81 pagesRaw Data RateKaos1980No ratings yet
- ALC SDH Basics and Alcatel SDH System Training Presentation 46 SlideDocument46 pagesALC SDH Basics and Alcatel SDH System Training Presentation 46 SlideMaster22No ratings yet
- LTE Resource BlocksDocument15 pagesLTE Resource BlocksNeoRa Ndivo RamsNo ratings yet
- LTE Physical Layer OverviewDocument11 pagesLTE Physical Layer OverviewBliss_aditya10No ratings yet
- ALC SDH Basics and Alcatel SDH System Training Presentation 46 SlideDocument46 pagesALC SDH Basics and Alcatel SDH System Training Presentation 46 SlideFrancisco Salvador MondlaneNo ratings yet
- Configuring SDH On 1-Port OC192/STM-64 or 8-Port OC3/12/48/STM-1/-4/-16 ModuleDocument18 pagesConfiguring SDH On 1-Port OC192/STM-64 or 8-Port OC3/12/48/STM-1/-4/-16 ModuleMostafaNo ratings yet
- How Is The UE Getting Information That It Is Scheduled?: Some Questions and Answers On LTE Radio Interface - Part1Document4 pagesHow Is The UE Getting Information That It Is Scheduled?: Some Questions and Answers On LTE Radio Interface - Part1Yassar ShahNo ratings yet
- List of Bluetooth Protocols - WikipediaDocument1 pageList of Bluetooth Protocols - WikipediathhNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Optical NetworkingDocument14 pagesSynchronous Optical Networkingpy thonNo ratings yet
- ALC-SDH Basics and Alcatel SDH System Training Presentation 46 SlideDocument46 pagesALC-SDH Basics and Alcatel SDH System Training Presentation 46 SlideJesper Ebong75% (4)
- Synchronous Optical NetworkingDocument14 pagesSynchronous Optical NetworkingPranab KumarNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Optical Networking: OSI ModelDocument12 pagesSynchronous Optical Networking: OSI ModelArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Air InterfaceDocument11 pagesAir InterfaceBhosdiwale ChachaNo ratings yet
- DVB-T2 modulator design supporting multiple PLP and auxiliary streamsDocument6 pagesDVB-T2 modulator design supporting multiple PLP and auxiliary streamsdan r.No ratings yet
- 802.11b/ISM PHY: (Spring 2004)Document5 pages802.11b/ISM PHY: (Spring 2004)Prashanth GSNo ratings yet
- LTE Network Planning - Huawei TechnologiesDocument54 pagesLTE Network Planning - Huawei Technologiessparksss123No ratings yet
- SDH Principle Issue 2.0Document101 pagesSDH Principle Issue 2.0M Tanvir Anwar100% (1)
- LTE Physical Layer OverviewDocument16 pagesLTE Physical Layer OverviewHasanShahabNo ratings yet
- SDH and SonetDocument40 pagesSDH and SonetSalim KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document18 pagesChapter 3ninapotNo ratings yet
- Lte FW BasicsDocument17 pagesLte FW BasicsAakriti MahteNo ratings yet
- Configuring and Understanding SDH SignalsDocument58 pagesConfiguring and Understanding SDH Signalsshuja behnaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On Multi Access OFDM (OFDMA) TechnologyDocument53 pagesTutorial On Multi Access OFDM (OFDMA) TechnologystevensnrNo ratings yet
- VHDL Simulation of Tu-11/Tu-12 in Synchronous Digital HierarchyDocument6 pagesVHDL Simulation of Tu-11/Tu-12 in Synchronous Digital HierarchyEditorijer IjerNo ratings yet
- Ax Spec FrameworkDocument37 pagesAx Spec FrameworkKanchan GorainNo ratings yet
- LTE FDD Throughput CalculationsDocument8 pagesLTE FDD Throughput CalculationsAhmed GamalNo ratings yet
