Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Supply Chain Management
Uploaded by
Isuru WijewardeneCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Supply Chain Management
Uploaded by
Isuru WijewardeneCopyright:
Available Formats
12-1
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain
Management
12-2
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain: the sequence of
organizations - their facilities,
functions, and activities - that are
involved in producing and delivering
a product or service.
12-3
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Warehouses
Factories
Processing centers
Distribution centers
Retail outlets
Offices
Facilities
12-4
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Typical Supply Chains
Purchasing
Receiving Storage Operations Storage
Production Distribution
12-5
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Typical Supply Chain for a Manufacturer
Supplier
Supplier
Supplier
Storage
}
Mfg. Dist. Retailer Customer Storage
12-6
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Supplier
Supplier
Storage
}
Service
Customer
Typical Supply Chain for a Service
12-7
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Customers are Suppliers
Initial
Supplier
Customer
Supplier
Customer
Supplier
Customer
Supplier
Final
Customer
12-8
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Improve operations
Increasing levels of outsourcing
Increasing transportation costs
Competitive pressures
Increasing globalization
Increasing importance of e-commerce
Complexity of supply chains
Manage inventories
Need for Supply Chain Management
12-9
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Benefits if Supply Chain Management
Organization Benefit
Campbell Soup Doubled inventory turnover rate
Hewlett-Packard Cut supply costs 75%
Sport Obermeyer Doubled profits and increased sales 60%
National Bicycle Increased market share from 5% to 29%
Wal-Mart Largest and most profitable retailer in the world
12-10
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Elements of Supply Chain Management
Deciding how to best move and store materials Logistics
Determining location of facilities Location
Monitoring supplier quality, delivery, and relations
Suppliers
Evaluating suppliers and supporting operations Purchasing
Meeting demand while managing inventory costs Inventory
Controlling quality, scheduling work Processing
Incorporating customer wants, mfg., and time Design
Predicting quantity and timing of demand Forecasting
Determining what customers want Customers
Typical Issues Element
12-11
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Increasing outsourcing
Increasing conversion to lean
production
Increasing globalization
Purchasing in Supply Chain Management
12-12
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Internal Supply Chain
External
Supply Chain
Internal
Supply Chain
Key:
Suppliers Distribution Customers Processing
12-13
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Issues
Quality control
Production planning and
control
Inventory policies
Purchasing policies
Production policies
Transportation policies
Quality policies
Design of the supply
chain, partnering
Operating Issues Tactical Issues
Strategic Issues
12-14
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
SCOR Metrics
Perspective Metrics
Reliability On-time delivery
Order fulfillment lead time
Fill rate (fraction of demand met from stock)
Perfect order fulfillment
Flexibility Supply chain response time
Upside production flexibility
Expenses Supply chain management costs
Warranty cost as a percent of revenue
Value added per employee
Assets/utilization Total inventory days of supply
Cash-to-cash cycle time
Net asset turns
12-15
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Logistics
Refers to the movement of materials and
information within a facility and to incoming
and out going shipments of goods and
materials
Logistics
12-16
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Logistics
Movement within the facility
Incoming and outgoing shipments
Bar coding
EDI
Distribution
JIT Deliveries
0
214800 232087768
12-17
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
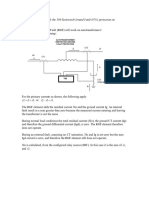
Supply Chain Management
Materials Movement
Figure 12-5
R
E
C
E
I
V
I
N
G
Storage
Work
center
Work center
Work center
Storage
Work
center
Storage
Shipping
12-18
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Increased productivity
Reduction of paperwork
Lead time and inventory reduction
Facilitation of just-in-time systems
Electronic transfer of funds
Improved control of operations
Reduction in clerical labor
Increased accuracy
Electronic Data Interchange
12-19
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Efficient consumer response (ECR) is a
supply chain management initiative
specific to the food industry
Reflects companies efforts to achieve
quick response using EDI and bar codes
Efficient Consumer Response
12-20
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Distribution requirements planning
(DRP) is a system for inventory
management and distribution planning
Extends the concepts of MRPII
Distribution Requirements Planning
12-21
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Management uses DRP to plan and
coordinate:
Transportation
Warehousing
