Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Autosys Sheduling Tool
Uploaded by
Rathan KumarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Autosys Sheduling Tool
Uploaded by
Rathan KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
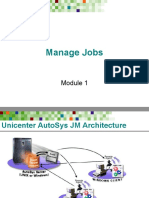
Autosys UNICENTRE is a job scheduling tool.
The following article provides a brief information about the commands essential for job scheduling. Autosys Job Management for UNIX This guide will be helpfull in giving basic idea about what autosys is, defining jobs to AutoSys, monitoring and managing jobs. Introduction to Autosys: AutoSys is an automated job control system for scheduling, monitoring, and reporting. These jobs can reside on any AutoSys-configured machine that is attached to a network. An AutoSys job is any single command, executable, script, or Windows batch file. Each AutoSys job definition contains a variety of qualifying attributes, including the conditions specifying when and where a job should be run. Defining Jobs : There are the two methods you can use to create job definitions: Using the AutoSys Graphical User Interface (GUI). Using the AutoSys Job Information Language (JIL) through a command-line interface. Autosys Jobs: Job Types and Structure : There are three types of jobs: command, file watcher, and box. As their names imply, command jobs execute commands, box jobs are containers that hold other jobs (including other boxes), and file watcher jobs watch for the arrival of a specified file. In the AutoSys environment, the box job (or box) is a container of other jobs. A box job can be used to organize and control process flow. The box itself performs no actions, although it can trigger other jobs to run. An important feature of this type of job is that boxes can be put inside of other boxes. Default Box Job Behavior: Some important rules to remember about boxes are Jobs run only once per box execution. Jobs in a box will start only if the box itself is running. As long as any job in a box is running, the box remains in RUNNING state; the box cannot complete until all jobs have run. By default, a box will return a status of SUCCESS only when all the jobs in the box have run and the status of all the jobs is "success. By default, a box will return a status of FAILURE only when all jobs in the box have run and the status of one or more of the jobs is "failure." Unless otherwise specified, a box will run indefinitely until it reaches a status of SUCCESS or FAILURE. Changing the state of a box to INACTIVE (via the sendevent command) changes the state of all the jobs in the box to INACTIVE. Job States and Status : AutoSys keeps track of the current state, or status, of every job. The value of a jobs status is used to determine when to start other jobs that are dependent on the job. The job status is displayed in the job report generated by the autorep command, and in the job report you can view in the Job Activity Console Following are the status of Autosys jobs:
INACTIVE : The job has not yet been processed. Either the job has never been run, or its status was intentionally altered to turn off its previous completion status ACTIVATED :The top-level box that this job is in is now in the RUNNING state, but the job itself has not started yet. STARTING : The event processor has initiated the start job procedure with the Remote Agent. RUNNING : The job is running. If the job is a box job, this value simply means that the jobs within the box may be started (other conditions permitting). If it is a command or file watcher job, the value means that the process is actually running on the remote machine. SUCCESS : The job exited with an exit code equal to or less than the maximum exit code for success. By default, only the exit code 0 is interpreted as success. If the job is a box job, this value means that all the jobs within the box have finished with the status SUCCESS (the default), or the Exit Condition for Box Success evaluated to true FAILURE : The job exited with an exit code greater than the maximum exit code for success. By default, any number greater than zero is interpreted as failure. AutoSys issues an alarm if a job fails TERMINATED : The job terminated while in the RUNNING state. A job can be terminated