Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Weir and Barrage Lecture
Uploaded by
Asghar Hussain Shah100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
116 views18 pageslk
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentlk
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
116 views18 pagesWeir and Barrage Lecture
Uploaded by
Asghar Hussain Shahlk
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
The weir is solid obstruction put across the
river to raise the water level and divert the
water into a canal.
The only difference between a weir and a barrage is of gates, that is the flow in
barrage is regulated by gates and that in weirs, by its crest height.
Barrages are costlier than weirs.
To rise the water level in the river to pre
determine elevation.
To eliminate fluctuation in the level of the river
and divert water into the canals at designed level.
To divert a part or whole of the water flowing in
the river, or stream to canals constructed
upstream of the barrage.
To train the river as far as practicable so that the
canal head work does not suffer from the
vagaries of the river due to river meandering.
To control silt entry into canals.
To delay floods.
Main body of the barrage, normal RCC slab which supports the
steel gate. In the X-Section it consists of :
Upstream concrete floor, to lengthen the path of seepage and to
project the middle portion where the pier, gates and bridge are
located.
A crest at the required height above the floor on which the gates
rest in their closed position.
Upstream glacis of suitable slope and shape. This joins the crest
to the downstream floor level. The hydraulic jump forms on the
glacis since it is more stable than on the horizontal floor, this
reduces length of concrete work on downstream side.
Downstream floor is built of concrete and is constructed so as to
contain the hydraulic jump. Thus it takes care of turbulence
which would otherwise cause erosion. It is also provided with
friction blocks of suitable shape and at a distance determined
through the hydraulic model experiment in order to increase
friction and destroy the residual kinetic energy.
Divide wall
The fish ladder
Sheet piles
Up stream piles
Intermediate sheet piles
Inverted filter
Flexible apron
The under sluices: scouring sluices
River training works
A wall constructed at right angle to the axis
of the weir separating the weir proper from
the under sluices (to keep heavy turbulence at
the nose of the wall, well away from upstream
protection of the sluices)
It extends upstream beyond the beginning of
canal HR. Downstream it extends up to the
end of loose protection of under sluices
launching apron)
This is to cover the hydraulic jump and the
resulting turbulence.
For movement of fish (negotiate the artificial
barrier in either direction)
Difference of level on the upstream and
downstream sides on the weir is split up into
water steps by means of baffle walls
constructed across the inclined chute of fish
ladder.
Velocity in chute must not be more than
3m/s
Grooved gate at upstream and downstream -
for effective control.
Made of mild steel, each portion being 1/2' to
2' in width and 1/2" thick and of the required
length, having groove to link with other.
Situated at the upstream end of the upstream
concrete floor driven into the soil beyond the
maximum possible scour that may occur.
Functions:
Protect barrage structure from scour
Reduce uplift pressure on barrage
To hold the sand compacted and densified
between two sheet piles in order to increase the
bearing capacity when barrage floor is designed
as raft.
Situated at the end of upstream and downstream
glacis. Protection to the main structure of
barrage (pier carrying the gates, road bridge and
the service bridge) in the event of the upstream
and downstream sheet piles collapsing due to
advancing scour or undermining. They also help
lengthen the seepage path and reduce uplift
pressure.
Downstream sheet piles: Placed at the end of
downstream concrete floor. Their main funtion is
to check the exit gradient. Their depth should be
greater than the possible scour
Provided between the downstream sheet piles
and the flexible protection. Typically 6" sand, 9"
coarse sand and 9" gravel. Filter may vary with
size of particles forming the river bed. It is
protected by placing over it concrete blocks of
sufficient weight and size. Slits are left between
the blocks to allow the water to escape.
Length should be 2 x downstream depth of
sheet.
Functions:
Check the escape of fine soil particles in the
seepage water.
Placed downstream of the filter
Consists of boulder large enough not to be
washed away by the highest likely velocity
The protection provided is enough as to
cover the slope of scour of 1 1/2 x depth of
scour as the upstream side of 2 x depth of
scour on the downstream side at the slope of
3.
Maintaining a deep channel in front of the Head regulator on the downstream side.
Functions:
As the bed of under sluice is not lower level than rest of the weir, most of the day,
whether flow unit will flow toward this pocket => easy diversion to channel
through Head regulator
Control silt entry into channel
Scour the silt (silt excavated and removed)
High velocity currents due to high differential head.
Pass the low floods without dropping
The shutter of the main weir, the raising of which entails good deal of labor and
time.
