Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ITIL 2011 - The Big Picture v.2.0 - CFN People
Uploaded by
Christian Feldbech NissenOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ITIL 2011 - The Big Picture v.2.0 - CFN People
Uploaded by
Christian Feldbech NissenCopyright:
Available Formats
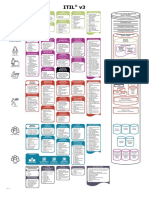
ITIL 2011 The big picture
Service lifecycle
Continual service improvement Service transition Service strategy
Customer Internal External
Service
Process
Business outcome
SLA
User
Metric
Value realized
Customer
Business Process Business Product Business Service
Service owner
Process owner
Metric
Metric
Metric
Metric
Metric
Process
Trigger Input Output
Service provider Utility - Fit for purpose
(Functionality) User requirement Customer-facing specification SERVICE Cost and price Business case (ROI / VOI)
Value added
Service value
Activity
Input Output
Warranty - Fit for use
(Availability, capacity, reliability, security, continuity, usability, compliance)
Service targets and levels Data People Application / Integration Processes Supporting services
Input
Service provider Internal Shared services unit External
Data, information and knowledge
Input Output
Activity
Output
Desired outcome
Money spent
Service assets
Service design
Service operation
Resources
Infrastructure Management
Activity
Role
OLA
Capabilities
Organization (Functions, roles) Knowledge Contract Supplier
Role Feedback
Service strategy
Determine perspective Form a position Craft and execute plans Adopt patterns of actions
Strategy management for IT services
Perform strategic assessment Generate strategy Execute strategy Measure and evaluate
Service portfolio management
Define Analyze Approve Charter
Financial management for IT services
Identify and track costs and income (Accounting) Budget Charge
Key documents
2 Vision and mission statements 2 Strategies, strategic and tactical plans and policies 2 Service requirements 2 Service charter 2 Service definitions, classification and visualization 2 Service models 2 Service packages 2 Option space 2 Cost model 2 Financial information and budgets 2 Business cases 2 Business impact analysis (BIA) 2 Patterns of business activity (PBAs) 2 User profiles (UPs) 2 Stakeholder definitions
Service knowledge management system (SKMS)
Key principles
Service management as a strategic asset Internal and external customers Internal and external services Core, enabling and enhancing services Value: Business outcomes, perceptions and preferences Functionality (utility), performance (warranty) and price Service packages Sourcing strategy Value networks
Demand management
Identify sources of demand forecasting Analyze and codify patterns of business activity (PBA) Match user profiles (UP) Manage activity-based demand Develop differentiated offerings (Service packages) Manage operational demand
Business relationship management
Handle requests Handle complaints Identify opportunities Manage business relationships throughout the service lifecycle
Presentation layer
Knowledge processing layer
Information integration layer
Service design
Plan and prepare Collect requirements Analyze Design Review and revise design Evaluate alternative solutions Procure and/or develop
Service catalogue management
Agree and document service definition and descritpion Agree service catalogue contents Produce and maintain service catalogue Interface with stakeholders
Availability management (Reactive and proactive)
Monitor, measure, analyze, report and review Investigate and instigate Assess and manage risk Implement countermeasures Plan and design Review and test
Information security management
Produce and maintain information security policy Implement security policy Assess and classify information assets and risks Impose and review security controls Monitor and manage security breaches and incidents Reduce security breaches Regularly assess, review and report security threats
Key documents