if a user sends a KILLJOB event or if it was defined to terminate if the box it is in failed. If the job itself fails, it has a FAILURE status, not a TERMINATED status. A job may also be terminated if it has exceeded the maximum run time (term_run_time attribute, if one was specified for the job), or if it was killed from the command line through a UNIX kill command. AutoSys issues an alarm if a job is terminated. RESTART : The job was unable to start due to hardware or application problems, and has been scheduled to restart. QUE_WAIT : The job can logically run (that is, all the starting conditions have been met), but there are not enough machine resources available. ON_HOLD : This job is on hold and will not be run until it receives the JOB_OFF_HOLD event. ON_ICE : This job is removed from all conditions and logic, but is still defined to AutoSys. Operationally, this condition is like deactivating the job. It will remain on ice until it receives the JOB_OFF_ICE event. The difference between "on hold" and "on ice" is that when an "on hold" job is taken off hold, if its starting conditions are already satisfied, it will be scheduled to run, and it will run. On the other hand, if an "on ice" job is taken "off ice," it will not start, even if its starting conditions are already satisfied. This job will not run until its starting conditions reoccur. The other major distinction is that jobs downstream from the job that is "on ice" will run as though the job succeeded. Whereas, all dependent jobs do not run when a job is on "on hold"nothing downstream from this job will run. Starting Parameters : AutoSys determines whether to start or not to start a job based on the evaluation of the starting conditions (or starting parameters) defined for the job. These conditions can be one or more of the following: Date and time scheduling parameters are met (it is or has passed the specified date and time). Starting Conditions specified in the job definition evaluate to true. For jobs in a box, the box must be in the RUNNING state. The current status of the job is not ON_HOLD or ON_ICE. Every time an event changes any of the above conditions, AutoSys finds all the jobs that may be affected by this change, and determines whether or not to start them. sample jil code / Writing jil code: jil = Job information language When using JIL to create a job definition, you enter the jil command to display the JIL prompt. Runs the Job Information Language (JIL) processor to add, update, and delete AutoSys jobs, machines,
monitors, and reports. Also used to insert one-time job override definitions. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------/* ----------------- SAP_UAT_MU03_C ----------------- */ insert_job: SAP_UAT_MU03_C job_type: c command: /local/SAP/processCheckUAT.sh machine: MU03-UAT owner: admin@MU03-UAT permission: gx,wx,mx,me days_of_week: all start_times: "15:00, 14:00" description: "Job used for Run testing of process" alarm_if_fail: 1 max_exit_success: 1 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------The above example is a simple jil code of autosys which we have to write if we want any particular job to be thru autosys. To Insert a new JIL code : issue command "jil" bash-3.00$ jiljil>>1> "The following prompt will appear" copy paste the jil code u have made example of jil code below........... At the end the "C" or "B" determines if the job is box job or child job. if the jil is inserted properly successfull message will come if any errors are there the jil code contains some errors.. if successfull exit; 2. Other way is to create a temp file named temp.jil which contains jil code on autosys server: give command. bash-3.00$ jil<> Functional Listing of AutoSys Commands : This section lists which AutoSys commands to use for specific tasks. All commands are for both Windows and UNIX, unless otherwise specified. Accessing Sybase : xql Checking System Status : autoflags autoping autosyslog chase chk_auto_up
