Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Waves Multiple Choice
Uploaded by
Ann LiuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Waves Multiple Choice
Uploaded by
Ann LiuCopyright:
Available Formats
Waves
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question and place that answer on your scantron. DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST 1. The source of all wave motion is a a. region of variable high and low pressure.
b. vibration.
c. movement of matter.
d. harmonic object.
2. The time needed for a wave to make one complete cycle is its a. frequency. b. velocity. c. amplitude. d. period. e. wavelength. 3. The distance between successive identical parts of a wave is called its a. frequency. b. period. c. velocity. d. amplitude. e. wavelength. 4. The Hertz is a a. special radio wave.
b. type of car.
c. unit of period.
d. unit of wavelength.
e. unit of frequency.
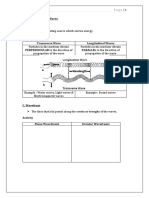
5. A wave created by shaking a rope up and down is called a a. Doppler wave. b. standing wave. c. longitudinal wave. 6. Which of the following is NOT a transverse wave? a. light. b. radio wave. c. sound. d. all of the above. 7. Sound is an example of a a. longitudinal wave. b. constructive wave.
d. constructive wave.
e. transverse wave.
e. none of the above
c. Doppler wave.
d. transverse wave.
e. standing wave.
8. When two or more waves are at the same place at the same time, the resulting effect is called a. a standing wave. b. a Doppler wave. c. a shock wave. d. interference. e. a period. 9. Where can you touch a standing wave on a rope without disturbing the wave? a. At a node b. At any place along the wave c. At an antinode 10. If you double the frequency of a vibrating object, its period a. halves. b. is quartered. c. doubles. 11. You dip your finger repeatedly into water and make waves. If you dip your finger more frequently, the wavelength of the waves a. lengthens. b. stays the same. c. shortens. 12. Two waves arrive at the same place at the same time exactly in step with each other. Each wave has an amplitude of 2.5 m. The resulting wave has an amplitude of a. 0.6 m. b. 1.3 m. c. 2.5 m. d. 5.0 m. e. 10.0 m. 13. The period of an ocean wave is 10 seconds. What is the waves frequency? a. 0.10 Hz b. 5.0 Hz c. 10.0 Hz d. 20.0 Hz e. 30.0 Hz 14. A certain ocean wave has a frequency of 0.07 hertz and a wavelength of 10 meters. What is the waves speed? a. 0.07 m/s b. 0.70 m/s c. 1.0 m/s d. 10 m/s e. 143 m/s
15. A weight on the end of a spring bobs up and down one complete cycle every 4.0 seconds. Its frequency is a. 0.25 hertz. b. 4.0 hertz. c. none of the above. 16. A weight suspended from a spring bobs up and back down again over a distance of 3.00 meters in 10.00 seconds. Its frequency is a. 0.10 hertz. b. 3.0 hertz. c. 10.0 hertz. d. none of the above 17. A cork floating in a pool oscillates up and down three complete cycles in 1 second as a wave passes by. The wave's wavelength is 2 meters. What is the wave's speed? a. 1 m/s b. 2 m/s c. 6 m/s d. 12 m/s e. More than 12 m/s 18. Radio waves travel at the speed of light, 300,000 km/s. The wavelength of a radio wave received at 200 megahertz is a. 0.7 m. b. 1.5 m. c. 6.7 m. d. 15 m. 19. If you increase the frequency of a wave, how the wave speed change if the medium does not change? a. it increases b. it decreases c. it stays the same d. none of these 20. If you increase the frequency of a wave, how the wave speed change if the medium changes and is more tense ( more tension)? a. it increases b. it decreases c. it stays the same d. none of these 21. When a wave reflects off a hard rigid barrier it reflects on the a. same side b. opposite side 22. When a wave reflects off a non rigid boundary (free end reflection) it reflects on the a. same side b. opposite side 23. The number of wave cycles per unit of time is called a. wavelength b. frequency c. period d. none of these 24. The equation for wave speed is a. speed =frequency/wavelength d. speed = wavelength x period
b. speed = frequency x wavelength
c. speed = frequency x period
True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 25. The time for a complete to and fro swing of a pendulum is its frequency. 26. The amplitude of a wave is the vertical distance from the midpoint to either the crest or the trough of the wave. 27. The distance between successive identical parts of a wave is its displacement. 28. The number of times a wave vibrates each second is its period. 29. A wave on a rope whose motion is at right angles to the direction of wave propagation is a longitudinal wave.