2 Service design policies and plans 2 Service acceptance criteria (SAC) and service level requirements (SLR) 2 Service definitions 2 Service catalogues 2 Service design package (SDP) 2 Solution designs 2 Architectures & standards 2 Processes 2 Measurement and metrics 2 Service level agreements (SLA), Contracts and operational level agreements (OLA) 2 Service reports 2 Service improvement plan (SIP) 2 Availability policy, plans, design criteria, risk analysis and reports 2 Capacity policy, plans, workload analysis, forecasts and reports 2 Business and IT service continuity policy, strategy, plans, risk and business impact analysis and reports 2 Business and information security policy, strategy, plans, risk analysis, classification, controls and reports 2 Supplier and contracts policy, strategy, plans and reports 2 RACI matrix
Service portfolio
Service catalogue views Business/customer service catalogue view Supporting service catalogue view
Service models
Key principles
Five aspects of holistic service design: v Service solutions for new or changed services v Management information systems and tools, especially the service portfolio v Technology architectures and management architectures v Processes v Measurement methods and metrics Balanced design: v Functionality v Resources v Schedule IT service design vs. business change The four Ps of service design: v People v Processes v Products (services,technology, tools) v Partners (suppliers, vendors) Service oriented architecture Design constraints Service delivery options and strategies
Service level management
Determine and agree requirements and make SLAs Monitor and report service performance Improve customer satisfaction Conduct service review Review and revise SLAs and underpinning agreements Develop relationships Maintain framework and templates
Capacity management (Business, service and component)
Pre-empt capacity issues Model and trend future needs Review current capacity Optimize/improve capacity Assess, agree and document requirements Plan new capacity
Design coordination
Overall: Define and maintain policies and methods Plan design resources and capabilities Coordinate design activities Manage design risks and issues Improve service design For each design: Plan individual designs Coordinate individual designs Monitor individual designs Review designs Handover service design packages
Service packages
Supplier management
Define requirements Evaluate suppliers/contracts Establish suppliers/contracts Manage performance Renew and/or terminate Categorize suppliers and maintain SCMIS
IT service continuity management
Initiate project Determine requirements and produce strategy Develop plans and implement strategy On going operation (Invoke the continuity plan)
Configuration management system (CMS)
Changes (Normal, standard and emergency changes) CMDB Releases (Release units and release packages)
Service transition
Plan and prepare Build and test Train and pilot Transfer, deploy, retire Review and close
Release and deployment management
Plan release and deployment Build and test release Deploy (deploy, transfer, retire) Provide early-life support Review and close
Service asset and configuration management
Manage and plan Identify configuration Control configuration Perform status accounting and reporting Verify and audit
Transition planning and support
Define transition strategy Define service transition lifecycle stages Prepare for service transition Plan and coordinate service transition Advice Provide administration Communicate Monitor and report progress
Key documents
2 Service transition strategies, policies, plans and budgets 2 Service packages 2 Service design package (SDP) 2 Service acceptance criteria (SAC) 2 SLAs, contracts and agreements 2 Change and configuration management policy, plans and reports 2 Change models 2 Requests for changes (RFC) and change records 2 Change schedules and plans 2 CAB agenda & minutes 2 Configuration models 2 Configuration baselines, status reports and audit reports 2 Release policies, plans, notes, packages and documentation 2 Service quality policy, risk policy, test strategy, test models, test plans, test reports and known errors 2 Build plans and documentation 2 Evaluation plans & reports 2 Deployment plans and reports 2 Service transition report 2 Knowledge management strategy
