Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 7
Uploaded by
Christina RaggioOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2 7
Uploaded by
Christina RaggioCopyright:
Available Formats
Create assignment, 00224, Homework 7, Mar 18 at 6:05 pm This print-out should have 19 questions.
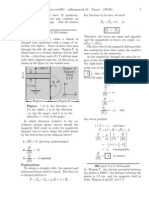
Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page nd all choices before answering. The due time is Central time. Charge in a Magnetic Field 04 29:01, trigonometry, multiple choice, > 1 min, xed. 001 A particle with charge q and mass m is undergoing circular motion with speed v. At t = 0, the particle is moving along the negative x axis in the plane perpendicular to the magnetic eld B, which points in the positive z direction in the gure below. y v x-axis in this instant v = v ; i
since it is moving in a circle, we need to talk about instantaneous direction. The force FB is equal to q v B at all times. We know that B is pointing in the z direction, so B = B k, and therefore FB = q v ( B k i) = q v B ( k) = q v B . i j The charge q is negative (q = |q|) , so FB = |q| v B = |q| v B ( . j j) All quantities are positive, so the actual direction in which FB points is the negative y direction, or a = . j keywords: Conceptual 17 02 29:01, highSchool, numeric, > 1 min, normal. 002 The strength of Earths magnetic eld B at the equator is approximately equal to 5 105 T, where T stands for tesla, the unit of magnetic eld. The force on a charge q moving in a direction perpendicular to a magnetic eld is given by F = q v B, where v is the speed of the particle. The direction of the force is given by the right-hand rule. Suppose you rub a balloon in your hair and your head acquires a static charge of 3 109 C. If you are at the equator and driving west at a speed of 30 m/s, what is the strength of the magnetic force on your head due to Earths magnetic eld? Correct answer: 4.5 1012 N. Explanation: Let : q = 3 109 C , v = 30 m/s , and B = 5 105 T .
B Find the direction of the instantaneous acceleration a at t = 0 if q is negative.
1. a = i 2. a = correct j 3. a = i 4. a = j 5. a = k 6. a = k i 7. a = k + 8. a = + i j i 9. a = k + 10. a = + k j Explanation: The particle is moving along the negative
Create assignment, 00224, Homework 7, Mar 18 at 6:05 pm
F = qvB = (3 109 C) (30 m/s) (5 105 T) = 4.5 1012 N . 003 What is the direction of that magnetic force? 1. east 2. west 3. north 4. south 5. upward correct 6. downward Explanation: The direction of the magnetic force is upward by the right-hand rule. 004 If you are at the equator and driving north at a speed of 30 m/s, what is direction of the magnetic force on your head? 1. east 2. west 3. north 4. south 5. upward 6. downward 7. There is no force. correct Explanation: The force is zero when your velocity is parallel to the magnetic eld. 005
If you are driving east, how fast would you have to drive in order for the magnetic force on your head to equal 200 N (probably enough to knock you over)? Correct answer: 1.33333 1015 m/s. Explanation: Let : F = 200 N , q = 3 109 C , B = 5 105 T . F = qvB F v= qB = 200 N (3 109 C) (5 105 T)
and
= 1.33333 1015 m/s . keywords: Conceptual 17 Q20 29:01, highSchool, multiple choice, < 1 min, xed. 006 A positively charged particle passes through a laboratory traveling in an easterly direction. There are both electric and magnetic eld in the room and their eects on the charged particle cancel. If the electric eld points upward, what must be the direction of the magnetic eld? 1. east 2. west 3. south correct 4. north 5. upward 6. downward Explanation: The force on the object due to the magnetic eld must point down in order to cancel the
