Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8086/8088 Instruction set guide
Uploaded by
Elvira VictoriaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
8086/8088 Instruction set guide
Uploaded by
Elvira VictoriaCopyright:
Available Formats
8/17/2011
Instruction Set
8086/8088 Instruction sets
OP Code Operational code, the code
that the machine understand and indicates what the computer will do. In
Mnemonics it is abbreviated Operand indicates the information
the form of Mnemonics instruction
Engr. Nio E. Merencilla
needed by the instruction in carrying out its task. An operand may contain a datum, address of the datum, or other information pertaining to the data to be acted on by the instruction.
Example
Classification of 8086/8088 Instruction Set
Operand
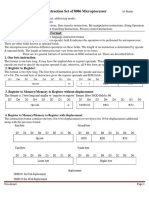
MOV AX , BX
OP Code
Data Transfer Instructions Arithmetic Instructions Bit Manipulation Instructions String Instructions Program Transfer Instructions Processor Control Instructions
Where: MOV is the Mnemonic for MOVE AX & BX is the Operand AX is the Destination operand BX is the Source operand
Data Transfer Instructions
These instructions are used to
MOV
Mnemonics for MOVE Move the content to/from
move data among registers, memory and the outside world. Also some instructions directly manipulate the stacks while other maybe used to alter the flags.
register/memory Syntax: MOV Destination , Source Example MOV AL,BL
8/17/2011
PUSH
Mnemonic for Push word to stack This instruction is used to save the
Stack
It is a collection of memory pointed
content of the register so that it can be used for other purpose. The saved data maybe copied into another register or written into memory called STACK
to by the Stack Pointer Register and Stack Segment Register. When we used to write data into the Stack we use this command PUSH Syntax: PUSH Source
Copy two bytes of data from register
or memory into the stack memory and then decrement SP by 2
POP
Mnemonic for POP word to stack This is the reverse of the PUSH Syntax:
POP Destination
8/17/2011
Retrieve two bytes of data from
stack memory and place it into a 16bit register or two memory locations then it increments SP by 2.
IN
Mnemonic for INPUT byte/word
from I/O Port.
This instruction is used to input
value from the I/O ports.
Syntax:
IN Accumulator , Port #
Transfers data from an external input
device with port address specified by the instruction to accumulator (AL, AX or EAX).
OUT
Mnemonic for OUTPUT
byte/word to I/O Port. This is the complement of the IN instruction. Syntax: OUT Port #, Accumulator
Transfers data from accumulator (AL,
AX or EAX) to an external output device with port address specified by the instruction.
LEA
Mnemonics for Load Effective
Address
This instruction is used to load the
offset of the source memory operand into one of the processors registers Syntax: LEA Destination , Source
8/17/2011
Loads a 16-bit register with offset
or effective address specified in the instruction.
PUSHF
Mnemonics for Push Flags onto
Stack
This instructions copy the
content of the Flag register into the Stack register. Syntax: PUSHF
POPF
Mnemonics for Pop Flags onto
XCHG
Mnemonics for Exchange data. This instruction is used to swap the
Stack This is the reverse operation of PUSHF Syntax: POPF
content of 8,16 or 32 bit operand.
One of the register must be a
processor register (excluding segment register). The other operand maybe a register or memory location
If the memory location is used as an
operand it is assumed to be within a data segment. Syntax: XCHG Destination , Source
8/17/2011
XLAT
Mnemonics for Translate Table. This instruction is used translate
It is used to translate a byte from one
one binary value to another. Syntax: XLAT
code to another code. XLAT replaces a byte in the AL register with a byte pointed to by BX in a lookup table in memory. Before the XLAT instruction can be executed, the lookup table containing values for the new code must be put in memory, andt he offset of the starting address of the lookup table must be loaded in BX. The code byte to be translated is put in AL.
LDS / LES
Mnemonics for Load pointer to DS / The 2nd 2 byte are copied into the
ES This instruction is used to load the two-16 bit register from a 4-byte block of memory The 1st 2 byte are copied into the register specified in the destination operand of the instruction
DS Syntax: LDS Destination , Source LES Destination , Source
Load 16-bit register and DS or ES
with words from four memory pointed by [mem]. Copies a word from two memory locations into 16-bit register specified in the instruction. It then copies a word from the next two memory locations into the DS or ES.