CMDB CMDB CMDB
Service requests Incidents
Key principles
Policies for service transition v Manage all changes through service transition v Common framework and standards v Re-use v Business driven transition v Stakeholder relationships v Effective controls and disciplines v Knowledge transfer v Release packages v Resource planning and management v Early involvement v Quality management and improvement Big bang vs. phased Push vs. pull Automation vs. manual Data-Information-Knowledge-Wisdom Managing people through service transitions
Change management
Create and record request for change (RFC) Review RFC Assess and evaluate change Authorize change build and test Coordinate change build and test Authorize change deployment Coordinate change deployment Review and close change record
Problems
Known error database (KEDB)
Service validation and testing
Manage validation and test Plan and design tests Verify test plan and test design Prepare test environment Perform tests Evaluate exit criteria and report Clean up test environments and close
Knowledge management
Define knowledge management strategy Transfer knowledge Manage data, information and knowledge Use the service knowledge management system (SKMS)
Service level agreements (SLAs)
Operational level agreements (OLAs)
Definitive media library (DML)
Change evaluation
Plan evaluation Evaluate predicted performance Evaluate actual performance
Supplier and contract management information system (SCMIS)
Key documents
2 Service operation policies and plans 2 Operational requirements 2 Event management policy, plans and reports 2 Incident management policy, plans and reports 2 Incident models 2 Major incident procedure 2 Request fulfillment policy, plans and reports 2 Request models 2 Problem management policy, plans and reports 2 Problem models 2 Information security policy, plans, classification, controls and reports 2 Processes 2 Technical documentation 2 Operational procedures and instructions 2 Functional documentation 2 User guides
Service operation
Monitor and control Manage services, components and activities Optimize Report
Request fulfillment
Receive request Log and validate request Categorize request Prioritize request Authorize request Review request Execute request model Close request
Access management
Request access Verify request Provide rights Check and monitor identity status Log and track access Remove or restrict rights
Event management
Generate event notification Detect event Log event Correlate and filter events (1st level) Categorize event Correlate events (2nd level) Select response Review actions Close event
Key principles
IT services vs. technology components Stability vs. responsiveness Quality vs. cost Reactive vs. proactive Involvemrnt in other service lifecycle stages Operational health Communication Documentation
Availability management information system (AMIS)
Capacity management information system (CMIS)
Security management information system (SMIS)
Incident management
Identify incident Log incident Categorize incident Prioritize incident Perform initial diagnosis Escalate incident Investigate and diagnose incident Resolve and recover incident Close incident
Problem management
Detect problem Log problem Categorize problem Prioritize problem Investigate and diagnose problem Find a workaround Raise a known error Resolve problem Close problem Review major problem
Common service operation activities
Monitor and control IT operations v Console management v Job scheduling v Backup and restore v Print and output management Facilities and data centre Technology v Mainframe v Server v Network v Storage and archive v Database v Directory services v Desktop v Mobile devices v Middleware v Internet/Web
Standard operating procedures (SOPs)
Events
Technical documentation
Access rights
Functions
Strategies, policies and plans
Reports
CSI register
Service desk
