Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Applications of Electromagnet
Uploaded by
Mohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Applications of Electromagnet
Uploaded by
Mohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiCopyright:
Available Formats
Applications of Electromagnet 1. There are many applications of electromagnets.
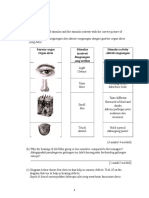
Label and describe the figure of each apparatus stated in the table below with its simple work-frame. 1) Electric bells
batteries
switch
1. When the switch is closed, the current flow will magnetized the soft-iron core 2. The soft iron armature is pulled toward electromagnet and hit the gong 3. At the same time, the contact will open and stop the current flows. No electromagnet. 4. The spring mechanism brings the armature back to its original position 5. The contacts close again and similar pocess is repeated.
springs
soft-iron core
contact
soft-iron armature gong
2) Electromagnetic Relays
1. When the switch A is closed, a small current flows in input circuit will magnetized the soft-iron core 2. The soft iron armature is attracted toward electromagnet 3. At the same time, the spring contact closed 4. A large current flows to high voltage circuit to operate the electrical
soft-iron core
to high voltage circuit
apparatus.
3) Telephone earpieces
Alloy diaphragm
1. A varying current received from the caller in telephone line 2. The varying current passes through solenoid and magnetized the soft-iron core 3. The electromagnet varies in magnetic strength according to the verifying current 4. The alloy diaphragm will attract to electromagnet by varying force 5. Sound produced as compression and
Soft-iron core
Permanent magnet solenoid
rarefaction of air particles
4) Circuit breakers
automatic switch to breaks Its operate as circuit to open when current becomes too large 1. When the current becomes high (ex: short circuit) the electromagnet strength increase suddenly 2. The iron catch is pulled toward electromagnet Its function to 3. The spring pulling apart the contacts 4. The circuit will break and the current 1. Opposite poles on the surface will flows stop immediately produces a stronger magnetic field to household 2. When the current is switched on, the soft appliances iron core is magnetized to become a very powerful magnet 3. Its lifts up iron and steel 4. When the crane has moved to new
spring
contacts
from main supply
5) Lifting Magnet
location, the current is switched off and move heavy objects or steel the soft-iron core is demagnetized from place to place 3. The objects will fall
North pole South pole
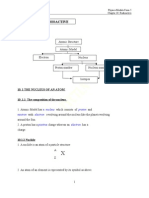
3.2: Force Acting on a Current-carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Fields 1. If a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic fields as shown in the experiment,
force
the conductor will experiences a ..
CShape iron Magne t
Freely conductor Long conductor
Power Supply
2. Draw the combination (called catapult field) of two electromagnetic fields below and
show the direction of movement of the conductor.
3. Flemings left-hand rule can be use to determine the direction of the force acting or
the motion of the conductor.
First Finger ( Field )
Thumb
( Thrust force )
N
Centre Finger ( Current )
Effect of Two Parallel Current-carrying Coils in a Magnetic Field 4. If two current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic fields as shown in the
repel
experiment, the conductor will experience or .. force between them.
attract
5. Complete the diagram for current with opposite direction flows in two parallel conductor
below:
repel The two conductor will .. to each other 6. Complete the diagram for current with same direction flows in two parallel conductor
below:
attract The two conductor will .. to each other
Turning Effect of a Current-carrying Coil in a Magnetic Field 7. Consider a current-carrying coil ABCD placed between the poles magnet as shown in the figure below.
upward
8. As the current flows through the coil from A to D, an ... (1) force acts on the downward
arm CD whereas a (3) force acts on the arms AB according to Flemings Left Hand rule.
N 1 Carbon brush current 4 A 3
Coil S B 2 D commutator C Magnet
Electrical energy
Kinetic energy
9. Draw the catapult filed formed and draw arrows to show the movement of arms AB and CD.
AB N
CD S
Direct Current Motor 10. Complete the four stages of the motion of DC motor below
Coil B 2 D
S
0 Degree : 0 Through carbon brushes Current Upwards / No flow : Yes
1 A
current
4 3
Downwards ... Arm AB clockwise : . Arm CD : Rotation : .