Create assignment, 00224, Homework 7, Mar 18 at 6:05 pm force due to the electric eld. Using the righthand rule, the magnetic eld must point south in order for the magnetic force to be directed downward. keywords: Field Direction 29:01, highSchool, multiple choice, < 1 min, xed. 007 The direction of the magnetic eld in a certain region of space is determined by ring a test charge into the region with its velocity in various directions in dierent trials. The eld direction is 1. one of the direction of the velocity when the magnetic eld is zero. 2. the direction of the velocity when the magnetic force is a maximum. 3. the direction of the magnetic force. 4. perpendicular to the velocity when the magnetic force is zero. 5. None of these correct Explanation: The magnetic eld direction can be determined according to the path of a charge which moves in the eld. Since F = qvB , the component of velocity along the magnetic eld doesnt contribute to the magnetic force; i.e., a charge moving along the magnetic eld will keep its motion status. On the contrary, if the initial velocity in perpendicular to the magnetic force, there will be a centripetal force so that the charge will undergo circular motion. keywords: Particle Deection 01 29:01, trigonometry, multiple choice, > 1 min, wording-variable. 008
A positively charged particle moving parallel to the z-axis enters a magnetic eld (pointing into of the page), as shown in the gure below. x B
+q
Figure: is in the x-direction, is is in the in the y-direction, and k z-direction. What is the initial direction of deection? 1. F = + correct 2. F = 3. F = +k 4. F = k 5. F = + 6. F = 7. F = 0 ; no deection Explanation: Basic Concepts: Charged Particle: Magnetic Force on a
F = qvB Right-hand rule for cross-products. F ; i.e., a unit vector in the F direcF F tion. Solution: The force is F = q v B. B = B () , v = v +k ,
and
Create assignment, 00224, Homework 7, Mar 18 at 6:05 pm q > 0 , therefore, F = +|q| v B = +|q| v B +k () = +|q| v B (+) F = + . a This is the rst of eight versions of the problem. keywords: Proton in a Magnetic Field 03 29:01, trigonometry, numeric, > 1 min, normal. 009 A proton moves at right angles to a magnetic eld of 0.1 T with a speed of 2 107 m/s. Find the magnitude of the acceleration of the proton. Correct answer: 1.91577 1014 m/s2 . Explanation: Let : B = 0.1 T and v = 2 107 m/s . b c
The gure represents two long, straight, parallel wires extending in a direction perpendicular to the page. The current in the left wire runs into the page and the current in the right runs out of the page.
What is the direction of the magnetic eld created by these wires at location a, b and c? (b is midway between the wires.) 1. up, up, down 2. up, down, up correct 3. down, down, up 4. down, zero, up 5. up, zero, down 6. down, up, down Explanation: By the right-hand rule the left wire has a clockwise eld and the right wire a counterclockwise eld. keywords: Serway CP 19 20 29:03, trigonometry, numeric, > 1 min, normal. 011 A thin, horizontal copper rod is 1 m long and has a mass of 50 g. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . What is the minimum current in the rod that will cause it to oat in a horizontal magnetic eld of 2 T? Correct answer: 0.245 A. Explanation: Let : = 1 m, m = 50 g = 0.05 kg , B = 2 T.
F = q v B sin = (1.60218 1019 C) (2 107 m/s)(0.1 T) = 3.20435 1013 N. From Newtons second law, a= F 3.20435 1013 N = m 1.67262 1027 kg
= 1.91577 1014 m/s2 .
keywords: Conceptual 17 Q01 29:02, highSchool, multiple choice, < 1 min, xed. 010
and
Create assignment, 00224, Homework 7, Mar 18 at 6:05 pm In order for the rod to oat, the magnetic force must have the same magnitude as the weight of the rod, so F = B I sin = m g mg I= . B sin The minimum value of I occurs when the denominator is largest (sin = 1), so Imin = (0.05 kg) (9.8 m/s2 ) (2 T) (1 m)
5. The direction of the magnetic eld is irrelevant. Explanation: The force on the heavy conductor due to the magnetic eld is F = I B. It is clear from the gure that, because the battery is causing the current, it ows to the right and through the heavy conductor. From the right hand rule the magnetic eld must point into or out of the page, respectively. 013 Assume a magnetic eld B points out of the plane of the page (and thus perpendicular to the plane of the circuit). The direction of the magnetic force on the heavy conductor is 1. into the page. 2. up. 3. to the right. 4. to the left. 5. out of the page.
