Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Competency Mapping - Techniques and Models
Uploaded by
Anitha Prabakar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views17 pagesCompetency mapping is used to identify the key skills, attributes, and behaviors that distinguish excellent performance from average performance. It involves assessing employees' competencies during recruitment, development, succession planning, and organizational analysis. Critical incident technique and repertory grid analysis are methods used to map competencies. There are different approaches to competency models, including organizational, human resource, team-based, and individual models. An effective competency model specifies the behaviors, knowledge, and motivations necessary for critical organizational results but must be based on actual data about employee competencies and performance.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCompetency mapping is used to identify the key skills, attributes, and behaviors that distinguish excellent performance from average performance. It involves assessing employees' competencies during recruitment, development, succession planning, and organizational analysis. Critical incident technique and repertory grid analysis are methods used to map competencies. There are different approaches to competency models, including organizational, human resource, team-based, and individual models. An effective competency model specifies the behaviors, knowledge, and motivations necessary for critical organizational results but must be based on actual data about employee competencies and performance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views17 pagesCompetency Mapping - Techniques and Models
Uploaded by
Anitha PrabakarCompetency mapping is used to identify the key skills, attributes, and behaviors that distinguish excellent performance from average performance. It involves assessing employees' competencies during recruitment, development, succession planning, and organizational analysis. Critical incident technique and repertory grid analysis are methods used to map competencies. There are different approaches to competency models, including organizational, human resource, team-based, and individual models. An effective competency model specifies the behaviors, knowledge, and motivations necessary for critical organizational results but must be based on actual data about employee competencies and performance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
It is about identifying preferred behaviours and
personal skills which distinguish excellent and
outstanding performance from the average.A
Competency is the ingredients (skills, knowledge,
attributes and behaviours) that contribute to
excellence.
What is Competency Mapping?
The use of Competencies can include: assessment
during recruitment, assessment during further
development; as a profile during assessment to guide
future development needs; succession planning and
promotion; organisational development analysis.
Techniques used to map Competencies include
Critical Incident Analysis and Repertory Grid.
When should Competencies be
used?
Respondents are asked to relate specific
incidents, which highlighted exemplary
behaviours in critical situations. This is based on
the assumption that the best and the worst of a
person surfaces in a crisis.
What is Critical incident technique?
What is Repertory Grid Analysis?
identify important attributes
for each attributes, establish a bipolar scale
with differentiable characteristics and
their opposites
Example: Assisting in selecting a computer
language
Attributes
Availability
Easy of Programming
Training Time
Orientation
Traits
high, low, symbolic, numeric
Attributes Trait Opposite
Availability
Widely Available Not available
Ease of
Programming
High Low
Training Time Low High
Orientation Symbolic Numeric
Business Applications of
Repertory Grid
Market Research
Quality Control
Job Analysis and Design
Decision Making
Organizational Approaches Models
HR Systems Approaches Models
Team Approaches Models
Individualistic Models
Organizational Approaches
Elliot Jaques provides a normative model of effective
hierarchical organizations with an emphasis on
competencies. The elements include the present and
potential competencies of individuals along the dimensions
of cognitive capacity, valuing the work, and non-disruptive
personality.
Peter Senges approach to a whole organization
competency model is captured in his notion of the "learning
organization." Its essential characteristics include nurturing
the growth of new capabilities, transformational learning for
survival, learning through performance and practice, and the
inseparability of process and content.
HR Systems Approaches
Dubois focuses on the whole human resources
system, but emphasizes competency improvements through
training and development strategies and programming: the
contingencies are driven by organizational strategy but
outcomes are focused on individual employees competency
enhancement.
Charles Snows contingency model links
organizational performance to HRM and competency.
Strategies depend on extent to which cause-effect relations
affecting organizational performance are known and degree
of formalized standards of desirable performance.
Team Approaches
Campions model, which applies to
professional work, suggests that teams
composed of individuals with complementary
competencies are more effective and have higher
levels of job satisfaction than teams whose
members have the same competency sets. This
is especially true for work that is complex and
varied in scope.
