Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Icroprocessor and Its Application
Uploaded by
kiratsandhu090 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views14 pagesThe document discusses the architecture and operations of the 8085 microprocessor. It describes the block diagram of a computer system using a microprocessor as the central processing unit. It outlines the organization of a microprocessor-based system including the arithmetic logic unit, register array, control unit, memory, and input/output systems. It also explains the register structure, arithmetic logic unit, bus organization, and timing/control functions of the 8085 microprocessor.
Original Description:
Original Title
13402_Lecture 2
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the architecture and operations of the 8085 microprocessor. It describes the block diagram of a computer system using a microprocessor as the central processing unit. It outlines the organization of a microprocessor-based system including the arithmetic logic unit, register array, control unit, memory, and input/output systems. It also explains the register structure, arithmetic logic unit, bus organization, and timing/control functions of the 8085 microprocessor.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views14 pagesIcroprocessor and Its Application
Uploaded by
kiratsandhu09The document discusses the architecture and operations of the 8085 microprocessor. It describes the block diagram of a computer system using a microprocessor as the central processing unit. It outlines the organization of a microprocessor-based system including the arithmetic logic unit, register array, control unit, memory, and input/output systems. It also explains the register structure, arithmetic logic unit, bus organization, and timing/control functions of the 8085 microprocessor.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
Bharat sankhlecha
MICROPROCESSOR AND ITS
APPLICATION
Bharat Sankhlecha bharat.sanklecha@lpu.co.in Sr. Lecturer Block 33 Room No. 203 Ch No. 18 M: 9501424515
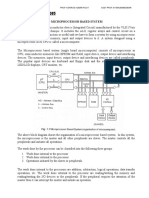
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF A COMPUTER WITH MICROPROCESSOR AS CPU
Bharat sankhlecha
Input
Microprocessor as CPU
Output
Memory
MICROPROCESSOR SYSTEM WITH BUS ARCHITECTURE
Bharat sankhlecha
ALU
Register Array
I/O Input/Output System Bus Memory ROM RAM
Control
ORGANIZATION OF A MICROPROCESSOR BASED SYSTEM
Microprocessor Arithmetic Logic Unit Register Array Control Unit Memory I/O (Input/Output) System Bus
Bharat sankhlecha
8085 MICROPROCESSOR
8085 ARCHITECTURE AND ITS OPERATIONS
The microprocessor is a programmable digital device, design with registers, Flip flops and timing elements. The microprocessor has set of instructions, designed internally, to manipulate data and communicate with peripherals. This process of data manipulation and communication is determined by the logic design of the microprocessor, called the architecture.
All the various functions performed by the microprocessor can be classified in three general categories:
Microprocessor-initiated operations Internal operations Peripheral (or externally initiated) operations
Register Structure ALU Bus Organization Timing and Control
8085 BUS STRUCTURE
MICROPROCESSOR INITIATED OPERATIONS AND 8085 BUS ORGANIZATION
The MPU performs primarily four operations: 1. Memory Read: Read data (or instructions) from memory 2. Memory Write : Write data (or instructions) into memory 3. I/O Read: Accepts data from input devices 4. I/O Write: Sends data to output devices All the operations are part of the communication process between the MPU and peripheral (including memory). To communicate with a peripheral (or a memory location), the MPU needs to perform the following steps: Step1: Identify the peripheral or the memory location (with its address) Step2: Transfer binary information (Data or instruction) Step3: Provide timing or synchronization signals.
EXAMPLE: MEMORY READ OPERATION
INTERNAL DATA OPERATIONS AND THE 8085 REGISTERS
The internal architecture of the 8085 microprocessor determines how and what operations can be performed with the data. These operations are: 1. Store 8-bit data. 2. Perform arithmetic and logical operations. 3. Test for conditions. 4. Sequence execution of instructions. 5. Store data temporarily during execution in the defined R/W memory location called stack. To perform these operations, the microprocessor requires registers, an arithmetic logic unit and control logic, and internal buses (paths for information flow)
PERIPHERAL OR EXTERNALLY INITIATED OPERATIONS
External devices can initiate the following operations, for which individual pins on the microprocessor chip are assigned : Reset, Interrupt, Ready, Hold.
