Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Disc How Ships Float
Uploaded by
The Calgary SunOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Disc How Ships Float
Uploaded by
The Calgary SunCopyright:
Available Formats
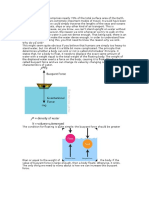
How mu ch d
How do ships oat?
The Greek Mathematician and inventor Archimedes lived during the 3rd century B.C. According to history he was in the bath one day when he discovered the principle of buoyancy which is the reason why huge Greek ships weighing thousands of pounds could oat on water. He noticed that as he lowered himself into the bath, the water displaced by his body overowed the sides and he realised that there was a relationship between his weight and the volume of water displaced.
DISCOVERY
ater weigh? s wFresh water has oe
Archimedes discovery
railing
a density of 1,000 kg/cubic metre. Ocean salt water has an average density of 1027 kg/cubic metre.
deck
Round-bottom displacement hull
deck
The hull (body of the ship below the main deck) is typically very wide and has a deep base line, or bottom.
The weight of sea water depends on a number of variables, including the temperature, the amount of salt (salinity) and whatever other foreign items may be present.
The Buoyancy Principle
Archimedes buoyancy principle:
frames (ribs) stringers
deck
A good portion of the interior of any boat is air. The average density of a boat the combination of the steel and the air is very light compared to the average density of water. So very little of the boat actually has to submerge into the water before it has displaced the weight of the boat. Vertical watertight dividers known as bulkheads are installed throughout the interior of the hull. These dividers keep damaged ships aoat by containing incoming water into a compartment or compartments, preventing the whole ship from ooding.
Ship weight: 1,000 kg Displaced water: 1,000 kg
A ship will oat when the weight of the water it displaces equals the weight of the ship and anything will oat if it is shaped to displace its own weight of water before it reaches the point where it will submerge.
cargo hold inner bottom
keel plate
outer bottom
Cruise ships are typically constructed with extrastrength steel and double hulls (a hull within a hull).
Rectanglar with rounded edges to dissipate drag. Allows large, heavy ships to move smoothly. Extremely stable. Passengers rarely feel any rocking or side-to-side movement. These hulls move uidly, but the resistance of the water makes them extremely slow.
Different materials have different densities but can have equal volume and therefore will have a different buoyancy. These objects are the same size (occupy same volume of space), but have different densities. Bowling ball will sink. Balloon will oat. The bowling ball weighs more than the weight of the water it displaces. The bowling ball has a low surface area to weight ratio.
Bowling ball vs. balloon
Why did the Concordia sink?
Costa Concordia Length: 290.2m Width: 35.5m Tonnage: 114,500 GT Displacement: 51,387 tonnes
A boat is essentially a hollow shell lled with air, meaning that it has a large surface area to weight ratio. Therefore, the boat will still be well above the surface when it has displaced its equivalent weight in water.
At 9:30 p.m. on Friday, Jan. 13, the cruise ship Costa Concordia struck rocks 300 metres off the island of Giglio, near the coast of Italy, ripping a hole in the hull. The captain had deviated from the deep water route usually taken by large ships to travel closer to shore.
When a boat takes on enough water it will become too heavy to remain buoyant.
The wash from a ship close to shore has no where to go and may have rebounded on the hull, causing the ship to roll.
