Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Skema Jawapan Kertas 2 - Physics (PPT 2012 F5)
Uploaded by
SuadrifRunDamahumCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Skema Jawapan Kertas 2 - Physics (PPT 2012 F5)
Uploaded by
SuadrifRunDamahumCopyright:
Available Formats
1 PPT 2012 PHYSICS FORM 5 MARKING SCHEME PHYSICS PAPER 2 NO 1(a) ANSWER MARKS 1 1 1 1 Total NO ANSWER 2(a) amplitude
e 2(b) This is due to energy lost because of friction 2(c) (i) period = 0.4 s (ii) frequency = 1/0.4 = 2.5 Hz 2(d) The period will increase Total ANSWER (i) voltmeter reading in Diagram 3.1 is higher than voltmeter reading in Diagram 3.2 // vice versa (ii) there is internal resistance in Diagram 3.2 3(b) E = V + Ir V = E Ir = 3 (1)(0.5) = 2.5 V 3(c) - straight line [ 1 mark] - emf [ 1 mark ] emf NO 3(a) 4 MARKS 1 1 1 1 1 5 MARKS 1 1 2
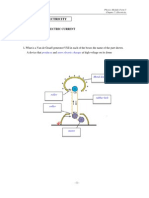
(i) Voltmeter (ii) To control the current by varying the resistance in the circuit 1(b) (i) Ammeter Y (ii) The smaller division in Y enables it to detect a smaller current // Ammeter Y can measure current up to 0.05 A but Ammeter X can only measure current up to 0.1 A
Total NO 4(a) ANSWER
6 MARKS 1 1 1 2
(i) Pendulum M (ii) M is forced to oscillate at its natural frequency (iii) Resonance 4(b) Period = 1/f = = 0.5 s 4(c)
Total
NO ANSWER 5(a) The angle of incidence when the angle of refraction is 90o. 5(b) The angle of incidence at point A is zero, so the angle of refraction is zero 5(c) (i) Prism P Increase the angle of incidence / i > 45o Prism Q Reduce the angle of incidence / i < 45o (ii) Glass is denser than air (iii) Diagram 5.1 Refract/ Bends away from the normal Diagram 5.2 totally reflected 5(d) Total internal reflection Total ANSWER (i) Parallel (ii) The other bulbs will still light up 6(b) (i) a bulb that uses 240 V will release 60 W of power (ii) P = VI I = 60/ 240 = 0.25 A (iii) P = V2/R R= = RT = 320 (iv) Arrange the bulbs in series Total NO ANSWER 7(a) A point that all parallel rays of light converge after reflection from the mirror 7(b) = 960 ( one bulb ) NO 6(a)
MARKS 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 8 MARKS 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 8 MARKS 1
7(c)
(i)
(ii) Reflection 7(d) (i) the bulb is placed at focal point
1 1
3 (ii) increase the curvature of the concave reflector Use bulb with higher power rating Total ANSWER A temporary magnet in which its magnetism is produced by a current-carrying conductor. 8(b) Right-hand grip rule 8(c) NO 8(a) 1 1 10 MARKS 1 1
7(e)
8(d) 2
8(e)
(i)
8(f)
1. South pole 2. North pole (ii) The polarity at the two ends will be reversed 1. Increase the current that flows through the wire 2. increase the number of turns in the coil for the same length of solenoid 3. Insert a soft iron core into the coil Total
2 1 3 12 MARKS 1
ANSWER (i) A virtual image is an image that cannot be formed on a screen (ii) - Lens J is thicker than lens K - The focal length of lens K is longer than that of lens J - The size of the image produced by lens J is bigger than that produced by lens , K - When the focal length increases the size of the image decreases - When the power of a lens increases, its focal length decreases 9(b) - Parallel light ray from the hot sun at infinity pass through a convex lens. - light rays are focused after passing through the lens - light rays are converged onto a very small area called the focal point of the lens - at the point, the intensity of light is great and the light energy causes an increase in temperature. When the spot on the paper becomes hot enough, the paper starts to burn. 9(c) (i) - P is used as the objective lens. Q is used as the eyepiece - P and Q are in line. The distance between the two lenses is 45 cm // the length of the telescope is 40 cm + 5 cm. - Parallel rays of starlight from distant stars converge at the focal point of the
NO 9(a)
4 eyepiece. - This will form an initial image, I, which is real, inverted and smaller than the actual object. - This image then becomes the object for the eyepiece - Under normal adjustment, the final image formed by the eyepiece will be at infinity. This image is virtual, inverted and magnified
9(c)
(ii) - Increase the diameter of the objective lens to let in more light - Increase the focal length of the objective lens or reduce the focal length of the eyepiece Total
2 2 20 MARKS 1
