Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Condenser
Uploaded by
SwatiChawlaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Condenser
Uploaded by
SwatiChawlaCopyright:
Available Formats
Name of Institution
ASET
CONDENSER
Submitted By:
Manish Rai
6MAE-5X
(A2305411275)
B.Tech(MAE)
Name of Institution
2
ASET
Definition
In systems involving heat transfer, a condenser is a device or unit
used to condense a substance from its gaseous to its liquid state,
typically by cooling it. In so doing, the latent heat is given up by the
substance, and will transfer to the condenser coolant.
The condenser is a heat exchanger that rejects heat from the
refrigerant to air, water, or some other fluid.
Name of Institution
3
ASET
The three common types of condensers are:
air-cooled,
water-cooled, and
evaporative.
Name of Institution
4
ASET
Name of Institution
5
ASET
Air cooled Condenser uses propeller type fans to draw outdoor air over a finned
heat surface.
The temperature difference between the hot refrigerant vapour that is flowing
through the tubes and the cooler outdoor air induces heat transfer. The resulting
reduction in the heat content of the refrigerant vapour causes it to condense into
liquid.
Within the final few lengths of condenser tubing (the subcooler), the liquid
refrigerant is further cooled below the temperature at which it was condensed.
Name of Institution
6
The air-cooled condenser is very popular in both residential and commercial
applications because of its convenience.
It requires very little maintenance and does not require the freeze protection and
water treatment that is necessary with a water-cooled condenser.
Additionally, it is favored in areas that have an inadequate or costly water supply,
or where the use of water for air conditioning is restricted.
Name of Institution
7
ASET
The benefit of subcooling on system performance can be demonstrated by
comparing the performance of a system with and without subcooling.
The change in enthalpy (the line from A to B) that occurs in the evaporator is
called the refrigeration effect. In comparison, the same system without
subcooling produces less refrigeration effect (the
line from A to B).
Name of Institution
8
ASET
Name of Institution
9
ASET
Evaporative Condensers are a modification of the air-cooled condenser.
Within this device, the refrigerant flows through tubes and air is drawn or blown
over the tubes by a fan.The difference is that water is sprayed on the tube
surfaces.
As the air passes over the coil, it causes a small portion of the water to
evaporate. This evaporation process absorbs heat from the coil, causing the
refrigerant vapour within the tubes to condense.
The remaining water then falls to the sump to be re-circulated and used again.
Subcooling of the refrigerant can be accomplished by piping the condensed
liquid back through another few rows of coil tubing
Name of Institution
10
ASET
Name of Institution
11
ASET
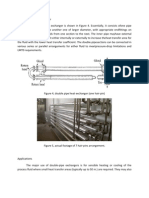
The shell-and-tube is the most common type of water-cooled condenser.
With this design, water is pumped through the tubes while the refrigerant vapor
fills the shell space surrounding the tubes. As heat is transferred from the
refrigerant to the water, the refrigerant vapor condenses on the tube surfaces.
The condensed liquid refrigerant then falls to the bottom of the shell, where it
flows through an enclosure that contains additional tubes (the subcooler).