IT operations management
Technical management
Application management Common improvement techniques
Continual service improvement
Plan Do Check Act
Seven-step improvement process
1. Identify the strategy for improvement 2. Define what you will measure 3. Gather data 4. Process data 5. Analyze information and data 6. Present and use information 7. Implement improvement
Key documents
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Continual service improvement policies and plans Corporate and IT vision, mission, goals and objectives Critical success factors (CSFs) Key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics and achievements Service level targets and achievements Balanced scorecard Service improvement plans (SIPs) Business cases Reporting policies and rules Reports and dashboards
Key principles
Continual service improvement approach Organizational change Ownership, roles, and responsibilities Knowledge management Service measurement IT governance
Assessment Gap analysis Benchmarking Service measurement Metrics and scorecards Service reporting SWOT Return on investment
Ver. 2.0
2012, CFN People A/S. Based on Cabinet Office ITIL material. ITIL is a registered trade mark of the Cabinet Office
( +45 40 19 14 64 * info@cfnpeople.com : www.cfnpeople.com
You might also like
- Future Business Requirements A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandFuture Business Requirements A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- CHART v.2.0 - ITSM - DRUCK PDFDocument1 pageCHART v.2.0 - ITSM - DRUCK PDFamirel80No ratings yet
- Global Job Title: Job Family: Location: Reporting To: GradeDocument4 pagesGlobal Job Title: Job Family: Location: Reporting To: GradeAngel ZurumucapioNo ratings yet
- ITIL Specialist CDS Brochure PDFDocument2 pagesITIL Specialist CDS Brochure PDFEugene Arkadiev0% (1)
- ITIL v3 CSI Sample Questions2Document35 pagesITIL v3 CSI Sample Questions2kultiwett100% (1)
- One Pager For PMDocument1 pageOne Pager For PMAdeel Khan LeghariNo ratings yet
- ITIL V3 Foundation Handbook IntroductionDocument11 pagesITIL V3 Foundation Handbook Introductionmadinewala100% (1)
- AgilePM and APM NotesDocument47 pagesAgilePM and APM NotesElliott O'BrartNo ratings yet
- Rock Star Service CatalogueDocument3 pagesRock Star Service Cataloguebob panic0% (1)
- Ba Project Checklist PDFDocument2 pagesBa Project Checklist PDFRiaNo ratings yet
- ITSM Training Module FinalDocument45 pagesITSM Training Module FinalBushra AlbalushiaNo ratings yet
- Forrester Service Catalog 2013 PDFDocument23 pagesForrester Service Catalog 2013 PDFenergitixNo ratings yet
- Ola Template FinalDocument8 pagesOla Template FinalBen MeijerNo ratings yet
- ITIL V3 Foundation Overview PDFDocument5 pagesITIL V3 Foundation Overview PDFYogesh2323No ratings yet
- ITIL V3 Foundation Handbook ContentsDocument2 pagesITIL V3 Foundation Handbook ContentsmadinewalaNo ratings yet
- Business Analysis Training Program Course ContentDocument2 pagesBusiness Analysis Training Program Course ContentSushil PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- What Is IT Service Management - ITIL - AXELOSDocument4 pagesWhat Is IT Service Management - ITIL - AXELOSaliNo ratings yet
- A Survey of Information Technology GoverDocument27 pagesA Survey of Information Technology GoverLeo CerenoNo ratings yet
- CS011A Career Investigation Project InteractiveDocument11 pagesCS011A Career Investigation Project Interactivejazz440No ratings yet
- Business Analyst Online TrainingDocument2 pagesBusiness Analyst Online TrainingTanishsadan ANo ratings yet
- Itl9340cl-B V3.intermediate - Malc SH Refmat E-Read Single v1.0 ItpDocument878 pagesItl9340cl-B V3.intermediate - Malc SH Refmat E-Read Single v1.0 Itprojalin dasNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesMarketing Plan TemplatePao EspiNo ratings yet
- ITSM Excellence With Proven Training From The Industry LeaderDocument4 pagesITSM Excellence With Proven Training From The Industry LeadermeetacooldudeNo ratings yet
- Process Improvement Calculations ToolsDocument65 pagesProcess Improvement Calculations ToolsNevets Nonnac100% (1)
