Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.9 Equilibrium of Force
Uploaded by
Jill Peary RajuOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.9 Equilibrium of Force
Uploaded by
Jill Peary RajuCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
9
1.
EQUILLIBRIUM OF FORCES
Two forces with magnitudes 3 N and 4 N act on an object Y as shown in Diagram 1. The object Y is placed on a smooth horizontal surface.
Diagram 1. (a) (b) By drawing a scaled parallelogram of forces to determine the resultant force on the object Y. If the mass of object Y is 2.0 kg, calculate its acceleration resulted from the resultant force.
(c)
State the direction and magnitude of a force that has to be applied on the object Y so that the object is in equilibrium. .
2.
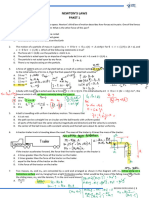
Diagram 2.1 shows two boys pushing a large box. After some time, the box still remains stationary.
Diagram 2.1 Diagram 2.2 shows an aircraft moving forward with a uniform velocity at a constant height.
(a)
Based on the situation in Diagram 2.1 and situation in Diagram 2.2, (i) state similarities about the magnitudes and directions of the forces F1 and F2 , F3 and F4 . magnitudes : . directions : ................ What is the net force in both situations? . Based on the answers in 5(a)(i) and 5(a)(ii), name the physics concept involved. Another aircraft has F3 than F4 . Describe the motion of this aircraft. . Explain the answer in 5(b)(i). .. ...
(ii)
(iii)
(b)
(i)
(ii)
3.
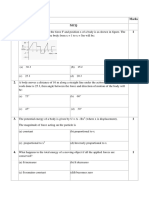
Figure shows a cyclist is riding along a road at a constant velocity. The total of downward force acting on the bicycle and the cyclist is 650 N. The normal reaction of the front tyre is 300 N and forward thrust is 200 N.
(a)
Calculate the normal reaction ,P acting on the rear tyre .
(b)
Give one reason why the total resistance, Q should be 200 N at that moment? . What will happen when the forward thrust is increased? .. Why the cyclist thrown forward when the bicycle runs over a stone.? .. Explain why the cyclist can gets serious injuries if he falls into the road which the surface is very hard. ..
(c)
(d)
(e)
4.
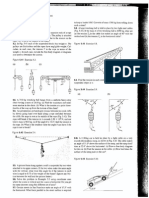
A student studies the effect of the movement of a lift on the readings of a weighing scale. The mass of the student is 50 kg. In this study, the student stands on a weighing scale in a lift as show in the following figure.
He records the readings of the weighing scale when the lift is at rest, moving up with acceleration, moving up with uniform velocity, moving down with uniform velocity and moving down with deceleration. The readings of the weighing scale in the study are shown in the following table.
(a)
The mass of the student is 50 kg.What is the weight of the student in newtons? . N State two types of movement of the lift when the reading on the weighing scale is equal to the mass of the student. 1... 2.. F is the resultant force that acts on the student. R is the normal reaction of the weighing scale on the student m is the mass of the student g is gravitational acceleration Write a general equation to show the relationship between F, R, m and g. . When the lift moves up with acceleration , the normal reaction is greater than his weight. Explain why ? (i) What is observed on the reading of the weighing scale when the lift moves down with an acceleration? . Give a reason for your answer in (e)(i).
