Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alkane Alkeneproperties
Uploaded by
Naguib ZakariaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alkane Alkeneproperties
Uploaded by
Naguib ZakariaCopyright:
Available Formats
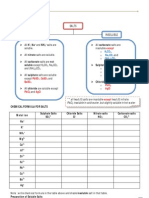
COMPARISON TABLE BETWEEN ALKANE AND ALKENE ALKANE ALKANE
Known as SATURATED HYDROCARBON because all carbon are bonded by single covalent bond
PROPERTIES OF HYDROCARBON
HOMOLOGOUS NAME GENERAL FORMULA PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
ALKENE ALKENE
Known as UNSATURATED HYDROCARBON because contains at least one double covalent bond between carbon atoms.
CnH2n + 2 , n =1, 2, 3 .
CnH2n , n = 2, 3, 4 .
Insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvent
Insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvent
Cannot conduct electricity in all state (solid or molten) Alkane cannot conduct electricity in solid or molten state because its in neutral molecule form Low melting and boiling point Alkane has a low melting and boiling point because molecules of alkane are bonded together with weak intermolecular forces (Van de Waals), so less energy is needed to overcome that forces. Less dense than water Alkane float on the water when mix with water **Physical properties of hydrocarbon is similar to physical properties of covalent compound.
Cannot conduct electricity in all state (solid or molten) Alkene cannot conduct electricity in solid or molten state because its in neutral molecule form Low melting and boiling point Alkene has a low melting and boiling point because molecules of alkene are bonded together with weak intermolecular forces (Van de Waals), so less energy is needed to overcome that forces. Less dense than water Alkene float on the water when mix with water
::MNZ http://chemclass4spm.blogspot.com::
COMPARISON TABLE BETWEEN ALKANE AND ALKENE ALKANE
Combustion process Alkane undergo complete combustion to produce CO2 and H2O CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O
PROPERTIES OF HYDROCARBON CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
COMBUSTION
**All hydrocarbon when burnt in excess of oxygen will produce Carbon dioxide(CO2) and Water(H2O). If incomplete combustion occurs (not enough oxygen) Carbon monoxide(CO) will produce.
ALKENE
Combustion process Alkene undergo complete combustion to produce CO2 and H2O C2H4 + 3O2 2CO2 + 2H2O Addition of HYDROGEN (HYDROGENATION) Alkene react with HYDROGEN (at 180 oC and presence a Nickel / Platinum as catalyst) C2H4 + H2 C2H6 (Temp 180 oC and Ni/Pt as catalyst) Addition of HALOGEN (HALOGENATION) Alkene react with HALOGEN (Cl2, Br2 or I2) C2H4 + Br2 C2H4Br2 Addition of HYDROGEN HALIDE (HCl or HBr) Alkene react with HYDROGEN HALIDE (HCl or HBr) C2H4 + HBr C2H5Br Addition of ACIDIFIED POTASSIUM MANGANATE (VII) (KMnO4) Alkene react with KMnO4 acidified C2H4 + H2O + [O] C2H4(OH)2 Addition of WATER (Hydration Reaction) Alkene react with WATER(gas) (300oC, 1atm and H3PO4 as a catalyst) C2H4 + H2O C2H5OH
Substitution process Occurs when alkane mix with halogen with presence of UV (sunlight) Each Hydrogen atom is substituted one by one by halogen atom. CH4 + Br2 CH3Br + HBr
::MNZ http://chemclass4spm.blogspot.com::
HOW TO DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN ALKANE AND ALKENE
REACTION ALKANE
Burnt in excess of oxygen to produce LESS SOOTY YELLOW FLAME Explanation C6H14 (Hexane) contains low percentage of carbon % of carbon = 83.7% ALKANE produce less sooty flame than ALKENE because percentage of carbon is higher in ALKENE than ALKANE
ALKENE
Burnt in excess of oxygen to produce MORE SOOTY YELLOW FLAME Explanation C6H12 (Hexene) contains low percentage of carbon % of carbon = 85.7% ALKENE produce more sooty flame than ALKANE because percentage of carbon is higher in ALKENE than ALKANE Observation: Brown colour of Bromine decolourised (change to colourless). Explanation: Alkene react with Bromine to produce bromoalkane