After the warm water leaves the condenser, it must either be disposed of or it
must be cooled before it can be reused by the condenser
Name of Institution
12
ASET
Name of Institution
13
ASET
Thank You
You might also like
- 3 Friotherm Pres Part1Document35 pages3 Friotherm Pres Part1wuenchuman100% (1)
- Commercial Refrigeration Systems ExplainedDocument11 pagesCommercial Refrigeration Systems ExplainedBenjie flor CalayegNo ratings yet
- 1.export of Spices From INDIA To UKDocument47 pages1.export of Spices From INDIA To UKArun Kumar100% (3)
- Refractory Dry Out Procedures SummaryDocument18 pagesRefractory Dry Out Procedures SummaryRajendran Srn100% (6)
- Load Estimating FundamentalsDocument60 pagesLoad Estimating Fundamentalskothat82100% (29)
- A Bell-Type Annealing Furnac PDFDocument9 pagesA Bell-Type Annealing Furnac PDFfercho-kun satochiNo ratings yet
- How Surface Condensers WorkDocument12 pagesHow Surface Condensers WorkPrabir Kumar Pati100% (1)
- Refrigeration System Components: - Vishakh GaneshDocument34 pagesRefrigeration System Components: - Vishakh GaneshS R Akhil KrishnanNo ratings yet
- 409 - 5 Refrigeration & Air ConditioningDocument104 pages409 - 5 Refrigeration & Air Conditioningisrat jahanNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Screw Compressors and Chilling Units PDFDocument8 pagesRefrigeration Screw Compressors and Chilling Units PDFAmandeep singhNo ratings yet
- Pipe Elements 1Document310 pagesPipe Elements 1Ryan Llona FernandezNo ratings yet
- 4.expansion DevicesDocument18 pages4.expansion DevicesAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Positioning of Air Cooled CondensersDocument9 pagesPositioning of Air Cooled CondensersAlexNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration FundamentalsDocument92 pagesRefrigeration FundamentalsThomas Westgate100% (1)
- CompressorsDocument51 pagesCompressorsReza RahmanudinNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled CondenserDocument7 pagesAir Cooled CondenserSaravanan RagupathyNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration 1Document13 pagesRefrigeration 1Vishwanathan RishanthNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant Selection ConsiderationsDocument27 pagesRefrigerant Selection Considerationsme12m113No ratings yet
- Essential Properties Required in A Refrigerant Are As FollowsDocument11 pagesEssential Properties Required in A Refrigerant Are As FollowssrybsantosNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal & Axial Compressors: Elements, Design, PerformanceDocument19 pagesCentrifugal & Axial Compressors: Elements, Design, Performancegm29No ratings yet
- Controlling Heat ExchangersDocument11 pagesControlling Heat ExchangersgermanaponteNo ratings yet
- Condenser & BoilerDocument33 pagesCondenser & BoilerShaun Patrick Albao100% (1)
- Faculty Development Programme On Recent Trends in Thermo-Fluids Engineering (RTTFE 2018)Document42 pagesFaculty Development Programme On Recent Trends in Thermo-Fluids Engineering (RTTFE 2018)Minhaz SixNo ratings yet
- Industrial BoilersDocument81 pagesIndustrial BoilersRavi PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Double Pipe Heat ExchangerDocument5 pagesDouble Pipe Heat ExchangerSheb LorenoNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Compressor Failure: Cause & Cure - Part 1Document5 pagesRefrigeration Compressor Failure: Cause & Cure - Part 1ADARSH GADDAMNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Refrigeration Plant CycleDocument4 pagesGroup 5 Refrigeration Plant CycleGigi SalesNo ratings yet
- EvaporatorDocument24 pagesEvaporatorS R Akhil KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Steam Traps: Used As A Energy SaverDocument47 pagesSteam Traps: Used As A Energy SaverAnonymous w6TIxI0G8lNo ratings yet
- Chiller CompressorDocument41 pagesChiller Compressorabidch143No ratings yet
- Vapor Absorption ChillerDocument38 pagesVapor Absorption ChillerKabir Sodhi100% (1)
