Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Presentation On Basic Sub-Station Automation System
Uploaded by
sajedarefinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Presentation On Basic Sub-Station Automation System
Uploaded by
sajedarefinCopyright:
Available Formats
Presentation on Substation Automation System (SAS)
Presented byAbu Isha Md. Sajed Arefin Deputy Manager System Protection & Metering Circle Power Grid Company of Bangladesh Ltd.
Definition Substation Automation System (SAS)
The most straightforward definition of SAS is that it can perform-
Local & remote access to the power system
Consisting of Manual & automatic functions
Consisting of communication links & interfaces to the switchgear objects within the substation and to the Network Control & Management Center.
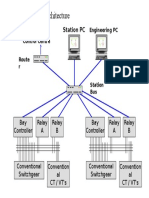
Traditional SAS architecture
Station PC
Control Centre Router Engineering PC
Station Bus
Bay Controller
Relay A
Relay B
Bay Controller
Relay A
Relay B
Conventional Switchgear
Conventional CT / VT's
Conventional Switchgear
Conventional CT / VT's
Brief History of SAS To dig out the history of SAS, lets go back more than 100 years when protective relays were introduced in power system for the first time. Microprocessor based Remote Terminal Units came into picture in 1984. Then in 1994 Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs) were introduced in the power system. And finally universal SAS standard IEC 61850 was introduced in 1997 to build the modern SAS architecture.
From RTU to SAS Architecture
Development of SAS over Time-
Basic Functions of SASBasic Functions Monitoring Functions Typical Examples of Functions Monitoring of switchgear status, transformer tap position & tap changer status etc. Monitoring of control & protection equipment soundness. Monitoring of electrical quantities, e.g. current, voltage, frequency, MW, MVAR etc. Monitoring of station auxiliary supply and DC system. Controlling of circuit breakers & disconnecting switches. opening & closing. Synchronization checking. Maintaining switchgear operational interlocking. Controlling of voltage regulation. Controlling of reactive power. Recording of monitoring data. Fault, disturbance and event recording. Protection of generator, transmission line, power transformer, busbar, RPC bank, distribution feeders, shunt capacitor, shunt reactor etc.
Control Functions
Recording Functions Protection Functions
Major Benefits of SAS Increases reliability and flexibility of the power system. Integrated protection & control accelerates response to problems. A new approach to predict voltage instability. Comparatively easy and cost effective maintenance. Intelligent under frequency initiated load shedding to avoid blackouts. Disturbance recording for fault location and power quality assessment. Power system condition assessment for better knowledge.
Communication in SASCommunication between the switchyard equipments to IEDs and communication between local SAS to network control centers are the backbone of modern SAS. Proper & flexible communications is the key feature to achieve the perfect score and reliability for SAS.
Communication structure of SAS
Communication in SAS- (cont.)
Communication with network control centers Proprietary Protocols RP570/571 (ABB) 8fW (Siemens) DNP3.0 (GE-Harris. DNP User Group) Modbus (Different users specially in power plants) Standard Protocols IEC 60870-5-101 IEC 60870-5-104 IEC 60870-6 IEC 61850
Communication in SAS- (cont.)
