Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ARAVIND
Uploaded by
Jackie Arul0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views60 pagessurvey camp
Original Title
ARAVIND PPT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsurvey camp
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views60 pagesARAVIND
Uploaded by
Jackie Arulsurvey camp
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 60
The surveying camp was conducted to
prepare the contour map of the mountain
at Ooty and to set a curve for the road to
access the nearby road for better access of
the roadway, etc.,
Surveying is an art of determining either
linear or angular measurements.
Levelling is the art of determining relative
height or elevations of different points on the
earth surface.
The elevation of a point has been defined as
its vertical distance above and below a given
reference level surface and usually a mean
sea level.
The levelling work can be carried out by using
direct method or indirect method.
The various method of surveying used during
the camp were,
Triangulation
Tachometric surveying,
Theodolite surveying
Compass surveying
Contouring, etc.
The following are the objectives of the
Survey camp:
To prepare contour maps for hills and
valleys of Ooty region
To determine the Longitudinal Section and
Cross Section of the proposed District Road
To determine the area of the polygon by
Open Traverse method using Tacheometer
To determine the area of the polygon by
Closed Traverse method using
Tacheometer
To determine the distance and angles using
the method of Triangulation
In this chapter we discussed about area we
surveyed. We did survey camp in Ooty,
Coonoor.
This hill station was selected because the
survey can be done with greater
understand like contouring of hill various lot
then a plan ground were the student can
be able to grasp the methodology and
procedures of surveying easily.
L/s and c/s of road survey the undulations
in a road varied more so that experimental
knowledge can be gained a lot.
From Coonoor it is 50 min drive of 20km
over a hill road with 36 hairpin bends in
Ooty road.
The location for which survey camp was
conducted is about 2240 meters above the mean
sea level.
Ooty is a hill station in Nilgiris district, Tamil nadu.
It located in the nilgiris range of hills in the Western
Ghats.
The name is derived from the mountain located at
its region in tamil nila means blue and giri means
mountain. It is also explained as nilgiris.
The latitude and longitude of ooty is
11.411842
o
N, 76.6959
o
E ; ooty hill area is
called the nilgiris.
It is situated at an altitude of 2240 meters
(7350 ft) above sea level. The highest point
in nilgiris is the Doda Betta , at 2,637 meter
(8,652 ft).
The total extent of ooty area is 36
km
2
. Ooty generally features pleasantly mild
conditions throughout the year.
However, nighttime in the months of
January and February is typically chilly.
Generally, the town appears to be eternally
stuck in the spring season.
Temperatures are relatively consistent
throughout the year; with average high
between approximately 512 C (4154 F).
The highest temperature ever recorded in
Ooty was 25 C (77 F), which by South
Asian standards is uncharacteristically low
for an all-time record high temperature.
The lowest temperature was 2 C
(28 F). The city sees on average about
1,250 mm (49 in) of precipitation annually,
with a marked drier season from December
through March.
The location for which survey camp was
conducted is about 2240 meters (7350 ft)
above the mean sea level and latitude
and longitude of ooty is 11.411842
o
N,
76.6959
o
E ;
INTRODUCTION
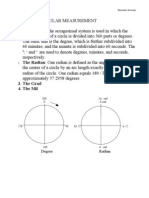
A contour is defined as an imaginary line of
constant elevation on the ground surface.
It can also be defined as the line of
intersection of level surface with the
ground surface.
For example, The line of intersection of the
ground surface of a still lake or pond with
the surrounding ground represents a
contour line
There are two methods of contouring:
Radial
Grid
RADIAL METHOD:
For contouring a hill nearby thalaikuntha
and Lake Mountain there are the un-
uniform slopes running below to the lake.
For taking regular intervals with instruments
and for preparing contour map is possible.
The contouring of the hill was divided to 6
batches and each batch was located to
cover the entire area of the hill.
Each batch is with instruments to set up at
their advised location.
At first the theodolite was setup at the
location and the primary arrangements
were made.