Individualistic Models
Traditional Person-Job Match Model
This model assumes that employees have jobs with specific and
identifiable tasks. Work is generally standardized and repetitive in
an organizational hierarchy. Job performance is readily verifiable.
This model works best with organizations defined by stable
environments
Strategy Based Model
This model assumes that employees have roles defined by the
organizations strategic goals. Work is flexibly defined and often
carried out in a flattened, decentralized or matrix structure. Role
performance is only partially verifiable. This model functions
most effectively in organizations in competitive, complex or highly
stressed environments.
Individualistic Models (contd)
The Strategy Development Model
This model assumes that employees with broad, strategic
attributes will create their own roles which interact to produce
the organizations strategy. Work is constantly evolving within a
network of organizational relationships. This model is described
in terms of organizations in chaotic, unpredictable, or very rapidly
changing environments.
Intellectual Capital Model
These models emphasize the linkages and dynamic
interaction among human capital, structural capital, and customer
(client) capital. These models stress the knowledge that resides in
employees and strategies to use it and value it differently.
Companies create and use the Competency models
to specify the employee behaviors, knowledge, and
motivations that they believe are
necessary to produce organizationally critical results.
But if the model is not quite right, the organization will
suffer. To determine the right model it is essential to
look at actual data -- assessments of employees
competencies and of the results they achieve.
As a conclusion we can say that ,it is
through the competencies of its employees
executives, managers, and individual
contributors -- that an organization
executes its strategy and achieves results
that are crucial to its success.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- (2010) Handbook Strategy As PracticeDocument367 pages(2010) Handbook Strategy As PracticeViniciusNo ratings yet
- (1)Document94 pages(1)Luigi TencoNo ratings yet
- FMCG Marketing and Sales: Organizing Trade Marketing, Category Management, and Shopper Marketing PDFDocument242 pagesFMCG Marketing and Sales: Organizing Trade Marketing, Category Management, and Shopper Marketing PDFSilmi KaffahNo ratings yet
- GSM BTS Over IP Deployment Troubleshooting GuideDocument27 pagesGSM BTS Over IP Deployment Troubleshooting GuideKeartichai Chomtaku100% (1)
- Brinton NietzscheDocument296 pagesBrinton Nietzschej1943No ratings yet
- Get It Up 1 - DAP AnDocument18 pagesGet It Up 1 - DAP AnAndreea EliescuNo ratings yet
- Teaching Language in ContextDocument41 pagesTeaching Language in ContextMárcio da Silva SantosNo ratings yet
- Nonaka and Takeuchi Knowledge Spiral ModelDocument18 pagesNonaka and Takeuchi Knowledge Spiral ModelkangdediNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Opportunities of Retailing in India During Covid-19 Pandemic Period - A Behavioural ApproachDocument1 pageChallenges and Opportunities of Retailing in India During Covid-19 Pandemic Period - A Behavioural ApproachAnitha PrabakarNo ratings yet
- MIS Unit IIDocument7 pagesMIS Unit IIAnitha PrabakarNo ratings yet
- Teachers and The Law: Do I Have A Contract?Document12 pagesTeachers and The Law: Do I Have A Contract?Anitha PrabakarNo ratings yet
- MM FinalDocument34 pagesMM FinalAnitha PrabakarNo ratings yet
- Teddy Wear: - 1 Step Kids StoreDocument26 pagesTeddy Wear: - 1 Step Kids StoreAnitha PrabakarNo ratings yet