SUSAN BATSFORD, GRAPHICS EDITOR, TWITTER @SBATS1/QMI AGENCY
You might also like
- Ship StabilityDocument8 pagesShip StabilityMahmoud SalamaNo ratings yet
- SUBMARINES & TORPEDOES: A HISTORY OF UNDERWATER WARFAREDocument24 pagesSUBMARINES & TORPEDOES: A HISTORY OF UNDERWATER WARFAREPrince MultaniNo ratings yet
- How Submarines Control Buoyancy to Submerge and SurfaceDocument15 pagesHow Submarines Control Buoyancy to Submerge and SurfaceJezreel EspañolaNo ratings yet
- BoatatatatatatatDocument6 pagesBoatatatatatatatjude albaoNo ratings yet
- World Boats 2033Document6 pagesWorld Boats 2033Jas SinNo ratings yet
- Buoyant Force of WaterDocument2 pagesBuoyant Force of Watermrdkm37No ratings yet
- Types and Uses of BoatsDocument1 pageTypes and Uses of BoatsEthan ZacharyNo ratings yet
- How Does Submarines Submerge and FloatDocument15 pagesHow Does Submarines Submerge and FloatYash YadavNo ratings yet
- KayakDocument12 pagesKayakAnonymous 4FVm26mbcONo ratings yet
- 2 Boats and BoatbuildingDocument13 pages2 Boats and BoatbuildingRachel Erica Guillero Buesing100% (1)
- Everything you need to know about boatsDocument11 pagesEverything you need to know about boatsIhsan1991 YusoffNo ratings yet
- BBBBBBBDocument5 pagesBBBBBBBjude albaoNo ratings yet
- Cruising - A View Through the Porthole: More than You Ever Wanted to Know about Taking a Cruise!From EverandCruising - A View Through the Porthole: More than You Ever Wanted to Know about Taking a Cruise!No ratings yet
- Archimedes PrincipleDocument32 pagesArchimedes PrincipleChuahSiewHoonNo ratings yet
- For Other Uses, See - Not To Be Confused With .: Boat (Disambiguation) ShipDocument2 pagesFor Other Uses, See - Not To Be Confused With .: Boat (Disambiguation) ShipJayantYadavNo ratings yet
- Stability and Control of Deeply Submerged Submarine - PptxnewDocument45 pagesStability and Control of Deeply Submerged Submarine - PptxnewNavin KumarNo ratings yet
- Heavy vs Light Boats and Hull Speed ExplainedDocument1 pageHeavy vs Light Boats and Hull Speed ExplainedbuddhaNo ratings yet
- Boat - WikipediaDocument11 pagesBoat - WikipediaAmitesh Tejaswi (B.A. LLB 16)No ratings yet
- Canoe - The World's Oldest WatercraftDocument6 pagesCanoe - The World's Oldest WatercraftSarvesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- BoatDocument1 pageBoatSaad AhsanNo ratings yet
- Discovering Archimedes' PrincipleDocument4 pagesDiscovering Archimedes' PrincipleJustine CaisipNo ratings yet
- Deep Water, Ancient Ships.Document246 pagesDeep Water, Ancient Ships.Rodrigo De Oliveira Torres100% (3)
- At 17 Metres Long, The Severn-Class Lifeboats Are The Largest Class of UK LifeboatDocument6 pagesAt 17 Metres Long, The Severn-Class Lifeboats Are The Largest Class of UK Lifeboatyoutube watcherNo ratings yet
- Calculate density, draft and displacement changesDocument30 pagesCalculate density, draft and displacement changesAnna E A. Camaño100% (2)
- The History of ShipsDocument4 pagesThe History of Shipsapi-351556416No ratings yet
- Cargo Handling - 2-2Document16 pagesCargo Handling - 2-2Beyza AlacagözNo ratings yet
- Sailing PDFDocument30 pagesSailing PDFJulie JacksonNo ratings yet
- Early Ships and Seafaring: Water Transport within EuropeFrom EverandEarly Ships and Seafaring: Water Transport within EuropeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sub-Marine PortfolioDocument9 pagesSub-Marine PortfolioalexNo ratings yet
- Harbour and Port Engineering GuideDocument101 pagesHarbour and Port Engineering Guidekhadar basha67% (3)
- Introduction To Ice Navigation PDFDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Ice Navigation PDFMarijaŽaper100% (2)
- How and Why Do Things FloatDocument25 pagesHow and Why Do Things Floatswaglordswag123No ratings yet
- From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: For Other Uses, SeeDocument13 pagesFrom Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: For Other Uses, Seecjcute91No ratings yet
- Characteristics of The Ship: A) FloatabilityDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of The Ship: A) FloatabilityStefanyNo ratings yet
- A History of the World in Sixteen ShipwrecksFrom EverandA History of the World in Sixteen ShipwrecksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (20)
