Professional Documents
Culture Documents
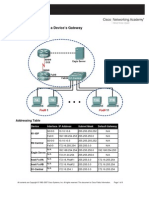
Lab 5.5.1: Examining A Device's Gateway: Topology Diagram
Uploaded by
Sergiy KalmukOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 5.5.1: Examining A Device's Gateway: Topology Diagram
Uploaded by
Sergiy KalmukCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab 5.5.
1: Examining a Devices Gateway
Topology Diagram
Addressing Table
Device R1-ISP Interface IP Address S0/0/0 Fa0/0 R2-Central S0/0/0 Fa0/0 N/A Eagle Server hostPod#A hostPod#B S1-Central N/A N/A N/A N/A 10.10.10.6 Subnet Mask Default Gateway
255.255.255.252 N/A N/A
192.168.254.253 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.5 172.16.255.254
255.255.255.252 10.10.10.6 255.255.0.0 N/A 192.168.254.253 N/A 172.16.255.254 172.16.255.254 172.16.255.254
192.168.254.254 255.255.255.0 172.31.24.254 172.16.Pod#.1 172.16.Pod#.2 172.16.254.1 255.255.255.0 255.255.0.0 255.255.0.0 255.255.0.0
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 1 of 8
CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals: OSI Network Layer
Lab 5.5.1: Examining a Devices Gateway
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to: Understand and explain the purpose of a gateway address. Understand how network information is configured on a Windows computer. Troubleshoot a hidden gateway address problem.
Background
An IP address is composed of a network portion and a host portion. A computer that communicates with another device must first know how to reach the device. For devices on the same local area network (LAN), the host portion of the IP address is used as the identifier. The network portion of the destination device is the same as the network portion of the host device. However, devices on different networks have different source and destination network numbers. The network portion of the IP address is used to identify when a packet must be sent to a gateway address, which is assigned to a network device that forwards packets between distant networks. A router is assigned the gateway address for all the devices on the LAN. One purpose of a router is to serve as an entry point for packets coming into the network and exit point for packets leaving the network. Gateway addresses are very important to users. Cisco estimates that 80 percent of network traffic will be destined to devices on other networks, and only 20 percent of network traffic will go to local devices. This is called the 80/20 rule. Therefore, if a gateway cannot be reached by the LAN devices, users will not be able to perform their job.
Scenario
Pod host computers must communicate with Eagle Server, but Eagle Server is located on a different network. If the pod host computer gateway address is not configured properly, connectivity with Eagle Server will fail. Using several common utilities, network configuration on a pod host computer will be verified.
Task 1: Understand and Explain the Purpose of a Gateway Address.
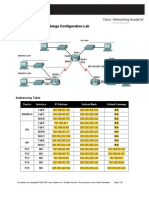
Figure 1. Communication Between LAN Devices For local area network (LAN) traffic, the gateway address is the address of the Ethernet device. Figure 1 shows two devices on the same network communicating with the ping command. Any device that has the same network addressin this example, 172.16.0.0is on the same LAN.
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 2 of 8
CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals: OSI Network Layer
Lab 5.5.1: Examining a Devices Gateway
Referring to Figure 1, what is the MAC address of the network device on IP address 172.16.1.1?
