Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ohm's Law Lab
Uploaded by
thetwilightsaga6Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ohm's Law Lab
Uploaded by
thetwilightsaga6Copyright:
Available Formats
29/03/12
Marina S.
Ohms Law Lab
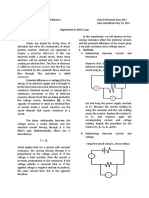
Purpose: To understand the correlation between voltage, current, and resistance. Hypothesis: If the voltage is increased then the current passing through the resistor will increase as well. Materials: Refer to grade 9 course pack, page 119, Ohms Law. Procedure: Refer to grade 9 course pack, pages 119 & 120, Ohms Law.
Observations: Table 1: Relation between resistance, current, and voltage. Resistor used: 10
1
29/03/12
Marina S.
Voltage (volts) 1.5V 0.13A
Current (amps)
Resistance (Ohms) R=V/I R=1.5/0.13 R=11.54 R=V/I R=3.0/0.27 R=11.11 R=V/I R=5.0/0.46 R=10.87 R=V/I R=6.0/0.55 R=10.9
3.0V
0.27A
5.0V
0.46A
6.0V
0.55A
Analysis: Voltage vs. Current graph on page 3. Questions: As the voltage increased the current increased as well. This is because the voltage provides energy to the circuit, the more voltage the faster the electrons move through the circuit. Current is the measure of how fast the electrons travel through the circuit, so if the voltage increased then the current of electrons increased too. If the voltage had been increased to 15V then the current of the circuit would increase to around 1.4A. This was predicted by the calculations shown below. Calculations: y=mx+b 15=(10.76)(x)+0 15= 10.76x 10.76=10.76
2
1.
2.
29/03/12
Marina S.
1.4=x
3. The slope of the voltage-current graph is related to resistance through Ohms law. Ohms law states that voltage is equivalent to current multiplied by resistance. Therefore the slope of the voltage-current graph is the resistance of the circuit. Conclusion: If the voltage is increased then current of the circuit will increase too. By using Ohms law you can find out a circuits voltage by multiplying the current and resistance.
You might also like
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Lab 5-Ohms LawDocument6 pagesLab 5-Ohms Lawapi-263500375No ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Charges and Ohm LawDocument12 pagesExperiment 2 Charges and Ohm Lawعلي محمودNo ratings yet
- Computational Fluid Dynamics: Principles and ApplicationsFrom EverandComputational Fluid Dynamics: Principles and ApplicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ohm's Law (Lab Report)Document7 pagesOhm's Law (Lab Report)yuta titeNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document6 pagesExperiment 2marthabervellyNo ratings yet
- Determination of Ohmic Relations Between CurrentDocument6 pagesDetermination of Ohmic Relations Between CurrentLeiko RaveloNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document7 pagesUnit 5NurFajrina MuthmainnahNo ratings yet
- Circuits LoveDocument10 pagesCircuits LoveMabethNo ratings yet
- 114 214ohmDocument11 pages114 214ohmHikmat Saeful BahriNo ratings yet
- EE 283 Dr. Janacek Name Yousif Alromaithi November 11, 2013 Experiment 5B Basic Ac Circuit AnalysisDocument8 pagesEE 283 Dr. Janacek Name Yousif Alromaithi November 11, 2013 Experiment 5B Basic Ac Circuit Analysisliverpool_darknightNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument10 pagesOhm's LawMohamed KamilNo ratings yet
- Phy12l E306 ISI-PaperDocument8 pagesPhy12l E306 ISI-PaperGrace ReyesNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Lab - Basic MeasurementsDocument2 pagesWeek 6 Lab - Basic MeasurementsRowen PratherNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab ReportDocument3 pagesPhysics Lab ReportRey Malvin SG PallominaNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits Lab ManualDocument18 pagesAC Circuits Lab ManualTyler AbercicleNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law ReportDocument8 pagesOhm's Law ReportFelicia Paya FrancisNo ratings yet
- Resistors and Resistor CircuitsDocument4 pagesResistors and Resistor CircuitsBhanu K PrakashNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law & ResistorsDocument42 pagesOhms Law & ResistorsJEAN RANCES RANIDONo ratings yet
- LabDocument2 pagesLabSean BursonNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesOhm's LawBelly JoeNo ratings yet