- LTE FDD Throughput CalculationsDocument8 pagesLTE FDD Throughput CalculationsMuhammad Ali KhalidNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Optical Networking From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesSynchronous Optical Networking From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSanjay Kumar ChaubeyNo ratings yet
- Packet Over SONET/SDH: Pocket GuideDocument64 pagesPacket Over SONET/SDH: Pocket GuidekajfahmNo ratings yet
- List of Bluetooth ProtocolsDocument4 pagesList of Bluetooth ProtocolsPratyush0% (1)
- Phat Trien Tu SDH Len OTN 2017.4.19 EnglishDocument9 pagesPhat Trien Tu SDH Len OTN 2017.4.19 Englishnobita3No ratings yet
- Guide to synchronous optical networking (SONET) and synchronous digital hierarchy (SDHDocument75 pagesGuide to synchronous optical networking (SONET) and synchronous digital hierarchy (SDHKyaw Zin OoNo ratings yet
- Wimax For Broadband Wireless Access: by S.Antony Suresh Babu Reg No:21409105002 Dept:Eee, 3 YearDocument24 pagesWimax For Broadband Wireless Access: by S.Antony Suresh Babu Reg No:21409105002 Dept:Eee, 3 YearThenpandian JakNo ratings yet
- OTA000001 SDH Review2005Document40 pagesOTA000001 SDH Review2005Luong NguyenNo ratings yet
- 11 Chapter 6 SDH Fundamentals (Book)Document27 pages11 Chapter 6 SDH Fundamentals (Book)gerzten100% (2)
- Ieee 802.11Document49 pagesIeee 802.11Jyoti ShekharNo ratings yet
- Ieee 802.16 WimaxDocument63 pagesIeee 802.16 WimaxIram NausheenNo ratings yet
- Chapter02.SDH Overview CPE Protection SchemesDocument16 pagesChapter02.SDH Overview CPE Protection SchemesVijaya KumariNo ratings yet
- SDH PrimerDocument7 pagesSDH PrimerRajesh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Implementation of HDLC Protocol Using VerilogDocument3 pagesImplementation of HDLC Protocol Using VerilogiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- LTE Network Planning TechnologiesDocument54 pagesLTE Network Planning TechnologiesFuzail KhanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On Multi Access OFDM (OFDMA) TechnologyDocument49 pagesTutorial On Multi Access OFDM (OFDMA) TechnologyTaquang DungNo ratings yet
- Computer Communication EC 407Document60 pagesComputer Communication EC 407Adarsh VkNo ratings yet
- DCF Throughput Analysis of IEEE 802.11a:g:n-Based Mobile LAN Over Correlated Fading ChannelDocument16 pagesDCF Throughput Analysis of IEEE 802.11a:g:n-Based Mobile LAN Over Correlated Fading ChannelLia AstuteNo ratings yet
- UMTS Channel PDFDocument47 pagesUMTS Channel PDFsayemboNo ratings yet
- Channel Coding: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications: Academic Press Library in Mobile and Wireless CommunicationsFrom EverandChannel Coding: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications: Academic Press Library in Mobile and Wireless CommunicationsNo ratings yet
- Indoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GFrom EverandIndoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- The Internet of Things: Key Applications and ProtocolsFrom EverandThe Internet of Things: Key Applications and ProtocolsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Arjun 10 operating manualDocument20 pagesArjun 10 operating manualshis100% (1)
- Manual de Herreria Una Guia Paso A Paso Lesur Luis Libro en Papel 9786071701251 Libreria El SotanoDocument3 pagesManual de Herreria Una Guia Paso A Paso Lesur Luis Libro en Papel 9786071701251 Libreria El Sotanodiego rotpeNo ratings yet
- Innolux V500HJ1-ME1 Datasheet, Specification, Stocks, Overview - Lcd-SourceDocument2 pagesInnolux V500HJ1-ME1 Datasheet, Specification, Stocks, Overview - Lcd-SourceJackeline MosquedaNo ratings yet
