Professional Documents
Culture Documents
History of Indian Architecture
Uploaded by
joshjethCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
History of Indian Architecture
Uploaded by
joshjethCopyright:
Available Formats
The history of Indian Architecture was shaped by the history of the Indian sub-continent Urban civilisation traceable to 2500
B.C. Cities of Harappa, Mohenjo daro Kushan Empire, Mauryan Empire, the Sunghas, Satvahanas Styles ranging from Hindu Temple to Islamic to Western Classical Architecture
Each city was surrounded by massive walls and gateways. They based their city streets on a grid system which were oriented east-west. Each street had a well organised drainage system. Houses and other buildings were made of sun dried or kiln fired mud brick.
Each house had an indoor and outdoor kitchen. Outdoor kitchen were used when it was warmer and the indoor kitchen was used, when it was colder. Wells are quite common and comprise one of the most recognizable feature of Harappan urbanism.
REMAINS OF THE HARAPPAN SITE
WELL
RUINS AT HARAPPAN SITE
Layout was based on a grid of streets which were laid out in perfect pattern. Buildings were particularly advanced. Structures were constructed of same size sun dried bricks of baked mud and burned wood. The public buildings also suggest a high degree of social organization. Granaries were designed with bays to receive carts delivering crops from the country side.
Renowned Great Bath came up during the Mohenjo-Daro. The elaborate bath area was very well built with a layer of natural tar to keep from leaking and in the centre was the pool.
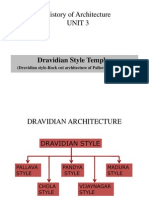
This style of architecture is based on the influence of 7 kingdoms in south India, namely: 1. The Pandyas(560-710 AD) 2. Pallavas(600-900 AD) 3.Cholas(848-1280 AD) 4. Rashtrakutas(753-973 AD) 5. Chalukyas(973-1180 AD) 6.Hoysalas(1100-1343 AD) 7. Vijayanagaras(1343-1565 AD)
MAIN FEATURES of Temple Architecture:
1.
The principal part, the actual temple itself, is called the Vimanam. It is always square in plan, and surmounted by a pyramidal roof of one or more stories; and it contains the cell in which the image of the god or his emblem is placed. The porches or Mantapams, which always cover and precede the door leading to the cell.
2.
3. Gate-pyramids, Gopurams, which are the principal features in the quadrangular enclosures that surround the more notable temples. 4. Pillard halls or Chaultrisproperly Chawadis -used for various purposes, and which are the invariable accompaniments of these temples.
Indian style of architecture is one of the most diverse ones in the history of the world Deep impact of religion: Hindu Temples, Buddhism, Islamic architecture Influence of dynasties: Architectural features of different dynasties have played significant role in shaping Indian architecture Impact of foreign invasion: The invasions of West Asian & European nations have also left their influence
You might also like
- Abdomen - FRCEM SuccessDocument275 pagesAbdomen - FRCEM SuccessAbin ThomasNo ratings yet
- Dravidian Temple and Indo-Aryan TempleDocument34 pagesDravidian Temple and Indo-Aryan TempleShivani Snigdha100% (1)
- THREE MAIN STYLES OF ANCIENT INDIAN TEMPLE ARCHITECTUREDocument10 pagesTHREE MAIN STYLES OF ANCIENT INDIAN TEMPLE ARCHITECTUREshivani lohiaNo ratings yet