____________________________________________________________________________
There are several Windows commands that will display a network gateway address. One popular command is netstat r. In the following transcript, the netstat r command is used to view the gateway addresses for this computer. The top highlight shows what gateway address is used to forward all network packets destined outside of the LAN. The quad-zero Network Destination and Netmask values, 0.0.0.0 and 0.0.0.0, refer to any network not specifically known. For any non-local network, this computer will use 172.16.255.254 as the default gateway. The second yellow highlight displays the information in human-readable form. More specific networks are reached through other gateway addresses. A local interface, called the loopback interface, is automatically assigned to the 127.0.0.0 network. This interface is used to identify the local host to local network services. Refer to the gray highlighted entry. Finally, any device on network 172.16.0.0 is accessed through gateway 172.16.1.2, the IP address for this Ethernet interface. This entry is highlighted in green. C:\>netstat r Route Table ======================================================================= Interface List 0x1 ......................... MS TCP Loopback interface 0x20005 ...00 16 76 ac a7 6a Intel(R) 82562V 10/100 Network Connection ======================================================================= ======================================================================= Active Routes: Network Destination Netmask Gateway Interface Metric 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.255.254 172.16.1.2 1 127.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 127.0.0.1 127.0.0.1 1 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 172.16.1.2 172.16.1.2 20 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.255 127.0.0.1 127.0.0.1 20 172.16.255.255 255.255.255.255 172.16.1.2 172.16.1.2 20 255.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 172.16.1.2 172.16.1.2 1 Default Gateway: 172.16.255.254 ======================================================================= Persistent Routes: None C:\>
Step 1: Open a terminal window on a pod host computer. What is the default gateway address?
____________________________________________________________________________
Step 2: Use the ping command to verify connectivity with IP address 127.0.0.1. Was the ping successful? __________
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 3 of 8
CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals: OSI Network Layer
Lab 5.5.1: Examining a Devices Gateway
Step 3: Use the ping command to ping different IP addresses on the 127.0.0.0 network, 127.10.1.1, and 127.255.255.255. Were responses successful? If not, why?
____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________
A default gateway address permits a network device to communicate with other devices on different networks. In essence, it is the door to other networks. All traffic destined to different networks must go through the network device that has the default gateway address.
Figure 2. Communication Between Devices on Different Networks As shown in Figure 2, communication between devices on different networks is different than on a LAN. Pod host computer #2, IP address 172.16.1.2, initiates a ping to IP address 192.168.254.254. Because network 172.16.0.0 is different from 192.168.254.0, the pod host computer requests the MAC address of the default gateway device. This gateway device, a router, responds with its MAC address. The computer composes the Layer 2 header with the destination MAC address of the router and places frames on the wire to the gateway device. Referring to Figure 2, what is the MAC address of the gateway device?
____________________________________________________________________________
Referring to Figure 2, what is the MAC address of the network device with IP address 192.168.254.254?
____________________________________________________________________________
Task 2: Understand how Network Information is Configured on a Windows Computer.
Many times connectivity issues are attributed to wrong network settings. In troubleshooting connectivity issues, several tools are available to quickly determine the network configuration for any Windows computer.
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 4 of 8
CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals: OSI Network Layer
Lab 5.5.1: Examining a Devices Gateway
Figure 3. Network Interface with Static IP Address Step 1: Examine network properties settings. One method that may be useful in determining the network interface IP properties is to examine the pod host computers Network Properties settings. To access this window: 1. Click Start > Control Panel > Network Connections. 2. Right-click Local Area Connection, and choose Properties. 3. On the General tab, scroll down the list of items in the pane, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and click the Properties button. A window similar to the one in Figure 3 will be displayed.
Figure 4. Network Interface with Dynamic IP Address However, a dynamic IP address may be configured, as shown in Figure 4. In this case, the Network Properties settings window is not very useful for determining IP address information.
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 5 of 8
CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals: OSI Network Layer
Lab 5.5.1: Examining a Devices Gateway
A more consistently reliable method for determining network settings on a Windows computer is to use the ipconfig command:
IP address for this pod host computer Subnet mask Default gateway address There are several options available with the ipconfig command, accessible with the command ipconfig /?. To show the most information about the network connections, use the command ipconfig /all.
Domain name server IP address
Step 2: Using the command ipconfig /all, fill in the following table with information from your pod host computer: Description IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway DNS Server Address
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 6 of 8
CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals: OSI Network Layer
Lab 5.5.1: Examining a Devices Gateway
Task 3: Troubleshoot a Hidden Gateway Address Problem.
