Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Understanding Physics Concepts Through Diagrams and Examples
Uploaded by
Angie Kong Su Mei0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views46 pagesscience spm
Original Title
Science Form 5 Chapter 5 Motion
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentscience spm
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
2K views46 pagesUnderstanding Physics Concepts Through Diagrams and Examples
Uploaded by
Angie Kong Su Meiscience spm
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 46
Ticker tape
1/ ? Hertz = time (s)
Frequency = 50 Hz
Time for 1 tick =1/50 = 0.02 s
Increasing velocity
Total velocity = 20cm/ 0.06s
= 333.33 cm/s
Decreasing velocity
Total velocity= 50 cm / 0.06
= 833.33 cm/s
20 cm
50 cm
Uniform velocity / zero acceleration
Total velocity= 30 / 0.06 = 500 cm/s
30 cm
Uniform = constant = no changes
Zero velocity = not moving
a) i) trolley moves with uniform/ constant velocity
ii) Velocity = 5cm/ 0.1 s = 50cm/s
b) i) 5cm ii) 10cm
c) Ticks will become closer to one another
2)
Time = 10 s
Distance, m
3 + 4 = 7m
Speed
7/ 10 = 0.7m/s
Displacement,m
5m
Velocity
5/10= 0.5 m/s
A
B
3m
4m
5m
Scalar, no direction
Vector, direction
2m/s 5m/s
8m/s
1s 1s
5) Acceleration = 5-2 / 1s = 3m/s2 Acceleration = 8-5/ 1 = 3m/s2
6) Time = 1/ 50 = 0.02 s
How many ticks? 5 ticks x 0.02 = 0.1 s
Velocity = 2.5 m / 0.1 s = 25 m/s (A)
7 ) speed = 1500 m / 300 s = 5m/s (B)
8) C
9) Speed = 4m / 2s = 2 m/s (C)
10) 200m/ 10 s = 20 m/s (C)
11)320 / 40 = 8 m/s (D)
12) Acceleration = 30 0 / 12 = 30 /12 = 2.5 m/s 2 (B)
Inertia: remain initial position, resistance of change
When a car/ bus:
At first Then The
passengers
Because
Not
moving,
stationary
Moves
forward
Throw /
jerk
backwards
Remain at
initial
position
Moving
forward
Suddenly
brake
Thrown
forwards
Remain
moving
forward
initial
Suddenly moves
forward
Body wants to maintain initial position
So, body will feel thrown backwards
initial
Suddenly brakes
Body wants to maintain initial position
So, body will feel thrown forward, as if car still
moving forward
stop
Momentum = mass x velocity
kgms
-1
= kg x ms
-1
Factors affecting momentum is:
a) Mass b) velocity
Momentum = force x time
Ns = N X s
100 Ns = 25 N X 4s
100 Ns = 50 N x 2s
So, when time decreases, force increases.
11) a)
i) Momentum is the product of mass and velocity
factors are mass and velocity
- The larger the mass , the larger the momentum
- The faster the velocity, the larger the momentum
ii) When time of collision decreases, the force
increases.
b) Dashboard
i) Prevent driver from hitting steering wheel
ii) It will crack but will not break to pieces
iii) Prevent passengers from thrown forward
iv) Provides stability, prevent skidding
v) Collapse first to protect passengers
vi) Absorb the impact of collision
Pressure = Force (N)
(Pa or Nm
-2
) Area (m
2
)
20 Pa = 100 N
5 m
2
Area , m
2
Force , N Pressure ,
Pa
Conclusion
10 100 N 100/10
= 10 Pa
Area increases,
pressure decrease
2.5 100 N 100/2.5
= 40 Pa
Area decreases,
pressure increase
If same shape, same area
Tied higher, higher force, higher pressure
a) When block is hung at higher location, it has
higher force and produce higher pressure
b) i) Height of wooden block, Force
ii) Depth of dent, pressure
c) 1.0 cm B= 0.4 cm
d) More than 1.0 cm, because smaller surface area
creates more pressure
Hydraulic system example:
1) Excavator
2) Hydraulic jack / mechanic/ garage lift
3) Hydraulic brake
4) Roller coaster
5) Dental chair
Fill with fluid ex: oil not water because:
1) Decrease friction
2) Prevent rust
3) Can distribute pressure evenly (Pascals Principle)
4) Do not create bubbles
A B
Force , N Surface
Area, m
2
A ? = 20 N 0.2 ? /0.2 = 100,
? = 20 N
B 1000 10 1000/10 = 100
Pressure = Force (N)
(Pa or Nm
-2
Area (m
2
)
Pressure at A = Pressure at B
A B
Force , N Surface
Area, m
2
A ? = 20 N 0.2 ? /0.2 = 100,
? = 20 N
B 1000 10 1000/10 = 100
Pressure = Force (N)
(Pa or Nm
-2
Area (m
2
)
Pressure at A = Pressure at B
10 / 0.02 = y / 4
F/ 0.02 = 10000/10
Lift = upthrust = upwards
Aeroplane is supported by upthrust force
Bernoullis Principle
Ex:
1) Aeroplane
2) Filter pump
3) Bunsen burner
4) Insecticide spray
Wind low velocity
High pressure
Wind high velocity
Low pressure
Gas, high velocity, low pressure
In comparison,
outside
atmospheric pressure
higher,
Pushes air/ oxygen in
VELOCITY INCREASES , PRESSURE DECREASES
If channel thinner,
velocity higher, Pressure even lower
Bernoullis Principle
Water flow
3) a) Pressure exerted/pushed by liquid does not
depend on the shape of container
b) ii) velocity of water increases along the tube. So,
the pressure decreases gradually.
