Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Shainin Notes
Uploaded by
kdsophieOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Shainin Notes
Uploaded by
kdsophieCopyright:
Available Formats
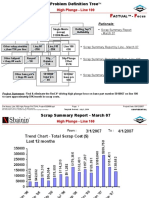
Progressive Search 1. Families of cause variation, family with the highest variation has the dominant cause.
Within piece magnet manufacturer Piece to piece within the same mfg Time to time day to day Cavity to cavity n/a Machine to machine Reynosa to Springfield Supplier to Supplier JMQ / Jaingman 2. Variation There is no special or common cause spikes in data. The strategy is to look for causes with a large effect. It can be hard to identify a dominant cause if there is an interaction between varying inputs in different families. There is a risk of focusing on fliers/outliers 3. The Shainin Process - It is innately sequential in nature Stage 1 - Diagnostic search is first in the process i. First you should establish a baseline to quantify the problem, taking into account all the variation ii. The baseline is used to verify we have selected the dominant cause Stage 2 - Establish an effective measurement system i. Need to consider not only the output measurement system but the input measurement systems. Stage 3 Progressive Search i. Tools Multi vary studies, stratification, group comparison(chi sq), and scatter correlation plots ii. Setup observational plans early in the stages of the search iii. The dominant cause is eliminated or reduced by changing the product design, the process, or the control plan. Stage 4 & 5 Confirmation of dominant cause i. DOE is used to confirm because of the possibility of confounding data ii. The levels of dominant causes (red x) are set at the extremes, to produce the BOB & WOW parts. Other inputs are held constant during the DOE iii. Full factorial design is recommended so that interactions among the suspects can be identified. iv. With a single suspect, SS recommends a six run experiment, with 3 replicates for each level. v. Full factorial is feasible since we have a short list of suspects vi. Tolerance Parallelogram(linear regression) is used to set process control limits. 4. Shainin Tools Isoplot is used to compare the relative size of the process & measurement system families of variation. i. Make 2 measurements on the same part, 30 parts ii. If the points lie on the 45 degree line then the variation is small
iii. AIAG recommends using ANOVA to evaluate the variation of the 2 components. Multivari i. Using shaft diameter 1. measure 3 places on the part within part variation 2. using 3 parts in a row to evaluate part-to-part variation 3. sampling every hour to capture time-to-time 4. evaluating 3 different machines for machine-to-machine variation Component Search & Variable Search i. Take the BOB & WOW with output values at the two extremes of the baseline distribution. ii. Units are disassembled & reassembled, evaluating assembly process iii. Units are disassembled & reassembled, evaluating components (swap) iv. Variable search is used when 4 or more suspects are identified Group Comparison for destructive testing i. We measure the inputs & find the extremes for each component by either continuous measurement or extreme binary inputs ii. Recommended analysis uses two sample nonparametric testing for each family BOB & WOW
You might also like
- IF The Result Is Higher That 1.25 The Component Is One The IMPORTANT RED X ContributorDocument4 pagesIF The Result Is Higher That 1.25 The Component Is One The IMPORTANT RED X ContributormanuelNo ratings yet
- Line 100 High Plunge FACTUAL Project 020808Document25 pagesLine 100 High Plunge FACTUAL Project 020808manuelNo ratings yet
- Component Search Method Introduction 37Document37 pagesComponent Search Method Introduction 37NRamaniNo ratings yet
- Shainin AmeliorDocument40 pagesShainin AmeliorOsman Tig100% (1)
- Proyecto X Roja PDFDocument301 pagesProyecto X Roja PDFadry220490No ratings yet
- 14 Variable Sampling Plan - StudentDocument17 pages14 Variable Sampling Plan - Studentsoonvy100% (1)
- Strategy Diagram ExamplesDocument8 pagesStrategy Diagram ExamplesmanuelNo ratings yet
- World Class Quality To Achieve Zero PPM 231111Document108 pagesWorld Class Quality To Achieve Zero PPM 231111Gyanesh_DBNo ratings yet
- Shainin - John Abrahamian Hartford Asq PDFDocument27 pagesShainin - John Abrahamian Hartford Asq PDFMickloSoberanNo ratings yet
- SEWS 121 IsoplotDocument42 pagesSEWS 121 Isoplotfernando garza100% (1)