The instrument was setup with the horizontal
and vertical angle at zero. Then the
horizontal angles and distance are
measured.
.
Same procedure was followed for the
remaining batches for measurement.
After the angle and distance of the other
batches were measured, the ranging rod was
kept at a distance along the downhill.
Then the leveling staff was kept at a distance
of 2m along the sight of the ranging rod, and
the vertical angle was measured and middle,
top, bottom readings were taken
The same procedure was followed for the
remaining downhill with the leveling staff at
2m intervals till the end of the hill.
Then with the help of all the readings of the
remaining batches the contour of the hill
was determined with the surface of the hill
contoured.
Tape (for distance measurement)
Prismatic compass (for angle measurement)
Tachometer with Tripod
Transit theodolite
Dumpy Level
Leveling Staff
Ranging Rods
Electronic theodolite
HILL CONTOURING
VALLEY CONTOURING
The horizontal control in geodetic survey is
established either by triangulation or
precise traverse.
In triangulation, the system consist of
number of interconnected triangles in
which length of only one line called the
base line and the angles of the triangles are
measured very precisely.
Knowing the length of one side and the
three angles, the length of other two sides
of each triangle can be computed.
The apexes of triangles are known as
triangulation stations and the whole figure is
called the triangulation system or the
triangulation figure.
D = KS cos + C cos
Where,
D = Distance from the point
K = 100 (constant)
S = Staff intercept (s) m
V = D tan
Where,
V = Vertical component
= Vertical angle
A = x AB x sin
Where,
A = Area of triangle
= angle between the two points
Tape (for distance measurement)
Prismatic compass (for angle measurement)
Tachometer with Tripod
Transit theodolite
Dumpy Level
Leveling Staff
Ranging Rods
Electronic theodolite
The instrument was placed at point A, and
the true north was fixed and was sight to
station S.
After those two points B & C were fixed on
the ground. From the station S the fixed
points B & C are focused.
The leveling staff was held at the fixed
points and the reading was noted.
After that the interior angles were
measured and each station observation
was recorded.
By using triangulation the vertical angles
between points are also measured, so that
heights can be calculated and sloping to
the horizontal plane.
Also calculations were made on the basis of
values recorded by observations
The triangulation diagram are shown in fig
Area of triangle ABE = 12,350 M
2
Area of triangle ABD = 24,624 M
2
Area of triangle ABE = 27,226 M
2
Traversing is the method of using lengths
and directions of lines between points to
determine positions of the points. Traversing
is normally associated with the field work of
measuring angles and distances between
points on the ground.
Closed traverses provide the primary
method used in checking surveying field
work.
CLOSE TRAVERSING
OPEN TRAVERSING
A closed traverse (polygonal, or loop
traverse) is a series of linked traverse lines
where the terminal point closes at the
starting point.
A closed traverse enables a check by
plotting or computation, with any gap
called the linear misclosure.
When within acceptable tolerances, the
misclosure can be distributed by adjusting
the bearings and distances of the traverse
lines using a systematic mathematical
method so the adjusted measurements
close.
Closed traverse is useful in marking the
boundaries of wood or
lakes. Construction and civil engineers
utilize this practice for preliminary surveys of
proposed projects in a particular
designated area. The terminal (ending)
point closes at the starting point
An open, or free traverse (link traverse),
consists of a series of linked traverse lines
which do not return to the starting point to
form a polygon.
Open survey is utilized in plotting a strip of
land which can then be used to plan a
route in road construction.
The formula used for calculating the horizontal
distance (D) is given as,
D = Ks cos
2
+ C cos
Where,
D is the horizontal distance in m
K is the arithmetic constant
S is the difference between the top and
bottom hair reading in m
C is the multiplication constant
is the vertical angle in degrees
The formula used to calculate the vertical
distance (V) is given as,
V = D tan
Where,
V is the vertical distance in m
D is the horizontal distance in m
is the vertical angle in degrees
Tape (for distance measurement)
Prismatic compass (for angle measurement)
Tachometer with Tripod
Transit theodolite
Dumpy Level
Leveling Staff
Ranging Rods
Electronic theodolite
The true north direction was fixed with the
help of the compass and then the
instrument was set up,in that direction.