- Resistance Was Discovered by Georg Simon Ohm. The Relationship and The Unit of ElectricalDocument4 pagesResistance Was Discovered by Georg Simon Ohm. The Relationship and The Unit of ElectricalAliNo ratings yet
- Teacher Notes Ohm'S LawDocument8 pagesTeacher Notes Ohm'S LawAlib BudiyantoNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument4 pagesOhms LawAshley O'Neal100% (7)
- Ohm's LawDocument12 pagesOhm's LawJerome BricenioNo ratings yet
- Exp5 DALANONDocument9 pagesExp5 DALANONWrenwil VidalNo ratings yet
- Basic Circuit Laws: Georg Ohm Kirchhoff's LawsDocument4 pagesBasic Circuit Laws: Georg Ohm Kirchhoff's LawsrezhabloNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law LabDocument4 pagesOhm's Law LabEamon Barkhordarian67% (3)
- PDF Integrated Physics Laboratory 2Document3 pagesPDF Integrated Physics Laboratory 2Audie WongNo ratings yet
- Vol Curr ResDocument3 pagesVol Curr ResElisa NovakNo ratings yet
- Ex PT 8 Formal ReportDocument2 pagesEx PT 8 Formal ReportJemVivarNo ratings yet
- Game Theory ModelDocument5 pagesGame Theory ModelMaliki ChannelNo ratings yet
- Here We'll Attempt To Explain Ohm's Law Basics!: WaterDocument2 pagesHere We'll Attempt To Explain Ohm's Law Basics!: WaterRoy Axel HabocNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument23 pagesOhms LawKana KioshiNo ratings yet
- To Analyze The OhmDocument2 pagesTo Analyze The OhmHana VvnaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2Document5 pagesGeneral Physics 2Nanzkie Andrei SamanNo ratings yet
- Series Circuits and Parrallel CircuitsDocument3 pagesSeries Circuits and Parrallel CircuitsshelbsNo ratings yet
- Voltage Power RatingsDocument13 pagesVoltage Power RatingsKhubaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Phy12l A4 E306 2Q1516Document4 pagesPhy12l A4 E306 2Q1516Michelle Mae Gonzaga Raagas100% (1)
- Physics 201L - Lab Report FALL 2021 - 22: Experiment Title Ohm's Law Group No. 2 Experiment No. 1 Section No. 51Document10 pagesPhysics 201L - Lab Report FALL 2021 - 22: Experiment Title Ohm's Law Group No. 2 Experiment No. 1 Section No. 51Dana AlabadlaNo ratings yet
- E306 Report - Parallel and Series CircuitsDocument5 pagesE306 Report - Parallel and Series CircuitsAbdul Rahman Mariscal100% (1)
- Experiment 2 Ohms LawDocument5 pagesExperiment 2 Ohms LawnatlasNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Electrical CircuitDocument10 pagesLab Report Electrical Circuitapi-341133750No ratings yet
- Ohm'S Law Using A Phet SimulationDocument7 pagesOhm'S Law Using A Phet SimulationMujtaba HassanNo ratings yet
- TLE10 Electronics Q1 Wk4 Parallel Circuit Resistance-EquivalentDocument15 pagesTLE10 Electronics Q1 Wk4 Parallel Circuit Resistance-Equivalentismael delosreyesNo ratings yet
- Chapter-12 Electricity Annexure 1DDocument8 pagesChapter-12 Electricity Annexure 1DSuhani GosainNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8: Series/Parallel Circuit Elements Laboratory ReportDocument7 pagesExperiment 8: Series/Parallel Circuit Elements Laboratory ReportIan Carlos Villamor LipardoNo ratings yet
- Pages From CHAPT3 OHMS LAW RedDocument13 pagesPages From CHAPT3 OHMS LAW RedsoniNo ratings yet
- Physics 221 Experiment 3: Simple DC Circuits and Resistors: October 1, 2008Document6 pagesPhysics 221 Experiment 3: Simple DC Circuits and Resistors: October 1, 2008lady GNo ratings yet
- Current Proportional Potential Difference Voltage ResistanceDocument32 pagesCurrent Proportional Potential Difference Voltage ResistanceSivaraj ChandrasekaranNo ratings yet
- Voltmeter Ammeter MethodDocument12 pagesVoltmeter Ammeter MethodMoh'd M. GharbiehNo ratings yet
- PHY150 Lab Report 3Document2 pagesPHY150 Lab Report 3Sal Sabeela RahmanNo ratings yet
- Advance Physics For Grade 10 STE StudentsDocument5 pagesAdvance Physics For Grade 10 STE StudentsJoshua AsuncionNo ratings yet
- NEE2202 PARALE LabWorkNo.1Document16 pagesNEE2202 PARALE LabWorkNo.1Ricelle Ann ParaleNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 Switching in Series Resistors Open Circuit File M13Document6 pagesExercise 1 Switching in Series Resistors Open Circuit File M13nicopatNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law To Find The Third Missing Value. Ohms Law Is Used Extensively in ElectronicsDocument3 pagesOhms Law To Find The Third Missing Value. Ohms Law Is Used Extensively in ElectronicsDarius Dave CruzNo ratings yet
- 25 Ohms Law v10 f14Document4 pages25 Ohms Law v10 f14SanjeevkumarSinghNo ratings yet