LAHF
Mnemonic for Load AH from Flag This command enable to load the
content of the flag register to the higher byte of the Accumulator Syntax: LAHF
8/17/2011
SAHF
This is one way to determine the
status of the flag by copying the LSByte of the flag to AH
Mnemonic for Store AH into Flag. This instruction is used to load a
new set of flags into the flag register by copying the content of AH register into the LSByte of the flag Syntax: SAHF
End
You might also like
- DCIT23 Assignment 4Document3 pagesDCIT23 Assignment 4Zed DeguzmanNo ratings yet
- Activity 2: Introduction To Turbo Assembler 2.1 Program Outcomes (Pos) Addressed by The ActivityDocument10 pagesActivity 2: Introduction To Turbo Assembler 2.1 Program Outcomes (Pos) Addressed by The ActivityKimCanillasVincereNo ratings yet
- Basic SAP-1 Computer Architecture ExplainedDocument9 pagesBasic SAP-1 Computer Architecture ExplainedAshna100% (1)
- ECE 113 The Public Telephone Network 4Document25 pagesECE 113 The Public Telephone Network 4Erven Micabalo UmbaoNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 - Data Transfer InstructionsDocument15 pagesLab 6 - Data Transfer InstructionsVityaNo ratings yet
- Instruction Set 8086Document104 pagesInstruction Set 8086Vishnu Shashank100% (1)
- 8086 Microprocessor Instruction SetDocument175 pages8086 Microprocessor Instruction SetRohtash SethiNo ratings yet
- MPMC UNIT 1 OwnDocument35 pagesMPMC UNIT 1 OwnchintuNo ratings yet
- Instruction Set 1Document40 pagesInstruction Set 1Play ListNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document9 pagesAssignment 2irum khanNo ratings yet
- COA UNIT 2 NotesDocument13 pagesCOA UNIT 2 Notesvirajnjr10No ratings yet
- MICDocument30 pagesMICP KalamkarNo ratings yet
- MICROPROCESSOR MCQDocument27 pagesMICROPROCESSOR MCQHusamHaskoNo ratings yet
- MIC NotesDocument17 pagesMIC Notesjhalodwalaaliasgar53No ratings yet
- 8086 Architecture and Addressing ModesDocument53 pages8086 Architecture and Addressing ModeskarthiNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors - III: Yashar HajiyevDocument83 pagesMicroprocessors - III: Yashar HajiyevMurad QəhramanovNo ratings yet
- 8051 Instruction SetDocument81 pages8051 Instruction SetSaket GargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-1Document31 pagesChapter 7-1Hashim Omar AbukarNo ratings yet
- 8086 Instruction SetDocument101 pages8086 Instruction SeterdvkNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document18 pagesUnit 2Vasunthara DNo ratings yet
- Practical 2 Data TransferDocument3 pagesPractical 2 Data TransferHet PatelNo ratings yet
- 8086 Instruction SetDocument101 pages8086 Instruction SetSai Krishna Kodali100% (1)
- 3-instruction-set-of-8086-microprocessorDocument17 pages3-instruction-set-of-8086-microprocessordon1298567No ratings yet
- Procedure and Macro in AssemblyDocument17 pagesProcedure and Macro in AssemblyroshaanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Data Transfer InstructionsDocument68 pagesChapter 3 - Data Transfer InstructionsDawit TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Ee 2354 Model Ans KeyDocument25 pagesEe 2354 Model Ans KeyHusamHaskoNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document12 pagesActivity 3api-548516280No ratings yet
- Expt 02Document9 pagesExpt 02Jack Roquid RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 5 6251119711560401156Document26 pages5 6251119711560401156Vineesh M MadathodiNo ratings yet
- Instruction SetDocument104 pagesInstruction SetKrishnaveni DhulipalaNo ratings yet