= 0.245 A . keywords: Suspended by Springs 29:03, trigonometry, numeric, > 1 min, normal. 012 A heavy conductor (mass m, length , resistance R ) is suspended by two springs each with spring constant k, and connected to a battery with electric potential V as shown in the gure. A magnetic eld B is now imposed. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 .
+ V spring k l R mg heavy conductor spring k -
6. down. correct 7. undetermined, since the conductor does not feel a force. Explanation: F =I B = I B ( k) = I B , and from the right hand rule, the force is downward. 014 With the magnetic eld pointing in the same direction as in the previous part, what happens to the magnetic force on the heavy conR ductor if the resistance R decreases to ? 2
Which direction should the magnetic eld point to have the most eect in raising or lowering the heavy conductor? 1. Parallel to the conductor 2. Perpendicular to the page correct 3. Vertical and in the plane of the page 4. In the plane of the page at a 45 angle to the conductor
Create assignment, 00224, Homework 7, Mar 18 at 6:05 pm 1. force stays the same 2. force doubles correct 3. force quadruples 4. force halves 5. force remains zero 6. force is quartered Explanation: V The current is given by I = , so if the R resistance R decreases by a factor of two, V V I = = 2 the current increases by a iR R factor of two. The force is F =I B =I B, Let : V = 24 V , R = 12 , = 0.5 m , K = 2 N/m , m = 2 kg , and g = 9.8 m/s2 .
weight of the heavy conductor o the springs if a heavy conductor mass 2 kg, length 0.5 m, resistance 12 is suspended by two springs each with spring constant 2 N/m, and connected to a battery with electric potential 24 V as shown in the gure. Correct answer: 19.6 T. Explanation:
The magnetic eld must provide enough force to balance the gravitational force: Fmag + Fgrav = 0 Fmag = I and Fgrav = m g , so I B = mg. Rearranging and using I = B= V , we obtain R B =I B
(since and B are perpendicular), so if the current doubles, the force doubles. 015 What direction should the magnetic eld point to be the most eective for lifting the heavy conductor? 1. vertical and downward 2. out of the page 3. vertical and upward 4. horizontal and to the right 5. horizontal and to the left 6. into the page correct Explanation: From the right hand rule the magnetic eld must point into the page to provide an upward force. 016 The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . What is the minimum magnetic eld strength required to completely take the
mgR V (2 kg) (9.8 m/s2 ) (12 ) = (0.5 m) (24 V)
= 19.6 T .
017 Now, consider the extension of the springs if the conductor is placed on them with no magnetic eld present. Calculate the magnetic eld strength required to double the extension of the spring. Correct answer: 19.6 T. Explanation:
Create assignment, 00224, Homework 7, Mar 18 at 6:05 pm The equation relating the force on a spring and the extension of the spring is F = kx. With no applied force x = 0 and the springs are not extended. With the magnetic eld o but the heavy conductor attached, the force of gravity extends the two springs (m g = k x). To double the extension, the applied force must be doubled, and the magnetic eld must provide a force equal to the gravitational force: Fgrav = Fmag . This is the same as the magnetic eld strength solved in the previous part, so B = 19.6 T . Note: The value of the spring constant is extraneous information. keywords: Alpha Particle 29:05, trigonometry, numeric, > 1 min, normal. 018 An alpha particle has a mass of 6.6 1027 kg and is accelerated by a voltage of 1 kV. The charge on a proton is 1.602181019 C. If a uniform magnetic eld of 0.065 T is maintained on the alpha particle and perpendicular to its velocity, what will be particles radius of curvature? Correct answer: 0.0987423 m. Explanation: Let : B = 0.065 T , V = 1 kV = 1000 V , m = 6.6 1027 kg , and q = 2 e = 3.20435 1019 C . keywords: The kinetic energy is K= 1 q2 B 2 r2 m v2 = = qV , 2 2m
so the particles radius of curvature is r= = 1 B 2V m q 2 (1000 V) (6.6 1027 kg) 3.20435 1019 C
1 0.065 T
= 0.0987423 m .