- Root Cause Analysis - ShaininapproachDocument6 pagesRoot Cause Analysis - ShaininapproachRaghavendra KalyanNo ratings yet
- Shainin Methodology An Alternative or An EffectiveDocument14 pagesShainin Methodology An Alternative or An EffectiveMarco SánchezNo ratings yet
- Shainin Vs Six SigmaDocument4 pagesShainin Vs Six Sigmabaro4518No ratings yet
- Red X Shainin OverviewDocument31 pagesRed X Shainin Overviewpkj009100% (2)
- Another Look at Dorian Shainin's Variable Search TechniqueDocument30 pagesAnother Look at Dorian Shainin's Variable Search Techniqueshivaprasadmvit100% (1)
- DOE Exercise BookDocument35 pagesDOE Exercise BooksigmasundarNo ratings yet
- Shainin Techniques PDFDocument4 pagesShainin Techniques PDFrm_muruganNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma ToolsDocument92 pagesSix Sigma ToolsjoseggNo ratings yet
- Shanin Techniques Jo MoorenDocument3 pagesShanin Techniques Jo MoorenAnonymous X0iytQQYJ6No ratings yet
- 5 9 Ravichandran Slides PDFDocument26 pages5 9 Ravichandran Slides PDFss2mrattriNo ratings yet
- DOE ShaininDocument200 pagesDOE ShaininAbhishek Kumar Singh100% (4)
- Doe Shainin Methods TipsDocument12 pagesDoe Shainin Methods Tipsshivaprasadmvit50% (2)
- Msa Guide MDocument114 pagesMsa Guide MRohit SoniNo ratings yet
- Process Capability: 99.73% of parts lie within the 6 σ limitsDocument10 pagesProcess Capability: 99.73% of parts lie within the 6 σ limitsrm_muruganNo ratings yet
- DOE ShaininDocument200 pagesDOE ShaininNatKTh100% (2)
- He Shainin SystemDocument20 pagesHe Shainin SystemSilvia Tria ApsariNo ratings yet
- Quality Management Exploring Taguchi Loss Function and Shainin MethodsDocument58 pagesQuality Management Exploring Taguchi Loss Function and Shainin MethodsUmashankar Gautam50% (2)
- Shain in TaguchiDocument8 pagesShain in TaguchisdvikkiNo ratings yet
- SE ToolsDocument37 pagesSE Toolsfernando garzaNo ratings yet
- ISO9 - IATF16 - Combo - GAP - March - 2017 - 1Document100 pagesISO9 - IATF16 - Combo - GAP - March - 2017 - 1Bruce GilchristNo ratings yet
- Jiju Antony, Mike Kaye (Auth.) - Experimental Quality - A Strategic Approach To Achieve and Improve Quality (2000, Springer US)Document259 pagesJiju Antony, Mike Kaye (Auth.) - Experimental Quality - A Strategic Approach To Achieve and Improve Quality (2000, Springer US)Grace De León NopeNo ratings yet
- 06 LS Analyze - RegressionAn - DOEDocument83 pages06 LS Analyze - RegressionAn - DOEFernando ValdezNo ratings yet
- ASQ Auto Shainin B Vs C WebinarDocument63 pagesASQ Auto Shainin B Vs C Webinarpkj009No ratings yet
- Shainin Tools PDFDocument17 pagesShainin Tools PDFDEVIKA PHULENo ratings yet
- SPC Training 2016Document116 pagesSPC Training 2016Remy Ellaine Souribio100% (1)
- QRQC Training ModuleDocument37 pagesQRQC Training Modulemoez100% (1)
- Supplier QRQC ImplementationDocument21 pagesSupplier QRQC ImplementationChristopher GILL100% (1)
- QRQC Training ProtocolDocument52 pagesQRQC Training ProtocolSudhagar P100% (1)
- Can Lean Six Sigma Drive Sales & Lower Costs?: Kush Shah, ChairmanDocument30 pagesCan Lean Six Sigma Drive Sales & Lower Costs?: Kush Shah, ChairmanMario Alejandro Charlin SteinNo ratings yet
- Phase DPMODocument65 pagesPhase DPMOKefin TajebNo ratings yet
- Shanin DOE - Six SigmaDocument7 pagesShanin DOE - Six SigmaBennett Matthews100% (1)
- DOEDocument126 pagesDOEsuryaksvidyuth0% (1)
- NOTES Software Quality ManagementDocument382 pagesNOTES Software Quality Managementgirish_kodagantiNo ratings yet
- Special Characteristics PDFDocument11 pagesSpecial Characteristics PDFKristof MCNo ratings yet
- 01 Process CapabilityDocument33 pages01 Process CapabilitySrinivasagam Venkataramanan100% (1)
- Measurement Systems: AnalysisDocument114 pagesMeasurement Systems: AnalysisAZIZ KUMARNo ratings yet
- CQI-12v2: Special Process: Coating System AssessmentDocument36 pagesCQI-12v2: Special Process: Coating System AssessmentHoang TanNo ratings yet
- SPCDocument49 pagesSPCadibhai06100% (7)
- APQP - QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesAPQP - QuestionnaireLOGANATHAN V100% (1)
- APQP Phases ActivitiesDocument1 pageAPQP Phases Activitiesaorto3919No ratings yet
- Daimler Process Signoff DocumentDocument228 pagesDaimler Process Signoff DocumentWolf Villarin100% (1)
- Statistical Process ControlDocument79 pagesStatistical Process ControlKrunal PandyaNo ratings yet
- PPAP TRGDocument102 pagesPPAP TRGArivazhagan Art100% (1)
- MSA Reference Manual 4th EditionDocument241 pagesMSA Reference Manual 4th EditionMukhammadali Shukuraliev100% (2)
