Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adc Dac
Uploaded by
chillness0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views16 pagesAnalog-to-digital converter, digital-to-analog converter
Original Title
adc_dac
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAnalog-to-digital converter, digital-to-analog converter
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views16 pagesAdc Dac
Uploaded by
chillnessAnalog-to-digital converter, digital-to-analog converter
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
Analog To Digital Converter, ADC
Converts analog signals to digital signals
dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors,
including the resolution (the number of output levels it can
quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the
quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small
timing errors that introduce additional noise)
Quantization Error
the noise introduced by quantization in an ideal
ADC
non-linear and signal-dependent
Qe = (LSB/2)
Signal to Quantization Noise Ratio
SQR = 20log(2^Q)
Q = number of quantization bit
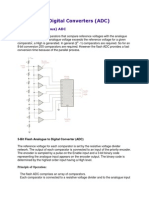
ADC Types
direct-conversion ADC or flash ADC has a bank of
comparators sampling the input signal in parallel, each
firing for their decoded voltage range.
successive-approximation ADC uses a comparator to
successively narrow a range that contains the input
voltage.
ADC Types
ramp-compare ADC produces a saw-tooth signal
that ramps up or down then quickly returns to zero
Wilkinson ADC
designed by D. H. Wilkinson in 1950
based on the comparison of an input
voltage with that produced by a
charging capacitor
ADC Types
integrating ADC (also dual-slope or multi-slope ADC)
applies the unknown input voltage to the input of an
integrator and allows the voltage to ramp for a fixed
time period (the run-up period).
delta-encoded ADC or counter-ramp has an up-down
counter that feeds a digital to analog converter (DAC)
ADC Types
pipeline ADC (also called subranging quantizer) uses
two or more steps of subranging. First, a coarse
conversion is done. In a second step, the difference to
the input signal is determined with a digital to analog
converter (DAC).
sigma-delta ADC (also known as a delta-sigma ADC)
oversamples the desired signal by a large factor and
filters the desired signal band
ADC Types
time-interleaved ADC uses M parallel ADCs where each ADC
samples data every Mth cycle of the effective sample clock
ADC with intermediate FM stage first uses a voltage-to-
frequency converter to convert the desired signal into an
oscillating signal with a frequency proportional to the voltage of
the desired signal, and then uses a frequency counter to convert
that frequency into a digital count proportional to the desired
signal voltage
Applications
Music recording
Digital signal processing
Scientific instruments
Examples
ADC ICs:
ADC0844 a moderate-speed device, showing a typical
conversion speed of 40 microsec.
ADC12181 a 12-bit, 10MHz converter with an internal
sample-and-hold; used for applications requiring both high
speed and high resolution
CS5396 offers stereo 24-bit resolution with a maximum
sampling rate of 96 kHz; dynamic range of 120 dB
Converts digital data (binary) to analog signals
suitability of a DAC for a particular application is
determined by six main parameters: physical size,
power consumption, resolution, speed, accuracy, cost
most DACs are implemented as integrated circuits
Digital To Analog Converter, ADC
Applications
Audio
Video
Mechanical
DAC Types
pulse-width modulator
Oversampling DACs or interpolating DACs
binary-weighted DAC
R-2R ladder DAC
Successive-Approximation or Cyclic DAC
thermometer-coded DAC
Hybrid DACs
Examples
DAC ICs: Examples
DAC0832 microprocessor-compatible 8-bit converter
DAC7545 12-bit linear converter
PCM1716 a stereo 24-bit converter designed specifically
for high quality digital audio apps.