Parallel Sections of Wires 30:03, trigonometry, multiple choice, > 1 min, xed. 019 Two identical parallel sections of wire are connected parallel to a battery as shown. The two sections of wire are free to move. When the switch is closed, the wires
1. will accelerate away each other. 2. will accelerate towards each other. correct 3. will heat up, and remain motionless. Explanation: Currents in the same direction attract each other, whereas parallel conductors carrying currents in opposite directions repel each other. The force can be computed by F =IlB. The magnetic eld lines generated by the two sections are shown as following, then apply
From Newtons second law, F = qvB = m v2 r qBr . v= m
Create assignment, 00224, Homework 7, Mar 18 at 6:05 pm above formula, one could determine the force between the sections is attractive. keywords:
You might also like
- Quest Electromagnetism 1 KeyDocument9 pagesQuest Electromagnetism 1 KeyCarlos OrtizNo ratings yet
- Q5Document14 pagesQ5Saad MohsinNo ratings yet
- HKPhO 18FJDFYJGJGHJHJHJGYJGYHFJFTJRTJFGJFGNGJYJTYJTYJTYDocument23 pagesHKPhO 18FJDFYJGJGHJHJHJGYJGYHFJFTJRTJFGJFGNGJYJTYJTYJTYSumihar SimangunsongNo ratings yet
- 10 Forces and Magnetic Fields QuestionsDocument6 pages10 Forces and Magnetic Fields QuestionsAnonymous oQEx3zNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Steady Electric and Magnetic FieldsDocument32 pagesModule 2 - Steady Electric and Magnetic FieldsBeverly Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- ch22 Physics SolutionsDocument20 pagesch22 Physics Solutionsalkalkindin1192848490% (1)
- Physics 1100: Magnetism SolutionsDocument12 pagesPhysics 1100: Magnetism Solutionstribhuvan guptaNo ratings yet
- Sample Problems Chap 21 CutnellDocument8 pagesSample Problems Chap 21 CutnellTaveesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- LCH 22Document52 pagesLCH 22sububillaNo ratings yet
- Electric and Magnetic FieldsDocument36 pagesElectric and Magnetic FieldsSuriani DharmaNo ratings yet
- Phy 303LDocument4 pagesPhy 303LnumbskullzNo ratings yet
- Notes on Common Exam 1 Electric Charge and FieldsDocument7 pagesNotes on Common Exam 1 Electric Charge and Fieldssergey500No ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect and MagnetismDocument12 pagesMagnetic Effect and Magnetismvishal_kalraNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For The Second Quarterly Test in Science 4aDocument7 pagesReviewer For The Second Quarterly Test in Science 4aDr.BlytheNo ratings yet
- Problem 27.68: Heimadæmi 6Document18 pagesProblem 27.68: Heimadæmi 6Taha AfzalNo ratings yet
- Problems Anproblems and Solutions On MagnetismDocument10 pagesProblems Anproblems and Solutions On MagnetismbluurryfaceNo ratings yet
- Quiz (Lecture 5) : Date: 14/3/2018 (Wednesday) Time: 2.15 PM VenueDocument50 pagesQuiz (Lecture 5) : Date: 14/3/2018 (Wednesday) Time: 2.15 PM VenueKoh Jiun AnNo ratings yet
- Solutions and Explanations for HW Chapter 27 BBDocument13 pagesSolutions and Explanations for HW Chapter 27 BBBecky DominguezNo ratings yet
- P132 ch29 PDFDocument9 pagesP132 ch29 PDFAlexNo ratings yet
- AP Physics B - Magnetic Fields and ForcesDocument21 pagesAP Physics B - Magnetic Fields and ForcesAudrey Patrick KallaNo ratings yet
- CH 33Document12 pagesCH 33ybobbyxNo ratings yet
- Magnetic FieldDocument15 pagesMagnetic FieldShiu Ping WongNo ratings yet
- Physics 114 Exam 2 Fall 2012Document13 pagesPhysics 114 Exam 2 Fall 2012angeluselinmortalNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Quest Electrostatics 2 KeyDocument6 pagesQuest Electrostatics 2 KeyCarlos OrtizNo ratings yet
- Magnetic FieldDocument7 pagesMagnetic FieldNishantYadavNo ratings yet