Capacity of under sluices:
For sufficient scouring capacity, its discharging capacity should be at least double
the canal discharge.
Should be able to pass the dry weather flow and low flood, without dropping the
weir shutter.
Capable of discharging 10 to 15% of high flood discharge
Guide banks:
Earthen embankments => stone pitching
Force the river into restricted channel, to ensure almost axial flow
near the weir site. (embankments in continuation of G-Banks. To
contain flood within flood plains)
Marginal Bunds:
Provided on the upstream in order to protect the area from
submergence due to rise in HFL, caused by afflux.
Groans or spurs:
Embankment type structures constructed transverse to river flood,
extending from the banks into the river (also transverse dykes)
Protect the bank from which they are extended by deflecting the
current away from the bank.
weir
D
i
v
i
d
e
w
a
l
l
Scouring sluices
Fish ladder
Fig.( component parts of weir and barrage )
RIVER
D
r
a
w
n
b
y
e
n
g
r
.
H
a
y
a
t
Crest shutter
Weir wall
Launching apron
Launching apron
Inverted filter
u/s pile
d/s pile
Pound level
Block protection
Weir drawn by Engr. Hayat
Barrage (sukker pakistan) Weir
You might also like
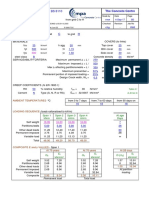
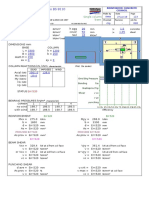
- RCC21 Subframe AnalysisDocument10 pagesRCC21 Subframe AnalysisAmit Kumar PaulNo ratings yet
- Section : Fy Mpa Fu Mpa ƳDocument27 pagesSection : Fy Mpa Fu Mpa ƳMadhav PurohitNo ratings yet
- Sluice Valve ChampersDocument34 pagesSluice Valve ChampersWessam NourNo ratings yet
- General Input:-: Moment & Shear Strength Design of Rectangular RC According ACI318M-08Document14 pagesGeneral Input:-: Moment & Shear Strength Design of Rectangular RC According ACI318M-08Maharajan McsNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheets To BS 8110: L (M) H (MM) BW (MM) HF (MM) Type BF (MM)Document10 pagesSpreadsheets To BS 8110: L (M) H (MM) BW (MM) HF (MM) Type BF (MM)hala_azhariNo ratings yet
- Water-Tank-Joint Pattern-Surface LoadDocument10 pagesWater-Tank-Joint Pattern-Surface LoadYakni IdrisNo ratings yet
- Project Area Sub Area Plant/Unit Code Se-Spml (JV) RevDocument13 pagesProject Area Sub Area Plant/Unit Code Se-Spml (JV) RevBanwari Lal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Rigorous Continuous BeamsDocument1 pageRigorous Continuous Beamsmdelacua2No ratings yet
- Indian Standard Radial GateDocument8 pagesIndian Standard Radial GateMirza FadlulahNo ratings yet
- 2 Forces On Cofferdams and Their Load CombinationDocument3 pages2 Forces On Cofferdams and Their Load Combinationsyahmi adliNo ratings yet
- Pad Foundation Design To Bs 81101997Document23 pagesPad Foundation Design To Bs 81101997Anonymous 66uWhphVNo ratings yet
- Fet Ci Lecture Notes Prof Quamrul Hassan Design-WeirDocument53 pagesFet Ci Lecture Notes Prof Quamrul Hassan Design-WeirVEDANT SHARMA 129No ratings yet
- Reinforcement Details of Raft Plan Fondation Plan: C4 C4 C5 C6 C6Document4 pagesReinforcement Details of Raft Plan Fondation Plan: C4 C4 C5 C6 C6Rama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Tehri Dam Retaining WallDocument26 pagesEstimation of Tehri Dam Retaining WallAbhi ShahNo ratings yet
- Design ChannelDocument11 pagesDesign Channelroid ghoziNo ratings yet
- DRAINAGE DESIGN CRITERIA for Elgin O'Hare West BypassDocument3 pagesDRAINAGE DESIGN CRITERIA for Elgin O'Hare West BypassonspsnonsNo ratings yet
- Bolt capacity and plate designDocument2 pagesBolt capacity and plate designvtalexNo ratings yet
- Design and Drawing of RC Structures: Dr. G.S.SureshDocument40 pagesDesign and Drawing of RC Structures: Dr. G.S.SureshLeroy TuscanoNo ratings yet
- Design of Thrust BlockDocument2 pagesDesign of Thrust Blocksumitanurag100% (1)
- Structural Design of Surge TankDocument3 pagesStructural Design of Surge TankSudan ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Loaded Flat PlatesDocument8 pagesLoaded Flat Platessloane01No ratings yet
- RCC11 Element DesignDocument6 pagesRCC11 Element Designredz00No ratings yet
- COLCALCDocument1 pageCOLCALCahmedhusseinkamelNo ratings yet