Workers
Equipment
Financial flows
Uses of DRP
12-22
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
E-Commerce: the use of electronic
technology to facilitate business
transactions
Applications include
Internet buying and selling
E-mail
Order and shipment tracking
Electronic data iterchange
E-Commerce
12-23
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Companies can:
Have a global presence
Improve competitiveness and quality
Analyze customer interests
Collect detailed information
Shorten supply chain response times
Realize substantial cost savings
Create virtual companies
Level the playing field for small companies
Advantages E-Commerce
12-24
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Customer expectations
Order quickly -> fast delivery
Order fulfillment
Order rate often exceeds ability to fulfill it
Inventory holding
Outsourcing loss of control
Internal holding costs
Disadvantages of E-Commerce
12-25
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Buyer exchange
MRO-catalog hub
Supplier exchange
BPO
Neutral exchange
B2B Market Places
12-26
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Develop strategic objectives and tactics
Integrate and coordinate activities in the
internal supply chain
Coordinate suppliers with customers
Coordinate planning and execution
Form strategic partnerships
Creating an Effective Supply Chain
12-27
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Quality
Cost
Flexibility
Velocity
Customer service
Supply Chain Performance Drivers
12-28
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Barriers to integration of organizations
Getting top management on board
Dealing with trade-offs
Small businesses
Variability and uncertainty
Long lead times
Challenges
12-29
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Lot-size-inventory
Bullwhip effect
Inventory-transportation costs
Lead time-transportation costs
Product variety-inventory
Cost-customer service
Trade-offs
12-30
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Bullwhip Effect
Tier 2
Suppliers
Tier 1
Suppliers
Producer Distributor Customers
Ordering
Amount of
inventory
=
12-31
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Operations Management, Seventh Edition, by William J. Stevenson
Copyright 2002 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Benefits and Drawbacks
Problem Potential
Improvement
Benefits Possible
Drawbacks
Large
inventories
Smaller, more frequent
deliveries
Reduced holding
costs
Traffic congestion
Increased costs
Long lead times Delayed differentiation
Disintermediation
Quick response
May not be feasible
May need absorb
functions
Large number of
parts
Modular Fewer parts
Simpler ordering
Less variety
Cost
Quality
Outsourcing Reduced cost, higher
quality
Loss of control
Variability Shorter lead times, better
forecasts
Able to match supply
and demand
Less variety
You might also like
- Registration Booklet Seminar SriLanka InteractiveDocument4 pagesRegistration Booklet Seminar SriLanka InteractiveIsuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- Mitochondrial Evolution - Michael GrayDocument17 pagesMitochondrial Evolution - Michael GrayIsuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- Mitochondrial Evolution - Michael GrayDocument17 pagesMitochondrial Evolution - Michael GrayIsuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- Final Layout Reactor HF05Document1 pageFinal Layout Reactor HF05Isuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Bank ProtectionDocument17 pagesCapacitor Bank ProtectionskisakNo ratings yet
- Cable Sizing and Its Effect On Thermal and Ampacity Values in UndDocument59 pagesCable Sizing and Its Effect On Thermal and Ampacity Values in UndabenitechNo ratings yet
- IEC61850 Interoperability and Implementation GET-20025E 150720 R007 LR PDFDocument18 pagesIEC61850 Interoperability and Implementation GET-20025E 150720 R007 LR PDFIsuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- OLD - ExistingDocument1 pageOLD - ExistingIsuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- T60 UR Settings FileDocument25 pagesT60 UR Settings FileIsuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- 6451 PercentageRestrained MT 20140319 WebDocument14 pages6451 PercentageRestrained MT 20140319 WebmohsinamanNo ratings yet
- 1MRG006131 en Integrated Protection Scheme For Pump-Storage Hydroelectric Power PlantDocument13 pages1MRG006131 en Integrated Protection Scheme For Pump-Storage Hydroelectric Power Planta_r_vijayanand6550No ratings yet
- 01c Rating Plate Capacitor BankDocument1 page01c Rating Plate Capacitor BankIsuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- T60 Basic Setting Example - Get8433Document2 pagesT60 Basic Setting Example - Get8433Isuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- Operation of Power TF During System Disturbances - GET-3237Document4 pagesOperation of Power TF During System Disturbances - GET-3237Isuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- Required Inputs For Relay Setting CalculationDocument6 pagesRequired Inputs For Relay Setting CalculationIsuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- GE B90 PresentationDocument71 pagesGE B90 PresentationIsuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- Current PolarizingDocument18 pagesCurrent PolarizingShafqat HussnainNo ratings yet