Converting cron to JIL (UNIX Only) : cron2jil Defining AutoSys Jobs or Machines : jil Defining Calendars : autocal, autocal_asc Reporting Job Status : autorep autostatus Starting AutoSys (UNIX Only) : eventor Stopping AutoSys : sendevent Using Autorep command: Function Reports information about a job, jobs within boxes, machines, and machine status. Also reports information about job overrides and global variables. Syntax autorep {-J job_name -M machine_name -G global_name} [-s -d -q -o over_num] [-r run_num] autorep -J (job name here) This will display a list of jobs with complete details with box/jobname, last/latest run date & time, status, exit code, etc. Viewing JIL code for any Autosys job autorep -J (job name here) -q To obtain the underlying JIL (Job Interaction Language) source code for any Autosys job, run command: To obtain the information of previous runs autorep -J (job name here) -r (No of runs back) example : autorep -J (job name here) -r 1 would generate a report for the job run one runs back ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Status Abbreviations The following table lists the abbreviations used in the ST (status) column of the autorep report, and gives the status for each abbreviation. AC - ACTIVATED FA - FAILURE IN - INACTIVE OH - ON_HOLD OI - ON_ICE QU - QUE_WAIT RE - RESTART RU - RUNNING ST - STARTING SU - SUCCESS TE - TERMINATED
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sendevent: sendevents to AutoSys for a variety of purposes, including starting or stopping AutoSys jobs, stopping the Event processor, and putting a job on hold. This command is also used to set AutoSys global variables or cancel a scheduled event. sendevent is normally used with "-E" & -J option -J job_name : Specifies the name of the job to which the specified event should be sent. This option is required for all events except STOP_DEMON, COMMENT, ALARM, or SET_GLOBAL -E event :Specifies the event to be sent. This option is required. Any one of the following events may be specified: STARTJOB KILLJOB DELETEJOB FORCE_STARTJOB JOB_ON_ICE JOB_OFF_ICE JOB_ON_HOLD JOB_OFF_HOLD CHANGE_STATUS STOP_DEMON CHANGE_PRIORITY COMMENT ALARM SET_GLOBAL SEND_SIGNAL Following are the example of sendevent command frequently used. ____________________________________________________________________ To start or force start a job manually using sendevent : sendevent E FORCE_STARTJOB -J "Job Name Here" sendevent -E STARTJOB -J "Job Name Here" To put jobs on OFF ICE or ON ICE : sendevent -E OFF_ICE -J "Job Name Here" sendevent -E ON_ICE -J "Job Name Here" ______________________________________________________________
autostatus: Reports the current status of a specific job, or the value of an AutoSys global variable. Ex: autostatus -J job_name, -S instance
AutoSys on Unix Cd to the "autouser" ($AUTOUSER) directory and "." (or source) the "ksh" file. Ex: ". ./autosys.ksh.machine"After installing AutoSys, first make sure that the DB is up and running. Check the installation by running the command chk_auto_up to verify connection to the DB and event processor. Enter the KEYS through "gatekeeper", add keys Run the "autosys_secure" command to set the AutoSys Edit and Exec Super users (and also to enter NT users/passwords) Start the Event Processor by running the command "eventor" Shutdown AutoSys: "sendevent -E STOP_DEMON" To start the AutoSys GUI set your DISPLAY and run the command "autosc &". NT: Start AutoSys from start->programs->AutoSys-> administrator ->Graphical User Interface ->Command Prompt Autosys Command Line Commands:
1. gatekeeper: Allows you to enter the License Keys which allow you to run AutoSys. 2. eventor [-M machine_name] : Starts the event processor. 3. autorep -J [ALL Job_name] [-q] [> file_name], -d (detail), -r (run number), -o (override)
Ex: autorep -J job_name -d autorep -J job_name -d autorep -J job_name -q > file_name queries the DB & save job Dfn. Into a file vi file_name When you want a report of a box use the -L0 option Autorep -J job_name -r -1 report on the job for the day -1 (prev day) Autorep -J job_name -r -5 report on the job for last 5th run
4. sendevent -E STARTJOB -J job_name : Normally start Autosys job.
sendevent -E FORCE_STARTJOB -J job_name : Forcefully starts Autosys job. [JOB_ON_ICE, JOB_OFF_ICE, JOB_ON_HOLD, JOB_OFF_HOLD, SET_GLOBAL, STOP_DEMON. . . .] sendevent -E STOP_DEMON - to stop AutoSys sendevent -E SET_GLOBAL -G "var_name=/home/mydir" : To set a variable in Autosys
sendevent -E SET_GLOBAL -G "var_name=DELETE" : To delete Autosys variable that is declared/set
5. 6. 7. 8.