After the instrument was set up the first point
was held. Then telescope was focused and
the readings were noted.
The theodolite was fitted with stadia
diaphragm and the staff readings are
taken.
By adjusting the upper and lower screws
the telescope is focused in the required
direction and the corresponding horizontal
and vertical angles and readings are
noted. Similarly the staff was held at
different positions around the lake and
readings were noted.
When the leveling staff was not visible, the
instrument was changed to the point where
the staff was held last.
Then the horizontal and vertical readings
are noted and the distance (D) is
calculated using the formulas. Then the
change in angle is noted.
Thus all the points are marked in a paper
and the clear outline of the lake is drawn
and the total area of the lake is calculated.
OPEN TRVERSING
CLOSE TRAVERSING GROUND
CLOSE TRAVERSING VALLEY
The Table for the traversing are shown in the
Annexure A.4,A.5&A.6.
The traversing diagram are shown in Figures
6.1, 6.2 & 6.3
The close traversing ground area = 10,600
m
2
The close traversing valley area = 16,870 m
2
Leveling is a branch of surveying the object
which is used,
To find the elevations of given points with
respect to a given or assumed datum.
To establish points at a given elevation or at
different elevation with respect to a given
or assumed datum.
BACK SIGHT - FORE SIGHT = LAST RL -
FIRST RL
Tape (for distance measurement)
Prismatic compass (for angle measurement)
Tachometer with Tripod
Transit theodolite
Dumpy Level
Leveling Staff
Ranging Rods
Electronic theodolite
Establish the bench mark near the starting
point of the proposed profile by running
check levels. Fix intermediate points at less
than the chain (or) tape length.
Then pegmeric the points at equal intervals
say 10m on the proposed alignment.
Setup the leveling alignment instrument
on the side of the alignment such that it
will cover maximum? Take the back sight
on the benchmark to determine the HS of
Instrument.
Hold the staff at equal interval points and
determine the reduce level of the points
by heights of instrument method
If any point is not visible clearly, take the
change points on turning points and the
levelling is continued.
Complex the profile leveling with necessary
checks.Repeat the same procedure till end.
After finishing the leveling, calculate the
elevations by the rise and fall method and
apply necessary checks.
You might also like
- Torsion in ShaftsDocument30 pagesTorsion in Shaftsdellibabu509No ratings yet
- Surveying: For Landscape ConstructionDocument31 pagesSurveying: For Landscape ConstructionJackie ArulNo ratings yet
- Ce415 Lec 2 4Document61 pagesCe415 Lec 2 4Jackie ArulNo ratings yet
- Runway Incursion and Visual AidsDocument64 pagesRunway Incursion and Visual AidsEndro RastadiNo ratings yet
- Balaji Institute of Engineering and Tchnology Thandalam, Chennai - 603 110 Applied Geology Question BankDocument5 pagesBalaji Institute of Engineering and Tchnology Thandalam, Chennai - 603 110 Applied Geology Question BankJackie ArulNo ratings yet
- Weathering and ErosionDocument53 pagesWeathering and ErosionJackie ArulNo ratings yet
- Elementary Surveying NotesDocument5 pagesElementary Surveying NotesJackie ArulNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- ASTM E92-17 Standard Test Methods For Vickers Hardness and Knoop Hardness of Metallic MaterialsDocument27 pagesASTM E92-17 Standard Test Methods For Vickers Hardness and Knoop Hardness of Metallic MaterialsCarlos Pinto Pradilla88% (8)