- CPE15 - Microprocessor SystemDocument16 pagesCPE15 - Microprocessor SystemPatrick GarciaNo ratings yet
- Programmable Digital Signal Processors: Commercial DSP Devices and Addressing ModesDocument5 pagesProgrammable Digital Signal Processors: Commercial DSP Devices and Addressing ModessannidhiguruprasadNo ratings yet
- Architecture of 8086 MicroprocessorDocument17 pagesArchitecture of 8086 MicroprocessorsreenimolNo ratings yet
- Module3 MicDocument10 pagesModule3 MicroshnibijuNo ratings yet
- L3 Programming ModeDocument44 pagesL3 Programming ModeLawal Ahmed ShehuNo ratings yet
- 8086 ProcessorDocument49 pages8086 ProcessorLolllNo ratings yet
- The 8086 Microprocessor: A 16-Bit Processor with 16-Bit Data Bus and 20-Bit Address BusDocument16 pagesThe 8086 Microprocessor: A 16-Bit Processor with 16-Bit Data Bus and 20-Bit Address BusNaveed RamzanNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor & Interfacing Page 1Document56 pagesMicroprocessor & Interfacing Page 1Archana TiwariNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor 8085 InstructionDocument9 pagesMicroprocessor 8085 InstructionRiazahmed9No ratings yet
- 8051 Instruction Set LectureDocument79 pages8051 Instruction Set LecturepremsonyNo ratings yet
- 8051 Instruction Set Rv01Document81 pages8051 Instruction Set Rv01lizhi0007No ratings yet
- 80c51 Family ArchitectureDocument15 pages80c51 Family Architectureenriquebadajoz5659No ratings yet
- Microprocessor Question Solve-21 (Mid+Dinal)Document29 pagesMicroprocessor Question Solve-21 (Mid+Dinal)Anik DasNo ratings yet
- MP Instruction SetDocument15 pagesMP Instruction SetKannan MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Question SolveDocument31 pagesMicroprocessor Question SolveAnik DasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Addressing ModesDocument26 pagesChapter 3 Addressing ModesephremketachewNo ratings yet
- 8086 Addressing Modes and Instruction FormatsDocument22 pages8086 Addressing Modes and Instruction FormatsJOFRE GONENo ratings yet
- 202004021910157352aksingh Phy MicroprocessorDocument20 pages202004021910157352aksingh Phy MicroprocessorAviNo ratings yet
- 8085 Programming Model and Instruction SetDocument90 pages8085 Programming Model and Instruction SettbijleNo ratings yet
- Assembly Lab 2Document9 pagesAssembly Lab 2Jefferson Medinaceli Malayao100% (1)
- 8051 Instruction SetDocument98 pages8051 Instruction SetSmt.N.Vasantha Gowri Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Instruction SetsDocument74 pagesChapter 4. Instruction SetsERMIAS AmanuelNo ratings yet
- 8051 Instruction SetDocument79 pages8051 Instruction Setgsathishbsa100% (1)
- COE014 Chapter3 Part6Document16 pagesCOE014 Chapter3 Part6eyrondorolaNo ratings yet
- VIMP Micro QuestionsDocument68 pagesVIMP Micro QuestionsayushnaleNo ratings yet
- Lec - 13 Flag, Stack and IO InsDocument12 pagesLec - 13 Flag, Stack and IO InsMUHAMMAD ABDULLAHNo ratings yet
- Memory Addressing and Instruction FormatsDocument9 pagesMemory Addressing and Instruction Formatsrobern ndoloNo ratings yet
- 8086 Architecture Addressing ModesDocument10 pages8086 Architecture Addressing ModesKumaran GNo ratings yet
- Assembly2 Language For 80x86 Processors1Document11 pagesAssembly2 Language For 80x86 Processors1Nakitare W. ErickNo ratings yet