NO ANSWER 10(a) Electric current is the rate of charge flow in a circuit 10(b) - The voltage supplied in Diagram 10.1 is less/ smaller than the voltage supplied in Diagram 10.2 - The bulbs in Diagram 10.2 light up brighter than that in Diagram 10.1 - The angle of deflection of the ammeter pointer in Diagram 10.2 is more than that in Diagram 10.1 10(c) (i) The higher the voltage supplied, the higher the current (ii) The higher the current, the brighter the bulb 10(d) - The current in both bulbs are the same as the total current - The effective resistance of the bulbs in the parallel circuit is less than that in the series circuit. - The total current in the parallel circuit is more than that in the series circuit. - Therefore, the two bulbs in Diagram 10.3 light up brighter than the bulbs in series connection as shown in Diagram 10.1 10(e) (i) type of the filament : - the filament should have a high melting point, - so the filament would not melt easily - the resistance of the filament should be high - so the bulb will light up brightly (ii) the glass of the bulb: - the glass should be transparent - so the loss of light intensity is minimum - the specific heat capacity of the glass should be high - so the glass does not easily become hot// the glass be able to withstand the intensity of heat from the filament. (iii) the pressure in the bulb :
1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
5 - the pressure in the bulb should be low - so the bulb will not blow when it gets too hot Total 1 20
NO ANSWER 11(a) Frequency 11(b) - high pitch sound has high frequency and short wavelength - frequency is inversely proportional to wavelength - the sound is not diffracted properly by the corner. Only student C can hear the sound clearly because he is nearest to the audio frequency generator. - a low pitch sound has low frequency and longer wavelength. The sound can be diffracted better by the corner. All the student can hear the sound clearly. 11(c) Characteristics Explanation Larger diameter Receives more signals The distance of the signal receiver This will produce a better reception. from the centre of the parabolic Distant signals which travel in parallel disc is the same as the focal length lines will be reflected and focused onto the receiver. The type of wave transmitted Has high frequency/ high energy/ short should be microwave wavelength, so is easily reflected The height of the parabolic disc The signal is not blocked/ easy to be from the ground should be high detected. K is chosen. Because the diameter of the parabolic disc is large, the distance of the signal receiver from the centre of the parabolic disc is the same as the focal length, it transmit microwave and has high position. 11(d) (i) Speed = distance / time = (2s) / t = (290) / 0.12 = 1500 m s-1 (ii) v = f = 1500 / 50000 = 0.03 m Total ANSWER The potential difference between two points is the work done in moving one coulomb of charge from one point to the other 12(b) (i) When I increases, V increases. R = V/I = gradient of the graph As current, I, increases, gradient increases, resistance, R, increases as temperature increases. (ii) Energy dissipated per second = VI When the current decreases, the energy dissipated decreases 12(c) Characteristics Filament must be made from tungsten wire Explanation Tungsten wire has a higher resistance per unit length / has higher melting point than copper NO 12(a)
MARKS 1 1 1 1 1
10
2 20 MARKS 1 1 1 1 1
10
6 Thin wire has greater resistance / becomes hot easily The tungsten wire is coiled Coiled wire is more efficient because a very long wire can be fitted into the glass bulb, concentrating heat and producing brighter light. The glass lamp filled with The tungsten wire will not evaporate easily at nitrogen gas at low pressure high temperature R is chosen. Because R use a thin tungsten wire as the filament, is coiled and contains nitrogen gas at low pressure in the bulb. 12(d) (i) P = VI I = 11/ 240 = 0.046 A (ii) heat energy lost per second = 11 10 =1J (iii) Efficiency = = 100% = 90.91 % Total 100% 2 The tungsten wire is thin
20
You might also like
- Chapter 7 - Electricity - Teacher's GuideDocument60 pagesChapter 7 - Electricity - Teacher's GuideLawrence HiewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Electricity - Teacher's GuideDocument60 pagesChapter 7 - Electricity - Teacher's GuideLawrence HiewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Radioactivity Teacher Guide1Document29 pagesChapter 10 Radioactivity Teacher Guide1SuadrifRunDamahumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Emagnet Teacher - EditedDocument46 pagesChapter 8 Emagnet Teacher - EditedSuadrifRunDamahum100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Teacher's GuideDocument33 pagesChapter 4 Teacher's GuideinezchewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Waves Teacher's Guide 2009Document40 pagesChapter 6 Waves Teacher's Guide 2009SuadrifRunDamahumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Light - Teacher'sDocument36 pagesChapter 5 Light - Teacher'sSuadrifRunDamahumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 ElectronicDocument36 pagesChapter 9 ElectronicSuadrifRunDamahumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Force & Pressure - TeacherDocument22 pagesChapter 3 Force & Pressure - TeacherSuadrifRunDamahumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Force and Motion TEACHER's GUIDEDocument44 pagesChapter 2 Force and Motion TEACHER's GUIDEShuganthi MasilamanyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 ElectronicDocument36 pagesChapter 9 ElectronicSuadrifRunDamahumNo ratings yet