Coil
S
current
900 Circuit broken at carbon brushes Degree : right Current flow : Yes / No left ..... clockwise due to inertia Arm AB : . Arm CD : Rotation : .
Coil
S
current
1800 Degree : through carbon brushes downward Current flow : Yes / No upward ..... clockwise Arm AB : . Arm CD : Rotation :
Coil
S
2700 Degree : Circuit broken at carbon brushes left Current flow : Yes / No right .....
current
clockwise due to inertia Arm AB : . Arm CD : Rotation : .
Comparison with Alternating Current Motor 11. Complete the diagram of AC motor below:
a.c supply
Factors that affect the speed of rotation of an electric motor 12. The magnitude of force acting on a conductor in a magnetic increases by: i. Increasing the current flow ii. Stronger magnet used 13. In conclusion, the speed of rotation of the coil also can increased by: i.
Increasing the current
ii. Using a stronger magnet iii. Increasing the number of turns on the coils .
Moving Coil Ammeter
The angle of deflection is directly proportional to the current flows in the coil The hair spring will restore the pointer back to its original position. The force acting causes the coil to rotate and lead the pointer to the deflection
When current flows in moving coil, magnetic field of radial magnet will interacts with magnetic field produce by the coil
You might also like
- Electricity and Its Heating and Chemical EffectsDocument7 pagesElectricity and Its Heating and Chemical EffectsManish Kedawat50% (2)
- Metals Non MetalsDocument49 pagesMetals Non MetalsthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Pressure and Hydraulics WorksheetDocument2 pagesPressure and Hydraulics WorksheetEsther SparksNo ratings yet
- Ac DCDocument3 pagesAc DCSachin NowalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties of SiliconDocument3 pagesChemical Properties of SiliconMuhammad Fajrul IkshanNo ratings yet
- Rocks Geography Study Material NotesDocument3 pagesRocks Geography Study Material NotesSTEPHEN AOCKIAM MNo ratings yet
- 07 Metamorphic RocksDocument17 pages07 Metamorphic Rocksjcasafranca0% (1)
- MagnetismDocument4 pagesMagnetismTalha MughalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument20 pagesChemistry Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesRahul RameshNo ratings yet
- MesozoicDocument11 pagesMesozoicGelo LibeloNo ratings yet
- Bahria Foundation Colleges (North) Centralized Notes of Short Questions (F.B.I.S.E) Physics SSC-IDocument63 pagesBahria Foundation Colleges (North) Centralized Notes of Short Questions (F.B.I.S.E) Physics SSC-IZaheer AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Physics MCQs on Circular Motion and SatellitesDocument3 pages1st Year Physics MCQs on Circular Motion and SatellitesBilal Jamil0% (1)
- Classification of ElementsDocument1 pageClassification of Elementsdan964No ratings yet
- DPS Biratnagar fee structure for classes KG to XIDocument7 pagesDPS Biratnagar fee structure for classes KG to XIwithraviNo ratings yet
- Metals and Their CompoundsDocument10 pagesMetals and Their CompoundsDravid AryaNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Theory PDFDocument35 pagesGravitation Theory PDFabhishek kalgudiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics - Gravitation NotesDocument9 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics - Gravitation NotesAyush GoelNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Metals and Non Metals NotesDocument12 pagesClass 10 Metals and Non Metals NotesShreyash VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Heredity (Class 10) NotesDocument4 pagesHeredity (Class 10) NotesAlok NaikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 & 8 Chem Study GuideDocument3 pagesChapter 7 & 8 Chem Study GuideseabreezeNo ratings yet