- Noahs Ark Article in AiGDocument6 pagesNoahs Ark Article in AiGNathan SmithNo ratings yet
- Canoeing and KayakingDocument63 pagesCanoeing and KayakingAlyssa Mae LargadoNo ratings yet
- Water Transportation Power PointDocument96 pagesWater Transportation Power PointHannah Calupit72% (18)
- SC Fair (Nave)Document17 pagesSC Fair (Nave)buddhaNo ratings yet
- Canoeing&KayakingDocument28 pagesCanoeing&KayakingJenalyn BustineraNo ratings yet
- Very Large Vessel HandlingDocument9 pagesVery Large Vessel HandlingCapt M J Thavapunithan John88% (8)
- THC 213 Sea TranspoDocument19 pagesTHC 213 Sea TranspoCyril Mae VillavelezNo ratings yet
- Berthing Structures: Piers, Jetties, Wharfs & DocksDocument15 pagesBerthing Structures: Piers, Jetties, Wharfs & Docksnithesh kumar jNo ratings yet
- Formation: Fringing Reef Atoll The Structure and Distribution of Coral ReefsDocument3 pagesFormation: Fringing Reef Atoll The Structure and Distribution of Coral ReefsIvanciuc AdrianNo ratings yet
- Running Head: A Brief History of The Submarine 0Document10 pagesRunning Head: A Brief History of The Submarine 0alexNo ratings yet
- General Ship KnowledgeDocument11 pagesGeneral Ship KnowledgeAbu Syeed Md. Aurangzeb Al MasumNo ratings yet
- Nautical CompendiumDocument24 pagesNautical CompendiumMatias100% (1)
- Alex Ingles)Document1 pageAlex Ingles)Alex MorenoNo ratings yet
- Eng HWDocument2 pagesEng HWr.elmasri2No ratings yet
- Ship NomenclatureDocument21 pagesShip NomenclatureRachel Erica Guillero BuesingNo ratings yet
- Reyes Jay Jay N. Seam6Document1 pageReyes Jay Jay N. Seam6Mj MalacaNo ratings yet
- Launching of SHIPDocument3 pagesLaunching of SHIPisrat jahanNo ratings yet
- Two Years Before the Mast - A Personal Narrative of Life at SeaFrom EverandTwo Years Before the Mast - A Personal Narrative of Life at SeaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (374)
- Maritime Archaeology: Maritime Archaeology (Also Known As Marine Archaeology) Is ADocument9 pagesMaritime Archaeology: Maritime Archaeology (Also Known As Marine Archaeology) Is ATarak DasNo ratings yet
- Garth Brooks DiscographyDocument1 pageGarth Brooks DiscographyThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- Garth Brooks Timeline and AccoladesDocument1 pageGarth Brooks Timeline and AccoladesThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- Female Bank RobberDocument1 pageFemale Bank RobberThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- Alberta PremiersDocument1 pageAlberta PremiersThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- Min DickensDocument1 pageMin DickensThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- Hockey Player Battle Scars GraphicDocument1 pageHockey Player Battle Scars GraphicThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- The PlattmanDocument1 pageThe PlattmanThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- PC PromisesDocument1 pagePC PromisesThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- 2012 Election Results MapsDocument1 page2012 Election Results MapsThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- How We VotedDocument1 pageHow We VotedThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- Min Young HeartDocument1 pageMin Young HeartThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- Wildrose Vs PCDocument1 pageWildrose Vs PCThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- 5min OscartimelineDocument1 page5min OscartimelineThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- Infographic: Soft-Tissue InjuriesDocument1 pageInfographic: Soft-Tissue InjuriesedsunonlineNo ratings yet
- Deadly ColdDocument1 pageDeadly ColdThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- 5min SouthpoleddDocument1 page5min SouthpoleddThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- Dustin Paxton Police InterviewDocument233 pagesDustin Paxton Police InterviewThe Calgary Sun67% (3)
- 5 Mins Cold SnapDocument1 page5 Mins Cold SnapThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- TimsgraphicDocument1 pageTimsgraphicThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar Inc.'s Windfall of CashDocument1 pageCaterpillar Inc.'s Windfall of CashThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- Dis Magnetic SoapDocument1 pageDis Magnetic SoapThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- On The HuntDocument1 pageOn The HuntThe London Free PressNo ratings yet