c) i) The pressure of water decreases when velocity
increases.
ii) Bernoullis Principle
In water,
We floats due to upthrust / water buoyancy/
buoyant force (not because of density)
Upthrust = Difference reading of spring balance
(outside water in water)
= apparent loss of weight, force, N 1 KG = 10 N
Archimedes Principle
Ex: stepping into a basin full of water
Water will overflows
Submarine can:
Position Ballast tank
Rises to top Release sea water
Sink to bottom Sea water flows in
F= 0.54 N
a) Weight = force = 0.54 N
b) i) 0.54-0.34 = 0.20 N
ii) Buoyancy = weight of displaced water = 0.20 N
iii) The apparent loss of weight is buoyancy of
water and equal to weight of fluid displaced
c) i) 1 kg = 10 N,
Density of oil and water?
Oil less dense, less than 0.20 N
ii) Archimedess Principle
P compression stroke
Q- power stroke
b) i) mixture of petrol and air is sucked in
ii) Spark park ignites the petrol and air
c) Q- power stroke
d) Uses internal combustion engine,
involve 4 movements of piston
a) i)mass of trolley
ii) velocity of trolley
b) i) Trolley X will produce deeper dent than Y.
ii) Object will bigger mass produces larger
momentum
c) The bigger the mass, the larger the momentum
a) i) X= thrust
Y lift, upthrust
ii) High speed of gases produced creates a
momentum backwards and pushes the jet forward
iii) Y- buoyancy, Bernoullis Principle
b) Weight = Lift
Drag = Thrust
8)
a) Liquid hydrogen
b) For combustion of fuel
c) Combustion of hydrogen and oxygen
d) i) Principle of Conservation of Momentum
ii) Rocket expels/release hot gases backwards
creates creates a momentum downwards and
pushes the rocket upwards
Crops/ plants fruits animal rubber Genetically Modified
Food (GMF)
- resist disease
- Need less
water
- looks better
(flowers)
- higher quality
- Sweeter
- Higher
yield
(hasil)
- Mature earlier
- More
milk/flesh/
eggs
- Faster to
produce
latex
- Higher yield
- Bigger/taller
- Higher yield
- Resist disease/ pest
(so can use less
insecticide)
More and new variety in:
Selective breeding: Example: Oil palm
Dura x Pisifera = Tenera ( more oil)
To maintain fertility of land:
1) Add fertiliser / baja
2) Mixed cultivation / penanaman
(different plants take up different
nutrients from soil)
3) Planting cover crops (ex: grass, to
prevent erosion, nutrient runoff when
rain)
To increase food production:
1) New machinery / equipment to harvest
and transplant seedlings paddy field
2) Educating farmers (new variety and tech)
3) Free land for development (FELDA)
4) Give free sample of new variety (resist
disease)
Pg 27
3. The aims.
a) To eliminate.