COMBUSTION
** Combustion of Hydrocarbon produced yellow with sooty flame.
ADDITION REACTION WITH BROMINE WATER
i. ii. iii. iv. 1 cm of Bromine is added into test tube 2 cm3 of alkane/alkene into the same test tube Shaken mixture gently Observe the changes
3
Observation: Brown colour of Bromine remains unchanged. Explanation: Alkane does not react with halogen. The reaction can be occurs with presence of UV
ADDITION REACTION WITH KMNO4 acidified
i. ii. iii. iv. 1 cm of KMNO4 acidified (using H2SO4) is added Observation: Purple colour of KMNO4 acidified remains unchanged. into test tube 2 cm3 of alkane/alkene into the same test tube Explanation: Alkane does not react with KMNO4 acidified. Shaken mixture gently Observe the changes
3
Observation: Brown colour of KMNO4 acidified decolourised (change to colourless). Explanation: Alkene react with KMNO4 acidified to produce diol compound
**ALKANES are chemically UNREACTIVE compound because ALKANES are SATURATED compound, but ALKENES are REACTIVE compound because they are UNSATURATED compound.
::MNZ http://chemclass4spm.blogspot.com::
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Chemical Bonding Assignment 2 AnswersDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding Assignment 2 AnswersdarylchenNo ratings yet
- Inorganic ChemistryDocument194 pagesInorganic ChemistryClarice Jenn Ramirez Malto67% (3)
- Test Bank For Microbiology An Introduction 12th Edition Tortora Funke CaseDocument14 pagesTest Bank For Microbiology An Introduction 12th Edition Tortora Funke Caseshriekacericg31u3100% (40)
- Gerald Pollack - WaterDocument44 pagesGerald Pollack - Watercrisolaris100% (6)
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure PDFDocument56 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure PDFAbhishek AgrahariNo ratings yet
- How To Solve Electrochemistry ProblemDocument1 pageHow To Solve Electrochemistry ProblemNaguib Zakaria67% (3)
- Periodic Table: Answering GuideDocument1 pagePeriodic Table: Answering GuideNaguib ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Glossary SPM ChemistryDocument6 pagesGlossary SPM ChemistryMus Staqim BesutNo ratings yet
- KIMIA K1 Trial 2008Document26 pagesKIMIA K1 Trial 2008Naguib ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Peka F5 1Document4 pagesPeka F5 1Naguib Zakaria88% (8)
- Rate of Reaction & Hydrocarbon Chemistry Form 5 Monthly Test 2-2010 1 Hour Test Form 5Document6 pagesRate of Reaction & Hydrocarbon Chemistry Form 5 Monthly Test 2-2010 1 Hour Test Form 5Naguib ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry TestDocument7 pagesElectrochemistry TestNaguib Zakaria100% (1)
- Periodic TableDocument2 pagesPeriodic TableNaguib Zakaria100% (1)
- Emperical Formula and Molecular FormulaDocument4 pagesEmperical Formula and Molecular FormulaNaguib Zakaria100% (1)
- Peka Form 5 2 (Exp No 1.3)Document3 pagesPeka Form 5 2 (Exp No 1.3)Naguib Zakaria100% (4)
- Rate of Reaction & Hydrocarbon Chemistry Form 5 Monthly Test 2-2010 1 Hour Test Form 5Document6 pagesRate of Reaction & Hydrocarbon Chemistry Form 5 Monthly Test 2-2010 1 Hour Test Form 5Naguib ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Revision: SMK Tunku Ampuan Najihah Chemistry Form 4 Monthly Test 3-2010 1 Hour Test Form 4Document7 pagesElectrochemistry Revision: SMK Tunku Ampuan Najihah Chemistry Form 4 Monthly Test 3-2010 1 Hour Test Form 4Naguib ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Mole ConceptDocument1 pageMole ConceptNaguib Zakaria67% (3)
- Rate of Reaction SMK Tunku Ampuan NajihahDocument8 pagesRate of Reaction SMK Tunku Ampuan NajihahNaguib ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Test 1 F4Document7 pagesTest 1 F4Naguib ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chap3 Form 4Document1 pageExercise Chap3 Form 4Naguib ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Chap 8: SaltDocument2 pagesChap 8: SaltNaguib Zakaria100% (1)
- Rateof Reaction Part 2Document5 pagesRateof Reaction Part 2Naguib ZakariaNo ratings yet
- CHAP8 Manufactured IndustryDocument12 pagesCHAP8 Manufactured IndustryNaguib Zakaria100% (2)