- Portfolio ManagemantDocument16 pagesPortfolio ManagemantShubham KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Itil® 4 Specialist: High-Velocity It Elearning Course: AudienceDocument3 pagesItil® 4 Specialist: High-Velocity It Elearning Course: AudienceEugene ArkadievNo ratings yet
- IT Governance - Performance Measures FinalDocument34 pagesIT Governance - Performance Measures FinalYuvi RajhaNo ratings yet
- The University of Oxford and Itil Case StudyDocument5 pagesThe University of Oxford and Itil Case StudylinamewsNo ratings yet
- Benefits Management RaghuBandreddiDocument11 pagesBenefits Management RaghuBandreddiAkhil Bandreddi100% (1)
- FrameworkDocument70 pagesFrameworkpaulaNo ratings yet
- Itil Capacity Management More Than Charts Over CoffeeDocument16 pagesItil Capacity Management More Than Charts Over CoffeeAhmed M. EzzatNo ratings yet
- ITIL Intermediate Capability RCVSample2 QUESTION BOOKLET v6.1Document9 pagesITIL Intermediate Capability RCVSample2 QUESTION BOOKLET v6.1Lucas Schimit0% (1)
- ITIL Service Operation Ver-1.2Document43 pagesITIL Service Operation Ver-1.2InvensislearningNo ratings yet
- 6 SLA Best Practices For Service Management SuccessDocument8 pages6 SLA Best Practices For Service Management SuccesssaitNo ratings yet
- ITIL v3 Sample Exams & AnswersDocument30 pagesITIL v3 Sample Exams & AnswersAila AliongoNo ratings yet
- ITSM Structure and RolesDocument12 pagesITSM Structure and RolesAno_NimskaNo ratings yet
- Trend AnalysisDocument5 pagesTrend AnalysisvijayskbNo ratings yet
- 5 Steps To Defining IT Services - A Hands On WorkbookDocument13 pages5 Steps To Defining IT Services - A Hands On WorkbookEdho ArmandoNo ratings yet
- SDLC Phase 04 Requirements Analysis Phase Multiple HardwareDocument14 pagesSDLC Phase 04 Requirements Analysis Phase Multiple HardwareAnita DickersonNo ratings yet
- ITIL 2011 FoundationsDocument245 pagesITIL 2011 FoundationsRicardo Adrian FedericoNo ratings yet
- Business Analyst Change Management in North NJ Resume Lana GropenDocument3 pagesBusiness Analyst Change Management in North NJ Resume Lana GropenLanaGropenNo ratings yet
- ITIL - Service Validation and TestingDocument17 pagesITIL - Service Validation and TestingFederico MarzulloNo ratings yet
- Agile ITIL Integration White PaperDocument11 pagesAgile ITIL Integration White PaperIqbalurNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Service Integration in A Multiprovider Environment Using COBIT 5Document9 pagesImplementation of Service Integration in A Multiprovider Environment Using COBIT 5hdoornboNo ratings yet
- ITIL v3 Poster 1Document1 pageITIL v3 Poster 1Andrea GiulianiNo ratings yet
- ITIL - Session 01 - ITIL QualificationDocument17 pagesITIL - Session 01 - ITIL QualificationAhmad Abdul HaqNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 2 - V6.1 - Scenario BookletDocument9 pagesSample Paper 2 - V6.1 - Scenario BookletMaheish AyyerNo ratings yet
- Introduction Itil Process MapDocument34 pagesIntroduction Itil Process MapJosé Luis Navarro PérezNo ratings yet
- 08a FX03 M o R Practitioner Sample Paper v1.3 - QuestionsDocument33 pages08a FX03 M o R Practitioner Sample Paper v1.3 - QuestionsrncsterNo ratings yet
- 02 Fundamentals of Business AnalysisDocument21 pages02 Fundamentals of Business AnalysisNInaAntalkNo ratings yet
- ITIL4FEN Practices v1.1Document42 pagesITIL4FEN Practices v1.1Wilfried Foalem100% (1)
- En - requirements-ElicitationTechniques (Compatibility Mode)Document30 pagesEn - requirements-ElicitationTechniques (Compatibility Mode)nmhuong90No ratings yet
- Itil and TOGAF 9.1: Two Frameworks: Tom Van Sante and Jeroen Ermers, KPN IT SolutionsDocument12 pagesItil and TOGAF 9.1: Two Frameworks: Tom Van Sante and Jeroen Ermers, KPN IT Solutionsarvind ronNo ratings yet
- ITIL AwarenessDocument17 pagesITIL AwarenessKedar TamhankarNo ratings yet
- ITIL Service DeliveryDocument1 pageITIL Service DeliverygringoricanNo ratings yet