- Em WaveDocument4 pagesEm WavethinkiitNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry Theory - EDocument26 pagesSurface Chemistry Theory - Ethinkiit100% (1)
- Student Rules RegulationsDocument2 pagesStudent Rules RegulationsMCHNo ratings yet
- Empirical Formula and Molecular Formulas 1Document23 pagesEmpirical Formula and Molecular Formulas 1gunapalshetty100% (1)
- Genetics and Heredity BiologyDocument7 pagesGenetics and Heredity BiologyMUDASIR REHMANNo ratings yet
- Demagnetization Methods for MPI ComponentsDocument2 pagesDemagnetization Methods for MPI Componentszaw lin ooNo ratings yet
- Ac Generator Components PrintDocument3 pagesAc Generator Components Printdempe24No ratings yet
- Open Book Test - OpticsDocument9 pagesOpen Book Test - OpticsGagandeep WadhawanNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Newton'S Law of GravitationDocument3 pagesGravitation Newton'S Law of Gravitationnot atallNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Analysis NotesDocument7 pagesDimensional Analysis Notes32 - VEDANSH JAISWALNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes Fbise FSC 2 CHAPTER - 19 THE ATOMIC NUCLEUSDocument5 pagesPhysics Notes Fbise FSC 2 CHAPTER - 19 THE ATOMIC NUCLEUSflyfalconNo ratings yet
- GravitationDocument45 pagesGravitationthinkiit100% (1)
- Thermodynamics PDFDocument122 pagesThermodynamics PDFPrateek Srivastava100% (1)
- Manual Electricty and MagnetismDocument13 pagesManual Electricty and MagnetismDennis Cosmod100% (1)
- Chapter 12 SulphurDocument3 pagesChapter 12 SulphurAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Meiosis NotesDocument7 pagesMitosis Meiosis NotesSophia Cook100% (1)
- Chapter Force and Pressure QuestionsDocument6 pagesChapter Force and Pressure QuestionsAkshit MalavNo ratings yet
- Gravitation Force and Apple Falling from TreeDocument2 pagesGravitation Force and Apple Falling from TreeSunil Das100% (1)
- 10 Cell Cycle N Cell Division-NotesDocument4 pages10 Cell Cycle N Cell Division-NotesAnanth Dharanidharan100% (1)
- Ecosystem: Department of Environmental Science, Pub Kamrup CollegeDocument8 pagesEcosystem: Department of Environmental Science, Pub Kamrup CollegeDebajit SarmaNo ratings yet
- ForceDocument26 pagesForceShinji100% (1)
- Aquatic Adaptations in Animals: A) Aquatic Adaptations in FishDocument7 pagesAquatic Adaptations in Animals: A) Aquatic Adaptations in FishSiri YerneniNo ratings yet
- 14thermal Expansion of Materials - 227-249Document11 pages14thermal Expansion of Materials - 227-249KAMAL KANT KUSHWAHANo ratings yet
- Nuclear PhysicsDocument20 pagesNuclear Physicssuneel SaiNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument49 pagesElectricitythinkiit100% (3)
- Heating Effect of ElectricityDocument8 pagesHeating Effect of ElectricityCarmella Mae Quidilig100% (1)
- Ohm's LawDocument13 pagesOhm's LawVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- Mercury in Glass Thermometer PDFDocument6 pagesMercury in Glass Thermometer PDFSirish Chand PutlaNo ratings yet
- Relation and FunctionDocument6 pagesRelation and FunctionMPS QUESTION PAPER SUBMISSIONNo ratings yet
- Class10 Science Notes Chapte3Document9 pagesClass10 Science Notes Chapte3PallaviGupta100% (1)
- Draft of Magnetic Particle Inspection of Hot Rolled 1045 Carbon SteelDocument48 pagesDraft of Magnetic Particle Inspection of Hot Rolled 1045 Carbon Steelmm11_ned100% (1)
- Parabola Theory EDocument16 pagesParabola Theory Ethinkiit100% (1)
- Chromatography IiDocument49 pagesChromatography Iimonsterbhai100% (2)
- Heredity Class 10Document40 pagesHeredity Class 10ChaithraNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument15 pagesUnit 3 - Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Propertiescpverma2811100% (1)
