Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transformer 3
Uploaded by
The pioneers rourkelaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transformer 3
Uploaded by
The pioneers rourkelaCopyright:
Available Formats
STUDY MATERIAL : ELECTRIC AL
TRANSFORMER
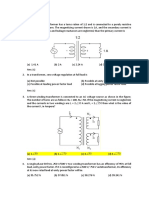
01. A transformer does not transfer (a) power current (d) impedance (e) none (b) voltage (c) (b) loss of 200 watt and eddy current loss of 100 watt. Its core loss at 60 Hz operation will be: 1) 432 W 2) 408 W 3) 384 W 4) 360 W 5) none 18. Can a 50 Hz transformer be used for 25 Hz, if the input voltage is maintained constant at the rated value corresponding to 50 Hz ?: 1) Yes, since the voltage is constant current level will not change. 2) No, flux will be doubled which will drive the core to excessive saturation. 3) No, owing to decreased resistance of transformer, input current will be doubled at the load. 4) Yes, at constant voltage insulation will not be overstressed. 5) none 19. A 220/440V, 50 Hz single phase transformer operates on 220V, 40Hz supply with secondary winding, then: 1) the eddy current loss and hysteresis loss of transformer decrease. 2) the eddy current loss and hysteresis loss of the transformer increase. 3) the hysteresis loss of the transformer increases while eddy current loss remains the same. 4) the hysteresis loss remains the same where as eddy current loss decreases. 5) none 20. The no load current in a transformer lags the applied voltage 0 0 0 0 by : 1) 90 2) 0 3) 75 4) 115 5) none 21. Magnetizing component of no load current is: 1) in phase with 0 the applied voltage. 2) leads the applied voltage by 90 . 3) lags 0 behind the applied voltage by 75 . 4) lags behind the applied 0 voltage by 90 . 5) none 22. In a transformer the exciting current has two components, the magnetizing component Im and core loss component Iw. Neglecting leakage impedance drop,:1) Im lags behind the 0 applied voltage by 90 while Iw is in phase with the applied voltage. 2) Im is in phase with the applied voltage while Iw lags 0 behind the applied voltage by 90 . 3) both of the components 0 Im and Iw lags behind the applied voltage by 90 . 4) both of the components are in phase with the applied voltage. 5) none 23. In a transformer the exciting current will be in phase quadrature with the impressed voltage provided: 1) only the leakage impedance drop is ignored. 2) only core loss is ignored 3) both leakage impedance and core loss are ignored 4) only no load power loss is ignored. 5) none 24. The power factor of a transformer on no load will be about: 1) 1 2) 0.75 3) 0.5 4) 0.35 5) none 25. The power factor of a transformer on no load is poor due to: 1) magnetizing reactance of the transformer 2) open circuited secondary 3)low primary winding resistance 4) low no load current. 5) none 26. If in a transformer core, a material having high reluctance path but having same hysteresis loop is employed: 1) Iw will increase 2) Im will increase 3) Im will decrease 4) both Iw and Im will increase 5) none 27. The primary ampere turns of a transformer are ___ its secondary ampere turns: 1) exactly equal to 2) approximately equal to 3) larger than 4) smaller than 5) none 28. The inductive reactance of a transformer depends on: 1) electromotive force 2) magnetomotive force 3) magnetic flux 4) leakage flux 5) none 29. The inductive reactance of a transformer depends on: 1) leakage flux 2) size of core 3) both 1 & 2 4) none 30. The magnetizing current for sinusoidal applied voltage will be: 1) always non-sinusoidal 2) always sinusoidal 3) sinusoidal or non sinusoidal depending upon the saturation point 4) none 31. The emf induced in the primary (a) in phase with the flux (b) 0 0 lags behind the flux by 90 (c) leads the flux by 90 (d) in phase opposition to flux (e) none 32. The leakage flux of a transformer is the flux which links (a) only with the primary winding (b) only with the secondary winding (c) either only with primary or only with the secondary winding (d) with both the primary and secondary winding. (e) none
02. The efficiency of a power transformer is around (a) 50% 60% (c) 80% (d) 95% (e) none