You might also like
- MP Module 1Document44 pagesMP Module 1Hari MuraliNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor & microcontroller introductionDocument20 pagesMicroprocessor & microcontroller introductionjeravi84No ratings yet
- Subject-Microprcessor Name - Pratyush Bidika REGD - NO-19MSCPHY05 Course Code-Phy.509 Subject-ElectronicsDocument15 pagesSubject-Microprcessor Name - Pratyush Bidika REGD - NO-19MSCPHY05 Course Code-Phy.509 Subject-Electronicspratyush bidikaNo ratings yet
- SEC1310Document169 pagesSEC1310Su YeeNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I: Introduction To Microprocessors: Microprocessor and MicrocontrollersDocument14 pagesUNIT-I: Introduction To Microprocessors: Microprocessor and MicrocontrollersGagandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I: Introduction To Microprocessors: Microprocessor and MicrocontrollersDocument14 pagesUNIT-I: Introduction To Microprocessors: Microprocessor and MicrocontrollersAtif HussainNo ratings yet
- Two Mark MicroprocessorDocument18 pagesTwo Mark MicroprocessorGopinathan MNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument35 pagesMicroprocessor ArchitecturesramukNo ratings yet
- Architecture 8085Document66 pagesArchitecture 8085ys013330No ratings yet
- MP LectureNote1 4Document30 pagesMP LectureNote1 4Yoseph ChalieNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors and InterfacingDocument125 pagesMicroprocessors and InterfacingRaja SekharNo ratings yet
- 8085 Note Final - 2Document35 pages8085 Note Final - 2durgaprasadNo ratings yet
- Microcontrollerpresentation 141213101338 Conversion Gate01Document41 pagesMicrocontrollerpresentation 141213101338 Conversion Gate01priyalNo ratings yet
- Course Title Microprocessor SystemDocument20 pagesCourse Title Microprocessor SystemElmustafa Sayed Ali AhmedNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. Electronics and Communications Microprocessors and Microcontrollers GuideDocument442 pagesM.Sc. Electronics and Communications Microprocessors and Microcontrollers GuideMegha Anand0% (1)
- Introduction To MicroprocessorDocument39 pagesIntroduction To MicroprocessorDeepika BansalNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor FINALDocument8 pagesMicroprocessor FINALbocemay268No ratings yet
- MPMC Unit-1Document27 pagesMPMC Unit-1downloadscribdpdfNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor and Interfacing: Authors:Ramesh.S.Gaonkar Badri Ram Douglas.V.Hall Liu and GibsonDocument52 pagesMicroprocessor and Interfacing: Authors:Ramesh.S.Gaonkar Badri Ram Douglas.V.Hall Liu and Gibsonavireddy1No ratings yet
- Loyola Icam College of Engineering and Technology Department of Ece Cs 2252 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers Question Bank With AnswersDocument38 pagesLoyola Icam College of Engineering and Technology Department of Ece Cs 2252 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers Question Bank With AnswersKarthik KarthiksNo ratings yet
- Lecture-1 (Introduction, Hardwired Logic) : MPI Unit 1Document34 pagesLecture-1 (Introduction, Hardwired Logic) : MPI Unit 1Tushar VermaNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic And Computer Organization UNIT – II 2.0) IntroductionDocument32 pagesDigital Logic And Computer Organization UNIT – II 2.0) IntroductionJit AggNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document85 pagesUnit 4Chadaram JagadishNo ratings yet
- Mico Ro ProcessorDocument12 pagesMico Ro ProcessorRX GamerNo ratings yet
- MP Manual 2Document73 pagesMP Manual 2Subir ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Basic CPU ArchitecturesDocument7 pagesLecture 2 Basic CPU ArchitecturesMohan Krishna Reddy KarriNo ratings yet