You might also like
- Applied Statics and Strength of Materials 6th Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesApplied Statics and Strength of Materials 6th Edition Ebook PDFteri.sanborn87695% (44)
- Employee Confidentiality and Non-Disclosure AgreementDocument5 pagesEmployee Confidentiality and Non-Disclosure AgreementshamoojeeNo ratings yet
- Study of Various ADCs and Compare Their Performance and ParametersDocument12 pagesStudy of Various ADCs and Compare Their Performance and ParametersijaertNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of Wipro LTDDocument101 pagesFinancial Analysis of Wipro LTDashwinchaudhary89% (18)
- Nama: Refin Ananda NIM: 3.32.17.0.20 Kelas: EK-3A Individual Presentation 2 Analog To Digital Converter 1. The Meaning of ADCDocument4 pagesNama: Refin Ananda NIM: 3.32.17.0.20 Kelas: EK-3A Individual Presentation 2 Analog To Digital Converter 1. The Meaning of ADCRifky Yoga PratamaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 6: Objective: ApparatusDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 6: Objective: ApparatusNioNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital Converters PresentationDocument15 pagesAnalog To Digital Converters Presentationnguyenphuonghuy1979100% (1)
- Dada Acquisition HRISDocument4 pagesDada Acquisition HRISDiponkerSahaNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConverterDocument14 pagesAnalog To Digital Converterparth bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Sensor and Transducers Group Discusses ADC TechniquesDocument8 pagesSensor and Transducers Group Discusses ADC TechniquesRam Vijay YadavNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital & Digital To Analog ConvertersDocument66 pagesAnalog To Digital & Digital To Analog ConvertersSai Krishna Kodali100% (1)
- Analog-To-Digital Conversion Btech IIIDocument50 pagesAnalog-To-Digital Conversion Btech IIILisa BhagatNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConvertersDocument11 pagesAnalog To Digital Convertersمحمد ماجدNo ratings yet
- A D ConverterDocument20 pagesA D ConverterRenu TyagiNo ratings yet
- Jadavpur University PPT on ADC: Workings & ApplicationsDocument35 pagesJadavpur University PPT on ADC: Workings & ApplicationsAmit BarNo ratings yet
- Digital-To-Analog Converter: Ideally Sampled SignalDocument8 pagesDigital-To-Analog Converter: Ideally Sampled SignalJMSTavaresNo ratings yet
- DAQDocument34 pagesDAQKhairul FahzanNo ratings yet
- DIGITAL TO ANALOG CONVERsionDocument8 pagesDIGITAL TO ANALOG CONVERsionTanmay HazraNo ratings yet
- Unit II DAS & Signal CommunicationDocument65 pagesUnit II DAS & Signal CommunicationHOD MechanicalNo ratings yet
- ADC Conversion GuideDocument81 pagesADC Conversion GuideUmang PatelNo ratings yet
- Jadavpur University: PptonDocument39 pagesJadavpur University: PptonAmit BarNo ratings yet
- ConvertersDocument32 pagesConvertersJeff's SKiNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConverterDocument11 pagesAnalog To Digital ConverterFf Fr100% (1)
- M5 CH3 Adc DacDocument4 pagesM5 CH3 Adc DacMilan PjNo ratings yet
- Course Topic 2. Discrete-Time Signals and Systems (16x9)Document28 pagesCourse Topic 2. Discrete-Time Signals and Systems (16x9)Gennelyn IsraelNo ratings yet
- Adc - DacDocument4 pagesAdc - DacShaheer TariqNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital Converter PDFDocument4 pagesAnalog To Digital Converter PDFtowfiqeeeNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConversionDocument27 pagesAnalog To Digital Conversionnguyenphuonghuy1979No ratings yet
- Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) ExplainedDocument12 pagesDigital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) ExplainedNirmal Kumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConverterDocument7 pagesAnalog To Digital Convertersaima alamNo ratings yet
- Adc 0804Document5 pagesAdc 0804gouttNo ratings yet