slow down bacteria
improve appearance
to maintain quality
Pasteurisation
Dehydration bacteria die/inactive, ex: milk powder
Pg 28: freezing: for imported meat (thawed)
Cooling for imported vege, fruits,
chicken (from market)
Freeze drying: sublime, (sublimation remove water)
Irradiation : lower nutrition
Pg 29 fUNCTION
S
example Sample food
favourings taste MSG ,
ester (fruity)
COLA, Ribena
colourings cake
preservatives Benzoic acid prevent
bacteria growth
Boric acid cause
cancer
COLA, Ribena
sweeteners Caramel
antioxidant Prevent oil
from
rancid
BHA, ascorbic acid
emulsifier Appearanc
e
stabiliser Consistent
appearanc
e
Cake
Bleaching Look
cleaner ,
for
appearanc
e
2. manipulation, modify traits, corn, potatoes, soya
beans
- Improve quality
3. Consecutive , different crops, soil fertility (subur),
nitroge. Pest control
4. Two farming activities, livestock (animal), vege.
5. Cerun - highlands, soil erosion, landflash.
6. Shifting cultivation hilly and mountain area
(pertanian pindah)
Pg 30
1. quality, quantity, new variety/machinery
2. MARDI, MPOB
3. High quality, protection
Land schemes:
RISDA (small farms)
FELDA
FELCRA
OIL PALMS
Pg 30
6.4
1. Food act 1983, food.1985, safety ,security
a) production, processing, distribution, safety,
quality, protecting rights
b) Labelled
i) Name
ii) Net weight
iii) Ingredients
iv) Expiry date
v) Name, address, manufacturer
vi) Method storing
No price
2. Nutrition fact, calori, HALAL
3. CAP, educating
4. Responsible, dishonest traders, exploiting
Pg 66 SectionC
9) a)
b) Rice yield low, improve production
i) The soil of his land is not fertile, infested by pests
and crops affected by diseases.
ii) Questions:
1) How can the farmer increase fertility of soil?
2) How can the farmer control pests and diseases?
iii) 1) Fertiliser added to the soil
2) Insecticides are sprayed or owl is reared to
prey on rats (biological control)
Methods Explanation
cooling Food stored at low temperature to slow down activity of bacteria
canning Food is boiled to kill bacteria and then sealed.
freezing Food frozen below 0C to stop bacteria activity
dehydration Water is removed and food kept at air tight
(i) emulsifier stabiliser
Mix 2 substances
for form emulsion
Differences Maintain consistency
and texture
Lecithin, gum example Agar, gelatin
(ii) Flavouring sweetener
Enhance taste differences Make food sweeter
MSG, ester example Caramel, aspartame
Page 64
5.
X Pasteurisation
Y Canning
Z dehydration
b) Heated 63C for 30 minutes
c) Can be kept for longer time/increase shelf
life
d) Dried under sun
200g
600g
Products made of synthetic rubber
wetsuit
Soles of shoes
tyres
200g
600g
8
Reading of stopwatch diagram 4.2 is
higher than 4.1
Time taken for diagram 4.2
higher because bigger inertia
than diagram 4.1
Inertia/ Time for tin to stop
Inertia is the ability of tin to stop itself from swinging.
Pituitary
gland
Adrenal gland
Increase heartbeat and
respiration for emergency
situation
Thyroid gland
goiter
Meiosis
Fertilisation
Rr Rr rr
rr
Meiosis
Fertilisation
Red roses
Rr
rr
1:1
Products made of synthetic rubber
wetsuit
Soles of shoes
tyres
Same group
Same chemical properties
Different physical properties
Increasing proton number
2.1 = 3
2.8.1 = 11
2.7 = 9
2.8 = 10
11
T
T
P,S
Q/T
isoprene
Formic acid ,
ethanoic acid (vinegar)
Solid-coagulate
X - ammonia
Vulcanised rubber (vulcanisation)
To form cross linkages between
Rubber molecules
Hydrogen,
Pop, burning splinter
P,S,Cal, MAZI,TLC
10)
a) Different metal shows different
reactivity with acid
b) i) To investigate reactivity of
metal with acid
ii) Manipulated: Type of metal
Responding: Reactivity of metal
Constant: size/mass of metal
iii) apparatus: test tube
Material: magnesium powder, zinc
powder, hydrochloric acid
vi) Different metal shows different
reactivity with acid.
More reactive metal will show more
reactivity with acid.
iv) Procedure:
Hydrochloric acid
Magnesium powder
Zinc powder
A
B
1. 10 cm 3 of hydrochloric acid
is added into test tube A.
2. 10 g of magnesium powder
is added.
3. Test tube B is repeated with
10g of zinc powder.