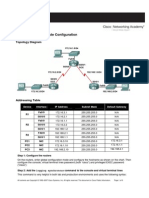
Figure 5. Topology Diagram
Device R1-ISP
Interface IP Address S0/0/0 Fa0/0 10.10.10.4
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
255.255.255.252 N/A N/A
192.168.254.253 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.3 172.16.255.254
R2-Central
S0/0/0 Fa0/0 N/A
255.255.255.252 10.10.10.4 255.255.0.0 N/A 192.168.254.253 N/A 172.16.255.254 172.16.255.254 172.16.255.254
Eagle Server hostPod#A hostPod#B S1-Central
192.168.254.254 255.255.255.0 172.31.24.254 172.16.Pod#.1 172.16.Pod#.2 172.16.254.1 255.255.255.0 255.255.0.0 255.255.0.0 255.255.0.0
N/A N/A N/A N/A
Table 1. Logical Address Assignments When troubleshooting network issues, a thorough understanding of the network can often assist in identifying the real problem. Refer to the network topology in Figure 5 and the logical IP address assignments in Table 1.
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 7 of 8
CCNA Exploration Network Fundamentals: OSI Network Layer
Lab 5.5.1: Examining a Devices Gateway
As the 3rd shift help desk Cisco engineer, you are asked for assistance from the help desk technician. The technician received a trouble ticket from a user on computer host-1A, complaining that computer host-11B, host-11B.example.com, does not respond to pings. The technician verified the cables and network settings on both computers, but nothing unusual was found. You check with the corporate network engineer, who reports that R2-Central has been temporarily brought down for a hardware upgrade. Nodding your head in understanding, you ask the technician to ping the IP address for host-11B, 172.16.11.2 from host-1A. The pings are successful. Then, you ask the technician to ping the gateway IP address, 172.16.254.254, and the pings fail. What is wrong?
____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________
You instruct the help desk technician to tell the user to use the IP address for host-11B temporarily, and the user is able to establish connectivity with the computer. Within the hour the gateway router is back on line, and normal network operation resumes.
Task 4: Reflection
A gateway address is critical to network connectivity, and in some instances LAN devices require a default gateway to communicate with other devices on the LAN. Using Windows command line utilities such as netstat r and ipconfig /all will report gateway settings on host computers.
Task 5: Challenge
Use Wireshark to capture a ping between two pod host computers. It may be necessary to restart the host computer to flush the DNS cache. First, use the hostname of the destination pod computer for DNS to reply with the destination IP address. Observe the communication sequence between network devices, especially the gateway. Next, capture a ping between network devices using only IP addresses. The gateway address should not be needed.
Task 6: Clean Up
Unless directed otherwise by the instructor, turn off power to the host computers. Remove anything that was brought into the lab, and leave the room ready for the next class.
All contents are Copyright 19922007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 8 of 8
You might also like
- Lab 5.5.1: Examining A Device's Gateway: Topology DiagramDocument8 pagesLab 5.5.1: Examining A Device's Gateway: Topology DiagramMichael John SantosNo ratings yet
- Lab 5.5.1: Examining A Device's Gateway: Topology DiagramDocument8 pagesLab 5.5.1: Examining A Device's Gateway: Topology DiagramJosh BautistaNo ratings yet
- E1 Lab 5 5 1 inDocument9 pagesE1 Lab 5 5 1 inArtyomSarseyevNo ratings yet