- Mauryan Architecture and Buddhist Stupa DevelopmentDocument31 pagesMauryan Architecture and Buddhist Stupa DevelopmentZafar Hayat Khan88% (8)
- Fatehpur SikriDocument12 pagesFatehpur SikriKashif KhanNo ratings yet
- Mughal ArchitectureDocument85 pagesMughal ArchitectureJanani Surender67% (3)
- Nagara Temple ArchitectureDocument24 pagesNagara Temple Architecturesalman75% (4)
- Retaining Wall DesignDocument55 pagesRetaining Wall DesignMohit Kohli100% (1)
- History of Architecture: Indian ArchitectureDocument18 pagesHistory of Architecture: Indian ArchitectureChin Tuason100% (1)
- 1.indo Aryan StyleDocument22 pages1.indo Aryan Styleasma m a57% (7)
- Inflation and DeflationDocument61 pagesInflation and Deflationjoshjeth100% (1)
- Inflation and DeflationDocument61 pagesInflation and Deflationjoshjeth100% (1)
- Indigenous Architecture of Kerala - Vernacular Architecture StudyDocument57 pagesIndigenous Architecture of Kerala - Vernacular Architecture StudyBhanuKhanna78% (32)
- Well FoundationDocument126 pagesWell Foundationjoshjeth0% (1)
- Well FoundationDocument126 pagesWell Foundationjoshjeth0% (1)
- Indian Architecture in Concept and Execution Case Study of Dravidian Temple ArchitectureDocument21 pagesIndian Architecture in Concept and Execution Case Study of Dravidian Temple ArchitectureLakshmiNarasimhan GN100% (4)
- Nagara StyleDocument42 pagesNagara StylePooja PAdhy50% (2)
- Indo Saracenic ArchitectureDocument6 pagesIndo Saracenic Architecturesm rNo ratings yet
- Isms PDFDocument9 pagesIsms PDFKevin CoNo ratings yet
- ARCHITECTURE IN CAMBODIADocument8 pagesARCHITECTURE IN CAMBODIAJohnBenedictRazNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture - III - by Shanmuga SirDocument118 pagesHistory of Architecture - III - by Shanmuga SirKarthik Suresh50% (2)
- Hindu Temple ArchitectureDocument12 pagesHindu Temple ArchitecturePrakritiNo ratings yet
- Re-Interpretation of Goan ArchitectureDocument27 pagesRe-Interpretation of Goan Architecturelester100% (3)
- ARC226 History of Architecture 2Document64 pagesARC226 History of Architecture 2Partha Sarathi Mishra75% (4)
- History of Indian Architecture - by Ashish NangiaDocument177 pagesHistory of Indian Architecture - by Ashish NangiaGSus79100% (6)
- Mughal Architecture and InfluenceDocument84 pagesMughal Architecture and InfluenceYesha Goti57% (7)
- Pataleshwar Cave FinalDocument3 pagesPataleshwar Cave FinalAbhishek AgrawalNo ratings yet
- City Heritage Development PlanDocument271 pagesCity Heritage Development PlanCHALLA MOUNICA100% (1)
- Lecture-8 Islamic Architecture - CombinedDocument81 pagesLecture-8 Islamic Architecture - CombinedLEKSHMI MJNo ratings yet
- ARC226 History of Architecture 9 PDFDocument19 pagesARC226 History of Architecture 9 PDFPartha Sarathi Mishra95% (21)
- Buddhist Architecture in IndiaDocument41 pagesBuddhist Architecture in IndiaAditi Shaw100% (2)
- Lecture 1 Rajasthan ArchitectureDocument25 pagesLecture 1 Rajasthan ArchitectureGurpreetSinghKalsi100% (1)
- Indian ArchitectureDocument39 pagesIndian ArchitectureAnnie Varghese100% (2)
- Difference Between North Indian and South Indian Temple ArchitectureDocument3 pagesDifference Between North Indian and South Indian Temple Architectureaditi3267% (9)
- Seven Cities of DelhiDocument32 pagesSeven Cities of Delhishahbaz288100% (1)