Communication within the substation Proprietary Protocols SPA (ABB) LON (ABB) Profibus (Siemens) DNP3.0 (GE-Harris. DNP User Group) UCA.2 (Utility communication architecture by EPRI/IEEE ) Standard Protocols IEC 60870-5-103 IEC 61850
Thank you
You might also like
- Substation AutomationDocument5 pagesSubstation AutomationRavi RaikarNo ratings yet
- Event Logger, Distrubance Recorder and Fault LocatorDocument12 pagesEvent Logger, Distrubance Recorder and Fault LocatorShila Nightingale Chittu100% (1)
- Presentation On Distribution Automation System (DAS)Document18 pagesPresentation On Distribution Automation System (DAS)A I Md. Sajed Arefin83% (6)
- Distribution Automation NewDocument21 pagesDistribution Automation Newvenki249No ratings yet
- High Low Impedance Busbar ProtectionDocument92 pagesHigh Low Impedance Busbar Protectionsugeng100% (1)
- Presentation On Earthing & LightningDocument30 pagesPresentation On Earthing & LightningBSUMANTHKUMARNo ratings yet
- 220/132 Grid Substation PresentationDocument19 pages220/132 Grid Substation PresentationRéyâńśh Sìņğhánìa100% (1)
- Section-4. Technical Specification For 220kv SwitchyardDocument140 pagesSection-4. Technical Specification For 220kv SwitchyardEric TaylorNo ratings yet
- Bus Bar Protection REV 1Document18 pagesBus Bar Protection REV 1Jai GuptaNo ratings yet
- Solar Insect Killer - 20191106Document17 pagesSolar Insect Killer - 20191106Vineet ChauhanNo ratings yet
- LCD Based Moving Message Display With PC DataDocument20 pagesLCD Based Moving Message Display With PC DataPrasanna Ravi100% (1)
- Carrier Current ProtectionDocument21 pagesCarrier Current ProtectionManendra Singh100% (2)
- Elecric Substation Practice (22633)Document9 pagesElecric Substation Practice (22633)vilas kumar67% (6)
- Comprehensive Introduction Substation DesignDocument4 pagesComprehensive Introduction Substation DesignJitendra MahidaNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks PSGDocument12 pages2 Marks PSGSyed Z100% (1)
- Bus Bar SchemesDocument35 pagesBus Bar SchemesbijoyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Power System AutomationDocument15 pagesLecture 6 - Power System AutomationAweSome, ST,MTNo ratings yet
- BSNL Telephone KnowledgeDocument27 pagesBSNL Telephone KnowledgeiamsudhirkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Output Equation of DC Machines.Document5 pagesOutput Equation of DC Machines.srinimeha@gmail.com0% (1)
- Automatic Generation ControlDocument5 pagesAutomatic Generation ControlMuhammad Nizamuddin100% (1)
- Dead Tank and Live TankDocument3 pagesDead Tank and Live Tanklalith kumar100% (1)
- History of Digital and Numerical RelaysDocument18 pagesHistory of Digital and Numerical RelaysPremlataAroraNo ratings yet
- CBIP draft meter standardsDocument22 pagesCBIP draft meter standardslalit123indiaNo ratings yet
- Protective Relays 2Document51 pagesProtective Relays 2Tejas PendkalkarNo ratings yet
- Bus Bar Design and ProtectionDocument58 pagesBus Bar Design and ProtectionMohammedSaadaniHassani100% (4)
- A Report On Mosfet BasedDocument30 pagesA Report On Mosfet Baseddinesh23723100% (1)
- LAN ReportDocument3 pagesLAN ReportMarife Monterde ArcenalNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker Maintenance Using Mobile Agent SoftwareDocument18 pagesCircuit Breaker Maintenance Using Mobile Agent SoftwareAshwin Gopinath80% (10)
- SS AutomationDocument29 pagesSS AutomationPartha Sarathi Manna100% (1)
- Meter, Meter Reading Instrument (MRI)Document80 pagesMeter, Meter Reading Instrument (MRI)Vaneet Gupta0% (1)
- Automation in SCADA, Substation & MeteringDocument82 pagesAutomation in SCADA, Substation & MeteringSudarshan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Multiple Fault Detection and Indication To Electricity BoardDocument74 pagesTransmission Line Multiple Fault Detection and Indication To Electricity BoardCrisp100% (1)
- Protection of SubstationDocument21 pagesProtection of SubstationDivyanshu Agarwal50% (2)