- Lab 5.6.2 Challenge RIP ConfigurationDocument4 pagesLab 5.6.2 Challenge RIP ConfigurationJosue Isahu Sanchez MedinaNo ratings yet
- IPv4 Addressing Lab ExplainedDocument15 pagesIPv4 Addressing Lab ExplainedMinhh TuNo ratings yet
- E2 Lab 11 6 2 InstructorDocument10 pagesE2 Lab 11 6 2 InstructorRuben De La CruzNo ratings yet
- TP Atelier Reseau 2Document8 pagesTP Atelier Reseau 2EMMANUEL MANGALANo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 OspfDocument10 pagesExperiment 8 OspfMoa AnwarNo ratings yet
- E2 Lab 5 6 2 InstructorDocument7 pagesE2 Lab 5 6 2 InstructorPedro Daniel Borja CisnerosNo ratings yet
- Module4 (LAB) - Serial ConfigurationDocument15 pagesModule4 (LAB) - Serial ConfigurationJoyce Ann Rufino100% (1)
- 5.2.1.7 Lab - Viewing The Switch MAC Address TableDocument5 pages5.2.1.7 Lab - Viewing The Switch MAC Address Tablecesar andres ruiz carpioNo ratings yet
- Lab 6.7.5Document3 pagesLab 6.7.5sirc_2552_379631412No ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Final Exam Answers 2011Document24 pagesCCNA 1 Final Exam Answers 2011funnwburbsNo ratings yet
- EIGRP E2 Lab 9 6 2Document8 pagesEIGRP E2 Lab 9 6 2bubuxErickNo ratings yet
- Lab1 - Configuring and Verifying A Small NetworkDocument4 pagesLab1 - Configuring and Verifying A Small NetworkkashifNo ratings yet
- ScenarioDocument5 pagesScenarioJuby Marie BaringNo ratings yet
- Lab 3.5.2: Subnetting Scenario 1: Topology DiagramDocument14 pagesLab 3.5.2: Subnetting Scenario 1: Topology Diagramdepeters3183No ratings yet
- ESwitching Lab 1 3 1Document12 pagesESwitching Lab 1 3 1Derek Ang Yew PinNo ratings yet
- E2 Lab 9 6 2Document8 pagesE2 Lab 9 6 2Ninja NuggetNo ratings yet
- Lab 5.6.2: Advanced RIP Configuration: Topology DiagramDocument7 pagesLab 5.6.2: Advanced RIP Configuration: Topology DiagramPaintMeAnEpicNo ratings yet
- 5.3.1.10 Lab - Using IOS CLI With Switch MAC Address TablesDocument5 pages5.3.1.10 Lab - Using IOS CLI With Switch MAC Address TablesThomas RamosNo ratings yet
- E2 Lab 7 5 2 InstructorDocument8 pagesE2 Lab 7 5 2 Instructoryang210% (1)
- Ccna Final 1Document21 pagesCcna Final 1jan1762No ratings yet
- Final Answers Ccna Exploration 1Document20 pagesFinal Answers Ccna Exploration 1Abhishek KunalNo ratings yet
- E2 Lab 2 8 2 InstructorDocument7 pagesE2 Lab 2 8 2 InstructorJosely MontillaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1.3.1Document12 pagesLab 1.3.1Alondra CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Lab: Basic Static Route Configuration: Topology DiagramDocument6 pagesLab: Basic Static Route Configuration: Topology Diagramchanda_banda272No ratings yet
- Lab 1.5.3: Challenge Router Configuration: Topology DiagramDocument4 pagesLab 1.5.3: Challenge Router Configuration: Topology DiagramMunkieBoneZNo ratings yet
- CCNA - Exploration Network Fundamentals - ENetwork Practice Final ExamDocument26 pagesCCNA - Exploration Network Fundamentals - ENetwork Practice Final Exambrone8No ratings yet
- Private IP Address Ranges and Network Device ConfigurationDocument61 pagesPrivate IP Address Ranges and Network Device ConfigurationTamer Abu-ShraikhNo ratings yet
- E1 PTAct 10-7-1 InstructorDocument3 pagesE1 PTAct 10-7-1 InstructorDamian SandakNo ratings yet
- 5.1.3.6 Lab - Viewing Network Device MAC AddressesDocument7 pages5.1.3.6 Lab - Viewing Network Device MAC Addressesbekirm10% (3)
- Lab 5.5.2: Examining A Route: Topology DiagramDocument7 pagesLab 5.5.2: Examining A Route: Topology Diagramlouie gonozNo ratings yet
- E2 Lab 2 8 2 InstructorDocument7 pagesE2 Lab 2 8 2 InstructorRicardo GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Report 1Document28 pagesReport 1zeeshan sohailNo ratings yet