- Histry of Arch - IslamicDocument50 pagesHistry of Arch - IslamicRavi ChandraNo ratings yet
- Planning of ShahjahanabadDocument22 pagesPlanning of ShahjahanabadAnirudh BabbarNo ratings yet
- Colonial Architecture: Colonial Architecture Is An Architectural Style From A Mother Country ThatDocument44 pagesColonial Architecture: Colonial Architecture Is An Architectural Style From A Mother Country ThatNikhil GoyalNo ratings yet
- South Indian Temple ArchitectureDocument54 pagesSouth Indian Temple ArchitectureSheshu SheshadriNo ratings yet
- Dravidian ArchitectureDocument25 pagesDravidian ArchitectureArun Unnikrishnan100% (2)
- Unit 2 Dravidian ArchitectureDocument45 pagesUnit 2 Dravidian ArchitectureSuraj86% (7)
- Indo Sarcenic ArchitectureDocument16 pagesIndo Sarcenic ArchitectureMaitreyi MuraliNo ratings yet
- Brihadisvara Temple, ThanjavurDocument22 pagesBrihadisvara Temple, ThanjavurAllen Antony Kurisingal100% (1)
- The Chalukayan Architecture: Submitted By: PANKAJ AR-1402 Epsha Ar-1423 SANCHIT AR-1424 Amit Ar-1433Document17 pagesThe Chalukayan Architecture: Submitted By: PANKAJ AR-1402 Epsha Ar-1423 SANCHIT AR-1424 Amit Ar-1433nikitaNo ratings yet
- Tibet: Tibetan Buddhism ArchitectureDocument30 pagesTibet: Tibetan Buddhism ArchitectureFrancis Carlo CondeNo ratings yet
- Ancient Indian ArchitectureDocument12 pagesAncient Indian Architecturekiran_a_c100% (2)
- Unit 3 Gupta & ChalukyaDocument20 pagesUnit 3 Gupta & ChalukyaKaamesh RaviselvanNo ratings yet
- Tomb of Muhammad ShahDocument13 pagesTomb of Muhammad ShahmonikaNo ratings yet
- Kandariya Mahadev Temple, largest and most ornate at KhajurahoDocument3 pagesKandariya Mahadev Temple, largest and most ornate at KhajurahoajNo ratings yet
- ARC226 History of Architecture 3Document48 pagesARC226 History of Architecture 3Partha Sarathi Mishra100% (1)
- Humayun Tomb PDFDocument12 pagesHumayun Tomb PDFShantanuShah33% (3)
- 5.vesara - Central Indian Style TempleDocument50 pages5.vesara - Central Indian Style TempleIsaa JatuNo ratings yet
- Indian ArchitectureDocument13 pagesIndian ArchitectureCliff Jason GulmaticoNo ratings yet
- Classical Revival and Indo-Saracenic Architecture in DelhiDocument29 pagesClassical Revival and Indo-Saracenic Architecture in DelhiAashu Sharma100% (1)
- B. v. DoshiDocument47 pagesB. v. Doshinonie09ashna100% (1)
- Nyatapola TempleDocument12 pagesNyatapola TempleSofia Estrada100% (1)
- Indo Aryan Temple Architecture in Orissa from 800-1250 ADDocument39 pagesIndo Aryan Temple Architecture in Orissa from 800-1250 ADHari Srinivas83% (6)
- Architecture of KeralaDocument18 pagesArchitecture of Keralasunil kumarNo ratings yet
- Early Chalukyan ArchitectureDocument10 pagesEarly Chalukyan Architecturerashi1717100% (1)
- Vaikunta Perumal TempleDocument11 pagesVaikunta Perumal TempleChandni MulakalaNo ratings yet
- Temple Architecture: Nagara and Dravidian StyleDocument30 pagesTemple Architecture: Nagara and Dravidian StyleNeeraj VashistNo ratings yet
- Provincial Style of Bengal Architecture Featured Drop Arches and Climate Responsive DesignDocument3 pagesProvincial Style of Bengal Architecture Featured Drop Arches and Climate Responsive DesignPøøjåNo ratings yet
- EVOLUTION OF SOUTH INDIAN TEMPLE ARCHITECTUREDocument21 pagesEVOLUTION OF SOUTH INDIAN TEMPLE ARCHITECTUREanusha sankarNo ratings yet