- Load Dispatch CenterDocument17 pagesLoad Dispatch CenterVrutuja Yeole100% (1)
- Energy Control Center Functions For Power SystemDocument9 pagesEnergy Control Center Functions For Power SystemtejaNo ratings yet
- Transformer ProtectionDocument31 pagesTransformer Protectionbijoy100% (1)
- ASHIDA Numerical RelayDocument29 pagesASHIDA Numerical RelayRitesh Jaiswal100% (1)
- Trip Circuit Supervision Relay Explained in Detail !!!!!!!Document6 pagesTrip Circuit Supervision Relay Explained in Detail !!!!!!!Manali PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Power Line Carrier CommunicationDocument23 pagesPower Line Carrier CommunicationMUDAM ALEKYANo ratings yet
- Power Flow in A Meshed SystemDocument2 pagesPower Flow in A Meshed Systemsabapathy170672100% (2)
- Power System AutomationDocument139 pagesPower System Automation08mpe026No ratings yet
- FSK ModulatorDocument37 pagesFSK ModulatorSidra FahimNo ratings yet
- SIFANG - CSC-2000 (V2) Substation Automation SCADA System Technical and Application Manual (0SF.492.118E) - V1.00Document88 pagesSIFANG - CSC-2000 (V2) Substation Automation SCADA System Technical and Application Manual (0SF.492.118E) - V1.00MarkusKunNo ratings yet
- Substation AutomationDocument110 pagesSubstation Automationdilipeline0% (1)
- 06-Computer Maintenance Tool - Rev GDocument24 pages06-Computer Maintenance Tool - Rev GrpshvjuNo ratings yet
- Overlapping Protective Zones DiagramDocument3 pagesOverlapping Protective Zones DiagramK.GuruCharan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Numerical Overcurrent Protection Relay - Argus 1Document4 pagesNumerical Overcurrent Protection Relay - Argus 1sulemanchNo ratings yet
- Interview QuestionsDocument5 pagesInterview QuestionsShahed HussainNo ratings yet
- Submited by:-VII Semester, IV Year Electrical Engineering Submitted ToDocument23 pagesSubmited by:-VII Semester, IV Year Electrical Engineering Submitted ToSunny Holmes0% (1)
- Substation Automation Basics - The Next GenerationDocument8 pagesSubstation Automation Basics - The Next GenerationAlly RaxaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Overload SizingDocument2 pagesThermal Overload SizingBeloved Gelou100% (1)
- Basic Sub Station Automation SystemDocument13 pagesBasic Sub Station Automation SystemMạnh Hiếu BùiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of An IEC 61850 Based Electric Substation Communication ArchitectureDocument6 pagesAnalysis of An IEC 61850 Based Electric Substation Communication ArchitectureHari NairNo ratings yet
- 94 NewDocument5 pages94 Newrachaide.saidNo ratings yet
- Integrating SCADA and Sap Operations For Electricity Process AutomationDocument3 pagesIntegrating SCADA and Sap Operations For Electricity Process AutomationHakim BenmajidNo ratings yet
- White Paper - Data Communication in Substation Automation System SAS - Part 1 Original 23353Document5 pagesWhite Paper - Data Communication in Substation Automation System SAS - Part 1 Original 23353sabrahimaNo ratings yet
- The Specification of Iec 61850 Based Substation Automation SystemsDocument8 pagesThe Specification of Iec 61850 Based Substation Automation Systemsyesfriend28No ratings yet
- Scad ADocument10 pagesScad AKhaddavi KhalifNo ratings yet
- SAS PresentationDocument24 pagesSAS PresentationGirish Chaitanya100% (2)
- Frs Scada Genl ServicesDocument4 pagesFrs Scada Genl ServicesAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Electrical Substation TypesDocument2 pagesElectrical Substation TypessajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Example of Protective Relay OperationDocument6 pagesExample of Protective Relay OperationsajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Traditional SAS ArchitectureDocument1 pageTraditional SAS ArchitecturesajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Electrical Substation - Primary ComponentsDocument1 pageElectrical Substation - Primary ComponentssajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Outputs of Protective RelaysDocument1 pageOutputs of Protective RelayssajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Inputs of Protective RelaysDocument1 pageInputs of Protective RelayssajedarefinNo ratings yet