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(ii)
You might also like
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2.9Document15 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 2.9Farain RashdiNo ratings yet
- Maria Rubatto Catholic School Physics Department Grade 9Document4 pagesMaria Rubatto Catholic School Physics Department Grade 9eyobNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Newton Law Worksheet ProblemsDocument2 pagesNewton Law Worksheet ProblemsTheOnesNo ratings yet
- Force and MotionDocument7 pagesForce and MotionDavidHutasoit100% (2)
- Physics Iup Itb Bab 2 - 3Document12 pagesPhysics Iup Itb Bab 2 - 3Emmyr FaiqNo ratings yet
- 101 French Verbs - The Art of ConjugationDocument15 pages101 French Verbs - The Art of Conjugationjkadiyala8207No ratings yet
- AJC TutorialDocument4 pagesAJC TutorialYong Ming HengNo ratings yet
- workbook-20230610021212815729-Free-Body-Diagrams-Practice-nDocument7 pagesworkbook-20230610021212815729-Free-Body-Diagrams-Practice-nnexuspivot.animatorNo ratings yet
- SECTION A: Objective Questions Instruction: Answer All Questions. 1. A B C D 2. A B C DDocument17 pagesSECTION A: Objective Questions Instruction: Answer All Questions. 1. A B C D 2. A B C DNurlailie Md JamilNo ratings yet
- 5.docx Work Energy PowerDocument12 pages5.docx Work Energy Powerjayesh1997No ratings yet
- Mechanics SummaryDocument27 pagesMechanics Summaryuse otherNo ratings yet
- Force: HKCEE Physics - 475091809Document15 pagesForce: HKCEE Physics - 475091809elty TanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document12 pagesLesson 5Ryan KoNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Forces Test 2017Document14 pagesKinematics Forces Test 2017yhhNo ratings yet
- CB_IX_Sci_Ch 11_Work and Energy_Specific QsDocument2 pagesCB_IX_Sci_Ch 11_Work and Energy_Specific Qsparamveerbilakhiya1234No ratings yet
- The Spiral SpringDocument11 pagesThe Spiral SpringAyogu Ebubechi GloryNo ratings yet
- PM TB Solutions C03Document5 pagesPM TB Solutions C03Vishwajeet Ujhoodha100% (5)
- 1.3 Equilibrium of Forces 2021Document6 pages1.3 Equilibrium of Forces 2021Nurul shazwaniNo ratings yet
- ρ v k, where p is a pressure, h a height,Document2 pagesρ v k, where p is a pressure, h a height,joeNo ratings yet
- The Inclined Plane (George Ricarrson - 2501987261)Document12 pagesThe Inclined Plane (George Ricarrson - 2501987261)George RYNo ratings yet
- Mechanos 1 CH 3Document7 pagesMechanos 1 CH 3Darlene BellesiaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions I: Exemplar Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 6 - Work, Energy, and PowerDocument24 pagesMultiple Choice Questions I: Exemplar Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 6 - Work, Energy, and PowerRajmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document19 pagesChapter 4Shashank ShekharNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion 1 QPDocument22 pagesCircular Motion 1 QPSofia TsymbalenkoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ReviewDocument3 pagesChapter 2 ReviewFlora DongNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power - S.R. - Part - 1Document7 pagesWork, Energy and Power - S.R. - Part - 1Abhimanyu BhasinNo ratings yet
- Newton - S Law of Motion QDocument3 pagesNewton - S Law of Motion QAmmar YasirNo ratings yet
- Statics ModuleDocument6 pagesStatics ModuleNafa HashimNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Forces - Nov. 2021Document8 pages2.2 Forces - Nov. 2021akram261104No ratings yet
- Chapter Questions Newton S LawsDocument8 pagesChapter Questions Newton S LawsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Vectors and Scalars in MechanicsDocument18 pagesVectors and Scalars in Mechanicsmardel11No ratings yet
- Worksheet on unit-1: Forces and MotionDocument12 pagesWorksheet on unit-1: Forces and MotionMD Rezaur Rahman Bhuiyan0% (1)
- Unit3 - MCQ - Practice: Ap Physics 1 Test BookletDocument24 pagesUnit3 - MCQ - Practice: Ap Physics 1 Test BookletMariale SalamancaNo ratings yet
- IB Physics Forces and Newton's Laws QuestionsDocument6 pagesIB Physics Forces and Newton's Laws QuestionsJad CharafeddineNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Dynamics Chapter ReviewDocument11 pagesModule 2 Dynamics Chapter ReviewAmelia RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion and Gravitation ExercisesDocument22 pagesCircular Motion and Gravitation Exercisesyuxing lieNo ratings yet