30. Sound waves are examples of longitudinal waves. 31. The unit of the period of a wave is the hertz. 32. When the high part of one wave fills in the low part of another wave, constructive interference occurs. 33. Nodes in a standing wave normally remain stationary. 34. If you tie a rope to a wall and shake the free end up and down just right, the reflected wave will be in and out of phase with the incident wave at fixed places along the rope and can form a standing wave. 35. The highest point on a wave is called a crest 36. The lowest point on a wave is called a crest 37. The distance between successive points on a wave is called its amplitude
Waves Answer Section
MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: KEY: 2. ANS: KEY: 3. ANS: KEY: 4. ANS: KEY: 5. ANS: KEY: 6. ANS: KEY: 7. ANS: KEY: 8. ANS: KEY: 9. ANS: KEY: 10. ANS: KEY: 11. ANS: KEY: 12. ANS: KEY: 13. ANS: KEY: 14. ANS: KEY: 15. ANS: KEY: 16. ANS: KEY: 17. ANS: KEY: 18. ANS: KEY: 19. ANS: 20. ANS: 21. ANS: 22. ANS: 23. ANS: 24. ANS: B PTS: 1 wave | motion D PTS: 1 time | period BLM: knowledge E PTS: 1 distance | wavelength E PTS: 1 Hertz | unit BLM: knowledge E PTS: 1 transverse | wave C PTS: 1 transverse | wave A PTS: 1 sound | wave BLM: knowledge D PTS: 1 interference BLM: knowledge A PTS: 1 node | standing A PTS: 1 frequency | vibrate | period C PTS: 1 frequency | wavelength D PTS: 1 amplitude | interference A PTS: 1 period | frequency B PTS: 1 wavelength | speed A PTS: 1 spring | frequency A PTS: 1 weight | spring | distance C PTS: 1 cycle | speed | wavelength B PTS: 1 wave | radio | hertz C PTS: 1 A PTS: 1 B PTS: 1 A PTS: 1 B PTS: 1 B PTS: 1 DIF: L1 BLM: knowledge DIF: L1 DIF: L1 BLM: knowledge DIF: L1 DIF: BLM: DIF: BLM: DIF: OBJ: 25.2 Wave Description OBJ: 25.1 Vibration Of A Pendulum OBJ: 25.2 Wave Description OBJ: 25.2 Wave Description
L1 OBJ: 25.5 Transverse Waves knowledge L2 OBJ: 25.6 Longitudinal Waves comprehension L1 OBJ: 25.6 Longitudinal Waves OBJ: 25.7 Interference 25.8 Standing Waves 25.2 Wave Description 25.3 Wave Motion 25.7 Interference 25.2 Wave Description 25.4 Wave Speed 25.2 Wave Description 25.2 Wave Description 25.4 Wave Speed 25.4 Wave Speed
DIF: L1 DIF: BLM: DIF: BLM: DIF: BLM: DIF: BLM: DIF: BLM: DIF: BLM: DIF: BLM: DIF: BLM: DIF: BLM: DIF: BLM:
L2 OBJ: comprehension L2 OBJ: application L2 OBJ: comprehension L2 OBJ: application L2 OBJ: application L2 OBJ: application L2 OBJ: application L2 OBJ: application L2 OBJ: application L2 OBJ: application
TRUE/FALSE 25. ANS: KEY: 26. ANS: KEY: 27. ANS: KEY: 28. ANS: KEY: 29. ANS: KEY: 30. ANS: KEY: 31. ANS: KEY: 32. ANS: KEY: 33. ANS: KEY: 34. ANS: KEY: 35. ANS: 36. ANS: 37. ANS: F PTS: 1 pendulum | frequency T PTS: 1 amplitude | crest F PTS: 1 distance | displacement F PTS: 1 vibrate | period F PTS: 1 longitudinal | wave T PTS: 1 sound | longitudinal F PTS: 1 period | hertz F PTS: 1 constructive | destructive T PTS: 1 node | standing T PTS: 1 reflect | incident | standing T PTS: 1 F PTS: 1 F PTS: 1 DIF: BLM: DIF: BLM: DIF: BLM: DIF: BLM: DIF: BLM: DIF: BLM: DIF: BLM: DIF: BLM: DIF: BLM: DIF: BLM: L1 OBJ: knowledge L1 OBJ: knowledge L1 OBJ: knowledge L1 OBJ: knowledge L1 OBJ: knowledge L1 OBJ: knowledge L1 OBJ: knowledge L1 OBJ: knowledge L1 OBJ: knowledge L2 OBJ: comprehension 25.1 Vibration Of A Pendulum 25.2 Wave Description 25.2 Wave Description 25.2 Wave Description 25.5 Transverse Waves 25.6 Longitudinal Waves 25.1 Vibration Of A Pendulum 25.7 Interference 25.8 Standing Waves 25.8 Standing Waves