- Design of Isolated Footing With Vertical Load Only - According To ACI 318M-99Document1 pageDesign of Isolated Footing With Vertical Load Only - According To ACI 318M-99mahmoud IbrahemNo ratings yet
- Summary of IS 3370 Detailing RequirementsDocument2 pagesSummary of IS 3370 Detailing RequirementsKanaiyalal N. ShethNo ratings yet
- Trash Racks and Safety GratesDocument4 pagesTrash Racks and Safety GratessanbarunNo ratings yet
- Weir Drawing SectionDocument1 pageWeir Drawing SectionAziz ul HakeemNo ratings yet
- 2 M High Free Standing WallDocument20 pages2 M High Free Standing WallAnonymous ciKyr0tNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel Structures by Ramchandra PDFDocument4 pagesDesign of Steel Structures by Ramchandra PDFAnkit TiwariNo ratings yet
- Design of a submerged slide gate structureDocument11 pagesDesign of a submerged slide gate structurealiNo ratings yet
- Rising Main Design SummaryDocument9 pagesRising Main Design SummaryJaspal SinghNo ratings yet
- Check Crack Width in Beam As Per IS 456Document4 pagesCheck Crack Width in Beam As Per IS 456Rupali ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Plate Girder BridgeDocument14 pagesPlate Girder BridgeDHANALAKSHMI G TeachingNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Calculation of Box Culvert: Bekri Primary Canal ##+### BBK1a 3-Barrel BoxDocument1 pageHydraulic Calculation of Box Culvert: Bekri Primary Canal ##+### BBK1a 3-Barrel BoxelfitaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Design of Desilting ChamberDocument4 pagesHydraulic Design of Desilting ChamberManojPatne0% (1)
- RCC12 Bending and Axial ForceDocument4 pagesRCC12 Bending and Axial ForceAbdul KarimNo ratings yet
- Design of Raft Foundation of Water TankDocument1 pageDesign of Raft Foundation of Water TankNIHARIKA KARETHANo ratings yet
- A Case Study of Bhogdoi River BasinDocument59 pagesA Case Study of Bhogdoi River Basinbimalgogoi100% (3)
- Crack Width Calculation BS 8100 BS 8007Document2 pagesCrack Width Calculation BS 8100 BS 8007Shaniha kkNo ratings yet
- Appendix - Ii: Principles of Construction, Material and Design of Ferrocement TankDocument5 pagesAppendix - Ii: Principles of Construction, Material and Design of Ferrocement TankbenzzenhdNo ratings yet
- DSR 2010-11 Pipes RatesDocument140 pagesDSR 2010-11 Pipes RatesDeepthy VasavanNo ratings yet
- 2152-0.50LL Esr-Str-Cal-01 - R1Document30 pages2152-0.50LL Esr-Str-Cal-01 - R1sssmitNo ratings yet
- Underground Water Tanks Guide Specifications0Document2 pagesUnderground Water Tanks Guide Specifications0Seifeldin Ali MarzoukNo ratings yet
- G EOTECHNICAL CAPACITY OF R. C. C PILEDocument1 pageG EOTECHNICAL CAPACITY OF R. C. C PILEChowdhury PriodeepNo ratings yet
- Bar Bending Schedule OF Box CulvertDocument1 pageBar Bending Schedule OF Box CulvertvishalNo ratings yet
- Slender Column - Sway Frame - ACI 318-08 Reinforced Concrete Design Example HassounDocument8 pagesSlender Column - Sway Frame - ACI 318-08 Reinforced Concrete Design Example HassounMike2322100% (1)
- Chute Design Part 1Document11 pagesChute Design Part 1Anorld WalkerNo ratings yet
- RCC43 Wide Beams (A & D)Document30 pagesRCC43 Wide Beams (A & D)ptslabNo ratings yet
- Thrust Block Design and Cost DetailsDocument8 pagesThrust Block Design and Cost DetailsMUTHUKKUMARAMNo ratings yet
- Manhole Design - AMRUT - Water Pressure & DryDocument13 pagesManhole Design - AMRUT - Water Pressure & Drynavneet3bawaNo ratings yet
- WSM Design of RCC BeamsDocument140 pagesWSM Design of RCC BeamssvchaudhariNo ratings yet
- 2395 CH 15Document19 pages2395 CH 15abdülkadir cebeciNo ratings yet
- BA 001 R0A (Without Mezzanine)Document1 pageBA 001 R0A (Without Mezzanine)Muhammad Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- NA To SS EN 1991-2-2012 - Amd 1Document6 pagesNA To SS EN 1991-2-2012 - Amd 1Olivia OeyNo ratings yet
- Equal angle steel profiles data sheetDocument2 pagesEqual angle steel profiles data sheetGalih PutraNo ratings yet
- Navigation Lock Design CalculationsDocument8 pagesNavigation Lock Design CalculationsReskyArandaNo ratings yet