- Vienna ModernDocument85 pagesVienna ModernZain ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Usage of Regular Expressions in NLPDocument7 pagesUsage of Regular Expressions in NLPInternational Journal of Research in Engineering and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Freezing pipes-FPSDocument2 pagesFreezing pipes-FPSBinu SulochananNo ratings yet
- Yasnac Mx-3 Fault Finding GuideDocument70 pagesYasnac Mx-3 Fault Finding Guidechidambaram kasi100% (1)
- UDR MANUFACTURE ManufacturesDocument8 pagesUDR MANUFACTURE ManufacturesQuadri Consultancy ServicesNo ratings yet
- Psib 20150212Document10 pagesPsib 20150212Léandre Ettekri NdriNo ratings yet
- Core 3Document2 pagesCore 3RidhiNo ratings yet
- Sooad ManualDocument19 pagesSooad ManualRakhiNo ratings yet
- You Yangs RP Visitor GuideDocument2 pagesYou Yangs RP Visitor GuideSomaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Gantt Chart - Gantt Chart Information, History and SoftwareDocument3 pagesWhat Is A Gantt Chart - Gantt Chart Information, History and SoftwareShaikh Saeed AlamNo ratings yet
- Part # Is 0032192-70: Eldorado Eldorado Eldorado Eldorado National National National NationalDocument1 pagePart # Is 0032192-70: Eldorado Eldorado Eldorado Eldorado National National National NationalmnvijaybabuNo ratings yet
- Saes N 004Document5 pagesSaes N 004Mo'tasem SerdanehNo ratings yet
- Final Defence 2078Document43 pagesFinal Defence 2078XxxNo ratings yet
- TI Oxydur PTB 206 - en PDFDocument5 pagesTI Oxydur PTB 206 - en PDFgonzalogvargas01100% (1)
- Manage Payment Process Profiles - 1Document1 pageManage Payment Process Profiles - 1I'm RangaNo ratings yet
- Concrete Pipe Installation Guide-CPMDocument17 pagesConcrete Pipe Installation Guide-CPMSankar CdmNo ratings yet
- Narayana 10 01 24 SR Star Co Scmodel A, B&C Jee Main GTM 12n Key&sDocument10 pagesNarayana 10 01 24 SR Star Co Scmodel A, B&C Jee Main GTM 12n Key&sReddyNo ratings yet
- Flow Charts Option: StartDocument13 pagesFlow Charts Option: StartbalabooksNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Testing of PPE For Eye and Face Protection FPDocument6 pages1.1 Testing of PPE For Eye and Face Protection FPWalter PossoNo ratings yet
- Specification - EstimationDocument4 pagesSpecification - EstimationVenkatesan VenkatNo ratings yet
- TSB 1106 - MFY Starter Solenoid - ChangeDocument1 pageTSB 1106 - MFY Starter Solenoid - ChangeChrisMNo ratings yet
- Twice As Sharp Operators ManualDocument34 pagesTwice As Sharp Operators ManualLeonardo CHTZNo ratings yet
- Fire Drencher System - Base-Engineer PDFDocument2 pagesFire Drencher System - Base-Engineer PDFpequenita34100% (1)
- Elevator Installation Contract - 2022 - CNMDocument5 pagesElevator Installation Contract - 2022 - CNMsolid groupNo ratings yet
- Otago:Polytechnic: National Diploma in Drinking Water AssessmentDocument33 pagesOtago:Polytechnic: National Diploma in Drinking Water AssessmentThomas CollinsNo ratings yet
- 2019 Zeta Zwheel Catalogs PDFDocument30 pages2019 Zeta Zwheel Catalogs PDFSales One - Plusgrow - IndiaNo ratings yet
- SHINI Hopper-Loader - SAL-400 SERIES MANUALDocument38 pagesSHINI Hopper-Loader - SAL-400 SERIES MANUALRick ChenNo ratings yet
- MMMDocument1 pageMMMkhan22imranNo ratings yet
- What Is AmplifierDocument18 pagesWhat Is AmplifierEbayLunaNo ratings yet