- Itil 2011 Process ModelDocument1 pageItil 2011 Process ModelAlexandru Dan GheorghiuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - ITIL Management PracticesDocument90 pagesLesson 6 - ITIL Management PracticesAlahor DelPubgNo ratings yet
- PID TemplateDocument25 pagesPID TemplateFreedomFreedomNo ratings yet
- Change And Release Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandChange And Release Management A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- A Day in The Life of A Shipbroker - Shipping and Freight ResourceDocument5 pagesA Day in The Life of A Shipbroker - Shipping and Freight ResourcetaufiqNo ratings yet
- Technology in BankingDocument92 pagesTechnology in BankingJason Amaral100% (2)
- IGCSE Accounting O Level p1 Answers PDFDocument17 pagesIGCSE Accounting O Level p1 Answers PDFNusaibah AssyifaNo ratings yet
- Cross Rates - August 23 2018Document1 pageCross Rates - August 23 2018Tiso Blackstar GroupNo ratings yet
- CH 4 In-Class Exercise 2 (Solutions)Document3 pagesCH 4 In-Class Exercise 2 (Solutions)Zenni T XinNo ratings yet
- Assured Savings Plan 1Document12 pagesAssured Savings Plan 1DnGNo ratings yet
- Certified Valuation Analyst-CVADocument4 pagesCertified Valuation Analyst-CVAamyhashemNo ratings yet
- Submitted By:: Mohi Ud Din Islamic University Neraian Sharif (Ajk)Document4 pagesSubmitted By:: Mohi Ud Din Islamic University Neraian Sharif (Ajk)banthNo ratings yet
- FWD TimelineDocument11 pagesFWD TimelineNhizza Dawn Aleria-Daligdig TuburanNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement (Tanzil Khan - 14-97982-2)Document3 pagesAcknowledgement (Tanzil Khan - 14-97982-2)Md. Saiful IslamNo ratings yet
- ISBP745 International Standard Banking PracticeDocument74 pagesISBP745 International Standard Banking PracticeMahendar Weezyholic Bist100% (1)
- Bcom ProjectDocument76 pagesBcom ProjectVictor Muto100% (1)
- Rohan Dhall: Career SummaryDocument5 pagesRohan Dhall: Career SummarySudhir Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Loan Disbursement and Recovery Procedures of BKBDocument10 pagesLoan Disbursement and Recovery Procedures of BKBFarhanChowdhuryMehdiNo ratings yet
- CRISIL Certificate Programme On Working Capital Appraisal and Monitoring Sept 2017Document4 pagesCRISIL Certificate Programme On Working Capital Appraisal and Monitoring Sept 2017rooptejaNo ratings yet
- BCD 4 Design and Build With Schedule of Contract AmendmentsDocument45 pagesBCD 4 Design and Build With Schedule of Contract AmendmentstsuakNo ratings yet
- Report On Recruitment of Life Advisors Bharti AXADocument84 pagesReport On Recruitment of Life Advisors Bharti AXAmegha140190No ratings yet
- Comprehension Questions: 1. What Are Minimum Lease Payments'?Document13 pagesComprehension Questions: 1. What Are Minimum Lease Payments'?Amit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Notice Inviting Tender (Nit) : (Bidding Document No. TP/068107C001/T/BS-IV/16)Document9 pagesNotice Inviting Tender (Nit) : (Bidding Document No. TP/068107C001/T/BS-IV/16)amitjustamitNo ratings yet
- HowTo TDS 88 India in SAP B1Document89 pagesHowTo TDS 88 India in SAP B1Satish Prabhakar DokeNo ratings yet
- Claimspaid 2021Document72 pagesClaimspaid 2021sNo ratings yet
- Renewal Notice: Policy No.P/141126/01/2019/003982Document1 pageRenewal Notice: Policy No.P/141126/01/2019/003982manoharNo ratings yet
- Banker's Lien: in The Creditor and Debtor Relationship Between The Banker andDocument30 pagesBanker's Lien: in The Creditor and Debtor Relationship Between The Banker andzviyedzo chimwaraNo ratings yet
- CSP Vendor Maintenance FormDocument4 pagesCSP Vendor Maintenance FormKurt FinkNo ratings yet
- 1307174808status of Microfinance in India 2016-17Document278 pages1307174808status of Microfinance in India 2016-17Om PrakashNo ratings yet
- General Ledger 3 ColmDocument2 pagesGeneral Ledger 3 ColmMary100% (7)
- Document 21649Document104 pagesDocument 21649Shalini CharuNo ratings yet
- Ketan Parekh ScamDocument10 pagesKetan Parekh ScamTusharNo ratings yet
- English - RESOLUTION - CASH FUND USAGE NEWS EVENTDocument4 pagesEnglish - RESOLUTION - CASH FUND USAGE NEWS EVENTUN Swissindo100% (3)