- As The Names ImplyDocument1 pageAs The Names ImplysajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Knowledge On Scheme ContinuationDocument3 pagesKnowledge On Scheme ContinuationsajedarefinNo ratings yet
- BEN RecordDocument1 pageBEN RecordsajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Example of Protective Relay OperationDocument6 pagesExample of Protective Relay OperationsajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Protection RequirementDocument1 pageProtection RequirementsajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Device NameDocument6 pagesDevice NamesajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Auto-Transformer Fault AnalysisDocument8 pagesThree Phase Auto-Transformer Fault AnalysiscuamiNo ratings yet
- Assessment Questionnaire On Understanding SLD & 3-Line Diagram and SS Busbar Arrangement, Understanding and Registering Operational Signals - Flags of Relay and Control PanelsDocument2 pagesAssessment Questionnaire On Understanding SLD & 3-Line Diagram and SS Busbar Arrangement, Understanding and Registering Operational Signals - Flags of Relay and Control PanelssajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Tele-Protection Signal List For 132 KV Line ProtectionDocument1 pageTele-Protection Signal List For 132 KV Line Protectionsajedarefin100% (1)
- Protection of Power TransformerDocument1 pageProtection of Power TransformersajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Knowledge On Electrical SymbolsDocument1 pageKnowledge On Electrical SymbolssajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Device NameDocument6 pagesDevice NamesajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Knowledge On Electrical Device NomenclatureDocument1 pageKnowledge On Electrical Device NomenclaturesajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts Needed To Understand Electrical Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageBasic Concepts Needed To Understand Electrical Schematic DiagramsajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Inputs of Protective RelaysDocument1 pageInputs of Protective RelayssajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Knowledge On Electrical Device NomenclatureDocument1 pageKnowledge On Electrical Device NomenclaturesajedarefinNo ratings yet
- 87T transformer differential relay test reportDocument3 pages87T transformer differential relay test reportsajedarefin0% (2)
- Setting Cooper Form 3A Recloser ControllersDocument5 pagesSetting Cooper Form 3A Recloser ControllerssajedarefinNo ratings yet
- MicroTrip Notes PDFDocument8 pagesMicroTrip Notes PDFsajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Setting NU-LEC CAPM4 Recloser Controllers in CAPEDocument7 pagesSetting NU-LEC CAPM4 Recloser Controllers in CAPEsajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Settings Transfer Utilities PDFDocument25 pagesSettings Transfer Utilities PDFsajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Breaker Duty User Guide PDFDocument79 pagesBreaker Duty User Guide PDFsajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Figures Tables Needed by CC Macro PDFDocument3 pagesFigures Tables Needed by CC Macro PDFsajedarefinNo ratings yet
- Flatpack2 IntegratedDocument2 pagesFlatpack2 IntegratedNeil BaillieNo ratings yet
- Cat - C4.4 - CaterpillarDocument8 pagesCat - C4.4 - CaterpillarBùi Thanh Nga50% (2)
- [Communications in Computer and Information Science 281] Muhammad Aamir, Javier Poncela (Auth.), Bhawani Shankar Chowdhry, Faisal Karim Shaikh, Dil Muhammad Akbar Hussain, Muhammad Aslam Uqaili (Eds.) - EmeDocument567 pages[Communications in Computer and Information Science 281] Muhammad Aamir, Javier Poncela (Auth.), Bhawani Shankar Chowdhry, Faisal Karim Shaikh, Dil Muhammad Akbar Hussain, Muhammad Aslam Uqaili (Eds.) - EmeHemanandNo ratings yet