- Ee6502 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers 2 Mark Question and Answers BY Ensolt ElakkiaDocument38 pagesEe6502 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers 2 Mark Question and Answers BY Ensolt ElakkiaBalaprakash VadivelNo ratings yet
- P6 NotesDocument84 pagesP6 NotesMorigere SubramanyabhatNo ratings yet
- Unit I Introduction To 8085 MicroprocessorDocument55 pagesUnit I Introduction To 8085 Microprocessorkiran sharmaNo ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocessor Architecture OverviewDocument12 pages8085 Microprocessor Architecture OverviewMandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For MPDocument38 pagesQuestion Bank For MPmekalajesiNo ratings yet
- 2nd CHAPTER MechatronicsDocument50 pages2nd CHAPTER MechatronicspremscrebdNo ratings yet
- Introduction To 8085 MicroprocessorDocument43 pagesIntroduction To 8085 MicroprocessorYosa Worku100% (1)
- 8085 ArchitectureDocument39 pages8085 Architecturemnnit_nitNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor OperationDocument3 pagesMicroprocessor OperationDeeplakhan BhanguNo ratings yet
- Iare Mpi Lecture Notes 0 PDFDocument158 pagesIare Mpi Lecture Notes 0 PDFPriya PreethiNo ratings yet
- The 8086 Processor Architecture in 40 CharactersDocument28 pagesThe 8086 Processor Architecture in 40 CharactersRajiv SivalingamNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Part 1 MicroprocessorDocument14 pagesUnit 4 Part 1 MicroprocessorMuthu KumaranNo ratings yet
- Mecha Unit IIDocument96 pagesMecha Unit IICAD With RaoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mechatronics: Microcontrollers and MicroprocessorsDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Mechatronics: Microcontrollers and MicroprocessorsAmanuel tadiwosNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors & Microcontrollers: Part A 1. What Is Microprocessor?Document21 pagesMicroprocessors & Microcontrollers: Part A 1. What Is Microprocessor?Nenu Meeku TelusaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Microprocessors and Their ComponentsDocument39 pagesIntroduction to Microprocessors and Their ComponentsSyaz ZanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Ed2Document47 pagesChapter 2 Ed2Muhammad AqeefNo ratings yet
- Microcontrollers: An IntroductionDocument10 pagesMicrocontrollers: An IntroductionAjay YANo ratings yet
- Unit 01: BEE-15ADocument22 pagesUnit 01: BEE-15APrashant SinghNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks MPDocument15 pages2 Marks MPGopinathan MNo ratings yet
- Introduction to MicroprocessorsDocument21 pagesIntroduction to MicroprocessorsMohit D MoreNo ratings yet
- Cs 2252-Microprocessors 2 NewDocument27 pagesCs 2252-Microprocessors 2 NewVaishnavi RaveNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument26 pagesMicroprocessor ArchitecturevozoscribdNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks MicroprocessorDocument17 pages2 Marks MicroprocessorShreyaNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Microprocessor of 8085 - 2024Document77 pages1.introduction To Microprocessor of 8085 - 2024sanchita4586No ratings yet
- Experiment No: 1: OBJECTIVE: To Study About The Bus Organization and Programmable Model ofDocument5 pagesExperiment No: 1: OBJECTIVE: To Study About The Bus Organization and Programmable Model ofRutul PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Introduction To MicroprocessorDocument39 pagesChapter 2 Introduction To MicroprocessorWann FarieraNo ratings yet
- MPMC Lecture1Document8 pagesMPMC Lecture1Soumya Ranjan PandaNo ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument38 pages8085 Microprocessor Architectureashley panganNo ratings yet
- Rakesh - Saxena@gitjaipur - Com 31303122020045036pmDocument52 pagesRakesh - Saxena@gitjaipur - Com 31303122020045036pmBadrinathNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960From EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960No ratings yet