- Matter Part 2Document4 pagesMatter Part 2Naguib ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Map ReactionDocument1 pageMap ReactionNaguib Zakaria100% (1)
- Chap 8 Part 1Document4 pagesChap 8 Part 1Naguib ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Matter Part 1Document4 pagesMatter Part 1Naguib ZakariaNo ratings yet
- 3.0 POLYMER Learning Outcome Student Ables To State The MeaningDocument2 pages3.0 POLYMER Learning Outcome Student Ables To State The MeaningNaguib Zakaria100% (1)
- Chap 8 Part 2Document3 pagesChap 8 Part 2Naguib ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Saltpg 1Document1 pageSaltpg 1Naguib ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry NoteDocument3 pagesElectrochemistry NoteNaguib Zakaria100% (3)
- Engg. Chemistry I PPT, GD, Case Study Topics Div-Data ScienceDocument11 pagesEngg. Chemistry I PPT, GD, Case Study Topics Div-Data ScienceUday BhartiyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Basbvbms of Pharmacology An Introduction To Pharmacodynamics 1000160027Document394 pagesChemical Basbvbms of Pharmacology An Introduction To Pharmacodynamics 1000160027Andres ZareNo ratings yet
- Biological Roles of Water - Why Is Water Necessary For Life - Science in The NewsDocument17 pagesBiological Roles of Water - Why Is Water Necessary For Life - Science in The NewsJoel SteveNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy TutorialDocument12 pagesSpectroscopy TutorialPratyush RanjanNo ratings yet
- 04 Organic ChemistryDocument17 pages04 Organic ChemistrysandeepNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding: Organic Chemistry, 6e (Smith)Document34 pagesChapter 1 Structure and Bonding: Organic Chemistry, 6e (Smith)Rahma AshrafNo ratings yet
- National Power Training Institute, Badarpur Syllabus of All SemestersDocument112 pagesNational Power Training Institute, Badarpur Syllabus of All SemestersVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Perera CHEM 151 F21 Sec006 0910Document10 pagesPerera CHEM 151 F21 Sec006 0910eortiz6131No ratings yet
- Sirius-4 4 29-Manual PDFDocument49 pagesSirius-4 4 29-Manual PDFJovanderson JacksonNo ratings yet
- Mole Concept AssignmentDocument4 pagesMole Concept AssignmentRoNNo ratings yet
- The Mechanism For The Esterification ReactionDocument5 pagesThe Mechanism For The Esterification Reactionuocmogiandi_aNo ratings yet
- The Nature of ConsciousnessDocument26 pagesThe Nature of Consciousnessapi-3702097No ratings yet
- Perfect Score Chemistry SBP 2012 - ModuleDocument98 pagesPerfect Score Chemistry SBP 2012 - ModuleAhmad RawiNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - ComplexationDocument48 pagesTopic 2 - ComplexationLokesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Stalagmites and Stalactites Are Composed of Ionic Compounds Calcium Carbonate and Magnesium CarbonateDocument50 pagesStalagmites and Stalactites Are Composed of Ionic Compounds Calcium Carbonate and Magnesium CarbonateAustin GirardNo ratings yet
- Vlits Chemistry SyllabusDocument35 pagesVlits Chemistry Syllabusdola indupriyaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Particles: Small Portion of Matter Molecules Atoms IonsDocument5 pagesChemistry Particles: Small Portion of Matter Molecules Atoms IonsMark Vincent OrdizNo ratings yet
- Density Functional TheoryDocument21 pagesDensity Functional TheoryDian KurniawatiNo ratings yet
- CHEM 749 "Computational Chemistry"Document3 pagesCHEM 749 "Computational Chemistry"BharatNo ratings yet
- Journal of Baltic Science Education, Vol. 16, No. 2, 2017Document141 pagesJournal of Baltic Science Education, Vol. 16, No. 2, 2017Scientia Socialis, Ltd.No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Full Chm556 2018Document206 pagesChapter 1 Full Chm556 2018Sabrina100% (1)
- CHE-01 Assignment 2021 (English)Document4 pagesCHE-01 Assignment 2021 (English)pranay mondalNo ratings yet
- S3 Materials SCIENCE 1Document12 pagesS3 Materials SCIENCE 1sbmpagiNo ratings yet
- 9702 p1 Properties of Matter AllDocument8 pages9702 p1 Properties of Matter AllNushanKhanNo ratings yet
- 1 The Mole ConceptDocument20 pages1 The Mole ConceptAlliyah Cecilio AndreaNo ratings yet