- AP Physics C E&M Unit 3 1. Magnetic Field and Force Homework SolutionDocument6 pagesAP Physics C E&M Unit 3 1. Magnetic Field and Force Homework SolutionmoonidiveNo ratings yet
- M20 66+Accelerating+Rod+on+a+RailDocument1 pageM20 66+Accelerating+Rod+on+a+RailEpic WinNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field and Magnetic Force: B V F FDocument21 pagesMagnetic Field and Magnetic Force: B V F FscholsarNo ratings yet
- Ch21magnetic Forces Material and DevicesDocument94 pagesCh21magnetic Forces Material and DevicesBewnet GetachewNo ratings yet
- CH 28 Physicsloncap 9 HelpDocument16 pagesCH 28 Physicsloncap 9 Helpjonjones666No ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETISMDocument158 pagesELECTROMAGNETISMEmmanuel OtienoNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Laws of MotinDocument32 pagesCH 5 Laws of MotinZeel ShahNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document10 pagesUnit 6Zelalem LemmaNo ratings yet
- HW8 A SolutionsDocument7 pagesHW8 A Solutionsmmsingh91No ratings yet
- MP EM Ass 14 Magnetic Force PDFDocument13 pagesMP EM Ass 14 Magnetic Force PDFAndrew LondonNo ratings yet
- P Module 6A PDFDocument52 pagesP Module 6A PDFSundareshwar SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 MagnetismDocument53 pagesChapter 5 MagnetismmunirahNo ratings yet
- Advanced Placement Physics Electricity and Magnetism: QQ F K R F E Q F Eq Q E K R Q E K RDocument5 pagesAdvanced Placement Physics Electricity and Magnetism: QQ F K R F E Q F Eq Q E K R Q E K RdvsfdcvNo ratings yet
- Lect 13Document27 pagesLect 13Aswin SivaramanNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism ReviewDocument6 pagesElectricity and Magnetism Reviewoogie boogiesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 MagnetismDocument77 pagesChapter 6 MagnetismsmartstudentsNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Home WorkDocument2 pagesMagnetism Home Workkaushik247No ratings yet
- Magnetism Part 3Document7 pagesMagnetism Part 3Marina MañolasNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field and Work: AlwaysDocument17 pagesMagnetic Field and Work: AlwaysSyed ShahabudeenNo ratings yet
- Magnetism Forces and Fields ExplainedDocument14 pagesMagnetism Forces and Fields ExplainedCamille SalasNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field Forces and Particle MotionDocument27 pagesMagnetic Field Forces and Particle Motionredsakkat100% (1)
- Physics 213-Problem Set 10-Solutions Fall 1997: 1. Reading AssignmentDocument4 pagesPhysics 213-Problem Set 10-Solutions Fall 1997: 1. Reading AssignmentNicolás KozakNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 28Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 28harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Ch21 SolutionDocument7 pagesTutorial Ch21 SolutiontonyformedNo ratings yet
- 21 Magnetic Forces and FieldsDocument11 pages21 Magnetic Forces and Fieldssoe0303No ratings yet
- The Magnetic Force: X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X XDocument35 pagesThe Magnetic Force: X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X XVineet KumarNo ratings yet
- Solution PDFDocument13 pagesSolution PDFShamariah BaileyNo ratings yet
- Exam 3Document13 pagesExam 3Michael Janusa100% (1)
- Alternating CurrentDocument17 pagesAlternating CurrentShinjiNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Let'S Check!Document6 pagesActivity 1: Let'S Check!Arlyn RagudosNo ratings yet
- SJPO 2017 General Round - Answer GuideDocument16 pagesSJPO 2017 General Round - Answer GuideDivyaNo ratings yet
- Quest Physics Homework MagnetismDocument5 pagesQuest Physics Homework MagnetismTyler SimmonsNo ratings yet