You might also like
- Lesson 6.2Document10 pagesLesson 6.2Tok PutihNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6.2 Physics F5Document10 pagesLesson 6.2 Physics F5Siti Arbaiyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 2019-2020 Unit 9 TestDocument3 pagesPhysical Science 2019-2020 Unit 9 TestersadoyanaNo ratings yet
- Waves A Level Practice QuestionsDocument6 pagesWaves A Level Practice QuestionsisaacsrandomsignupsNo ratings yet
- Test 12H Review AnswersDocument7 pagesTest 12H Review Answerstedien252No ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument7 pagesPDF DocumentShammany AlsuwaidiiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Waves Notes2Document99 pagesIntroduction To Waves Notes2Ma. Elizabeth CusiNo ratings yet
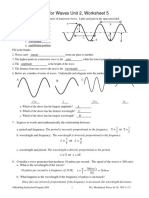
- Unit 2 Worksheet 5 Aurora High SchoolDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Worksheet 5 Aurora High SchoolシューゴNo ratings yet
- Longitudinal Waves Are Waves That Travel Parallel To The Direction of MotionDocument21 pagesLongitudinal Waves Are Waves That Travel Parallel To The Direction of MotionshreyaNo ratings yet
- Igcse 31 PropertiesofwavesDocument23 pagesIgcse 31 PropertiesofwavesHany ElGezawy100% (1)
- Properties of WavesDocument4 pagesProperties of WavesrohmawatiNo ratings yet
- Wave Motion and SoundDocument8 pagesWave Motion and SoundyididiyayibNo ratings yet
- Waves: By: Chris Lembalemba (Chrislembalemba@yahoo - Co M)Document33 pagesWaves: By: Chris Lembalemba (Chrislembalemba@yahoo - Co M)Michael GalarioNo ratings yet
- Lecture03 Mechanical WavesDocument3 pagesLecture03 Mechanical WavesVICTORIA OMEGA JARAMILLANo ratings yet
- F5 WavesDocument29 pagesF5 WavesThayabaran MunusamyNo ratings yet
- Waves: Name - TeacherDocument47 pagesWaves: Name - TeachersaadNo ratings yet
- Introduction to WavesDocument3 pagesIntroduction to WavesChristanique McIntoshNo ratings yet
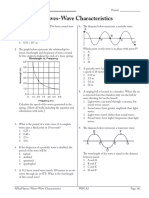
- ExamView - Waves and Sound - Practice TestDocument9 pagesExamView - Waves and Sound - Practice TestMohan RajNo ratings yet
- Examview Waves and Sound Practice Test4Document9 pagesExamview Waves and Sound Practice Test4Tajay Billings100% (1)
- Online Phys12 Mid ExamDocument3 pagesOnline Phys12 Mid ExamJanisa SacariaNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Waves: Prior Knowledge QuestionsDocument7 pagesStudent Exploration: Waves: Prior Knowledge QuestionsJACK CAMPBELL100% (2)
- WavesDocument4 pagesWavesMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Wave Introduction Wave Types Wave FrequencyDocument4 pagesWave Introduction Wave Types Wave FrequencySheryl LafuenteNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Waves: Types, Properties and CalculationsDocument4 pagesIntroduction to Waves: Types, Properties and Calculationsmary ann espinaNo ratings yet
- 01 1 Wave Motion PDFDocument8 pages01 1 Wave Motion PDFReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- OHSP Module 15 Waves - Carriers of Energy PDFDocument22 pagesOHSP Module 15 Waves - Carriers of Energy PDFFLORA MAY VILLANUEVANo ratings yet
- Tadamun Social Society Imamu-Nawawi Secondary Schools Bosaso-Puntland-Somalia Assignment: Subject Physics Classes: Form FourDocument13 pagesTadamun Social Society Imamu-Nawawi Secondary Schools Bosaso-Puntland-Somalia Assignment: Subject Physics Classes: Form FourIbrahim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Ch1 - STDDocument40 pagesCh1 - STDmalakbasahalNo ratings yet