- Admission Form - Top School in NoidaDocument2 pagesAdmission Form - Top School in Noidaindus vallyNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Notes Chapter 1 Studyguide360Document24 pagesClass 11 Physics Notes Chapter 1 Studyguide360Allmagicalme YTNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Student)Document48 pagesChapter 8 Student)Peggy Esther YongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Electromagnet Teachers Guide 2009Document257 pagesChapter 8 Electromagnet Teachers Guide 2009ashok100% (2)
- JPN Pahang Physics Module Form 5 Chapter 8: Electromagnetism Guide <40Document47 pagesJPN Pahang Physics Module Form 5 Chapter 8: Electromagnetism Guide <40kenenathNo ratings yet
- Form 4: Indices and Logarithms Chapter 5 GuideDocument12 pagesForm 4: Indices and Logarithms Chapter 5 GuideMohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiNo ratings yet
- Form 4: Indices and Logarithms Chapter 5 GuideDocument12 pagesForm 4: Indices and Logarithms Chapter 5 GuideMohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiNo ratings yet
- Sains Tingkatan 2 (2015)Document17 pagesSains Tingkatan 2 (2015)Mariana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Trial 2016 Pahang P1 P2Document89 pagesTrial 2016 Pahang P1 P2Mohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiNo ratings yet
- Section B P2 PPT 2017Document10 pagesSection B P2 PPT 2017Mohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiNo ratings yet
- SMK Bandar Puchong Jaya (B) : MingguDocument1 pageSMK Bandar Puchong Jaya (B) : MingguMohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiNo ratings yet
- Maths QuizDocument1 pageMaths QuizMohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiNo ratings yet
- Maths Learning Area: Matrices Learning ObjDocument2 pagesMaths Learning Area: Matrices Learning ObjMohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiNo ratings yet
- Modul A Set 2Document6 pagesModul A Set 2Mia SheraNo ratings yet
- Modul A Set 4Document6 pagesModul A Set 4Mia SheraNo ratings yet
- Rumus-Rumus Berikut Boloeh Membantu Anda Menjawab Soalan. Simbol-Simbol Yang Diberi Adalah Yang Biasa DigunaanDocument4 pagesRumus-Rumus Berikut Boloeh Membantu Anda Menjawab Soalan. Simbol-Simbol Yang Diberi Adalah Yang Biasa DigunaanMohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics SPM Module A Set 6Document6 pagesMathematics SPM Module A Set 6Narzuki YaacobNo ratings yet
- Attending Physicians Statement (Medical)Document3 pagesAttending Physicians Statement (Medical)Mohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiNo ratings yet
- Rumus-Rumus Berikut Boloeh Membantu Anda Menjawab Soalan. Simbol-Simbol Yang Diberi Adalah Yang Biasa DigunaanDocument4 pagesRumus-Rumus Berikut Boloeh Membantu Anda Menjawab Soalan. Simbol-Simbol Yang Diberi Adalah Yang Biasa DigunaanMohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiNo ratings yet
- Modul A Set 1Document7 pagesModul A Set 1Mia SheraNo ratings yet
- Modul B Set 3Document5 pagesModul B Set 3Mohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Radioactivity Teacher Guide1Document29 pagesChapter 10 Radioactivity Teacher Guide1Mohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiNo ratings yet
- Audit Akademik Bahasa MelayuDocument15 pagesAudit Akademik Bahasa MelayusofhanalizaNo ratings yet
- Latih Tubi Mathematics SPM (Module B Set 4) : Jabatan Pelajaran Kedah Darul AmanDocument5 pagesLatih Tubi Mathematics SPM (Module B Set 4) : Jabatan Pelajaran Kedah Darul AmanMohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiNo ratings yet
- Modul B Set 1Document7 pagesModul B Set 1Mohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Compounds 1Document20 pagesOrganic Chemistry Compounds 1silvio1980100% (3)
- Form 04 Chapter 4 Heat M4Document19 pagesForm 04 Chapter 4 Heat M4Mohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial TransformationsDocument6 pagesTutorial TransformationsMohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiNo ratings yet