03. The power transformer is a constant ___device. (a) current (b) voltage (c) main flux (d) power (e) none 04. Transformer action requires a : (a) constant magnetic flux (b) increasing magnetic flux alternating magnetic flux (d) alternating electric flux 05. The flux created by the current flowing through the primary winding induces emf in (a) primary winding only (b) secondary winding only (c) transformer core only (d) both primary and secondary windings (e) none 06. If rated dc voltage is applied instead of ac to the primary of a transformer, then :1) secondary of transformer will burn. 2) primary of transformer will burn. 3) secondary voltage will be excessively high. 4) there will be no secondary voltage 5) none 07. An ideal transformer does not change: 1) voltage 3) current 4) none 2) power
08. For an ideal transformer the windings should have: 1) maximum resistance on primary side and least resistance on secondary side. 2) least resistance on primary side and maximum resistance on secondary side. 3) equal resistances on primary and secondary sides. 4) no ohmic resistances on either side. 5) none 09. A transformer steps up the voltage by a factor of 100. The ratio of current in primary to that in the secondary is: 1) 1 2) 100 3) 0.01 4) 0.1 5) none 10. For an ideal transformer having transformation ratio 1/n, :1) V1 = nV2, I2 = - nI1 2) V2 = nV1, I2 = - nI1 3) V1= nV2, I2 = I1/n 4) V1 =nV2,I2= - I1/n 5) none 11. If the applied voltage of a certain transformer is increased by 50% and the frequency is reduced to 50% (assuming that the magnetic circuit remains unaltered), the maximum core flux density will (a) change to three times the original value (b) change to 1.5 times the original value (c) change to 0.5 times the original value (d) remain the same as original. (e) none 12. If the supply frequency to a transformer is increased keeping the supply voltage constant, then (a) both magnetizing component and core loss component of current will increase. (b) both magnetizing component and core loss component of current will decrease. magnetizing component of current will increase while core loss component of current will decrease. (d) magnetizing component of current will decrease while core loss component of current will increase. (e) none 13. In a transformer operating at constant voltage if the input frequency increases, the core loss (a) increases (b) decreases (c) remains constant (d) increases as square of the frequency. 14. If the frequency of input voltage to a transformer is increased keeping the magnitude of voltage unchanged, then (a) both hysteresis loss and eddy current loss in the core will increase. (b) hysteresis loss will increase but eddy current loss will decrease. (c) hysteresis loss will decrease but eddy current loss will increase. (d) hysteresis loss will decrease but eddy current loss will remain unchanged. (e) none 15. 1 KVA, 230V, 50 Hz, single phase transformer has an eddy current loss of 30 watts. The eddy current loss when the transformer is excited by a dc source of same voltage will be: 1) 30 watts 2) more than 30 watt 3) less than 30 watts 4) zero watt 5) none 16. A transformer has hysteresis loss of 30 watt at 240 V, 60 Hz. The hysteresis loss at 200 V, 50 Hz will be: 1) 28 watt 2) 25 watt 3) 30 watt 4) 36 watt 5) none 17. At 50 Hz operation a single phase transformer has hysteresis
You might also like
- 00 - Electrical Machines - 1Document7 pages00 - Electrical Machines - 1Bskster BskNo ratings yet
- Ac MachineDocument18 pagesAc MachinePeter John VicenteNo ratings yet
- Transformers Objective Type Questions and AnswersDocument11 pagesTransformers Objective Type Questions and AnswersJabir Sijas100% (1)
- Electrical Engg QuestionsDocument8 pagesElectrical Engg QuestionsRavi SoniNo ratings yet
- Electrical TransformersDocument10 pagesElectrical TransformersSindhu ManchukondaNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks MCQ WITH ANSWER PC-EE-401Document4 pages2 Marks MCQ WITH ANSWER PC-EE-401Sanjoy PathakNo ratings yet
- MCQ Transformer MasterDocument12 pagesMCQ Transformer MasterDeepak Choudhary DC67% (3)