chk_auto_up: checks to see if event processor and the DB are both up. autoping -m machine: verify that both client & server are correctly configured. cron2jil -f cronfile [-d outdir] [-I incl_file] [-m machine] [-p prefix] jil: To insert autosys job directly into the DB /* ----------------- template test.jil ----------------- */ insert_job: template job_type: c box_name: box1 command: <unix command i.e. ls -l> machine: localhost owner: $jil < test.jil
9. autosyslog -e: same as tail -f autosys_log_file. This command must be run from the
machine where the server resides if used with the -e option. Else it can be used with the -J option to see that job's run log. 10. job_depends: -[cdt] -J jobname [-F "mm/dd/yy time"] [-T "mm/dd/yy time"] (Note: It will only print out the first occurrence found) 11. monbro -n monitor_name: Allows you to run from command line monitor/browser programs previously created using the monitor/browser GUI.exec superuser: AUTOSYS superuser 12. autocal_asc full_cal_name: prints, adds & deletes custom calendar definitions. 13. autostatus: Reports the current status of a specific job, or the value of an AutoSys global variable. Ex: autostatus -J job_name, -S instance 14. autotimezone -l : Allows additions, deletions, and queries to the timezones table (-l provides list). 15. autotrack: Tracks & report changes to the AutoSys DB. Ex: autotrack -l 2 (level 2) [sets the tracking level] autotrack -U sys -v (user sys: verbose) To start using the autotrack utility type: autotrack -u to set tracking level 1 or 2. By default it is set to 0. Autotrack -l will list the current tracking level. Options -[J, U, m, F, T, and t] are to request reporting on a specific Job, User, machine, time window (-F -T), and event type (t). Type is used in conjunction w/other parameters. autotrack w/no arguments retrieves information an all events omitting detail. -v option is for verbose. 16. autosys_secure: to change edit, exec superusers, change DB passwd, change remote authentication method.
17. chase [-AE]: Makes sure that jobs claiming to be running in the client machine are
running. The "-E" option restarts the job.
18. archive_events: to archive events in the DB which are older than x days to prev DB from
becoming full.
19. clean_files: Deletes old remote agent log files. It does it by searching the DB for all
machines which have had jobs started on them.
20. autostatad: to get the status of a PeopleSoft job. You can define one of the user definable
buttons to view PeopleSoft job: Autocons*userButton1Label: Adapter Status.
You might also like
- Autosys - A Job Scheduling ToolDocument15 pagesAutosys - A Job Scheduling ToolPrAvEeN522No ratings yet
- Base SAS Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesFrom EverandBase SAS Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNo ratings yet
- Autosys Interview Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesAutosys Interview Questions and Answerssenthil100% (1)
- Complete Guide to Using OKRs for Goal SettingDocument17 pagesComplete Guide to Using OKRs for Goal SettingReynaldo Alonso Jose Gomez100% (1)
- Autosys commands guideDocument39 pagesAutosys commands guidesantosh_panditpurNo ratings yet
- Using the Command Line for DataStage JobsDocument7 pagesUsing the Command Line for DataStage JobsSreenivas MudamNo ratings yet
- Talend FaqDocument8 pagesTalend FaqbabjeereddyNo ratings yet
- Why Control-M is better than other scheduling toolsDocument8 pagesWhy Control-M is better than other scheduling toolsnadeem baigNo ratings yet
- What Is Difference Between Server Jobs and Parallel Jobs? Ans:-Server JobsDocument71 pagesWhat Is Difference Between Server Jobs and Parallel Jobs? Ans:-Server JobsDinesh SanodiyaNo ratings yet
- Standards and Issues For Error Handling in WorkflowsDocument6 pagesStandards and Issues For Error Handling in WorkflowsshobhitnarulaNo ratings yet
- Data Stage FaqsDocument47 pagesData Stage FaqsVamsi Krishna EmanyNo ratings yet