- MPHG2009-Chapter 10 RadioactivityDocument30 pagesMPHG2009-Chapter 10 RadioactivityMohd Khairul Anuar100% (4)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Physics Teacher's Guide 2009Document18 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Physics Teacher's Guide 2009SuadrifRunDamahumNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- CFD Analysis of Engine Room VentilationDocument10 pagesCFD Analysis of Engine Room VentilationTARIQUL EMONNo ratings yet
- Eutectic Solution PDFDocument2 pagesEutectic Solution PDFMelissaNo ratings yet
- Reso Paper 1Document63 pagesReso Paper 1Gurjeet KaurNo ratings yet
- Machines and Mechanisms CourseworkDocument30 pagesMachines and Mechanisms Courseworksaad hussainNo ratings yet
- Mastertop 530 12-04Document3 pagesMastertop 530 12-04djrote4No ratings yet
- Is.12889.1989 2Document10 pagesIs.12889.1989 2Agniva Dutta100% (1)
- Designing Effective Static Tests For Spacecraft Structures - Sarafin (Ler) - Part6Document1 pageDesigning Effective Static Tests For Spacecraft Structures - Sarafin (Ler) - Part6JizzPontesNo ratings yet
- Tie Requirements For RC Columns Bresler Gilbert ACI SJ 1961Document16 pagesTie Requirements For RC Columns Bresler Gilbert ACI SJ 1961oggy1844No ratings yet
- 20 LettersDocument2 pages20 LettersRenz Anthony Espino100% (1)
- Electropolishing Using Ionic Liquids: A Greener AlternativeDocument26 pagesElectropolishing Using Ionic Liquids: A Greener AlternativetetirichieNo ratings yet
- Code Calculations: Api 570 - Piping Inspector Certification Preparatory CourseDocument8 pagesCode Calculations: Api 570 - Piping Inspector Certification Preparatory Coursevishal bailurNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Systems GuideDocument9 pagesRefrigeration Systems GuideericNo ratings yet
- A Review of Theories of The L-H TransitionDocument74 pagesA Review of Theories of The L-H TransitionpincoNo ratings yet
- Measuring Nuclear Radii with Diffraction Scattering, Atomic X-Rays, and Mirror NuclidesDocument15 pagesMeasuring Nuclear Radii with Diffraction Scattering, Atomic X-Rays, and Mirror NuclidesAbhi LagwalNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Basic Concepts: Chapter OneDocument2 pagesIntroduction and Basic Concepts: Chapter OneseidNo ratings yet
- Heat - 4e - Chap08 - Internal Convection-StDocument48 pagesHeat - 4e - Chap08 - Internal Convection-Stfu MozaNo ratings yet
- VECTORS AND SCALARSgggggggggggggDocument5 pagesVECTORS AND SCALARSgggggggggggggVIDISHANo ratings yet
- Deign Final Project Review (120me0012) (Autosaved)Document14 pagesDeign Final Project Review (120me0012) (Autosaved)VfhhdfvhhNo ratings yet
- A Soil Has A BulkDocument12 pagesA Soil Has A BulkMaverick Timbol100% (1)
- CPP U11 LectureDocument49 pagesCPP U11 LectureAmanda KompNo ratings yet
- Preprints202305 1449 v2Document29 pagesPreprints202305 1449 v2Suaib VCSNo ratings yet
- Ideal and Real Gas LawsDocument74 pagesIdeal and Real Gas LawsAlex LeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Bonding General ConceptsDocument79 pagesChapter 8 Bonding General Conceptsabd jafNo ratings yet
- Cement Evaluation Tool PDFDocument7 pagesCement Evaluation Tool PDFHamed SadeghiNo ratings yet
- Solubility, Solubility Product, Precipitation Titration, GravimetryDocument10 pagesSolubility, Solubility Product, Precipitation Titration, GravimetrySURESH100% (3)
- The Mechanism of The Catalytic Oxidation of Hydrogen SulfideDocument9 pagesThe Mechanism of The Catalytic Oxidation of Hydrogen SulfideThảo LêNo ratings yet
- CHFEN 3553 Final ExamDocument7 pagesCHFEN 3553 Final ExamRam chandraNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Soundings Stability - ActivitiesDocument9 pagesAtmospheric Soundings Stability - ActivitiesAdrià Chavanel I SaltóNo ratings yet
- Scientific Devices (B) Pvt. LTD.: Instruction Manual FOR by - Pass RotameterDocument5 pagesScientific Devices (B) Pvt. LTD.: Instruction Manual FOR by - Pass RotameterfaqdaniNo ratings yet
- Power Plant ChemistryDocument101 pagesPower Plant ChemistryNaveen ChodagiriNo ratings yet