- Multiple-choice questions and answers on transformersDocument6 pagesMultiple-choice questions and answers on transformershakkı_aNo ratings yet
- Transformer Fundamentals ExplainedDocument83 pagesTransformer Fundamentals Explainedlvb123No ratings yet
- Electrical Machines MCQsDocument12 pagesElectrical Machines MCQssalman bhattiNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument2 pagesQuestionsmalladhinagarjunaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 MathsDocument34 pagesModule 1 Mathstonyl1972No ratings yet
- Electrical Exam Questions and AnswersDocument68 pagesElectrical Exam Questions and AnswersRoyston LimNo ratings yet
- Q&A 3 Transformer & DC MachinesDocument20 pagesQ&A 3 Transformer & DC Machinessaravanan chennanNo ratings yet
- Quiz1 2 3Document8 pagesQuiz1 2 3Motasem MrwanNo ratings yet
- Physics XII CH 7 CASE STUDY Alternating CurrentDocument19 pagesPhysics XII CH 7 CASE STUDY Alternating CurrentNjan KL16么PorottaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 AnsDocument1 pageAssignment 3 AnsmariahNo ratings yet
- Test Emc1Document2 pagesTest Emc1Omkar SheteNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document96 pagesModule 3Zbor Zbor100% (2)
- EASA 66 Module 3 (Club66) QuestionDocument78 pagesEASA 66 Module 3 (Club66) QuestionsureshrnalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5-8Document11 pagesChapter 5-8amandykov16magzhanNo ratings yet
- Vinayaka Missions Aviation Academy, Salem Set-1 Total Questions-104 Time-75 Min. Module 3-Electrical FundamentalsDocument8 pagesVinayaka Missions Aviation Academy, Salem Set-1 Total Questions-104 Time-75 Min. Module 3-Electrical FundamentalsRavishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- QUESTION BOOKLET OF BASIC ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERINGDocument12 pagesQUESTION BOOKLET OF BASIC ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERINGakashbanerjee2779No ratings yet
- MCQ On Emi & AcDocument23 pagesMCQ On Emi & AcmanishphyNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document74 pagesModule 3Jacky ChingNo ratings yet
- Tangedco Eee 2Document122 pagesTangedco Eee 2rigNo ratings yet
- EEE 203 Energy Conversion ProblemsDocument20 pagesEEE 203 Energy Conversion ProblemsthiagoomNo ratings yet
- Ambati Lokeswara ReddyDocument8 pagesAmbati Lokeswara ReddyVaraprasad GantaNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 3 TransformersDocument35 pagesChapter # 3 TransformersPrabu ÑÖnïtzNo ratings yet
- Smart Screen 6Document11 pagesSmart Screen 6leslie94No ratings yet
- Transformers_objectives_examDocument11 pagesTransformers_objectives_examRaj Kumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Transformers & EM Conversion PDFDocument75 pagesTransformers & EM Conversion PDFAbraham OseitutuNo ratings yet
- Elect Questions For Paper IIDocument49 pagesElect Questions For Paper IIavijayakumar_1964No ratings yet
- TransformerDocument9 pagesTransformerBashaer coNo ratings yet
- 03B. Alternating Current (154-166)Document13 pages03B. Alternating Current (154-166)Mupli RajeshNo ratings yet
- Transformers Obj Questions PDFDocument8 pagesTransformers Obj Questions PDFphaniputta100% (2)
- Module 3 - Electrical FundamentalsDocument43 pagesModule 3 - Electrical FundamentalsAhmed ShaMoon100% (1)
- Proposed 15 Numerical Problems For PresentationDocument8 pagesProposed 15 Numerical Problems For PresentationalexNo ratings yet
- Machines PDFDocument11 pagesMachines PDF15BEE1120 ISHAV SHARDANo ratings yet
- EASA Module 3i MCQ (114 Questions)Document46 pagesEASA Module 3i MCQ (114 Questions)Junaid YounusNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 Electrical FundamentalsDocument150 pagesMODULE 3 Electrical Fundamentalsmr daie0% (1)
- Module 3Document73 pagesModule 3Mahesh Shalinda MendisNo ratings yet
- Isro 1 PDFDocument14 pagesIsro 1 PDFSamuel Pakianathan EEENo ratings yet
- Question OnlineDocument28 pagesQuestion OnlineThennali RamanNo ratings yet
- CAT II – EEE 2208: PHYSICAL ELECTRONICS II 2022/2023 DUE 01/12/2022 5 PMDocument2 pagesCAT II – EEE 2208: PHYSICAL ELECTRONICS II 2022/2023 DUE 01/12/2022 5 PMPaul KabiruNo ratings yet
- 4 1 Alternating CurrentDocument24 pages4 1 Alternating CurrentAnonymous Dt6TyXqNo ratings yet