4. The reactivity between test
tube A and B is compared.
v) Type of metal Reactivity of metal
Magnesium
Zinc
11a)
b) Problem: Smoke from factories cause air
pollution
Clarification: Factories release smoke and
poisonous gas that affect the health and
environment
Methods: 1) Build tall chimney
2. install filter at chimney
3. Enforce the law
4. Organize clean environment campaign
Human activities Effect
1) Illegal logging Destruction of forest
Destroy habitat
2) Open burning Cause haze, air pollution
Cause respiratory problem
12)
a)
b)
c) Common characteristics:
They are made of synthetic rubber which is heat resistant and less
elastic.
Two examples: Hose of bunsen burner, electrical insulator
Non-example: rubber band
Actual concept: Synthetic rubber is rubber that resist heat, less
elastic and resist oxidation.
Natural rubber Differences Synthetic rubber
Low Heat resistant High
yes Easily oxidised no
more elastic less
higher Ability to absorb
sound
lower
Natural rubber Synthetic rubber
Household glove, car tyres Hoses, laboratory gloves
Yellow book , page 12
Question 10)
a) Natural immunity is the ability to resist disease because body
produces antibody when affected once.
Example: chicken pox, measles
The person will no longer be affected by the disease.
b)i) Identify: Cholera outbreak affects the health of villagers
ii) Cholera is a infectious disease caused by bacteria, spread
through contaminated food and water, causing vomiting and
stomachache.
iii) 1. Water is purified and boiled before drinking.
2. Patients are treated and non-patients are vaccinated.
3. Treat water supply with chlorine by government.
4. Cleanliness is maintained by correctly disposing garbage and
prevent infestation of flies, rats and cockroaches.
You might also like
- Skema Jawapan Kertas 2 PDFDocument5 pagesSkema Jawapan Kertas 2 PDFdarwishmajidNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 - Book Back QuestionsDocument51 pagesGrade 8 - Book Back QuestionsMusa ImranNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Forces and EnergyDocument47 pagesUnit 3 Forces and Energy4w7b9kkyp8No ratings yet
- Sect. 8.1 SpeedDocument19 pagesSect. 8.1 SpeedSuresh ParamuNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme Essay Question: Answer Q1Document5 pagesMarking Scheme Essay Question: Answer Q1jesunathan44@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Gerak Gempur IIDocument4 pagesJawapan Gerak Gempur IIrenuNo ratings yet
- Pascal's PrincipleDocument38 pagesPascal's Principlesweetdream100% (6)
- Dls 212 - Selected Topics in General Physics: University of Northern PhilippinesDocument56 pagesDls 212 - Selected Topics in General Physics: University of Northern PhilippinesKennedy Fieldad Vagay100% (5)
- Good Morning Everyone!Document50 pagesGood Morning Everyone!fizaali87No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1Ahmad A OmarNo ratings yet
- Activated SludgeDocument14 pagesActivated Sludgemosaad khadrNo ratings yet
- DEFINITIONDocument12 pagesDEFINITIONAshenafi .ANo ratings yet
- Workshop CalculationDocument98 pagesWorkshop CalculationTeguh SetionoNo ratings yet
- Jabatan Pelajaran Terengganu Science Marking SchemeDocument5 pagesJabatan Pelajaran Terengganu Science Marking SchemeHanisah RazaliNo ratings yet
- Pressure in Gases & LiquidsDocument13 pagesPressure in Gases & LiquidsGanesh Lad100% (2)
- Tugas Filia Responsi SedimentasiDocument22 pagesTugas Filia Responsi SedimentasiHevliza TiaraNo ratings yet
- Physics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 Forces & PressureDocument25 pagesPhysics Module Form 4 Chapter 3 Forces & PressureMisratul A'la Mahyuddin100% (2)
- Waste Water ProjectDocument17 pagesWaste Water ProjectMuhammad Ilham ZulkipllyNo ratings yet
- BB Skema P2 B&C 2011Document15 pagesBB Skema P2 B&C 2011Shahrul AnisNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Scalar Quantities and Vector Quantities: Example 1.1Document5 pages1.3 Scalar Quantities and Vector Quantities: Example 1.1ilchwanNo ratings yet