- Wireless AssignmentDocument7 pagesWireless AssignmentJawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document23 pagesChapter 4Tejan Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital IO: Group MembersDocument7 pagesAnalog To Digital IO: Group MembersRam Vijay YadavNo ratings yet
- ConvertersDocument6 pagesConvertersmathiyosNo ratings yet
- 5-10-12 - Analog To Digital ConverterDocument49 pages5-10-12 - Analog To Digital ConverterjagdaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Analog-To-digital ConvertionDocument9 pagesBasics of Analog-To-digital ConvertionThanh Nhan LeNo ratings yet
- ADCDocument2 pagesADCMayilsamy MayilNo ratings yet
- DAC&ADC (EngineeringDuniya - Com)Document24 pagesDAC&ADC (EngineeringDuniya - Com)ramanaidu10% (1)
- Lecture 04-Embedded Systems-Fall 2023Document23 pagesLecture 04-Embedded Systems-Fall 2023Sherif SaidNo ratings yet
- Data ConversionDocument4 pagesData ConversionpauliNo ratings yet
- Fairchild Lm7805cDocument5 pagesFairchild Lm7805cGautam BalharaNo ratings yet
- Adc - DacDocument12 pagesAdc - Dacapi-3714361No ratings yet
- Analog To Digital Converter - Block Diagram, Types Its ApplicationsDocument10 pagesAnalog To Digital Converter - Block Diagram, Types Its ApplicationsNikka Hernandez FloresNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConvertersDocument11 pagesAnalog To Digital ConvertersAshutosh YadavNo ratings yet
- Digital-to-Analog Analog-to-Digital: Interface Part IV MicroprocessorDocument30 pagesDigital-to-Analog Analog-to-Digital: Interface Part IV MicroprocessorVineeth KumarNo ratings yet
- Inverters SpecsDocument11 pagesInverters SpecsbhuwaneshtakNo ratings yet
- Digital-to-Analog Analog-to-Digital: Dr. Syed Faiz AhmedDocument69 pagesDigital-to-Analog Analog-to-Digital: Dr. Syed Faiz AhmedmuraliNo ratings yet
- Adc DacDocument12 pagesAdc DacSonu SauravNo ratings yet
- Digital-to-Analog Analog-to-Digital Conversions: Microprocessor InterfaceDocument34 pagesDigital-to-Analog Analog-to-Digital Conversions: Microprocessor Interfaceeugen lupuNo ratings yet
- Digital Control SystemDocument23 pagesDigital Control SystemBHAVNA AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual DAC-SignedDocument10 pagesLab Manual DAC-Signedabidrk_21789100% (2)
- Analog To DigitalDocument46 pagesAnalog To DigitalSaleem HaddadNo ratings yet
- The Digital Lock-In AmplifierDocument4 pagesThe Digital Lock-In AmplifierBob HwknsNo ratings yet
- Adc 26.12.22Document38 pagesAdc 26.12.22Mrs.S.Divya BMENo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConverterDocument4 pagesAnalog To Digital Convertermuzamiru Kahise sayumweNo ratings yet
- ADCDocument3 pagesADCnandan_dubey93No ratings yet
- DEC LAB REPORT-06Document9 pagesDEC LAB REPORT-06anon_776365175No ratings yet
- I. Analog To Digital ConversionDocument1 pageI. Analog To Digital ConversionMariel Mae A. MaculbeNo ratings yet
- Adc DacDocument22 pagesAdc DacPrasad ChikkamNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsFrom EverandAnalog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- AbstractDocument1 pageAbstractchillnessNo ratings yet
- Airtime RateDocument2 pagesAirtime RatechillnessNo ratings yet
- NumericalsDocument7 pagesNumericalschillnessNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument1 pageAbstractchillnessNo ratings yet
- Automated Poultry Management SystemDocument1 pageAutomated Poultry Management Systemchillness0% (1)
- AbstractDocument1 pageAbstractchillnessNo ratings yet
- SatellitesDocument13 pagesSatelliteschillnessNo ratings yet
- Numerical MethodsDocument7 pagesNumerical MethodschillnessNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument1 pageAbstractchillnessNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument1 pageAbstractchillnessNo ratings yet
- Loran Navigation SystemDocument11 pagesLoran Navigation Systemchillness100% (1)
- AbstractDocument1 pageAbstractchillnessNo ratings yet