- History of ArchitectureDocument17 pagesHistory of ArchitectureHarshene KrishnamurhtyNo ratings yet
- History of Architecture - Module 1.1Document15 pagesHistory of Architecture - Module 1.1Noori Dhillon0% (1)
- Kerala Petrochemical Park DPR Revised for AmbalamughalDocument362 pagesKerala Petrochemical Park DPR Revised for AmbalamughalVinu VaviNo ratings yet
- ArtsDocument7 pagesArtsjoshjethNo ratings yet
- EURO Crisis, Greece Elections, Italian Marines Case, EU-India RelationsDocument92 pagesEURO Crisis, Greece Elections, Italian Marines Case, EU-India RelationsjoshjethNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundations PPTRDocument31 pagesPile Foundations PPTRjoshjethNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Corrosion in Reinforced Cement ConcreteDocument18 pagesMechanism of Corrosion in Reinforced Cement ConcretejoshjethNo ratings yet
- Bridge Me 1Document333 pagesBridge Me 1amawauceNo ratings yet
- Bearing CapacityDocument28 pagesBearing CapacityjoshjethNo ratings yet
- Gs Score PolityDocument42 pagesGs Score PolityAyush RaiNo ratings yet
- Culture Complete Notes MrunalDocument51 pagesCulture Complete Notes Mrunalamarsinha198767% (6)
- Deterioration of ConcreteDocument14 pagesDeterioration of ConcretejoshjethNo ratings yet
- Deterioration of ConcreteDocument14 pagesDeterioration of ConcretejoshjethNo ratings yet
- Straw Bale ConstructionDocument23 pagesStraw Bale Constructionjoshjeth67% (3)
- Value of Travel TimeDocument22 pagesValue of Travel TimejoshjethNo ratings yet
- Straw Bale ConstructionDocument23 pagesStraw Bale Constructionjoshjeth67% (3)
- PollutionDocument36 pagesPollutionjoshjethNo ratings yet
- Calibration Techniques for Trace Metal Analysis by Atomic SpectroscopyDocument32 pagesCalibration Techniques for Trace Metal Analysis by Atomic SpectroscopyjoshjethNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Corrosion in Reinforced Cement ConcreteDocument14 pagesMechanism of Corrosion in Reinforced Cement ConcretejoshjethNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution CLASS Nov'08Document109 pagesAir Pollution CLASS Nov'08joshjethNo ratings yet
- BearingsDocument40 pagesBearingsjoshjethNo ratings yet
- Central Bank Functions and ResponsibilitiesDocument82 pagesCentral Bank Functions and Responsibilitiesjoshjeth100% (1)
- Groundwater ContaminationDocument25 pagesGroundwater ContaminationjoshjethNo ratings yet
- 1) Solid Waste Disposal and ManagementDocument70 pages1) Solid Waste Disposal and ManagementDrRagesh P PNo ratings yet
- EIADocument11 pagesEIAjoshjeth100% (1)
- MONEY2Document33 pagesMONEY2joshjethNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa Case Study: Adefuin, Jay Rovillos, Noemie MDocument40 pagesPlacenta Previa Case Study: Adefuin, Jay Rovillos, Noemie MMikes CastroNo ratings yet
- 07.03.09 Chest Physiotherapy PDFDocument9 pages07.03.09 Chest Physiotherapy PDFRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- ROMUS 2012 Flooring CatalogueDocument20 pagesROMUS 2012 Flooring CatalogueDan George IIINo ratings yet
- Pitch Manual SpecializedDocument20 pagesPitch Manual SpecializedRoberto Gomez100% (1)
- Discuss The Challenges For Firms To Operate in The Hard-Boiled Confectionery Market in India?Document4 pagesDiscuss The Challenges For Firms To Operate in The Hard-Boiled Confectionery Market in India?harryNo ratings yet