- FelicitysjourneyDocument1 pageFelicitysjourneyThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- 5min SalvageconcordiaDocument1 page5min SalvageconcordiaThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- Infographic: Winter InjuriesDocument1 pageInfographic: Winter InjuriesedsunonlineNo ratings yet
- Infographic: Germs! They're Hiding ...Document1 pageInfographic: Germs! They're Hiding ...edsunonlineNo ratings yet
- 5 Min Chinese New YearDocument1 page5 Min Chinese New YearThe Calgary Sun100% (1)
- 5mins HaitiDocument1 page5mins HaitiThe Calgary SunNo ratings yet
- Draft of Reflection PaperDocument2 pagesDraft of Reflection PaperAkshaya LakshminarasimhanNo ratings yet
- Ball Bearings 1Document17 pagesBall Bearings 1ManicharanNo ratings yet
- Ms - Installation of Electric PVC Conduits and AccessoriesDocument6 pagesMs - Installation of Electric PVC Conduits and AccessoriesDuel TimeNo ratings yet
- Agile in a Nutshell: Uncovering Better Ways of Developing SoftwareDocument1 pageAgile in a Nutshell: Uncovering Better Ways of Developing SoftwaresamprasNo ratings yet
- Structure damage assessment using Repair ManagerDocument10 pagesStructure damage assessment using Repair ManagerJokenny WilliamNo ratings yet
- B767 BrakesDocument6 pagesB767 BrakesGustavo Avila RodriguezNo ratings yet
- ABB PS Range BrouchureDocument12 pagesABB PS Range BrouchureguigfsNo ratings yet
- Industrial Profile of Bhavnagar DistrictDocument19 pagesIndustrial Profile of Bhavnagar Districtsiddharth singhNo ratings yet
- Auto Parts Inventory SystemDocument4 pagesAuto Parts Inventory SystemVince Ryan L. ArboledaNo ratings yet
- A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)Document4 pagesA Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)GebeyehuNo ratings yet
- Approval Form For Material Gate Pass 内部出门证: COD Muhammed Thanzeel 8424503 0580281560Document1 pageApproval Form For Material Gate Pass 内部出门证: COD Muhammed Thanzeel 8424503 0580281560Muhammed ThanzeelNo ratings yet
- GCC Automotive Salary GuideDocument19 pagesGCC Automotive Salary GuidemfakhrulNo ratings yet
- Brazil Plastic IndustryDocument11 pagesBrazil Plastic IndustryminhiseNo ratings yet
- WM Stock Upload ProcedureDocument9 pagesWM Stock Upload ProcedurejalalhussainrshNo ratings yet
- Iso 3601-2 - 2016Document66 pagesIso 3601-2 - 2016Roby Mastre100% (1)
- Mule ESB 3 User GuideDocument804 pagesMule ESB 3 User GuideTruong Tien DungNo ratings yet
- HiTEC-5724 PDS PDFDocument2 pagesHiTEC-5724 PDS PDFahmetNo ratings yet
- Minar TMTDocument67 pagesMinar TMTJaffar T K Karulai100% (3)
- Kansai Group Corporation Invoice for Vehicle Export to MaldivesDocument1 pageKansai Group Corporation Invoice for Vehicle Export to MaldivesIbrahim JaleelNo ratings yet
- Describe The Health and Safety Requirements and Safe Working Practices and Procedures Required For The Hand Fitting Activities UndertakenDocument7 pagesDescribe The Health and Safety Requirements and Safe Working Practices and Procedures Required For The Hand Fitting Activities UndertakenPxre LxckNo ratings yet
- Ganesh Bharadwaj H S-Resume-2023Document6 pagesGanesh Bharadwaj H S-Resume-2023Bharadwaj's ArohanaNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Conversion Optimization by ConversionXLDocument43 pagesEssentials of Conversion Optimization by ConversionXLJohn Sald100% (1)
- FPSO Design and Conversion-A Designer ApproachDocument21 pagesFPSO Design and Conversion-A Designer ApproachDzakyHaidar100% (1)
- Baron 55Document1,113 pagesBaron 55Dú VieiraNo ratings yet
- JD TM-DC BSG-MT 1Document2 pagesJD TM-DC BSG-MT 1Anshuman Tiwari 4-Year B.Tech. Mining EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Sample Forms WPS PQRDocument22 pagesSample Forms WPS PQRGMNo ratings yet
- Case Study Star EngineeringDocument5 pagesCase Study Star EngineeringSaurabh Jha0% (2)
- BookDocument170 pagesBookPriscyla RoqueNo ratings yet
- Wheels of Thunder October 2012Document84 pagesWheels of Thunder October 2012Scott RobinsonNo ratings yet
- DB KAF 4.3 en WebDocument14 pagesDB KAF 4.3 en WebnawajhaNo ratings yet