- 8085 Instructions: Institute of Lifelong Learning, University of DelhiDocument21 pages8085 Instructions: Institute of Lifelong Learning, University of DelhiMonika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Configure Customer Vendor Integration in S4 HANA Using Business PartnersDocument64 pagesConfigure Customer Vendor Integration in S4 HANA Using Business PartnersRakesh Gupta100% (2)
- JSF Best Practices Javaserver Faces Session TipsDocument8 pagesJSF Best Practices Javaserver Faces Session TipsMed MedNo ratings yet
- B WAS40P Part1 MAN2104Document12 pagesB WAS40P Part1 MAN2104Tsvetan PenevNo ratings yet
- Pascals TriangleDocument6 pagesPascals TriangleGeethangalin VaanavinothanNo ratings yet
- Peoria Rivermen Social Media AnalysisDocument27 pagesPeoria Rivermen Social Media AnalysisWill QuinnNo ratings yet
- One Stop Shop For Buying, Selling & Renting BooksDocument38 pagesOne Stop Shop For Buying, Selling & Renting Booksapi-402842914No ratings yet
- ASAM - AE - MCD 1 XCP - AS - SxI Transport Layer - V1 5 0Document18 pagesASAM - AE - MCD 1 XCP - AS - SxI Transport Layer - V1 5 0cruse2015100% (1)
- CS6310 A4 Architecture - Design Fall2022Document8 pagesCS6310 A4 Architecture - Design Fall2022Phillip DieppaNo ratings yet
- Test Design Techniques: Istqb Certified Tester - Foundation LevelDocument112 pagesTest Design Techniques: Istqb Certified Tester - Foundation LevelAnonymous Uk3rVZDVFNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9608/11Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9608/11Zaki JrNo ratings yet
- Figure 4-35. Modelsim Altera Starter Edition: Hello World!Document5 pagesFigure 4-35. Modelsim Altera Starter Edition: Hello World!ali alilouNo ratings yet
- Surviving The SOC Revolution: A Guide To Platform-Based DesignDocument9 pagesSurviving The SOC Revolution: A Guide To Platform-Based DesignRamesh YrNo ratings yet
- Business Intelligence Value PropositionDocument14 pagesBusiness Intelligence Value PropositionMax RobertsNo ratings yet
- M.E. EXAM Time TableDocument7 pagesM.E. EXAM Time Tablepa390786No ratings yet
- Engineering Is An Art When It's Learnt Right: Me& NinoDocument5 pagesEngineering Is An Art When It's Learnt Right: Me& NinoMohit SinghNo ratings yet
- Understanding Relational Databases in 40 CharactersDocument18 pagesUnderstanding Relational Databases in 40 CharactersKristine MagsayoNo ratings yet
- 5600 User Guide 571702011 Ver0600 ENGDocument116 pages5600 User Guide 571702011 Ver0600 ENGm2ryusNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument19 pagesUntitledAmaan JamburaNo ratings yet
- Defect Tracking SystemDocument32 pagesDefect Tracking SystemRajdeep SinhaNo ratings yet
- KeyDocument13 pagesKeyNicolae FloreaNo ratings yet
- DCTN Lsqmdocu63774Document21 pagesDCTN Lsqmdocu63774Bharani KumarNo ratings yet
- Course CIT711Document14 pagesCourse CIT711usoroukNo ratings yet
- Hydro GeoAnalyst-Demo GuideDocument93 pagesHydro GeoAnalyst-Demo GuidehusseinNo ratings yet
- CCC AntisurgeDocument2 pagesCCC AntisurgeDamian Wahlig100% (1)
- Digital Marketing Marketing Tools: Franchise AdvertisingDocument29 pagesDigital Marketing Marketing Tools: Franchise AdvertisingMohammedAlQureshiNo ratings yet
- Drawing Sketches Solid ModelsDocument66 pagesDrawing Sketches Solid ModelsBriciu Sebastian100% (1)
- Axiocam 105 Color - User GuideDocument21 pagesAxiocam 105 Color - User GuideSinan ChenNo ratings yet
- TBMC12Document10 pagesTBMC12Joel E ValenciaNo ratings yet
- OBIA-FC Ref PDFDocument618 pagesOBIA-FC Ref PDFahmed_sftNo ratings yet
- Generating PDF With Animations Using LaTeXDocument6 pagesGenerating PDF With Animations Using LaTeXchristos032No ratings yet