- A Working Guide To Process Equipments Upto 22062016Document37 pagesA Working Guide To Process Equipments Upto 22062016DPKRSTGINo ratings yet
- Radial Flow Gas TurbinesDocument20 pagesRadial Flow Gas TurbinesAnggita Dwi LiestyosiwiNo ratings yet
- Steam Condensers and Evaporators ExplainedDocument32 pagesSteam Condensers and Evaporators Explainedvipul sharma100% (1)
- Refrigeration & Air Conditioning Laboratory Manual Course Code: ME344 B.Tech 6 SemDocument53 pagesRefrigeration & Air Conditioning Laboratory Manual Course Code: ME344 B.Tech 6 SemYour dadNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower PowerPointDocument12 pagesCooling Tower PowerPointHaerNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument16 pagesHeat Exchangeratulbhogare7100% (1)
- Cascade Refrigeration System (Report)Document8 pagesCascade Refrigeration System (Report)THE PUBGTV100% (1)
- Pur-15-02 - Air Purger Type PurDocument4 pagesPur-15-02 - Air Purger Type PurAnderson Giovanny Herrera DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Power 101: Flue Gas Heat Recovery in Power PlantsDocument6 pagesPower 101: Flue Gas Heat Recovery in Power PlantsknsaravanaNo ratings yet
- Vol-1, Issue-5Document7 pagesVol-1, Issue-5Ijrei JournalNo ratings yet
- Flash Steam SystemDocument4 pagesFlash Steam SystemAnonymous CX51waINo ratings yet
- Distillation PresentationDocument38 pagesDistillation PresentationMohamed BalbaaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 CompressorsDocument9 pagesExperiment No. 1 CompressorsgmNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 - Atmospheric DistillationDocument3 pagesExperiment 3 - Atmospheric DistillationrestofficalNo ratings yet
- Packed Column Design GuideDocument32 pagesPacked Column Design GuideAnaBelenMedranoBarrientosNo ratings yet
- What Is Lamont Boiler?Document3 pagesWhat Is Lamont Boiler?Muhammad Fahmi HidayatullohNo ratings yet
- Draft Boiler and FurnaceDocument8 pagesDraft Boiler and FurnaceJayandi FitraNo ratings yet
- Buffer & Barrier Fluids Plan 52Document4 pagesBuffer & Barrier Fluids Plan 52gatita_salemNo ratings yet
- Indirect refrigeration handbookDocument158 pagesIndirect refrigeration handbookJohn MackenzieNo ratings yet
- Vapour AbsorptionDocument10 pagesVapour Absorptiongayakwad12_ramNo ratings yet
- Pumps in Parallel or Serial ConnectionDocument7 pagesPumps in Parallel or Serial Connectionyarzar17No ratings yet
- Ebae 161 92 Ram Pump JenningsDocument6 pagesEbae 161 92 Ram Pump JenningsGaguk Triosona PraditaNo ratings yet
- Balance Point of Compressor and Capillary TubeDocument13 pagesBalance Point of Compressor and Capillary TubeMonojit KonarNo ratings yet
- Refrigerant System Components and ControlsDocument16 pagesRefrigerant System Components and ControlssrybsantosNo ratings yet
- Design of Cooling TowerDocument4 pagesDesign of Cooling TowerHadis ShojaeiNo ratings yet
- CHEG351 Mass Transfer. Spring 2008Document275 pagesCHEG351 Mass Transfer. Spring 2008Daniela AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Steam TurbineDocument77 pagesSteam TurbineAmit KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Condenser in Power PlantDocument20 pagesCondenser in Power PlantPrabir Kumar PatiNo ratings yet
- CondensorDocument20 pagesCondensorLaka 98No ratings yet
- Cooling TowersDocument40 pagesCooling Towers1000 Subscribers Without a Video100% (2)
- CondensersDocument25 pagesCondensersARSAL HASHMINo ratings yet
- Chilled Water Air-conditioning System ComponentsDocument30 pagesChilled Water Air-conditioning System ComponentsMalik MussaNo ratings yet
- Components of VCRS NewDocument37 pagesComponents of VCRS Newmesfn derbNo ratings yet
- Vapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle ExplainedDocument16 pagesVapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle ExplainedDiether RigorNo ratings yet
- Project ParivriddhiDocument1 pageProject ParivriddhiSwatiChawlaNo ratings yet
- SYNOPSISDocument7 pagesSYNOPSISSwatiChawlaNo ratings yet
- Real Estate Mutual Fund PPT Dessert at IonDocument13 pagesReal Estate Mutual Fund PPT Dessert at IonSwatiChawlaNo ratings yet