- AutosysDocument19 pagesAutosysAjayNo ratings yet
- Autosys Interview PreparationDocument9 pagesAutosys Interview PreparationVinod KalahNo ratings yet
- Autosys DetailsDocument33 pagesAutosys Detailsrajesh716No ratings yet
- Autosys Unix CommandsDocument4 pagesAutosys Unix CommandsRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Lookup PDFDocument5 pagesDynamic Lookup PDFBhanwar Rajveer SinghNo ratings yet
- Autosys Cheat Sheet From CADocument4 pagesAutosys Cheat Sheet From CAwaltert1No ratings yet
- Informatica AdminDocument13 pagesInformatica AdminVikas SinhaNo ratings yet
- AutoSys r11.3 Understanding Job Scheduling Dependencies V3Document30 pagesAutoSys r11.3 Understanding Job Scheduling Dependencies V3shahbazbNo ratings yet
- Control M TopicsDocument5 pagesControl M TopicsVinod Kumar0% (1)
- Manual Helix Delta t6 PDFDocument309 pagesManual Helix Delta t6 PDFKikiDiansyah100% (1)
- Goldengate Interview Questions GuideDocument3 pagesGoldengate Interview Questions GuidesachinNo ratings yet
- ASM Interview QuestionsDocument44 pagesASM Interview QuestionsKumar KNo ratings yet
- Why Do We Need Control-M When I Can Use Cron Jobs or Windows Task Scheduler?Document8 pagesWhy Do We Need Control-M When I Can Use Cron Jobs or Windows Task Scheduler?nadeem baigNo ratings yet
- Selenium With PythonDocument4 pagesSelenium With Pythonmagillani100% (2)
- C Programming Book in Urdu PDFDocument4 pagesC Programming Book in Urdu PDFSandeep sahuNo ratings yet
- DataStage Configuration FileDocument7 pagesDataStage Configuration FilerachitNo ratings yet
- Top 50 Informatica Interview QuestionsDocument8 pagesTop 50 Informatica Interview QuestionsjanaketlNo ratings yet
- Autosys Job Management For UNIXDocument17 pagesAutosys Job Management For UNIXTata SairameshNo ratings yet
- Job SequencerDocument19 pagesJob Sequenceraddubey2No ratings yet
- AutosysDocument6 pagesAutosysravidwhwNo ratings yet
- Autosys - Computer Associates (CA)Document180 pagesAutosys - Computer Associates (CA)Tilak Kumar Dhar100% (1)
- Auto SysDocument4 pagesAuto SysJack MarionNo ratings yet
- Manage Jobs in Unicenter AutoSys JMDocument43 pagesManage Jobs in Unicenter AutoSys JMsubash pradhanNo ratings yet
- Autosys ResumeDocument4 pagesAutosys ResumeMohini VermaNo ratings yet
- 11-AutoSys Basic Commands Quick ReferenceDocument1 page11-AutoSys Basic Commands Quick Referenceactmon123100% (1)
- Informatica Realtime Scenarios With VideoDocument2 pagesInformatica Realtime Scenarios With VideoYugandar ChandragiriNo ratings yet
- Autosys CommandsDocument4 pagesAutosys Commandsnaveenr3No ratings yet
- SOL PLSQL Database FundamentalsDocument17 pagesSOL PLSQL Database FundamentalsAyal100% (1)
- Performance Tuning: Eliminate Source and Target Database BottlenecksDocument11 pagesPerformance Tuning: Eliminate Source and Target Database BottlenecksSannat ChouguleNo ratings yet
- IDQ Mappings From Cleanse FunctionsDocument4 pagesIDQ Mappings From Cleanse FunctionsVenkata Sri HarshaNo ratings yet
- Resume BhaskarGupta DataStageDocument16 pagesResume BhaskarGupta DataStageBhaskar Gupta MadalaNo ratings yet
- Datastage Performance Guide PDFDocument108 pagesDatastage Performance Guide PDFbsvbrajaNo ratings yet
- When Do You Go For Data Transfer Transformation: BenefitsDocument5 pagesWhen Do You Go For Data Transfer Transformation: BenefitsRamkoti VemulaNo ratings yet
- Basic SQL Queries GuideDocument18 pagesBasic SQL Queries GuideSuperstarNo ratings yet
- Datastage - Job Sequence Invocation & ControlDocument19 pagesDatastage - Job Sequence Invocation & ControlRMNo ratings yet
- Looping Informatica PDFDocument4 pagesLooping Informatica PDFAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- Unix and InformaticaDocument4 pagesUnix and InformaticaOm SachdevNo ratings yet
- Reset Autosys job statuses dailyDocument4 pagesReset Autosys job statuses dailyzipzapdhoomNo ratings yet
