Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ospf Lab Opnet It Guru
Uploaded by
SherazOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ospf Lab Opnet It Guru
Uploaded by
SherazCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Module: Wired and Wireless C04606
OSPF: Open Shortest Path First
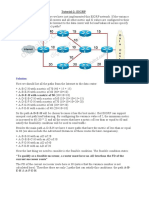
1). In the lab two scenarios Areas and Balanced scenarios are opposite compare to No_Areas scenario. In No_Areas the metric (cost) of the path from Router A to Router C via Router D and Router E is 15 this route is chosen as it the best path delivery. To fully understand the result and analysis we observe Router B and Router H which are least metric (cost) 40. Therefore, any of these routes can be chosen. Routers first look for the destination address in their routing table in their own area first before sending the packet in scenario Area otherwise any other alternative is selected. Router A, B, C is in same area. Router A to Router C is directly routed here the metric (cost) is 20 which are more than in the No_Areas scenario. In balanced scenario Router B to Router H metric cost 40 applies as load is share by both routes B, Router H and it is distributed over two paths. 2(a). No_Areas Scenario 2 (b). Areas Scenario
the above table is opposite than the previous one. The main difference shows the routes selection for few destinations and the metric (cost) of the routes. What we find In routing table of Router A to network 192.0.2.0 cost is 40 it could be using the Router B or Router C which is interesting. Whereas Router B interface address is 192.0.1.2 and Router C interface address is 192.0.11.2. 2(c) Balanced Scenario
Router A take different route to reach at different routers with difference of metric (cost).The Metric represents the total cost of routers. To have a understanding we take a example in Router A routing table, Router A to network 192.0.11.0 costs 25, how does it cost 25 well it does starts from Router D (where Router D interface is 192.0.5.2) next hop and via Router A, Router D, E, G, and H therefore metric(cost) is five + five + five + ten= twenty-five.
in the above routing table of Router A balanced scenario showing that it is much similar to the routing
Student Name: Sheraz Salim
Student ID: 20388626
2 table of Router A in No_Areas. Router A has same metric (cost). 4). The results are generated of the network topology after link failure occurred. No_Areas Routing Table before link Failure
Module: Wired and Wireless C04606 The link state database generated database of Router A. When network have link failure occurred at 100 seconds however LSA timestamp is 105.there is no link metric (cost) to address 192.0.6.0.
The routing table of Router A No_Areas after link failure.
5).the graph shows the generated result of No_Areas and Q4_No_Areas_Failure scenario. Both results are compared Traffic Sent (bits/sec) in this scenario. we disabled the OSPF Sim Efficiency in Q4_No_Areas_Failure by doing disabling the OSFP Sim Efficiency will let allow routing table to update. However we didn t disabled them in No_Areas.
The routing table of Router A make changes cause of link failure are as fallowing. Different routes take place on higher metric (cost) for example 192.0.8.0, 192.0.11.0, 192.0.4.0, 192.0.2.0. IP address 192.0.6.0 after failed link there is no route available for the network.
Conclusion The OSPF lab give brief technical aspect how it works. By reading some more material on www.cisco.com the lab clear the understanding of how to implement and diagnose OSPF protocols. OPNET it guru make the OSPF more easy to play and analysis the result we get from this lab. The lab show us the link state database of router.
Student Name: Sheraz Salim
Student ID: 20388626
3 Reference 1. Cisco system, web address http://ciscosystems.com/en/US/tech/tk365/tec hnologies_white_paper09186a0080094e9e.sht ml 2. Cisco system, Cisco Networking Academy, Routing Module. 3. RFC 1246
Module: Wired and Wireless C04606
Student Name: Sheraz Salim
Student ID: 20388626
You might also like
- Factor Participating and Impacting E-Markets Pioneers Behavioral TrackingDocument7 pagesFactor Participating and Impacting E-Markets Pioneers Behavioral Trackingindex PubNo ratings yet