- Friction AutoDocument24 pagesFriction AutoSayyadh Rahamath BabaNo ratings yet
- HW 3Document6 pagesHW 3Stephanie TeoNo ratings yet
- FORCESDocument4 pagesFORCESTani JNo ratings yet
- Strain Energy Method-2Document31 pagesStrain Energy Method-2pengniumNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Resolution of Forces + 1.3 Equilibrium of Forces 2021Document13 pages1.2 Resolution of Forces + 1.3 Equilibrium of Forces 2021pravin manikamNo ratings yet
- Applied Fluid Mechanics - 05 Bouyancy and StabilityDocument29 pagesApplied Fluid Mechanics - 05 Bouyancy and Stabilitysourz1875% (4)
- Worksheet: Hooke's Law: Q1.A Student Suspended A Spring From A Laboratory Stand and Then Hung A Weight From TheDocument11 pagesWorksheet: Hooke's Law: Q1.A Student Suspended A Spring From A Laboratory Stand and Then Hung A Weight From Thefatimahehe31323No ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument5 pagesCircular MotionPraphul MalolNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Effects of ForcesDocument8 pages2.5 Effects of ForcesNURUL FAEZAH BINTI MUSTAPA MoeNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion ExplainedDocument4 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion Explainedshiva ram prasad pulagamNo ratings yet
- Free Body DiagramsDocument4 pagesFree Body DiagramsMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Physics Matters For GCEDocument4 pagesPhysics Matters For GCEno one46% (13)
- Kinetic Energy and Work ExplainedDocument26 pagesKinetic Energy and Work ExplainedRetno IstighfariniNo ratings yet
- 2023-2024-Class XI-Physics-Part 5-AWDocument10 pages2023-2024-Class XI-Physics-Part 5-AWjimmyemandeeNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Physics Extended 10th Edition Halliday Test Bank DownloadDocument26 pagesFundamentals of Physics Extended 10th Edition Halliday Test Bank DownloadChristel Amos100% (24)
- Fundamentals of Physics Halliday 10th Edition Test BankDocument26 pagesFundamentals of Physics Halliday 10th Edition Test BankBenjaminMartinezqmae100% (39)
- AP Physics Notes - Newton's Laws of MotionDocument9 pagesAP Physics Notes - Newton's Laws of MotionAndy HeNo ratings yet
- GP1 S 14 Chap 5 ProblemsDocument14 pagesGP1 S 14 Chap 5 ProblemsUmbina Gescery100% (1)
- 额外作业U1MCQ1DMotionDocument13 pages额外作业U1MCQ1DMotionharry yangNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion Practice Sheet 1Document7 pagesForces and Motion Practice Sheet 1inder191No ratings yet
- Ujian 1 Sains Form 1 2017Document8 pagesUjian 1 Sains Form 1 2017Jill Peary RajuNo ratings yet
- Seminar Kertas 3 Fizik SPMDocument26 pagesSeminar Kertas 3 Fizik SPMMaZs AmIrulNo ratings yet
- Bahulu's HouseDocument137 pagesBahulu's Houseaim_nainaNo ratings yet
- CH1SCIENTIFICINVESTIGATIONDocument6 pagesCH1SCIENTIFICINVESTIGATIONAmsyidi AsmidaNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2.1Document17 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 2.1Farain RashdiNo ratings yet
- SEKOLAH MENENGAH KEBANGSAAN TABUAN JAYA SCIENCE PAPER 2 EXAMDocument13 pagesSEKOLAH MENENGAH KEBANGSAAN TABUAN JAYA SCIENCE PAPER 2 EXAMJill Peary RajuNo ratings yet
- RPPTB Science Form 5Document28 pagesRPPTB Science Form 5Jill Peary RajuNo ratings yet
- Bimbingan Malam 2012 Soalan 10Document8 pagesBimbingan Malam 2012 Soalan 10Jill Peary RajuNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro To PhysicsDocument33 pages1 Intro To Physicsharshasoni100% (6)
- Soalan 11 Sains f5Document8 pagesSoalan 11 Sains f5Jill Peary RajuNo ratings yet
- Trial Physics 2012Document11 pagesTrial Physics 2012Jill Peary RajuNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics f4 2013Document29 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Physics f4 2013Jill Peary RajuNo ratings yet
- Modul SC GraphDocument2 pagesModul SC GraphJill Peary RajuNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Ohms Law 09Document12 pages7.2 Ohms Law 09Jill Peary RajuNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics f4 2013 EditedDocument9 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Physics f4 2013 EditedJill Peary RajuNo ratings yet
- 3.1 PressureDocument15 pages3.1 PressureJill Peary RajuNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document1 pageExercise 1Elvon EdwardNo ratings yet
- Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011Document19 pagesPeperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011Jill Peary RajuNo ratings yet