- E105 - FrictionDocument11 pagesE105 - FrictionvinceNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Actuators (Continued) : 1.5acceleration and Deceleration of Cylinder LoadsDocument13 pagesHydraulic Actuators (Continued) : 1.5acceleration and Deceleration of Cylinder LoadsAkshay AggrawalNo ratings yet
- Energy ConservationDocument250 pagesEnergy ConservationSchreiber_DiesesNo ratings yet
- PHY 107 Experiment 4Document7 pagesPHY 107 Experiment 4Just IteNo ratings yet
- 300123Document15 pages300123Basharat Ali HaiderNo ratings yet
- TOM Thomas Bevan PDFDocument640 pagesTOM Thomas Bevan PDFDebashishNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Force and Electrostatic FieldDocument4 pagesElectrostatic Force and Electrostatic FieldGurpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Albert Einstein - Simple English Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFDocument10 pagesAlbert Einstein - Simple English Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFPuneet PriyangueNo ratings yet
- Stability of A Floating Body!Document18 pagesStability of A Floating Body!M. ShayanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Physics 5054/12Document16 pagesCambridge O Level: Physics 5054/12dxD.T.C.dxNo ratings yet
- To Determine The Mass of A Given Body Using A Metre ScaleDocument13 pagesTo Determine The Mass of A Given Body Using A Metre ScaleSAGAR DASNo ratings yet
- Motion(A) - Speed, Acceleration, Distance CalculationsDocument6 pagesMotion(A) - Speed, Acceleration, Distance Calculations许某No ratings yet
- Delegate Angel Salazar Jr. Memorial SchoolDocument4 pagesDelegate Angel Salazar Jr. Memorial Schoolcharis m. alejoNo ratings yet
- Statics Course NotesDocument274 pagesStatics Course NotesSubin IdikulaNo ratings yet
- Esolutions Manual - Powered by CogneroDocument11 pagesEsolutions Manual - Powered by Cogneroジャンロイド ドゥーゴーNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document15 pagesLesson 4Ryan KoNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS 149: Lecture 5: - Chapter 2Document28 pagesPHYSICS 149: Lecture 5: - Chapter 2Sourav PandaNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument13 pagesElectrostaticssjo0567% (3)
- PracticeDocument3 pagesPracticeBea BarratoNo ratings yet
- Physics Entrance Exam Review Questions A PDFDocument9 pagesPhysics Entrance Exam Review Questions A PDFsuan_143100% (6)
- Center of Mass and Linear MomentumDocument20 pagesCenter of Mass and Linear Momentumsojib yeasinNo ratings yet
- Water Bottle Flipping PhysicsDocument8 pagesWater Bottle Flipping Physicsanon_734398465No ratings yet
- FTS-30 - Paper-2 - JEE Advanced-2020 - 19-09-2020 PDFDocument15 pagesFTS-30 - Paper-2 - JEE Advanced-2020 - 19-09-2020 PDFVIKRAM SINGHNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Potential Energy of A Linear Magnetic Track GunDocument14 pagesMagnetic Potential Energy of A Linear Magnetic Track GunNick CanningNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notebook WorksheetDocument197 pagesChemistry Notebook Worksheettaipantai100% (2)
- Report 4Document6 pagesReport 4Paul Adrian JavénNo ratings yet
- Lecture Powerpoints: Physics For Scientists and Engineers, With Modern Physics, 4 EditionDocument42 pagesLecture Powerpoints: Physics For Scientists and Engineers, With Modern Physics, 4 EditionAmyy Michelle CalderonnNo ratings yet
- NBTS-02 (A) RM (P1) 23-12-2023 QPDocument21 pagesNBTS-02 (A) RM (P1) 23-12-2023 QPsurajmeherakawfdNo ratings yet
- Persamaan Yang Digunakan Dan Contoh PerhitunganDocument3 pagesPersamaan Yang Digunakan Dan Contoh PerhitunganMuslihatur RNo ratings yet
- Problem 2.36Document2 pagesProblem 2.36Juan Francisco Garcia Arroyo0% (2)