- Image Steganography Using HBC and RDH TechniqueDocument4 pagesImage Steganography Using HBC and RDH TechniqueATSNo ratings yet
- Teddy Wear: - 1 Step Kids StoreDocument26 pagesTeddy Wear: - 1 Step Kids StoreAnitha PrabakarNo ratings yet
- Image Steganography Using RDH and HBC TechniquesDocument24 pagesImage Steganography Using RDH and HBC TechniquesAnitha PrabakarNo ratings yet
- Role of Corporate Socail Responsibility in Rural India by S.pavai & A.anithaDocument21 pagesRole of Corporate Socail Responsibility in Rural India by S.pavai & A.anithaAnitha PrabakarNo ratings yet
- Maggi Final PTTDocument25 pagesMaggi Final PTTAnitha PrabakarNo ratings yet
- Brain Teaser 6Document29 pagesBrain Teaser 6Anitha PrabakarNo ratings yet
- Sri. Loknath Behera IPS IGP (HQ) Police Headquarters ThiruvananthapuramDocument15 pagesSri. Loknath Behera IPS IGP (HQ) Police Headquarters ThiruvananthapuramxlntyogeshNo ratings yet
- Sales LetterDocument12 pagesSales LetterAnitha PrabakarNo ratings yet
- EASTC Course ListingDocument6 pagesEASTC Course ListingTHABISILE MBATHANo ratings yet
- Best AI Essay WriterDocument2 pagesBest AI Essay WriterPeter JhonsonNo ratings yet
- SelfDocument2 pagesSelfglezamaeNo ratings yet
- Tensile Load Testing in COMSOLDocument15 pagesTensile Load Testing in COMSOLSyed TaimurNo ratings yet
- Models Show Nature's RealityDocument7 pagesModels Show Nature's RealityanaNo ratings yet
- George ResumeDocument3 pagesGeorge Resumeapi-287298572No ratings yet
- Ch02 Why Waterfall Model FailDocument12 pagesCh02 Why Waterfall Model Failetl_manNo ratings yet
- 1 Magazines: Reading ComprehensionDocument8 pages1 Magazines: Reading ComprehensionKetevan KhokhiashviliNo ratings yet
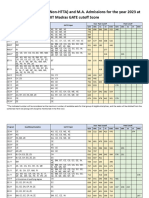
- M.Tech 2023 CutoffDocument6 pagesM.Tech 2023 Cutoffmshail30No ratings yet
- Zimbabwe School Examinations Council Physics 9188/4: T-1Ufakose HighDocument6 pagesZimbabwe School Examinations Council Physics 9188/4: T-1Ufakose HighLaura MkandlaNo ratings yet
- Sloan - Brochur BBBDocument24 pagesSloan - Brochur BBBarunpdnNo ratings yet
- Premiere Products Exercise Chapter 8 Complete SolutionDocument6 pagesPremiere Products Exercise Chapter 8 Complete SolutionMatthew BeckwithNo ratings yet
- C++ Project On Payroll ManagementDocument5 pagesC++ Project On Payroll ManagementGameo CraftNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 10 Curriculum MapDocument9 pagesMapeh 10 Curriculum MapJoshua LamzonNo ratings yet
- Anuja Anil Vichare Resume 5-19-14Document3 pagesAnuja Anil Vichare Resume 5-19-14api-310188038No ratings yet
- HSBC Praise Team Self-Evaluations - Vocal/Instrumental/TechDocument3 pagesHSBC Praise Team Self-Evaluations - Vocal/Instrumental/TechEric Powell100% (2)
- Multidimensional Locus of Control Attitude Scale Levenson Miller 1976 JPSPDocument10 pagesMultidimensional Locus of Control Attitude Scale Levenson Miller 1976 JPSPAnnaNedelcuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Reading Comprehension: Vocabulary Task: Match Words in The First List To Their Meaning in The SecondDocument8 pagesChapter 2: Reading Comprehension: Vocabulary Task: Match Words in The First List To Their Meaning in The SecondPape Serigne DiopNo ratings yet
- Reading: Good for the Mind in Many WaysDocument9 pagesReading: Good for the Mind in Many WaysYoussra FathiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law UniversityDocument6 pagesDr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law UniversityShivam VermaNo ratings yet
- Data Mining Applications and TechniquesDocument52 pagesData Mining Applications and TechniquesDinesh ChandNo ratings yet
- Session Plan FBSDocument17 pagesSession Plan FBSorabelle punoNo ratings yet