- What Is Codename OneDocument18 pagesWhat Is Codename OneنورالدنياNo ratings yet
- 10.8.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge - InstructorDocument11 pages10.8.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge - InstructorMichael oliverosNo ratings yet
- The Secure Zone Routing Protocol (SZRP) 1Document24 pagesThe Secure Zone Routing Protocol (SZRP) 1Kamalakar ReddyNo ratings yet
- ERouting Final Exam - CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0) (rbm668)Document19 pagesERouting Final Exam - CCNA Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0) (rbm668)rbm668No ratings yet
- TP-1 VPN Configuration Lab Using Routers in Cisco Packet TracerDocument5 pagesTP-1 VPN Configuration Lab Using Routers in Cisco Packet TracerKhaoula RAZZAKINo ratings yet
- Resume Ranking: Maitri Bhagat, Riddhima Chinchane, Shweta JhaDocument9 pagesResume Ranking: Maitri Bhagat, Riddhima Chinchane, Shweta JhaVIVA-TECH IJRINo ratings yet
- Manage Virtual Machines with Hyper-VDocument15 pagesManage Virtual Machines with Hyper-VmassNo ratings yet
- Exam Viewer - Module 2 Exam - CCNA 1 French (Version 3.1)Document9 pagesExam Viewer - Module 2 Exam - CCNA 1 French (Version 3.1)SAGALOGNo ratings yet
- Huawei Hcia-Iot V2.0 Certification Exam OutlineDocument2 pagesHuawei Hcia-Iot V2.0 Certification Exam OutlineCarlos Solís TrinidadNo ratings yet
- OPENCV - Topic 04 - Histogram SpecificationDocument5 pagesOPENCV - Topic 04 - Histogram Specificationhuahongquan2007100% (1)
- C Mid-Term Exam Problems for Programming, Matrix, Recursion, MaximumDocument6 pagesC Mid-Term Exam Problems for Programming, Matrix, Recursion, Maximum張帕姆No ratings yet
- 6.2.3.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv3 Instructions IG PDFDocument3 pages6.2.3.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv3 Instructions IG PDFMauricioMuñozNo ratings yet
- Install and Test ODL-BE and Mininet in CentOS VMsDocument6 pagesInstall and Test ODL-BE and Mininet in CentOS VMsroshan.ranatunge5703No ratings yet
- 6.2.3.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv3 InstructionsDocument2 pages6.2.3.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv3 Instructionsbubblybubbles19000% (1)
- MERISEDocument4 pagesMERISEZAKARIA SALHINo ratings yet
- QCM PDFDocument185 pagesQCM PDFRania MabroukNo ratings yet
- Rip OPNET IT GURUDocument3 pagesRip OPNET IT GURUSheraz80% (5)
- How To Create A SSL Certificate On Apache For Debian 7 PDFDocument4 pagesHow To Create A SSL Certificate On Apache For Debian 7 PDFLucas SoaresNo ratings yet
- Nis Linux HPCDocument268 pagesNis Linux HPCyeldasbabuNo ratings yet
- Ccna 1Document16 pagesCcna 1aboubakrysyNo ratings yet
- IPCop With DansGuardian Installation and ConfigurationDocument6 pagesIPCop With DansGuardian Installation and ConfigurationnopeiccoNo ratings yet
- Configure Stateless and Stateful DHCPv6 TopologyDocument4 pagesConfigure Stateless and Stateful DHCPv6 TopologyPFENo ratings yet
- JavaFx Using Scene Builder and With JDBC ConnectivityDocument9 pagesJavaFx Using Scene Builder and With JDBC ConnectivityNikith ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Neural Network (RNN)Document26 pagesRecurrent Neural Network (RNN)shubh agrawalNo ratings yet
- 3.2.1.8 Packet Tracer - Configuring RIPv2 Instructions - ILMDocument3 pages3.2.1.8 Packet Tracer - Configuring RIPv2 Instructions - ILMBasri wandiNo ratings yet
- Blue Modern Company Profile PresentationDocument34 pagesBlue Modern Company Profile PresentationSonia ChaabouniNo ratings yet
- SMTP POP3 IMAP Protocol NotesDocument43 pagesSMTP POP3 IMAP Protocol NotesChidambaramNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma DMAIC DMADV PDFDocument3 pagesSix Sigma DMAIC DMADV PDFromedic36No ratings yet
- QCM VlanDocument9 pagesQCM VlanWala BenrhoumaNo ratings yet
- Hive ExercisesDocument2 pagesHive ExercisessandeepNo ratings yet
- OSPF QuestionsDocument6 pagesOSPF Questionsstorm2010No ratings yet
- Mastering With Ros: Turlebot3: How To Use Opencv in RosDocument21 pagesMastering With Ros: Turlebot3: How To Use Opencv in RosHusam Abu ZourNo ratings yet
- Proceedings ICWIT08Document381 pagesProceedings ICWIT08dzcsconfNo ratings yet
- OpenFlow 1.2Document83 pagesOpenFlow 1.2Yahya NursalimNo ratings yet