- Methods of Time Synchronization: Eric Sagen and Kenneth Workman, Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, IncDocument7 pagesMethods of Time Synchronization: Eric Sagen and Kenneth Workman, Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, IncAnonymous 9VcxlFErfNo ratings yet
- Handbook-GRID CODEDocument123 pagesHandbook-GRID CODEabhijitNo ratings yet
- Cigre StatcomDocument170 pagesCigre StatcomМиша ГабриеловNo ratings yet
- PSG Group Discussion QuestionsDocument3 pagesPSG Group Discussion Questionspvanitha143No ratings yet
- Resume ZahidDocument7 pagesResume ZahidEngr Irfan AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Steam Turbine Ranges - 1Document7 pagesSteam Turbine Ranges - 1Alex OrdazNo ratings yet
- Synchronous MotorsDocument11 pagesSynchronous MotorsSanjay GhoshNo ratings yet
- Alpha CatalogDocument180 pagesAlpha CatalogTopcom Toki-Voki100% (1)
- P1662/D8.0, March 2016 - IEEE Draft Recommended Practice For Design and Application of Power Electronics in Electrical Power SystemsDocument63 pagesP1662/D8.0, March 2016 - IEEE Draft Recommended Practice For Design and Application of Power Electronics in Electrical Power SystemsHgoglezNo ratings yet
- 032 EEE135 OutDocument2 pages032 EEE135 OutribeirofabianoNo ratings yet
- MMUP OdelonDocument29 pagesMMUP Odelonatik100% (27)
- Distribution Line Performance and Reliability Improvement Through Feeder Reconfiguration in Dessie TownDocument53 pagesDistribution Line Performance and Reliability Improvement Through Feeder Reconfiguration in Dessie TownAnonymous fxCgVPgNo ratings yet
- HTS DC Cable Line Project On-Going Activities in RussiaDocument4 pagesHTS DC Cable Line Project On-Going Activities in RussiaSubba PappuNo ratings yet
- Ex Ecm2Document4 pagesEx Ecm2rodruren01No ratings yet
- Internship Report of Rafsun Jani SarkerDocument17 pagesInternship Report of Rafsun Jani SarkerRafsun JaniNo ratings yet
- Protective Relay Training CoursesDocument5 pagesProtective Relay Training CoursesdenramrNo ratings yet
- 2.single Line Diagram L2Document12 pages2.single Line Diagram L2Rajat RaiNo ratings yet
- Standard Approach To Perform Power System Stability Studies in Oil and Gas PlantsDocument13 pagesStandard Approach To Perform Power System Stability Studies in Oil and Gas PlantsShailesh ChettyNo ratings yet
- Fuente Rectificadora Enatel PSX24 800W A 2400WDocument2 pagesFuente Rectificadora Enatel PSX24 800W A 2400WFranco Cortez100% (1)
- Tutorial-List IEEEDocument1 pageTutorial-List IEEEBodhi KiranNo ratings yet
- IV I Results Nov 2015Document91 pagesIV I Results Nov 2015Ann ThomasNo ratings yet
- SWITCHGEAR AND PROTECTION RELAYSDocument54 pagesSWITCHGEAR AND PROTECTION RELAYSPardha Saradhi JNo ratings yet
- Protection Systems Impedance RelaysDocument41 pagesProtection Systems Impedance RelaysMonika LeonitaNo ratings yet
- Energy Control Center Functions For Power SystemDocument9 pagesEnergy Control Center Functions For Power SystemtejaNo ratings yet
- Load Frequency Control in Three Area Power System Using Fuzzy Logic ControllerDocument6 pagesLoad Frequency Control in Three Area Power System Using Fuzzy Logic ControllerEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- PSSEDocument6 pagesPSSESyed Faizan AliNo ratings yet
- Power System Research PapersDocument5 pagesPower System Research Papersknztwaulg100% (1)






















































































![[Communications in Computer and Information Science 281] Muhammad Aamir, Javier Poncela (Auth.), Bhawani Shankar Chowdhry, Faisal Karim Shaikh, Dil Muhammad Akbar Hussain, Muhammad Aslam Uqaili (Eds.) - Eme](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/380392245/149x198/62a280e94a/1527538539?v=1)

