- Waves Quarter 3 Week 4Document6 pagesWaves Quarter 3 Week 4marieleempuriheheNo ratings yet
- Wave and SoundDocument19 pagesWave and Soundanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Solutions To Practice Test 3Document18 pagesSolutions To Practice Test 3Trey CrossNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Waves AnswersDocument66 pages3.3 Waves Answersmarkmattesz06No ratings yet
- Ppsb-Class X - Physics-Sound MCQDocument7 pagesPpsb-Class X - Physics-Sound MCQKrishna Agarwal [PRIMUS]No ratings yet
- Dynamics of Marine Vessels MR 333 - Sheet 2Document3 pagesDynamics of Marine Vessels MR 333 - Sheet 2Mohamed AtefNo ratings yet
- !!!RENAME!!!: Waves Assignment #1 Types of Waves - Part B: Transverse WavesDocument4 pages!!!RENAME!!!: Waves Assignment #1 Types of Waves - Part B: Transverse WavesJanaarthNo ratings yet
- Lesson 17 Wave MotionDocument8 pagesLesson 17 Wave MotionAlex Jr. Rosadiño C.No ratings yet
- 29 Waves-Wave CharacteristicsDocument9 pages29 Waves-Wave CharacteristicseltytanNo ratings yet
- A Wave Is A Phenomenon In: Which Energy Is Transferred ThroughDocument53 pagesA Wave Is A Phenomenon In: Which Energy Is Transferred ThroughAlan MeysamianNo ratings yet
- fIZIK 1Document14 pagesfIZIK 1AaronAlwynNo ratings yet
- Wave MotionDocument39 pagesWave MotionRecee josephNo ratings yet
- As 23a WavesDocument42 pagesAs 23a WavesHany ElGezawyNo ratings yet
- We Will See The Difference of That Two WaveDocument3 pagesWe Will See The Difference of That Two WaveM Ramadhan ANo ratings yet
- Advanced G10 Physics Revision Materials Chapter 4 AnswerKeyDocument6 pagesAdvanced G10 Physics Revision Materials Chapter 4 AnswerKeyAhmed Mohamed Mohamed Elsaid SallamNo ratings yet
- Wave PropertiesDocument122 pagesWave PropertiesschlemielzNo ratings yet
- Waves and Wave MotionDocument15 pagesWaves and Wave MotionDom Christian Last100% (1)
- Chapter 14 Practice Quiz SolutionsDocument3 pagesChapter 14 Practice Quiz SolutionsNano MohammadNo ratings yet
- Chapter2of Physics Question and AnswersDocument4 pagesChapter2of Physics Question and AnswersE-SKUUL ACADEMYNo ratings yet
- Doppler Effect For Sound: and Review of WaveDocument25 pagesDoppler Effect For Sound: and Review of WaveSHEENA MAE DALGUNTASNo ratings yet
- 10 WavesDocument36 pages10 Wavesfitrifisika07No ratings yet
- Physics Form 5 Chapter 1Document39 pagesPhysics Form 5 Chapter 1Leong Laichuo40% (5)
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- CHP 15-2 Wave Characteristics PDFDocument8 pagesCHP 15-2 Wave Characteristics PDFLakshyaNo ratings yet
- Waves and Sound PacketDocument16 pagesWaves and Sound PacketKaito EspinaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Interference N Diffraction of WavesDocument10 pagesNotes On Interference N Diffraction of WavesHubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- How Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Do Waves Behave? How Are They Measured? Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound and Elastic Waves: Frequently Asked QuestionsFrom EverandUltrasound and Elastic Waves: Frequently Asked QuestionsNo ratings yet
- Module 10 - PowerpointDocument23 pagesModule 10 - PowerpointKathleen Joy RuizNo ratings yet
- 9th Sound Test - 1Document2 pages9th Sound Test - 1Janardan SunilNo ratings yet
- IAT-1 AME Answer KeyDocument2 pagesIAT-1 AME Answer KeyNaveenNo ratings yet