- Components of BarrageDocument5 pagesComponents of BarrageWaqas QureshiNo ratings yet
- 7-Diversion Head WorksDocument23 pages7-Diversion Head Workswajid malikNo ratings yet
- Components of A BarrageDocument21 pagesComponents of A BarrageEngr.Hamid Ismail CheemaNo ratings yet
- Lec 11 Bituminous MaterialsDocument6 pagesLec 11 Bituminous Materialsamjad aliNo ratings yet
- ACI The New Model Code Feb 2013Document87 pagesACI The New Model Code Feb 2013Asghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Lecture#15: Sub Structure: Sub-Structure or Foundation Is The Lower Portion of The Building, UsuallyDocument3 pagesLecture#15: Sub Structure: Sub-Structure or Foundation Is The Lower Portion of The Building, UsuallyAsghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 AggregatesDocument8 pagesLec 2 AggregatesAsghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Lecture #01: BY Engineer Asghar Hussain ShahDocument9 pagesLecture #01: BY Engineer Asghar Hussain ShahAsghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- EE150 Network Analysis-II Course OutlineDocument1 pageEE150 Network Analysis-II Course OutlineAsghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument5 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentAsghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- ASTM Standards Catalog 2013Document22 pagesASTM Standards Catalog 2013dassoumennNo ratings yet
- Lecture #01: BY Engineer Asghar Hussain ShahDocument9 pagesLecture #01: BY Engineer Asghar Hussain ShahAsghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Technology - EE463Document1 pageHigh Voltage Technology - EE463Asghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Lecture #01: BY Engineer Asghar Hussain ShahDocument9 pagesLecture #01: BY Engineer Asghar Hussain ShahAsghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document16 pagesChapter 03Iqbal HossainNo ratings yet
- Class 7thDocument15 pagesClass 7thAsghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Feild Theory - EE315 - 14-07-2008Document2 pagesElectromagnetic Feild Theory - EE315 - 14-07-2008Asghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture - CS252Document2 pagesComputer Architecture - CS252Asghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- K.G Topics For DecorationDocument13 pagesK.G Topics For DecorationAsghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Industrial Management MGT 427Document2 pagesIndustrial Management MGT 427Asghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Communications Skills - ENG 112Document1 pageCommunications Skills - ENG 112Asghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Technology - EE463Document1 pageHigh Voltage Technology - EE463Asghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Physics I - GS111Document2 pagesPhysics I - GS111Asghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Class NurseryDocument1 pageSyllabus Class NurseryAsghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument5 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentAsghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Large residential plot plan layout dimensionsDocument1 pageLarge residential plot plan layout dimensionsAsghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Abid 1 PDFDocument1 pageAbid 1 PDFAsghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Kaka G Tangarr-ModelDocument1 pageKaka G Tangarr-ModelAsghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Abid 2 PDFDocument1 pageAbid 2 PDFAsghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- 2.final Structure25.07.2015-Model PDFDocument1 page2.final Structure25.07.2015-Model PDFAsghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Abid 1Document1 pageAbid 1Asghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 AggregatesDocument8 pagesLec 2 AggregatesAsghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 CementsDocument7 pagesLec 3 CementsAsghar Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Basic Soil Mechanics 07Document1 pageBasic Soil Mechanics 07Jay CeeNo ratings yet