- Rab Cetak1gfngffgDocument27 pagesRab Cetak1gfngffgBagus SyahalaNo ratings yet
- Solved Problem of First Three Chapters by Asif RasheedDocument10 pagesSolved Problem of First Three Chapters by Asif RasheedAsif Rasheed RajputNo ratings yet
- Problems Oscillation SDocument6 pagesProblems Oscillation SLakshyaNo ratings yet
- MODULE - 4 - PF10urface Areas, Statistics, Probability.c01bde6Document119 pagesMODULE - 4 - PF10urface Areas, Statistics, Probability.c01bde6Sanskriti Thakur100% (1)
- Perhitungan Panjang BatangDocument8 pagesPerhitungan Panjang Batangferdian10No ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Lab Assignment GuideDocument4 pagesPlate Tectonics Lab Assignment GuideTonni TonishNo ratings yet
- Tugas Neraca Massa Dan EnergiDocument13 pagesTugas Neraca Massa Dan EnergiAlya SholikhatulNo ratings yet
- Planning and Design of Single Storey Residential BuildingDocument38 pagesPlanning and Design of Single Storey Residential Buildingsai thesis100% (2)
- Design of The PileDocument6 pagesDesign of The PileWilliam Garcia OlayaNo ratings yet
- Principle of Working of Grit ChamberDocument11 pagesPrinciple of Working of Grit ChamberAhmed Amedi100% (3)
- PressureDocument17 pagesPressurePrashant sapkota100% (1)
- Physics F4 MS 1Document7 pagesPhysics F4 MS 1kiruimeshack04No ratings yet
- Pressure Question Bank Class VIII PhysicsDocument4 pagesPressure Question Bank Class VIII PhysicsAshish GambhirNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument73 pagesFluid MechanicswyvfallNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Structures Design ExamplesDocument8 pagesHydraulic Structures Design ExamplesKenenisa BultiNo ratings yet
- GCSE Physics Forces in Action Answers and Mark SchemesDocument11 pagesGCSE Physics Forces in Action Answers and Mark SchemesLelon OngNo ratings yet
- Septic Tank Sizing - SPLENDORDocument1 pageSeptic Tank Sizing - SPLENDORRashel HasanNo ratings yet
- Particle physics announcements and aimsDocument23 pagesParticle physics announcements and aimsReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- As.1 AnswersDocument16 pagesAs.1 AnswersStuuNo ratings yet
- DJJ2093 Test 1 Dis2014Document10 pagesDJJ2093 Test 1 Dis2014Mr MickeyNo ratings yet
- Problem Set No 10Document3 pagesProblem Set No 10JohnCarloBernardoNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument345 pagesPhysicsjoanthanbiederman100% (1)
- Set 3 1. State Why Does The Fireman Suit Made From Asbestos (ADocument3 pagesSet 3 1. State Why Does The Fireman Suit Made From Asbestos (AEncik Amir KamalNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Essential College Physics 1st Edition RexDocument14 pagesTest Bank For Essential College Physics 1st Edition Rexharoldbrownorcnxeijgd100% (23)
- Bab v. Pengujian Kualitas Kayu IngDocument17 pagesBab v. Pengujian Kualitas Kayu IngRadenBagusArdiNo ratings yet
- LAS AGRICROP Q3 WEEK 3 To 4Document25 pagesLAS AGRICROP Q3 WEEK 3 To 4Fermo Gadayan RamosNo ratings yet
- Monoethanolamine Design 2520of 2520equipmentsDocument54 pagesMonoethanolamine Design 2520of 2520equipmentsbhaskar5377No ratings yet
- Pondasi 3 Bor Pile-TerzagiDocument23 pagesPondasi 3 Bor Pile-TerzagiMochammad ShokehNo ratings yet
- Example From CH 1 To CH 6Document21 pagesExample From CH 1 To CH 6SteveNo ratings yet
- HW11 - Fluids PDFDocument5 pagesHW11 - Fluids PDFBradley NartowtNo ratings yet
- 8th Phy Paper 2022 2nd TermDocument2 pages8th Phy Paper 2022 2nd TermmaniNo ratings yet
- Physics P2 SPM 2014 MelakaDocument9 pagesPhysics P2 SPM 2014 MelakaLeeZiangNo ratings yet
- Bab 1: Pengenalan Kepada Fizik Bahagian A: Period Time For 10 OscillationsDocument19 pagesBab 1: Pengenalan Kepada Fizik Bahagian A: Period Time For 10 OscillationslapokNo ratings yet
- Ch6 SolutionsDocument66 pagesCh6 SolutionsAtikah Rosely100% (1)
- CUNY City Tech PHY 1.2 Practice Final ExamDocument4 pagesCUNY City Tech PHY 1.2 Practice Final ExamberoodyNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument3 pagesReproductionRos Mawar MelatiNo ratings yet