- Modul B Set 1Document7 pagesModul B Set 1Mohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiNo ratings yet
- Form 04 Chapter 4 Heat M4Document19 pagesForm 04 Chapter 4 Heat M4Mohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiNo ratings yet
- Skema Maths f4 p1Document1 pageSkema Maths f4 p1Mohd Nurul Hafiz AlawiNo ratings yet
- SPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Physics AnswersDocument14 pagesSPM Percubaan 2008 SBP Physics AnswersChinWynn.com80% (5)
- Marking Scheme Physics P1P2P3 SPM Kelantan 2009Document9 pagesMarking Scheme Physics P1P2P3 SPM Kelantan 2009Mohd Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Redox WorksheetDocument3 pagesRedox WorksheetMin Chong100% (2)
- Green HRMDocument16 pagesGreen HRMgtiiie100% (1)
- Quick guide to installing RTH2310 programmable thermostatDocument24 pagesQuick guide to installing RTH2310 programmable thermostatludwig428No ratings yet
- Spanish C27-800ekwStandbyLowBSFC EMCP4Document6 pagesSpanish C27-800ekwStandbyLowBSFC EMCP4KeivinMCNo ratings yet
- MttoDocument12 pagesMttoEsteban ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Giovenzana Handling System PDFDocument82 pagesGiovenzana Handling System PDFAlejandroNo ratings yet
- Tanker Management Self Assessment LP BriefingDocument11 pagesTanker Management Self Assessment LP BriefingSlimNo ratings yet
- POME Plant CostDocument8 pagesPOME Plant Costtamil vaanan100% (1)
- ABJ PresentationDocument51 pagesABJ PresentationMarvin CastelinoNo ratings yet
- The Right To Housing (1945-2017) - The Preservation of Post-WWII European NeighbourhoodsDocument6 pagesThe Right To Housing (1945-2017) - The Preservation of Post-WWII European Neighbourhoodsmarcos256No ratings yet
- HVAC Patterson BrochureDocument9 pagesHVAC Patterson BrochureAnonymous 5RhHmNmgJNo ratings yet
- Position Paper Usability of Life Cycle Assessment For Cradle To Cradle Purposes WDocument42 pagesPosition Paper Usability of Life Cycle Assessment For Cradle To Cradle Purposes WZhofran BintangNo ratings yet
- WS852 WS853 enDocument80 pagesWS852 WS853 enthailanNo ratings yet
- Split Type Air Conditioner Installation ManualDocument10 pagesSplit Type Air Conditioner Installation ManualChalitha Nayana Hewawasam100% (1)
- Wilo Pump Catalog PDFDocument94 pagesWilo Pump Catalog PDFgogame2014100% (1)
- DC Supply System For Thermal Power PlantDocument27 pagesDC Supply System For Thermal Power PlantAshwani Dogra86% (7)
- Good Practice Guide Managing Installation of PV SystemsDocument28 pagesGood Practice Guide Managing Installation of PV Systemszeljkoc21No ratings yet
- Project Report On Solar Power Plant PDFDocument10 pagesProject Report On Solar Power Plant PDFDev Ananth50% (2)
- Fire Water Make Up PumpDocument7 pagesFire Water Make Up PumpAlvin SmithNo ratings yet
- Battery Charger CKT Using SCRDocument20 pagesBattery Charger CKT Using SCRSai Shashank AkulaNo ratings yet
- Partes IngersollDocument56 pagesPartes IngersollDaniel Arbeláez100% (7)
- 2012-13 AC Motors Starters PDFDocument20 pages2012-13 AC Motors Starters PDFkggganiNo ratings yet
- 2ND Training Cidi MutfakDocument31 pages2ND Training Cidi Mutfakrakan alnajiNo ratings yet
- Schneider Electric Gulf Provides Complete Energy SolutionsDocument8 pagesSchneider Electric Gulf Provides Complete Energy SolutionsPMV DeptNo ratings yet
- Manitoba Hydro Annual Report 2015-16Document116 pagesManitoba Hydro Annual Report 2015-16ChrisDcaNo ratings yet
- 314 2-Ac15Document115 pages314 2-Ac15Romner CordovaNo ratings yet
- Company Profile Improvia EnergiDocument16 pagesCompany Profile Improvia EnergiRulli Rachman100% (1)
- Dynamelt S Series APS Adhesive Supply UnitDocument2 pagesDynamelt S Series APS Adhesive Supply UnitITWDynatecNo ratings yet
- Recp. CompressorDocument12 pagesRecp. CompressorrajeevkumarrajeevNo ratings yet