- MySQL Interview Questions and Answers For Experienced and FreshersDocument5 pagesMySQL Interview Questions and Answers For Experienced and FreshersMohmad Ashik M ANo ratings yet
- UNICENTER AUTOSYS JM COMMANDS GUIDEDocument17 pagesUNICENTER AUTOSYS JM COMMANDS GUIDE2BatulNo ratings yet
- Production Support IssuesDocument1 pageProduction Support IssuesDudi KumarNo ratings yet
- Oracle DBA Interview QuestionsDocument2 pagesOracle DBA Interview QuestionsPankaj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Transformer All FunctionsDocument47 pagesTransformer All FunctionsBhaskar Reddy100% (1)
- PLSQLDocument16 pagesPLSQLilakya sriNo ratings yet
- DB2 9 System Administration for z/OS: Certification Study Guide: Exam 737From EverandDB2 9 System Administration for z/OS: Certification Study Guide: Exam 737Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- BMC Control-M 7: A Journey from Traditional Batch Scheduling to Workload AutomationFrom EverandBMC Control-M 7: A Journey from Traditional Batch Scheduling to Workload AutomationNo ratings yet
- Chi Patrat PDFDocument14 pagesChi Patrat PDFvNo ratings yet
- Automotive Welding Technician Level4Document38 pagesAutomotive Welding Technician Level4BalvinderNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.03Document15 pagesAssignment No.03Om TNo ratings yet
- Poly Works S DK Reference GuideDocument44 pagesPoly Works S DK Reference GuidetiborNo ratings yet
- Lexmark X746 User Guide PDFDocument350 pagesLexmark X746 User Guide PDFalinsandyNo ratings yet
- An Advanced AES Algorithm Using Swap and 400 Bit Data Block With Flexible S-Box in Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesAn Advanced AES Algorithm Using Swap and 400 Bit Data Block With Flexible S-Box in Cloud ComputingusuimisakiNo ratings yet
- Sokolova M A Gintovt K P Tikhonova I S Tikhonova R M TeoretiDocument148 pagesSokolova M A Gintovt K P Tikhonova I S Tikhonova R M TeoretiAnonymous CahwvQDP1HNo ratings yet
- Indusoft Studio LimitsDocument1 pageIndusoft Studio LimitsMarlosFerreiraNo ratings yet
- 3300 XL Series NSV Datasheet EnglishDocument7 pages3300 XL Series NSV Datasheet EnglishCecep AtmegaNo ratings yet
- FilelistDocument35 pagesFilelistDionisie DamaschinNo ratings yet
- Topics for Online Computerized Tests in Programming, Networking & Other FieldsDocument6 pagesTopics for Online Computerized Tests in Programming, Networking & Other FieldssonujaglanNo ratings yet
- Manik and An Parthasarathy ProfileDocument4 pagesManik and An Parthasarathy ProfileManikandan ParthasarathyNo ratings yet
- Lab 521Document8 pagesLab 521Shashitharan PonnambalanNo ratings yet
- V510-14-15ikb HMM enDocument98 pagesV510-14-15ikb HMM endesignanddrawing cphclwNo ratings yet
- Hicalc ManualDocument46 pagesHicalc ManualYasir ShigileeniNo ratings yet
- Calibre XRC CB Ds PDFDocument2 pagesCalibre XRC CB Ds PDFMandy WuNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Ethical Hacking CourseDocument33 pagesDiploma in Ethical Hacking CourseWaseem AkramNo ratings yet
- DentsDocument1 pageDentsKTFNo ratings yet
- Standard Netburner Software and ProtocolsDocument4 pagesStandard Netburner Software and Protocolsflo72afNo ratings yet
- ROOT Basic Course PDFDocument374 pagesROOT Basic Course PDFjoao da silvaNo ratings yet
- Focus ERP & Implementation Methodology DocuementDocument42 pagesFocus ERP & Implementation Methodology DocuementRuban ThomasNo ratings yet
- Assembly ProceduresDocument7 pagesAssembly Proceduresalex sandersNo ratings yet
- Java Tutorial - BalajiDocument11 pagesJava Tutorial - BalajiBalaji Kumar100% (1)
- F8 - Introduction To An Advanced Verification Methodology PDFDocument71 pagesF8 - Introduction To An Advanced Verification Methodology PDF陈晟音乐族--王子No ratings yet
- Learning BeagleBone Python Programming - Sample ChapterDocument16 pagesLearning BeagleBone Python Programming - Sample ChapterPackt Publishing100% (2)
- SIM Ch4 PDFDocument20 pagesSIM Ch4 PDFRomi SaputraNo ratings yet