- LM5148-Q1 80-V, Automotive, Synchronous, Buck DC/DC Controller With Ultra-Low I and Dual Random Spread SpectrumDocument69 pagesLM5148-Q1 80-V, Automotive, Synchronous, Buck DC/DC Controller With Ultra-Low I and Dual Random Spread SpectrumAnjuNo ratings yet
- Course Description: Adama Science and Technology UniversityDocument7 pagesCourse Description: Adama Science and Technology UniversityTesfaye OlanaNo ratings yet
- How To Set Up A Home Network RouterDocument2 pagesHow To Set Up A Home Network RouterTosha ColemanNo ratings yet
- SDPDocument6 pagesSDPJay SuguitanNo ratings yet
- Adsp BF592Document44 pagesAdsp BF592waqarsuparcoNo ratings yet
- Cap 8 PDFDocument6 pagesCap 8 PDFmo02jum0% (1)
- NTE261 (NPN) & NTE262 (PNP) Silicon Complementary Transistors Darlington Power AmplifierDocument2 pagesNTE261 (NPN) & NTE262 (PNP) Silicon Complementary Transistors Darlington Power Amplifiercriman45No ratings yet
- AC Notes Zaki SaudagarDocument18 pagesAC Notes Zaki Saudagaraltashabts7No ratings yet
- Universal Subscriber Identity Module (USIM) Application Toolkit (USAT)Document123 pagesUniversal Subscriber Identity Module (USIM) Application Toolkit (USAT)Som BompellyNo ratings yet
- Introduction to VLSI Design and Bio-SensorsDocument60 pagesIntroduction to VLSI Design and Bio-Sensorssadia santaNo ratings yet
- Msplan Group 1 PDFDocument6 pagesMsplan Group 1 PDFmohanNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture CS401: Sabanci University Erkays@sabanciuniv - EduDocument20 pagesComputer Architecture CS401: Sabanci University Erkays@sabanciuniv - EduSumit GuptaNo ratings yet
- 3) WHITLOCK DNFT DatasheetDocument1 page3) WHITLOCK DNFT DatasheetAizat RomainoNo ratings yet
- Led Lighting Power Controller: Features ApplicationsDocument36 pagesLed Lighting Power Controller: Features ApplicationsVaibhavNo ratings yet
- Resources Chapter 32 StudentDocument3 pagesResources Chapter 32 StudentJA55EENo ratings yet
- 354-GPRS Capacity Calculation DocumentDocument5 pages354-GPRS Capacity Calculation Documentsharad_rbl4379No ratings yet
- Agilent Dual Directional Coupler 778D 100 To 2000 MHZ: Data SheetDocument4 pagesAgilent Dual Directional Coupler 778D 100 To 2000 MHZ: Data Sheetdanilo espinozaNo ratings yet
- Current Status and Future Applications For DMD - Based Projection DisplaysDocument4 pagesCurrent Status and Future Applications For DMD - Based Projection Displaysgangwar_neeteshNo ratings yet
- Manual IntellinetDocument28 pagesManual IntellinetXiime M. MartiinezNo ratings yet
- Trihal Technical Data Sheet Reduced Losses Gea126b PDFDocument4 pagesTrihal Technical Data Sheet Reduced Losses Gea126b PDFtduskoNo ratings yet
- Parameter Huawei PDFDocument21 pagesParameter Huawei PDFMarwahNo ratings yet
- Design and Secure The Computer NetworkDocument74 pagesDesign and Secure The Computer NetworkGenene GebreNo ratings yet
- POE Transformers for Power over Ethernet ApplicationsDocument10 pagesPOE Transformers for Power over Ethernet Applicationsa04205No ratings yet
- Jed Sep 17Document55 pagesJed Sep 17kashif100% (1)
- Module 1a A Brief History of Computer ArchitectureDocument53 pagesModule 1a A Brief History of Computer ArchitectureMairos Kunze BongaNo ratings yet
- Life of A Tube Guy - Back StoryDocument1 pageLife of A Tube Guy - Back StoryTonino ScacchiNo ratings yet
- Akriti PDF ThesisDocument97 pagesAkriti PDF ThesisAshutoshSharmaNo ratings yet