- Como Inhibir Las Corrientes Magnetizantes en Los Relés T60 yDocument1 pageComo Inhibir Las Corrientes Magnetizantes en Los Relés T60 yfreddy riveraNo ratings yet
- ISIS TutorialDocument80 pagesISIS Tutorialstefan_nikola100% (1)
- RGF Protection Setting Example For Auto-Transformers - Get8428Document3 pagesRGF Protection Setting Example For Auto-Transformers - Get8428Isuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- T60 CT Connections - Get8430 PDFDocument2 pagesT60 CT Connections - Get8430 PDFIsuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- RGF Protection Setting ExampleDocument2 pagesRGF Protection Setting ExampleIsuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- CEAIP Part 3 Kelaniya GSS Clamps Connectors Test ReportsDocument12 pagesCEAIP Part 3 Kelaniya GSS Clamps Connectors Test ReportsIsuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- High Impedance Resistor CalculationDocument1 pageHigh Impedance Resistor CalculationIsuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- AAUP Membership ApplicationDocument2 pagesAAUP Membership ApplicationIsuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- ISIS TutorialDocument80 pagesISIS Tutorialstefan_nikola100% (1)
- AAUP Membership ApplicationDocument2 pagesAAUP Membership ApplicationIsuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- IEC61850 Interoperability and Implementation GET-20025E 150720 R007 LRDocument18 pagesIEC61850 Interoperability and Implementation GET-20025E 150720 R007 LRIsuru Wijewardene100% (1)
- Trade Finance Guide 2008Document32 pagesTrade Finance Guide 2008David Hathaway100% (1)
- MBA - MIS Assignment AnswerDocument20 pagesMBA - MIS Assignment AnswerIsuru WijewardeneNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- E - BusinessDocument223 pagesE - BusinessSM Friend100% (1)
- Western Pharmaceuticals Supply Chain OptimizationDocument5 pagesWestern Pharmaceuticals Supply Chain Optimizationmohamed mohamedgalal100% (2)
- Shared Value Literature Review Implications For FuDocument14 pagesShared Value Literature Review Implications For Fumonu100% (1)
- What Is WCOMDocument14 pagesWhat Is WCOMP S Lakshmi Kanthan100% (1)
- DVC V1 Supply Chain Redesigning FOR LegoDocument17 pagesDVC V1 Supply Chain Redesigning FOR LegoNiddal El-JabriNo ratings yet
- FICCI-Accenture - Circular Economy Report - OptVer PDFDocument70 pagesFICCI-Accenture - Circular Economy Report - OptVer PDFDebanu MahapatraNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management (2nd Edition)Document31 pagesSupply Chain Management (2nd Edition)aditya tiwariNo ratings yet
- CSCP Notes by RaviDocument2 pagesCSCP Notes by RaviAnimorphs17% (6)
- Uk Salary Survey 2017Document50 pagesUk Salary Survey 2017sceptNo ratings yet
- Cargill CDP Climate Response 2021Document58 pagesCargill CDP Climate Response 2021Ánh ÁnhNo ratings yet
- Assignment-2 Management Information SystemDocument11 pagesAssignment-2 Management Information SystemAsim AzmiNo ratings yet
- Why Executing Strategy Is A Tough Management JobDocument25 pagesWhy Executing Strategy Is A Tough Management JobramapvkNo ratings yet
- Supplier Enablement Program Checklist: Phase Step Description 1. Identify Project Team Program PlanningDocument4 pagesSupplier Enablement Program Checklist: Phase Step Description 1. Identify Project Team Program PlanningbupeshNo ratings yet
- UnileverDocument49 pagesUnileverSana JavedNo ratings yet
- Building Informa On Management: A Standard Framework and Guide To BS 1192Document22 pagesBuilding Informa On Management: A Standard Framework and Guide To BS 1192ranggarangNo ratings yet
- FE University Group Marketing Plan for PHirst Park HomesDocument34 pagesFE University Group Marketing Plan for PHirst Park HomesGiella MagnayeNo ratings yet
- Business Model CanvasDocument1 pageBusiness Model CanvasAntor Podder 1721325No ratings yet
- Questionnaire On MbaDocument5 pagesQuestionnaire On MbaMagesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Sourcing Strategy and Supplier Relationships: Alliances Versus EprocurementDocument2 pagesSourcing Strategy and Supplier Relationships: Alliances Versus EprocurementAnas WarisNo ratings yet
- Apparel Accessories and Footwear Standard - en GBDocument29 pagesApparel Accessories and Footwear Standard - en GBKihyun KwonNo ratings yet
- Harley DavidsonDocument9 pagesHarley DavidsonCrystalNo ratings yet
- SCM Part 1Document52 pagesSCM Part 1Prasath VelumaniNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Sustainable Purchasing and SupplyDocument4 pagesThe Importance of Sustainable Purchasing and SupplyBelajar MONo ratings yet
- Tam Poster Nov 14 HRDocument1 pageTam Poster Nov 14 HRleniadz2No ratings yet
- POX SCRUBBER PROJECT EXECUTION PLANDocument7 pagesPOX SCRUBBER PROJECT EXECUTION PLANPham Thai TuyenNo ratings yet
- Full MCQ SCMDocument87 pagesFull MCQ SCMFidas RoyNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit ReportDocument7 pagesInternal Audit ReportsarahbeeNo ratings yet
- Global: Best of GreenDocument46 pagesGlobal: Best of GreenNicole RacomaNo ratings yet
- Intel Lund 120502Document30 pagesIntel Lund 120502RizkiNo ratings yet
- Boeing Digital Transformation Presentation 2018Document10 pagesBoeing Digital Transformation Presentation 2018putra briskaNo ratings yet