- Solution PT Activity 7.6.1: Packet Tracer Skills Integratio..Document13 pagesSolution PT Activity 7.6.1: Packet Tracer Skills Integratio..BasmaOueslati100% (1)
- Engaging with Volunteering Gap YearsDocument2 pagesEngaging with Volunteering Gap YearsBalkis HmidiNo ratings yet
- Comp Sci - IJCSEITR - Cryptanalytic JH and BLAKE - Priyanka Wadhwani - OPaidDocument12 pagesComp Sci - IJCSEITR - Cryptanalytic JH and BLAKE - Priyanka Wadhwani - OPaidTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- CCNA Exploration 4.0 ERouting Final Exam 50 Questions 100%Document19 pagesCCNA Exploration 4.0 ERouting Final Exam 50 Questions 100%Fuuton Ransenshuriken100% (5)
- Final Paper Resit Exam For Python Programming Making GuideDocument10 pagesFinal Paper Resit Exam For Python Programming Making GuideckiadjNo ratings yet
- DHCP and NAT - Knowledge BaseDocument6 pagesDHCP and NAT - Knowledge BaseHasib Hamidul HaqueNo ratings yet
- HCNA ReviewerDocument69 pagesHCNA ReviewerFranz Mejorada Ccie100% (5)
- CCNA 3 v7 Modules 13 - 14: Emerging Network Technologies Exam AnswersDocument11 pagesCCNA 3 v7 Modules 13 - 14: Emerging Network Technologies Exam AnswersLeandro J. HinestrozaNo ratings yet
- 3.2.1.8 Packet Tracer - Configuring RIPv2 Instructions PDFDocument2 pages3.2.1.8 Packet Tracer - Configuring RIPv2 Instructions PDFWalter JonesNo ratings yet
- Ospf Lab Opnet It GuruDocument3 pagesOspf Lab Opnet It GuruMateo KeretićNo ratings yet
- Report Simulation Assignment 5Document22 pagesReport Simulation Assignment 5Ebraheem Alhaddad100% (5)
- Ee534 Lab7 (Duong - Le)Document9 pagesEe534 Lab7 (Duong - Le)Rock RáchNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument14 pagesReportKaishavi UmrethwalaNo ratings yet
- Erouting V4.0 Final Pattern 2: Expect Minimum Percentage: 90.2%Document23 pagesErouting V4.0 Final Pattern 2: Expect Minimum Percentage: 90.2%mike6453bNo ratings yet
- 6 IP Routing Part2Document13 pages6 IP Routing Part2Oualid OuadahNo ratings yet
- ICND 2 FullDocument59 pagesICND 2 FullTony ChienNo ratings yet
- Passed H12Document13 pagesPassed H12Anonymous cs4BLczE0% (1)
- Router routing minimum 90.2Document20 pagesRouter routing minimum 90.2Andrzej JędrzejczykNo ratings yet
- CCNA Exploration 2: Module Final Exam Answers 2Document8 pagesCCNA Exploration 2: Module Final Exam Answers 2Peter PoelmansNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument4 pagesAssignmentHima Bindhu BusireddyNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 SolutionsDocument5 pagesHomework 1 SolutionsANAMITRA BHAR (RA1811003010684)No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document4 pagesTutorial 2A'ziz MoNo ratings yet
- Routers primary functions packet switching path selectionDocument80 pagesRouters primary functions packet switching path selectionFrancesco MuraNo ratings yet
- Network Layer - RoutingDocument83 pagesNetwork Layer - RoutingRohan BhattadNo ratings yet
- HCNA ExerciseDocument11 pagesHCNA ExerciseReinaldo Evan100% (1)
- Code of Conduct Constipation ClinicDocument4 pagesCode of Conduct Constipation ClinicSherazNo ratings yet
- gn3 Na3 t4 Ipv6 - MigrationDocument26 pagesgn3 Na3 t4 Ipv6 - MigrationSherazNo ratings yet
- Gns3 Switch SetupDocument1 pageGns3 Switch SetupSherazNo ratings yet
- Rip OPNET IT GURUDocument3 pagesRip OPNET IT GURUSheraz80% (5)
- Book1 (Version 1)Document4 pagesBook1 (Version 1)SherazNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 OPNET IT GURUDocument3 pagesLab 3 OPNET IT GURUSherazNo ratings yet
- CRN 2011 Top VarsDocument28 pagesCRN 2011 Top VarsSherazNo ratings yet
- Network Simulation ToolsDocument4 pagesNetwork Simulation ToolsSherazNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 OPNET IT GURUDocument3 pagesLab 2 OPNET IT GURUSherazNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 OPNET IT GURUDocument4 pagesLab 1 OPNET IT GURUSherazNo ratings yet
- Project ManagmentDocument12 pagesProject ManagmentSherazNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Firewall Policies To Manage Network TrafficDocument3 pagesEvaluating Firewall Policies To Manage Network TrafficSherazNo ratings yet
- OPNET - MODELER - MANET Attacks ThesisDocument81 pagesOPNET - MODELER - MANET Attacks ThesisSheraz80% (5)
- Final ProjectDocument81 pagesFinal ProjectSheraz100% (1)