Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Linear Motion
Uploaded by
Mohd NuhCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Linear Motion
Uploaded by
Mohd NuhCopyright:
Available Formats
LINEAR MOTION
OBJECTIVES 1- To analyze linear motion of a moving object. 2- To determine displacement, velocity and acceleration of a linear motion. INFERENCE 1- Linear motion is a motion along a straight line. 2- It can be uniform when constant velocity is zero acceleration or non-uniform when a variable velocity is non-zero acceleration. 3- Deceleration is the decrease of velocity over a period of time. HYPOTHESIS 1- Velocity is speed in a given direction. 2- Acceleration is the increase of velocity over a period of time. APPARATUS 123456789Ticker timer Carbonized ticker tape Runway Power supply Trolley Jumper wire Ruler Lab jack/clamp Cellophane tape
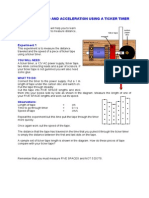
PROCEDURES 1- Apparatus had been set up in Figure 1. 2- The runway is inclined about 1m 3m, so that the trolley will roll down freely from rest without any applied force. 3- The ticker tape was attached to the trolley by using cellophane tape. 4- The ticker timer had been switch on and releases the trolley freely.
Figure 1
Figure 2 1. Mark and number every 10th dot as Figure 2. 2. Ticker tape had been cut and paste into 10-dot strips on the graph paper as Figure 3.
RESULTS
1 2 3 4
Number of 10-dot strips Total time, t total = number of strips x 0.2 Total displacement of the trolley Average velocity of the trolley V= total displacement total time Acceleration of the trolley A. Initial velocity u= length of first strip time for 10 dots B. Final velocity v= length of first strip time for 10 dots C. Time for acceleration , t (number of strips 1) x (time for 10 dots) D. Acceleration a= v-u t Average velocity V average = v + u 2
5 1s 1.912m
1.912m/s
52.5 m/s
327.5m/s 0.8s
1375m/s2
190 m/s
QUESTION: 1- Is there any difference in the value of average velocity between Result 4 and 6? Explain your answer. Yes, because CONCLUSION:
You might also like
- LAB 2 Linear MotionDocument6 pagesLAB 2 Linear Motionsyazwanshapawi100% (5)
- Linear MotionDocument9 pagesLinear MotionShanti Thanarajan33% (3)
- Cambridge Kinematics EssayDocument12 pagesCambridge Kinematics EssaySuresh SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- Practical 1.1: Displacement-Time GraphsDocument1 pagePractical 1.1: Displacement-Time GraphsMohammedNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Lab Report Eng ScienceDocument12 pagesExperiment 2 Lab Report Eng ScienceKiddozesNo ratings yet
- Science Enginering Lab Report - Experiment 2 (Liner Motion)Document3 pagesScience Enginering Lab Report - Experiment 2 (Liner Motion)Q Hydar Q Hydar33% (3)
- Physics 3B Mechanics ExperimentsDocument19 pagesPhysics 3B Mechanics ExperimentsMobasshir RoyhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter2pp010 020 PDFDocument11 pagesChapter2pp010 020 PDFInderMaheshNo ratings yet
- Ticker Timer IntroductionDocument3 pagesTicker Timer IntroductionTuisyen Geliga67% (3)
- Unit 1.1 - Mechanics - Kinematics (Student)Document12 pagesUnit 1.1 - Mechanics - Kinematics (Student)Quay Wei KwangNo ratings yet
- Engineering Council Certificate Level: Mechanical and Structural Engineering C105Document14 pagesEngineering Council Certificate Level: Mechanical and Structural Engineering C105satoni12No ratings yet
- Kinematics Motion SpeedDocument10 pagesKinematics Motion SpeedDyna MoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Council Dynamics of Mechanical Systems D225 Tutorial 1 Linear and Angular Displacement, Velocity and AccelerationDocument9 pagesEngineering Council Dynamics of Mechanical Systems D225 Tutorial 1 Linear and Angular Displacement, Velocity and AccelerationTawanda KasekeNo ratings yet
- Labsheet Linear MotionDocument6 pagesLabsheet Linear MotionGnabryNo ratings yet
- Physics s.3 Week 7 MinDocument8 pagesPhysics s.3 Week 7 Minsam lubakeneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Force and Motion (Teacher)Document58 pagesChapter 2 Force and Motion (Teacher)Fahmi Ami100% (1)