- Verbs and Past Tense Form 4 EnglishDocument6 pagesVerbs and Past Tense Form 4 EnglishAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Secondary Growth of PlantsDocument13 pagesSecondary Growth of PlantsAngie Kong Su Mei50% (2)
- Countable NounsDocument5 pagesCountable NounsAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 I Trigonometry II StudentDocument41 pagesChapter 15 I Trigonometry II StudentAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Functions Pure MathsDocument20 pagesFunctions Pure MathsAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Verbs and Past Tense Form 4 EnglishDocument6 pagesVerbs and Past Tense Form 4 EnglishAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Essay 2) Identify: To Prepare Soap From Palm Oil and Sodium Hydroxide. Labelled Diagram: 1)Document2 pagesEssay 2) Identify: To Prepare Soap From Palm Oil and Sodium Hydroxide. Labelled Diagram: 1)Angie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Simple Present and Present Continuous Tenses GuideDocument9 pagesSimple Present and Present Continuous Tenses GuideAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Electromagnet Teacher's Guide 2009Document48 pagesChapter 8 Electromagnet Teacher's Guide 2009Mohd Khairul Anuar100% (18)
- Countable NounsDocument5 pagesCountable NounsAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Stem and Leaf DiagramsDocument1 pageStem and Leaf DiagramsAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Adverbs StudentsDocument4 pagesAdverbs StudentsAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Carbon Compounds ChapterDocument2 pagesCarbon Compounds ChapterAngie Kong Su Mei67% (3)
- CZ Grandmother 1. Loving 3. Attentive 2. Caring 4. Understanding 5. Wonderful / Best Grandmother in The WorldDocument5 pagesCZ Grandmother 1. Loving 3. Attentive 2. Caring 4. Understanding 5. Wonderful / Best Grandmother in The WorldAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Physics Heat F4Ch4studentDocument9 pagesPhysics Heat F4Ch4studentAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Scientific investigation stepsDocument4 pagesScientific investigation stepsAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Verbs and Past Tense Form 4 EnglishDocument6 pagesVerbs and Past Tense Form 4 EnglishAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 5 Carbon Carboxilic Acid and Ester StudentDocument10 pagesChemistry 5 Carbon Carboxilic Acid and Ester StudentAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Fertilisation Reproduction Systems Pregnancy Birth ControlDocument2 pagesFertilisation Reproduction Systems Pregnancy Birth ControlAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Carbon Compounds and Their PropertiesDocument23 pagesCarbon Compounds and Their PropertiesAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Science Form 5 NutritionDocument5 pagesScience Form 5 NutritionAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Stem and Leaf DiagramsDocument1 pageStem and Leaf DiagramsAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Verbs and Past Tense Form 4 EnglishDocument6 pagesVerbs and Past Tense Form 4 EnglishAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Science Form 5 Chapter 3 Preservation Conservation StudentDocument8 pagesScience Form 5 Chapter 3 Preservation Conservation StudentAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Physics 4 Understanding LensesDocument4 pagesPhysics 4 Understanding LensesAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- f3 Science c6 Land and Resources StudentDocument36 pagesf3 Science c6 Land and Resources StudentAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Contoh Modul LKS IPADocument12 pagesContoh Modul LKS IPAasep_mulyana_4No ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2.9Document15 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 2.9Farain RashdiNo ratings yet
- DNC MagazineDocument49 pagesDNC MagazineNizamudheen kNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection For LithiumDocument2 pagesFire Protection For LithiumSofiqNo ratings yet