- PSI AP Physics 1: Simple Harmonic Motion Practice ProblemsDocument18 pagesPSI AP Physics 1: Simple Harmonic Motion Practice ProblemsamanNo ratings yet
- PascovibradorDocument4 pagesPascovibradordavidjl_299No ratings yet
- Acoustics and Sound InsulationDocument13 pagesAcoustics and Sound InsulationRajit AryaNo ratings yet
- Plate 2 Unijuction Unilateral Transistor (Marte)Document4 pagesPlate 2 Unijuction Unilateral Transistor (Marte)CloudFarmInnovations IncorporatedNo ratings yet
- 01-07-Wave Making ResistanceDocument47 pages01-07-Wave Making Resistancerahmahmed200kNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Therapy I: Aditya Johan .R, M.FisDocument17 pagesUltrasound Therapy I: Aditya Johan .R, M.FisDinda RishaldiNo ratings yet
- Soalan Latihan Utk Wave Utk SPMDocument19 pagesSoalan Latihan Utk Wave Utk SPMnurulsyafiqah93No ratings yet
- Bandwidth Enhancement of Antenna Arrays UtilizingDocument9 pagesBandwidth Enhancement of Antenna Arrays UtilizingRamya RNo ratings yet
- Kenwood TH-G71A-E Service ManualDocument28 pagesKenwood TH-G71A-E Service ManualΓΙΩΡΓΟΣ ΚΑΚΑΦΛΙΚΑΣNo ratings yet
- 332HW3Document3 pages332HW3Adinda ForeverNo ratings yet
- Note-We Have I: Unit-V-Electromagnetic Waves Gist, Formulae and Shortcut FourmulaeDocument4 pagesNote-We Have I: Unit-V-Electromagnetic Waves Gist, Formulae and Shortcut FourmulaeanikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Mobile Radio Propagation PDFDocument72 pagesChapter 4 Mobile Radio Propagation PDFWhatsapp StoriesNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 Q2 Module 5 Week 5 REVISEDDocument19 pagesSCIENCE 10 Q2 Module 5 Week 5 REVISEDJohn Clifford Ambaic JayomaNo ratings yet
- Oscillations PDFDocument10 pagesOscillations PDFmanas nikhilNo ratings yet
- 64842a72faee930018ed803f - ## - Atomic Structure - DPP-08 (Of Lec-11) - Arjuna NEET 2024Document4 pages64842a72faee930018ed803f - ## - Atomic Structure - DPP-08 (Of Lec-11) - Arjuna NEET 2024Lalit SinghNo ratings yet
- Challenging Practice Questions MixDocument62 pagesChallenging Practice Questions Mixmarjan familiNo ratings yet
- OMEGA LTD Commercial Offer QuartzDocument2 pagesOMEGA LTD Commercial Offer QuartzAgung SuryadiNo ratings yet
- UT Testing-Self Study Notes 20140807Document2,085 pagesUT Testing-Self Study Notes 20140807yivkehNo ratings yet
- Edexcel As Physics Unit 2 Revision PowerpointDocument92 pagesEdexcel As Physics Unit 2 Revision PowerpointAnonymous tlSLEPRRe92% (12)
- Unit 3 - Practice Exam QuestionsDocument35 pagesUnit 3 - Practice Exam QuestionscripzrafNo ratings yet
- The effects of light waves and their propertiesDocument148 pagesThe effects of light waves and their propertiesAhmed KhalilNo ratings yet
- Fresnel PDFDocument6 pagesFresnel PDFJyotirmoy BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Pendulam - Magnetic ReportDocument31 pagesPendulam - Magnetic ReportpramodassNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument15 pagesPhysicsKim Al-Gin Rayos ManongsongNo ratings yet
- ELASTICITYDocument22 pagesELASTICITYLokesh MuralidaraNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Description of a WaveDocument3 pagesMathematical Description of a WaveSubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- Attewell - Attenuation of Ground Vibrations From Pile Driving, 1973Document4 pagesAttewell - Attenuation of Ground Vibrations From Pile Driving, 1973Max ShashkinNo ratings yet