- PilotageDocument5 pagesPilotagechillnessNo ratings yet
- R A 9292 PDFDocument18 pagesR A 9292 PDFDaryl Langamon Uy CruzNo ratings yet
- Carnot CycleDocument6 pagesCarnot CyclechillnessNo ratings yet
- Alternative Method of Connecting SCRs To A LoadDocument6 pagesAlternative Method of Connecting SCRs To A LoadchillnessNo ratings yet
- Condition Based Monitoring System Using IoTDocument5 pagesCondition Based Monitoring System Using IoTKaranMuvvalaRaoNo ratings yet
- Busbar sizing recommendations for Masterpact circuit breakersDocument1 pageBusbar sizing recommendations for Masterpact circuit breakersVikram SinghNo ratings yet
- Level 10 Halfling For DCCDocument1 pageLevel 10 Halfling For DCCQunariNo ratings yet
- Exercise-01: JEE-PhysicsDocument52 pagesExercise-01: JEE-Physicsjk rNo ratings yet
- Consumers ' Usage and Adoption of E-Pharmacy in India: Mallika SrivastavaDocument16 pagesConsumers ' Usage and Adoption of E-Pharmacy in India: Mallika SrivastavaSundaravel ElangovanNo ratings yet
- Journals OREF Vs ORIF D3rd RadiusDocument9 pagesJournals OREF Vs ORIF D3rd RadiusironNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Exercise, May 3rdDocument3 pagesReading Comprehension Exercise, May 3rdPalupi Salwa BerliantiNo ratings yet
- Empanelment of Architect-Consultant - Work Costing More Than 200 Lacs. (Category-B)Document6 pagesEmpanelment of Architect-Consultant - Work Costing More Than 200 Lacs. (Category-B)HARSHITRAJ KOTIYANo ratings yet
- Shopping Mall: Computer Application - IiiDocument15 pagesShopping Mall: Computer Application - IiiShadowdare VirkNo ratings yet
- CALCULUS PHYSICS MIDTERMDocument41 pagesCALCULUS PHYSICS MIDTERMMACARIO QTNo ratings yet
- Lab StoryDocument21 pagesLab StoryAbdul QadirNo ratings yet
- Copula and Multivariate Dependencies: Eric MarsdenDocument48 pagesCopula and Multivariate Dependencies: Eric MarsdenJeampierr Jiménez CheroNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet - Matrices and DeterminantsDocument2 pagesRevision Worksheet - Matrices and DeterminantsAryaNo ratings yet
- KPUPDocument38 pagesKPUPRoda ES Jimbert50% (2)
- There Is There Are Exercise 1Document3 pagesThere Is There Are Exercise 1Chindy AriestaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance, Corporate Profitability Toward Corporate Social Responsibility Disclosure and Corporate Value (Comparative Study in Indonesia, China and India Stock Exchange in 2013-2016) .Document18 pagesCorporate Governance, Corporate Profitability Toward Corporate Social Responsibility Disclosure and Corporate Value (Comparative Study in Indonesia, China and India Stock Exchange in 2013-2016) .Lia asnamNo ratings yet
- Nokia CaseDocument28 pagesNokia CaseErykah Faith PerezNo ratings yet
- Job Order Costing: Patrick Louie E. Reyes, CTT, Micb, Rca, CpaDocument45 pagesJob Order Costing: Patrick Louie E. Reyes, CTT, Micb, Rca, CpaClaudette Clemente100% (1)
- Baobab MenuDocument4 pagesBaobab Menuperseverence mahlamvanaNo ratings yet
- WWW - Commonsensemedia - OrgDocument3 pagesWWW - Commonsensemedia - Orgkbeik001No ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument3 pagesManagerial EconomicsGuruKPONo ratings yet
- Pemaknaan School Well-Being Pada Siswa SMP: Indigenous ResearchDocument16 pagesPemaknaan School Well-Being Pada Siswa SMP: Indigenous ResearchAri HendriawanNo ratings yet
- A Reconfigurable Wing For Biomimetic AircraftDocument12 pagesA Reconfigurable Wing For Biomimetic AircraftMoses DevaprasannaNo ratings yet
- Kaydon Dry Gas SealDocument12 pagesKaydon Dry Gas Sealxsi666No ratings yet
- The Smith Generator BlueprintsDocument36 pagesThe Smith Generator BlueprintsZoran AleksicNo ratings yet
- Kate Elizabeth Bokan-Smith ThesisDocument262 pagesKate Elizabeth Bokan-Smith ThesisOlyaGumenNo ratings yet
- Letter From Attorneys General To 3MDocument5 pagesLetter From Attorneys General To 3MHonolulu Star-AdvertiserNo ratings yet