- Junior Engineers (Civil, Mechanical, Electrical, & Quantity Surveying & Contract) Examination, 2016Document36 pagesJunior Engineers (Civil, Mechanical, Electrical, & Quantity Surveying & Contract) Examination, 2016sai manojNo ratings yet
- Modelling of Cyclic Soil DegradationDocument110 pagesModelling of Cyclic Soil Degradationdogen1980No ratings yet
- Weirs & Barrages 2Document44 pagesWeirs & Barrages 2muhammad adnannNo ratings yet
- Pond Construction:: Some Practical ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesPond Construction:: Some Practical ConsiderationsRodolfo Martinez CadenaNo ratings yet
- Permeability Test Discussion of TheoryDocument3 pagesPermeability Test Discussion of TheoryBryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Soil Tests and IndecesDocument8 pagesModule 2 Soil Tests and IndecesAljon Avila0% (1)
- SEEP W ManualDocument205 pagesSEEP W ManualmichealkilleenNo ratings yet
- Paper 8 - Road Construction On Peat Soil May 2014 (Rev)Document16 pagesPaper 8 - Road Construction On Peat Soil May 2014 (Rev)Roziman Hj HajonNo ratings yet
- ConsolidationDocument66 pagesConsolidationEdDie Endra100% (2)
- CIVIL ENGINEERING BOARD TABLE OF SPECIFICATIONS FOR HYDRAULICS AND GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERINGDocument2 pagesCIVIL ENGINEERING BOARD TABLE OF SPECIFICATIONS FOR HYDRAULICS AND GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERINGKristelle Anne GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 In-Situ StressesDocument47 pagesLec 3 In-Situ StressesSaleemAhmadMalik100% (1)
- Technical Manual For Lpile 2018: (Using Data Format Version 10)Document250 pagesTechnical Manual For Lpile 2018: (Using Data Format Version 10)Hao LuoNo ratings yet
- PP Pt. GsiDocument1 pagePP Pt. Gsimuhammad rizkiNo ratings yet
- Foundation 2Document37 pagesFoundation 2HemenMoNo ratings yet
- Earthen Dams: Ancient Structures Built With Natural MaterialsDocument66 pagesEarthen Dams: Ancient Structures Built With Natural MaterialsFarhan KaziNo ratings yet
- Discussion On Interfaces Between Embankments and Concrete Dams and Their InstrumentationDocument11 pagesDiscussion On Interfaces Between Embankments and Concrete Dams and Their InstrumentationMarcelo ProtzNo ratings yet
- Compressibility of SoilDocument32 pagesCompressibility of SoilDiecon Irish Arboleda50% (2)
- Record: Highway ResearchDocument88 pagesRecord: Highway ResearchPartha SahaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Earthquake Resistant Retaining Wall Design Version 1Document80 pagesModule 6 Earthquake Resistant Retaining Wall Design Version 1Edence PuahNo ratings yet
- GATE 2012 CE Question Paper: Simpson's Rule, Annual Precipitation, Poisson's RatioDocument15 pagesGATE 2012 CE Question Paper: Simpson's Rule, Annual Precipitation, Poisson's RatioPK PhilavongNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Structures: Chapter One Elements of Dam EngineeringDocument49 pagesHydraulic Structures: Chapter One Elements of Dam EngineeringBura AshxNo ratings yet
- Permeability: G Acceleration Due To Gravity V Velocity U Pressure Where H Total HeadDocument22 pagesPermeability: G Acceleration Due To Gravity V Velocity U Pressure Where H Total HeadSabiha sultanaNo ratings yet
- Planning and feasibility considerations for small earth damsDocument7 pagesPlanning and feasibility considerations for small earth damssamoonibrahimNo ratings yet
- Burns & Mayne 1998 - CPTU Permeability EnvironmentalDocument154 pagesBurns & Mayne 1998 - CPTU Permeability EnvironmentalAdrián FernándezNo ratings yet
- Advanced Soil Mechanics - Course NotesDocument49 pagesAdvanced Soil Mechanics - Course NotesMarius Strydom100% (3)
- Guidelines for Geosynthetic Reinforced Embankments on Soft SoilsDocument40 pagesGuidelines for Geosynthetic Reinforced Embankments on Soft SoilsManish Kumar Singh100% (1)
- Soil Properties PDFDocument7 pagesSoil Properties PDFKshitija NadgoudaNo ratings yet
- Why Critical State Soil Mechanics Should Be Taught To All Civil Engineers-AireyDocument8 pagesWhy Critical State Soil Mechanics Should Be Taught To All Civil Engineers-AireyAnonymous GnfGTwNo ratings yet