- Supplier Performance Management Process A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionFrom EverandSupplier Performance Management Process A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNo ratings yet
- Practical Note Book for Lab ExperimentsDocument34 pagesPractical Note Book for Lab ExperimentsQurat ul AinNo ratings yet
- Winter Quarter 2006-2007 ACADEMIC YEAR: Analysis, Wiley-Interscience, 1998Document17 pagesWinter Quarter 2006-2007 ACADEMIC YEAR: Analysis, Wiley-Interscience, 1998YusranNo ratings yet
- The Research DesignDocument7 pagesThe Research DesignKean CardenasNo ratings yet
- Shaninin TechniquesDocument11 pagesShaninin TechniquesJaspreet KapoorNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical validation: Standard curves, calibrationDocument7 pagesPharmaceutical validation: Standard curves, calibrationAnum FaryalNo ratings yet
- Eviews Training For Iain Salatiga Talent Scouting Program: By: Anton BawonoDocument10 pagesEviews Training For Iain Salatiga Talent Scouting Program: By: Anton BawonoHamdan YuafiNo ratings yet
- SPANOVADocument16 pagesSPANOVACress Lorraine SorianoNo ratings yet
- Hoffman Stanley - IR As Social ScienceDocument21 pagesHoffman Stanley - IR As Social ScienceradetzkyNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry: A Foundation for Understanding Our Natural WorldDocument16 pagesBasic Chemistry: A Foundation for Understanding Our Natural WorldVanessa JabagatNo ratings yet
- Design of Experiments OverviewDocument6 pagesDesign of Experiments Overviewdaveawoods100% (1)
- Representation and Summary of Data - Location (Questions)Document4 pagesRepresentation and Summary of Data - Location (Questions)Hassan HussainNo ratings yet
- Teacher'S Resource PackDocument128 pagesTeacher'S Resource Packirenetis100% (3)
- Physical Quantities and MeasurementDocument9 pagesPhysical Quantities and MeasurementAzim Memeng75% (4)
- Multivariate StatisticsDocument6 pagesMultivariate Statisticsbenjamin212No ratings yet
- ANJAC Science Instrumentation Centre ChargesDocument4 pagesANJAC Science Instrumentation Centre Charges16 Malola KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Statistics NotesDocument109 pagesStatistics NotesFavour NyamburaNo ratings yet
- Acific Training On Sampling Methods For Producing Core Data Items For Agricultural and Rural StatisticsDocument10 pagesAcific Training On Sampling Methods For Producing Core Data Items For Agricultural and Rural StatisticsElegant AspireNo ratings yet
- 01 Koshy Et Al CH 01 PDFDocument24 pages01 Koshy Et Al CH 01 PDFiamgodrajeshNo ratings yet
- When Clothes Become Fashion DesignDocument255 pagesWhen Clothes Become Fashion DesignAulia Suminar Ayu93% (14)
- Business SimulationDocument27 pagesBusiness SimulationDanny HeldtNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics - Hypothesis Testing, Chi Square and AnnovaDocument7 pagesBusiness Statistics - Hypothesis Testing, Chi Square and AnnovaRavindra BabuNo ratings yet
- Strengths and WeaknessesDocument4 pagesStrengths and WeaknessesShela MesyanaNo ratings yet
- Criminological ResearchDocument5 pagesCriminological ResearchkimkimkouiNo ratings yet
- QUALI Conclusions and Recommendations FormulationDocument6 pagesQUALI Conclusions and Recommendations FormulationNiño Mendoza MabatoNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Assignment FinalDocument1 pageHypothesis Assignment FinalSarah Angelica RobielosNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology: A Scientific Search for KnowledgeDocument48 pagesResearch Methodology: A Scientific Search for Knowledgeashwath44100% (8)
- Template Jurnal PhotonDocument3 pagesTemplate Jurnal PhotonnacenkNo ratings yet
- Decision-Making Based On Data AnalyticsDocument3 pagesDecision-Making Based On Data AnalyticsJMFMNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior of Bottled WaterDocument55 pagesConsumer Behavior of Bottled Watersonia23singh247100% (1)
- Probabilistic Models ExplainedDocument29 pagesProbabilistic Models ExplainedClara Agustin StephaniNo ratings yet
- File 1 - 65Document4 pagesFile 1 - 65Chuah Chong Yang100% (1)
- Building Neural Network Models For Time Series: A Statistical ApproachDocument27 pagesBuilding Neural Network Models For Time Series: A Statistical Approachjuan carlosNo ratings yet
- 7 QCDocument71 pages7 QCEjaz HasanNo ratings yet
- ECE531 Screencast 2.1: Introduction To The Cramer-Rao Lower Bound (CRLB)Document5 pagesECE531 Screencast 2.1: Introduction To The Cramer-Rao Lower Bound (CRLB)Karthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- CritiqueDocument1 pageCritiqueAndre Philip Castillo TacderasNo ratings yet