- Investigative Role of Media: Responsibility To The Society Kathakali NandiDocument9 pagesInvestigative Role of Media: Responsibility To The Society Kathakali NandidigitalspiderNo ratings yet
- Investigative Role of Media: Responsibility To The Society Kathakali NandiDocument9 pagesInvestigative Role of Media: Responsibility To The Society Kathakali NandidigitalspiderNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: 1.1 Objectives of The StudyDocument64 pagesChapter-1: 1.1 Objectives of The StudySwatiChawlaNo ratings yet
- Challenges of DohaDocument2 pagesChallenges of DohaSwatiChawlaNo ratings yet
- Project Report DdmerDocument48 pagesProject Report Ddmersanskriti100% (1)
- Full Product Line Catalogue 2018 MITSUBISHI PDFDocument117 pagesFull Product Line Catalogue 2018 MITSUBISHI PDFBogdan AdrianNo ratings yet
- Building Fire Safety EssentialsDocument11 pagesBuilding Fire Safety Essentialsbrijesh varshneyNo ratings yet
- V.GUARD Evacuated Tube Solar Water HeaterDocument2 pagesV.GUARD Evacuated Tube Solar Water HeatersharmaNo ratings yet
- 2230 18 483 01 0407 LQDocument4 pages2230 18 483 01 0407 LQByTxxxNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - ME692 - Welding TechnologyDocument33 pagesLecture 1 - ME692 - Welding Technologypramrahar20No ratings yet
- Armfield Blast and Fluid Bed Freezer Ficha TecnicaDocument2 pagesArmfield Blast and Fluid Bed Freezer Ficha TecnicaErik RMNo ratings yet
- 1kz-Te Cooling System PDFDocument14 pages1kz-Te Cooling System PDFwill meridith100% (2)
- Office Quality Grade MatrixDocument3 pagesOffice Quality Grade MatrixleninamoNo ratings yet
- VRV/VRF Variable Refrigerant Volume (Or Flow) Technology: April 2010Document2 pagesVRV/VRF Variable Refrigerant Volume (Or Flow) Technology: April 2010rijothomasv777No ratings yet
- Thesis FinalDocument60 pagesThesis FinalAmit Naidu100% (1)
- IntroTHT 2e Chapter1Document10 pagesIntroTHT 2e Chapter1cse0909No ratings yet
- Aircon Heat Load Calculation Sheet: Project Name: Vu Quang Address: Bach Dang, Da NangDocument55 pagesAircon Heat Load Calculation Sheet: Project Name: Vu Quang Address: Bach Dang, Da NangquangvuNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering Sample Test PapersDocument5 pagesThermal Engineering Sample Test Papersabhinavgiri17No ratings yet
- Installing Seismic Restraints For Mechanical EquipmentDocument158 pagesInstalling Seismic Restraints For Mechanical EquipmentinitbashNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Air CoolerDocument2 pagesIntroduction of Air CoolerHarshal Madgulkar (Harsh)100% (1)
- Operation & Maintenance Manual: For Khartoum North Power Station-Phase Iii (2×100Mw) ProjectDocument7 pagesOperation & Maintenance Manual: For Khartoum North Power Station-Phase Iii (2×100Mw) ProjectVivek SakthiNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Fire Hazards and How Fires SpreadDocument6 pagesPhysical Properties of Fire Hazards and How Fires SpreadBedrddine AggounNo ratings yet
- HMTDocument37 pagesHMTVaibhav Vithoba NaikNo ratings yet
- BTech Heat and Mass Transfer Theory Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesBTech Heat and Mass Transfer Theory Exam QuestionsSuryaNo ratings yet
- Heat Pipe PaperDocument5 pagesHeat Pipe PaperInquiry XEEPLNo ratings yet
- Fire Resistance Design of Composite Slabs in Building Structures: From Research To PracticeDocument8 pagesFire Resistance Design of Composite Slabs in Building Structures: From Research To PracticeJamaell BlackNo ratings yet
- 001 Energy Conservation and Ea PGDCDocument157 pages001 Energy Conservation and Ea PGDCsaiNo ratings yet
- ST 40.02 Air ConditioningDocument4 pagesST 40.02 Air ConditioningMaksim.em001No ratings yet
- Process Flow Diagrams (Project Standards and Specifications)Document13 pagesProcess Flow Diagrams (Project Standards and Specifications)Hafizh IlyasaNo ratings yet
- Where Business Happens Where Happens: SupportDocument19 pagesWhere Business Happens Where Happens: SupportRahul RamtekkarNo ratings yet