- Ccna1 Practice Final ExamDocument15 pagesCcna1 Practice Final ExamMyra KuykendallNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Static Default RouteDocument8 pagesLab 4 Static Default RouteLipp00 M0MANo ratings yet
- Ccna-4-Final Exam-Full 100% PassDocument15 pagesCcna-4-Final Exam-Full 100% PassChristan CalvaridoNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 Final 2012 Exam AnswersDocument65 pagesCCNA 1 Final 2012 Exam Answerserzza storeNo ratings yet
- E2 Lab 7 5 2Document8 pagesE2 Lab 7 5 2Ninja NuggetNo ratings yet
- E2 Lab 2 8 2Document7 pagesE2 Lab 2 8 2Ninja NuggetNo ratings yet
- Ccna2 Labs AnswersDocument69 pagesCcna2 Labs Answerschadi_lb67% (6)
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationFrom EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo ratings yet
- Cisco Packet Tracer Implementation: Building and Configuring Networks: 1, #1From EverandCisco Packet Tracer Implementation: Building and Configuring Networks: 1, #1No ratings yet
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- CCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamFrom EverandCCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamNo ratings yet
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102From EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3From EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3No ratings yet
- C Programming for the Pc the Mac and the Arduino Microcontroller SystemFrom EverandC Programming for the Pc the Mac and the Arduino Microcontroller SystemNo ratings yet
- CompTIA A+ CertMike: Prepare. Practice. Pass the Test! Get Certified!: Core 1 Exam 220-1101From EverandCompTIA A+ CertMike: Prepare. Practice. Pass the Test! Get Certified!: Core 1 Exam 220-1101No ratings yet
- 4-3 56Document3 pages4-3 56Sergiy KalmukNo ratings yet
- Tshoot Chapter 2 MyMouDocument6 pagesTshoot Chapter 2 MyMouSergiy KalmukNo ratings yet
- Range Limiting Factors FactorsssDocument2 pagesRange Limiting Factors FactorsssSergiy KalmukNo ratings yet
- Ccnpv6 Route Lab2 1Document13 pagesCcnpv6 Route Lab2 1Sergiy KalmukNo ratings yet
- SOLUTIONS That I Can Copy and PASTE Krypton - Fhda.edu - Mmurperfefhy - Cnet-53f - Resources - ISM Book Exercise SolutionsDocument32 pagesSOLUTIONS That I Can Copy and PASTE Krypton - Fhda.edu - Mmurperfefhy - Cnet-53f - Resources - ISM Book Exercise SolutionsSergiy KalmukNo ratings yet
- Citizen FB1350 and Others 3-8-2014hihg Quality BESt ScriptDocument1 pageCitizen FB1350 and Others 3-8-2014hihg Quality BESt ScriptSergiy KalmukNo ratings yet
- CCNPv6 ROUTE Lab2-6 EIGRP Challenge StudentDocument3 pagesCCNPv6 ROUTE Lab2-6 EIGRP Challenge StudentChristopher FieldsNo ratings yet
- Switch Chapter 1 CCNP 66Document10 pagesSwitch Chapter 1 CCNP 66Sergiy KalmukNo ratings yet
- Module 8: Object-Based and Unified Storage 1Document24 pagesModule 8: Object-Based and Unified Storage 1Sergiy Kalmuk0% (1)
- Lab 2-1 EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies: Learning ObjectivesDocument12 pagesLab 2-1 EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies: Learning ObjectivesSergiy KalmukNo ratings yet
- MCST 2015 - Module 1 PDFDocument75 pagesMCST 2015 - Module 1 PDFSergiy KalmukNo ratings yet
- Assessment Results Chapter 1 Test Taken 1st TimeDocument1 pageAssessment Results Chapter 1 Test Taken 1st TimeSergiy KalmukNo ratings yet
- Networking Academy User ProfileDocument2 pagesNetworking Academy User ProfileSergiy KalmukNo ratings yet
- Lab 2-1 EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies: Learning ObjectivesDocument12 pagesLab 2-1 EIGRP Configuration, Bandwidth, and Adjacencies: Learning ObjectivesSergiy KalmukNo ratings yet