- Module 3 QsDocument44 pagesModule 3 QsSatishReddyNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document82 pagesModule 3Yu-Hsiang LoNo ratings yet
- Problem Set (Exercises)Document10 pagesProblem Set (Exercises)John A. CenizaNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering TopicsDocument92 pagesElectronics and Telecommunication Engineering TopicswienNo ratings yet
- Quiz 26Document2 pagesQuiz 26shamsul aminNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics ProblemsDocument6 pagesPower Electronics ProblemsLu'ay AlmassriNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument68 pagesBasic Electrical Engineeringahg#No ratings yet
- Vidya Pratishthan's College of Engineering, BaramatiDocument9 pagesVidya Pratishthan's College of Engineering, BaramatiSamir Navinchandra PatelNo ratings yet
- EE Legit TermsDocument14 pagesEE Legit TermsLester James SaingNo ratings yet
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- L & T Catalogue 8Document3 pagesL & T Catalogue 8amulya00428No ratings yet
- ATV LXM Is Option Modules S1A45591 09Document8 pagesATV LXM Is Option Modules S1A45591 09MatthewmcconagiNo ratings yet
- User Manual: MGC120 Petrol Genset ControllerDocument20 pagesUser Manual: MGC120 Petrol Genset ControlleraltieresmirandaNo ratings yet
- How Generators Create ElectricityDocument7 pagesHow Generators Create ElectricityshivNo ratings yet
- Nema Pe5 1997Document46 pagesNema Pe5 1997Horacio EneroNo ratings yet
- RTD ConverterDocument1 pageRTD Converterbagja wigunaNo ratings yet
- C-94693-902 BOM (3080 ESM Switchgear Control Panel)Document11 pagesC-94693-902 BOM (3080 ESM Switchgear Control Panel)Waseem RazaNo ratings yet
- Surse MINIMAXDocument2 pagesSurse MINIMAXRadu67% (3)
- LT PanelDocument9 pagesLT PanelraviNo ratings yet
- Technical D ATA: Diesel Generating SetDocument4 pagesTechnical D ATA: Diesel Generating SetTikaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Prodcut Certification by SirimDocument20 pagesElectrical Prodcut Certification by Sirimsimbua72No ratings yet
- MS-N Contactor Catalogue December 2007Document89 pagesMS-N Contactor Catalogue December 2007Mohammad AmerNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Control Using ThyristorDocument7 pagesDC Motor Control Using Thyristor2020-200282No ratings yet
- Providing Sustainable Rural Electrification ServicesDocument45 pagesProviding Sustainable Rural Electrification ServicesAndre SNo ratings yet
- Socomec Masterys BC & Delphys BCDocument2 pagesSocomec Masterys BC & Delphys BCsy4nNo ratings yet
- DX90 Manual PDFDocument28 pagesDX90 Manual PDFAnonymous uw1GPbmen5No ratings yet
- Computer Hardware BookDocument336 pagesComputer Hardware BookbharathydglNo ratings yet
- TMEIC Manual PDFDocument2 pagesTMEIC Manual PDFKhoi DangNo ratings yet
- Malik Arif Ite FinalDocument57 pagesMalik Arif Ite FinalzohaibNo ratings yet
- Rele Temporizador ScheinederDocument4 pagesRele Temporizador ScheinederJasson da GiedreNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Intelligent Energy Meter User Manual: ES925 SeriesDocument4 pages3 Phase Intelligent Energy Meter User Manual: ES925 SeriesMbgardNo ratings yet
- DC Generators Unit 1Document96 pagesDC Generators Unit 1a s prakash rao100% (1)
- CT & PT CalculationsDocument10 pagesCT & PT CalculationsAbhishek RajputNo ratings yet
- Replacement of HV CablesDocument41 pagesReplacement of HV CablesMahdiNo ratings yet
- 12v Battery ChargersDocument45 pages12v Battery ChargersPhani Sharma100% (1)
- Page 1 of 13 Run Date/Time: 12 /04/2022 15:19:57Document3 pagesPage 1 of 13 Run Date/Time: 12 /04/2022 15:19:57Amit SharmaNo ratings yet
- UNIGEN en - Technical Documentation PDFDocument24 pagesUNIGEN en - Technical Documentation PDFMiroslav VasicNo ratings yet
- HV Ref ManualDocument88 pagesHV Ref ManualSumit VermaNo ratings yet
- Online 6kVA: 94% Eficacia Factor de Potencia de 0.9 (4.5kW deDocument2 pagesOnline 6kVA: 94% Eficacia Factor de Potencia de 0.9 (4.5kW deVictor BlancoNo ratings yet
- DC-AC Converter: PWM Inverter Operation and DesignDocument13 pagesDC-AC Converter: PWM Inverter Operation and Designnataphon kabkaewNo ratings yet