- D2.07 Non Segregated Phase Bus DuctsDocument3 pagesD2.07 Non Segregated Phase Bus DuctsSaraswatapalitNo ratings yet
- Arduino Oscilloscope ProjectDocument12 pagesArduino Oscilloscope ProjectSathya Narayan100% (1)
- MAXCLEAN WIPER-600 S4ff7987c7ba99Document2 pagesMAXCLEAN WIPER-600 S4ff7987c7ba99Amirul ShamNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Properties of Lithium Bromide Water Solutions at High TemperaturesDocument17 pagesThermodynamic Properties of Lithium Bromide Water Solutions at High TemperaturesAnonymous 7IKdlmNo ratings yet
- Santosh ResumeDocument4 pagesSantosh ResumeSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- CNH-FIAT-NEW HOLLAND Tractor Components CatalogueDocument523 pagesCNH-FIAT-NEW HOLLAND Tractor Components Catalogueomni_parts100% (2)
- UDN6118ADocument8 pagesUDN6118AkizonzNo ratings yet
- Europass CV Aristeidis TsialosDocument3 pagesEuropass CV Aristeidis Tsialoso_pythagoriosNo ratings yet
- UM4730 Integration GuideDocument0 pagesUM4730 Integration Guidenarse8488No ratings yet
- BTW69 1200Document5 pagesBTW69 1200GiraldoCarpioRamosNo ratings yet
- Estimate For Proposed Residence Of: Mr. M.P.G. Sanath Wasantha LalDocument10 pagesEstimate For Proposed Residence Of: Mr. M.P.G. Sanath Wasantha LalchathuragunarathnaNo ratings yet
- Expt 2 - Thevenin-NortonDocument10 pagesExpt 2 - Thevenin-NortonNitin KhetadeNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Pub The City Amp Guilds Textbookbook 2 Electrical Installations For The Level 3 Apprenticeship 5357 Level 3 Advanced Technical Diploma 8202 Amp Level 3 Diploma 2365 1510432256 9781510432253Document610 pagesDokumen - Pub The City Amp Guilds Textbookbook 2 Electrical Installations For The Level 3 Apprenticeship 5357 Level 3 Advanced Technical Diploma 8202 Amp Level 3 Diploma 2365 1510432256 9781510432253Abdulrahim Abdulhasiz100% (1)
- Safety Swivel Lifting Eye Bolts Load CapacitiesDocument1 pageSafety Swivel Lifting Eye Bolts Load CapacitiesRaul G. MartinezNo ratings yet
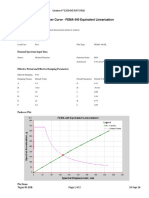
- FEMA 440 equivalent linearization pushover analysisDocument2 pagesFEMA 440 equivalent linearization pushover analysisAdam JrNo ratings yet
- GM-MS45 hydraulic valve technical specificationsDocument21 pagesGM-MS45 hydraulic valve technical specificationsDUVAN GARNICANo ratings yet
- Charles Rennie MackintoshDocument14 pagesCharles Rennie MackintoshRadu Stefan100% (1)
- Avk Gate Valve, Flanged, Pn10/16 02/60-0045: EN 558-2 S.15/DIN F5, Clockwise To OpenDocument3 pagesAvk Gate Valve, Flanged, Pn10/16 02/60-0045: EN 558-2 S.15/DIN F5, Clockwise To OpenMohamed SayedNo ratings yet
- Flow Through Pipe Presentation by 4 StudentsDocument18 pagesFlow Through Pipe Presentation by 4 StudentsDurgesh KolheNo ratings yet
- As 1815.3-2007 Metallic Materials - Rockwell Hardness Test Calibration of Reference Blocks (Scales A B C D EDocument3 pagesAs 1815.3-2007 Metallic Materials - Rockwell Hardness Test Calibration of Reference Blocks (Scales A B C D ESAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Manual Intel D815EEA2-D815EPEA2 P3 Socket370Document146 pagesManual Intel D815EEA2-D815EPEA2 P3 Socket370Raul MejicanoNo ratings yet
- General Purpose Polyester Laminating Resin GuideDocument3 pagesGeneral Purpose Polyester Laminating Resin Guidewongpengchiong7205100% (1)
- Aerodynamic and Mechanical Design of An 8 - 1 Pressure Ratio Centrifugal CompressorDocument147 pagesAerodynamic and Mechanical Design of An 8 - 1 Pressure Ratio Centrifugal CompressorvincemugnaioNo ratings yet
- Top Plate - Qad-28 Sample Inspection ReportDocument3 pagesTop Plate - Qad-28 Sample Inspection ReportazadNo ratings yet
- PhasorDocument7 pagesPhasorRaed MohsenNo ratings yet
- 14.09.13 PPT On System TransientsDocument61 pages14.09.13 PPT On System TransientsRaja ShekarNo ratings yet
- Long Range Identification and Tracking (LRIT)Document2 pagesLong Range Identification and Tracking (LRIT)Giorgi KandelakiNo ratings yet
- Mahindra&mahindraDocument95 pagesMahindra&mahindraAshik R GowdaNo ratings yet