- CCNAS Chapter 1 CCNA Security 1Document10 pagesCCNAS Chapter 1 CCNA Security 1Sergiy KalmukNo ratings yet
- 2 17Document18 pages2 17Gerald Morales ChaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 - RatioDocument5 pagesGrade 7 - RatioHâu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography Wet Nurse SlaveryDocument7 pagesAnnotated Bibliography Wet Nurse SlaveryNicholas MusauNo ratings yet
- Fondazione Prada - January 2019Document6 pagesFondazione Prada - January 2019ArtdataNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report MTBDocument9 pagesAccomplishment Report MTBRay Marcial Jamolin MacabutasNo ratings yet
- Pak Steel Product Price ListDocument6 pagesPak Steel Product Price ListHamid NaveedNo ratings yet
- CoA Judgment - Kwan Ngen Wah V Julita Binti TinggalDocument25 pagesCoA Judgment - Kwan Ngen Wah V Julita Binti TinggalSerzan HassnarNo ratings yet
- Classical Philosophies Guide Business Ethics DecisionsDocument48 pagesClassical Philosophies Guide Business Ethics DecisionsDanielyn GestopaNo ratings yet
- Eastern PhilosophyDocument70 pagesEastern PhilosophyRedimto RoseteNo ratings yet
- Group 1 ResearchDocument28 pagesGroup 1 ResearchKrysler EguiaNo ratings yet
- Who Gsap 2017Document56 pagesWho Gsap 2017Mirzania Mahya FathiaNo ratings yet
- Education Secretaries 10Document6 pagesEducation Secretaries 10Patrick AdamsNo ratings yet
- Coalbed Methane - Principle & PracticeDocument510 pagesCoalbed Methane - Principle & PracticeDevananda Narah67% (9)
- Face Reading NotesDocument8 pagesFace Reading NotesNabeel TirmaziNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics: Ninth Canadian EditionDocument48 pagesMacroeconomics: Ninth Canadian EditionUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- BT - Cat35fr005 - Field Report LaafDocument21 pagesBT - Cat35fr005 - Field Report LaafFabianoBorg100% (2)
- Contemporary Management Education: Piet NaudéDocument147 pagesContemporary Management Education: Piet Naudérolorot958No ratings yet
- Intercape Sleepliner Ticket from Cape Town to JohannesburgDocument1 pageIntercape Sleepliner Ticket from Cape Town to JohannesburgRobert Bailey100% (1)
- Hitachi Energy BESS PQpluSDocument9 pagesHitachi Energy BESS PQpluSelpancaseroNo ratings yet
- Punjab's Domestic Electrical Appliances Cluster Diagnostic StudyDocument82 pagesPunjab's Domestic Electrical Appliances Cluster Diagnostic StudyShahzaib HussainNo ratings yet
- Appendix F - Property ValueDocument11 pagesAppendix F - Property ValueTown of Colonie LandfillNo ratings yet
- International Portfolio TheoryDocument27 pagesInternational Portfolio TheoryDaleesha SanyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Etiquettes Inc IntroductionsDocument8 pagesBasic Etiquettes Inc Introductionsayesha akhtarNo ratings yet
- Airtel A OligopolyDocument43 pagesAirtel A OligopolyMRINAL KAUL100% (1)
- Culturally Appropriate Communication in Malaysia Budi Bahasa As Warranty Component in Malaysian DiscourseDocument15 pagesCulturally Appropriate Communication in Malaysia Budi Bahasa As Warranty Component in Malaysian DiscourseNur FarihaNo ratings yet
- GE15 ULOcDocument5 pagesGE15 ULOcKyle Adrian MartinezNo ratings yet
- Taylor Campbell FeatureDocument5 pagesTaylor Campbell Featureapi-666625755No ratings yet
- Service Industries LimitedDocument48 pagesService Industries Limitedmuhammadtaimoorkhan86% (7)
- Marketing MetricsDocument29 pagesMarketing Metricscameron.king1202No ratings yet
- TheoriesDocument87 pagesTheoriesCzari MuñozNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Introduction Lecture#1Document12 pagesFinancial Management Introduction Lecture#1Rameez Ramzan AliNo ratings yet