- AnalysisDocument8 pagesAnalysisCatherine N. CapalosNo ratings yet
- E102 KinematicsDocument8 pagesE102 KinematicsKenneth PeraNo ratings yet
- Understanding How Pendulum Length Affects PeriodDocument52 pagesUnderstanding How Pendulum Length Affects PeriodSyafiq HazwanNo ratings yet
- MTM 1Document77 pagesMTM 1GowthamNo ratings yet
- Physics Experiments GuideDocument51 pagesPhysics Experiments GuideDulshan Dulshann67% (3)
- Muhammad Shahid Shafi, Jianhui Lu, Zhenpeng Song and Yingqun FuDocument7 pagesMuhammad Shahid Shafi, Jianhui Lu, Zhenpeng Song and Yingqun Fujeremytoh89No ratings yet
- Please Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierDocument11 pagesPlease Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierZoul HasleyNo ratings yet
- 7CL L-14, ExercisesDocument6 pages7CL L-14, ExercisesArish IzaanNo ratings yet
- CH - 13: Motion and TimeDocument14 pagesCH - 13: Motion and TimeDeepak KansalNo ratings yet
- مختبر الفيزياء الطبية - pendulumDocument6 pagesمختبر الفيزياء الطبية - pendulumm9ngmnsxp4No ratings yet
- Accelerated Uniform Rectilinear MotionDocument7 pagesAccelerated Uniform Rectilinear MotionYanuar Alfa100% (2)
- Pendulum Experiment - Determining GDocument3 pagesPendulum Experiment - Determining Ggeoff100% (1)
- AccelerationDocument13 pagesAccelerationJuhaida HabaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Linear and MotionDocument45 pagesChapter 2 Linear and MotionYoga RajNo ratings yet
- Practical 2.1: Determining The Acceleration of A TrolleyDocument1 pagePractical 2.1: Determining The Acceleration of A TrolleyMohammedNo ratings yet
- Physic Lab Report Exp.5 Simple Harmonic MotionDocument14 pagesPhysic Lab Report Exp.5 Simple Harmonic Motioniqmalaqish05No ratings yet
- 1.3 Determination of The Mass of Solid and Liquid Bodies 6.1 Uniform Motion in A Straight LineDocument9 pages1.3 Determination of The Mass of Solid and Liquid Bodies 6.1 Uniform Motion in A Straight LineAlmaykevin GallegosNo ratings yet
- Analyze Motion with Ticker TapeDocument3 pagesAnalyze Motion with Ticker TapeKiddozesNo ratings yet
- NOTES - MOTION AND TIME CLASS VIIsahfghfjfgjhfgDocument8 pagesNOTES - MOTION AND TIME CLASS VIIsahfghfjfgjhfgForex lolNo ratings yet
- Moment of Inertia LabDocument8 pagesMoment of Inertia Labill4565No ratings yet
- F4 ExperimentsDocument52 pagesF4 ExperimentsKiTTy94% (16)
- Mechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandMechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Applications of Derivatives Rate of Change (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Rate of Change (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Clock Cleaning and Repairing - With a Chapter on Adding Quarter-Chimes to a Grandfather ClockFrom EverandClock Cleaning and Repairing - With a Chapter on Adding Quarter-Chimes to a Grandfather ClockRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Selected Problems in Physics with AnswersFrom EverandSelected Problems in Physics with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- Enhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsFrom EverandEnhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reservoir Engineering in Modern Oilfields: Vertical, Deviated, Horizontal and Multilateral Well SystemsFrom EverandReservoir Engineering in Modern Oilfields: Vertical, Deviated, Horizontal and Multilateral Well SystemsNo ratings yet
- Understanding Modern Dive Computers and Operation: Protocols, Models, Tests, Data, Risk and ApplicationsFrom EverandUnderstanding Modern Dive Computers and Operation: Protocols, Models, Tests, Data, Risk and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Clock Repairing and Making - A Practical Handbook Dealing With The Tools, Materials and Methods Used in Cleaning and Repairing all Kinds of English and Foreign Timepieces, Striking and Chiming and the Making of English ClocksFrom EverandClock Repairing and Making - A Practical Handbook Dealing With The Tools, Materials and Methods Used in Cleaning and Repairing all Kinds of English and Foreign Timepieces, Striking and Chiming and the Making of English ClocksNo ratings yet