- Telco XPOL MIMO Industrial Class Solid Dish AntennaDocument4 pagesTelco XPOL MIMO Industrial Class Solid Dish AntennaOmar PerezNo ratings yet
- CANAL (T) Canal Soth FloridaDocument115 pagesCANAL (T) Canal Soth FloridaMIKHA2014No ratings yet
- Tetracyclines: Dr. Md. Rageeb Md. Usman Associate Professor Department of PharmacognosyDocument21 pagesTetracyclines: Dr. Md. Rageeb Md. Usman Associate Professor Department of PharmacognosyAnonymous TCbZigVqNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of The 16 TH WLCDocument640 pagesProceedings of The 16 TH WLCSabrinaNo ratings yet
- O2 Orthodontic Lab Catalog PDFDocument20 pagesO2 Orthodontic Lab Catalog PDFplayer osamaNo ratings yet
- Helmitin R 14030Document3 pagesHelmitin R 14030katie.snapeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Finite Element Methods (2001) (En) (489s)Document489 pagesIntroduction To Finite Element Methods (2001) (En) (489s)green77parkNo ratings yet
- QP (2016) 2Document1 pageQP (2016) 2pedro carrapicoNo ratings yet
- The Simple PendulumDocument5 pagesThe Simple PendulumDexter TorringtonNo ratings yet
- Retaining Wall-Masonry Design and Calculation SpreadsheetDocument6 pagesRetaining Wall-Masonry Design and Calculation SpreadsheetfarrukhNo ratings yet
- Awakening The MindDocument21 pagesAwakening The MindhhhumNo ratings yet
- Clausius TheoremDocument3 pagesClausius TheoremNitish KumarNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Calculations of The Ground Plane Inductance Associated With A Printed Circuit BoardDocument46 pagesAnalysis and Calculations of The Ground Plane Inductance Associated With A Printed Circuit BoardAbdel-Rahman SaifedinNo ratings yet
- Motor Wiring Diagram: D.C. Motor ConnectionsDocument1 pageMotor Wiring Diagram: D.C. Motor Connectionsczds6594No ratings yet
- Fake News Poems by Martin Ott Book PreviewDocument21 pagesFake News Poems by Martin Ott Book PreviewBlazeVOX [books]No ratings yet
- SB Z Audio2Document2 pagesSB Z Audio2api-151773256No ratings yet
- Interpreting Piping and Instrumentation DiagramsDocument41 pagesInterpreting Piping and Instrumentation DiagramsFredric Tun100% (2)
- Are Hypomineralized Primary Molars and Canines Associated With Molar-Incisor HypomineralizationDocument5 pagesAre Hypomineralized Primary Molars and Canines Associated With Molar-Incisor HypomineralizationDr Chevyndra100% (1)
- Internship ReportDocument18 pagesInternship ReportRathan Kumar SMNo ratings yet
- Who will buy electric vehicles Segmenting the young Indian buyers using cluster analysisDocument12 pagesWho will buy electric vehicles Segmenting the young Indian buyers using cluster analysisbhasker sharmaNo ratings yet
- Features Integration of Differential Binomial: DX BX A X P N MDocument4 pagesFeatures Integration of Differential Binomial: DX BX A X P N Mابو سامرNo ratings yet
- Product ListDocument4 pagesProduct ListyuvashreeNo ratings yet
- Antennas Since Hertz and MarconiDocument7 pagesAntennas Since Hertz and MarconiTaiwo Ayodeji100% (1)
- B. Pharmacy 2nd Year Subjects Syllabus PDF B Pharm Second Year 3 4 Semester PDF DOWNLOADDocument25 pagesB. Pharmacy 2nd Year Subjects Syllabus PDF B Pharm Second Year 3 4 Semester PDF DOWNLOADarshad alamNo ratings yet