- Digital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesFrom EverandDigital Electronics, Computer Architecture and Microprocessor Design PrinciplesNo ratings yet
- John Smith Skills-ReportDocument12 pagesJohn Smith Skills-ReportkupetikapamNo ratings yet
- Understanding and Configuring 802.1X Port-Based AuthenticationDocument22 pagesUnderstanding and Configuring 802.1X Port-Based AuthenticationUmAiR ANo ratings yet
- AniteDocument7 pagesAniteRavi SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- DSA Maps and SetsDocument1 pageDSA Maps and SetsJohnmark PadillaNo ratings yet
- Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML) : Unit 5Document12 pagesHyper Text Markup Language (HTML) : Unit 5Lavanya lokeshNo ratings yet
- Assignment 9Document17 pagesAssignment 9Mysha AnowarNo ratings yet
- Career Guidance Website PresentationDocument17 pagesCareer Guidance Website PresentationSandhya SalunkeNo ratings yet
- 04-Web Configuration CommandsDocument8 pages04-Web Configuration Commandsagung nurilhamNo ratings yet
- VH5110A Manual ENDocument23 pagesVH5110A Manual ENDiana AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Distributed and Cooperative Hierarchical Intrusion Detection On ManetsDocument9 pagesDistributed and Cooperative Hierarchical Intrusion Detection On ManetsleloiboiNo ratings yet
- Trina Ford ResumeDocument1 pageTrina Ford Resumeapi-550948784No ratings yet
- TR Openstack Skills Path Infographic f29301 202106 enDocument1 pageTR Openstack Skills Path Infographic f29301 202106 enPradeep KandasamyNo ratings yet
- Ship Main Engine Operation Simulator Based on PLCDocument6 pagesShip Main Engine Operation Simulator Based on PLCmohanNo ratings yet
- Avaya Port MatrixDocument22 pagesAvaya Port MatrixAshishNo ratings yet
- Praveen (Resume)Document3 pagesPraveen (Resume)Jones RayenNo ratings yet
- Procure To Pay' ProcessDocument16 pagesProcure To Pay' ProcessDiwahar PuraviNo ratings yet
- Simatic S7-300: The Universal, Small Control System Supplemented by New, Compact CpusDocument18 pagesSimatic S7-300: The Universal, Small Control System Supplemented by New, Compact CpusSunil SinghNo ratings yet
- DFT Scan Insertion: VLSI Testing and Design For TestabilityDocument19 pagesDFT Scan Insertion: VLSI Testing and Design For TestabilityHuzur AhmedNo ratings yet
- CYRUS PIG 82DAC QXR v2Document2 pagesCYRUS PIG 82DAC QXR v2José Juan Gonzalvez SansNo ratings yet
- What Is An "Algorithm?"Document46 pagesWhat Is An "Algorithm?"Chan DavidNo ratings yet
- COMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore Campus: Lab Terminal Exam (Spring-2020)Document5 pagesCOMSATS University Islamabad, Lahore Campus: Lab Terminal Exam (Spring-2020)Hafiz Hassan JawadNo ratings yet
- Designer's Toolbox - 101 Resources For Drafters, Designers & Architecture StudentsDocument20 pagesDesigner's Toolbox - 101 Resources For Drafters, Designers & Architecture StudentsBonzibit Zibit100% (1)
- Software ET-View / ET-Diag: (Figures Show German Version)Document2 pagesSoftware ET-View / ET-Diag: (Figures Show German Version)iocsachinNo ratings yet
- KiCadLikeaPro3e - Course - Companion (1 Dec 2021 at 4-06-00 PM)Document128 pagesKiCadLikeaPro3e - Course - Companion (1 Dec 2021 at 4-06-00 PM)mejoe mejoeNo ratings yet
- Iphone 15 - WikipediaDocument8 pagesIphone 15 - WikipediaaNo ratings yet
- Major Project FileDocument53 pagesMajor Project FileGaurav KushwahNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Serie ADAMsDocument36 pagesDatasheet Serie ADAMsRafael FloresNo ratings yet
- Ch2. Core of Embedded SystemsDocument15 pagesCh2. Core of Embedded SystemsnikhilpawanikarNo ratings yet
- 7232 01 Data Management Trends Powerpoint Template 16x9Document11 pages7232 01 Data Management Trends Powerpoint Template 16x9Eduardo Espinoza GCPNo ratings yet