Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thread Cutting Fundamentals
Uploaded by
jaydip2410chhatralaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thread Cutting Fundamentals
Uploaded by
jaydip2410chhatralaCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Threads and
Thread Cutting
Session 11
2
Threads
Thread
Helical ridge of uniform section formed on
inside or outside of cylinder or cone
Used for several purposes:
Fasten devices such as screws, bolts, studs,
and nuts
Provide accurate measurement, as in
micrometer
Transmit motion
Increase force
3
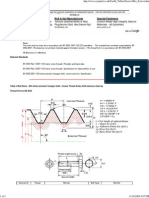
Thread Terminology
4
Thread Terminology
Screw thread
Helical ridge of uniform section formed on
inside or outside of cylinder or cone
External thread
Cut on external surface or cone
Internal thread
Produced on inside of cylinder or cone
5
Thread Terminology
Major Diameter
Commonly known as the outside diameter .
On a screw thread, the major diameter is the
largest diameter of the thread on the screw or
nut.
6
Thread Terminology
Minor Diameter
Called the root diameter, the minor diameter is
the smallest diameter of the thread on the
screw or nut.
7
Pitch diameter
Diameter of imaginary cylinder that passes
through thread at point where groove and
thread widths are equal
Equal to major diameter minus single depth
of thread
Tolerance and allowances given at pitch
diameter line
Thread Terminology
8
Thread Terminology
Number of Threads
The number of threads per inch.
9
Thread Terminology
Pitch
The distance from a given point on one
thread to a corresponding point on the very
next thread
10
Thread Terminology
Lead
The distance a screw thread advances
in one revolution.
The lead and the pitch of a single lead
thread are the same.
On double lead threads, the lead is twice
the pitch.
A double lead thread has two start points.
11
Single Lead Double Lead
Thread Terminology
12
Root
Bottom surface joining sides of two
adjacent threads
External thread on minor diameter
Internal thread on major diameter
Thread Terminology
13
Crest
Top surface joining two sides of thread
External thread on major diameter
Internal thread on minor diameter
Thread Terminology
14
Flank
Thread surface that connects crest
with root
Thread Terminology
15
Depth of thread
Distance between crest and root measured
perpendicular to axis
Thread Terminology
16
Angle of thread
Included angle between sides of
thread measured in axial plane
Thread Terminology
17
Helix angle
Angle that thread makes with plane
perpendicular to thread axis
Thread Terminology
18
Right-hand thread
Helical ridge of uniform cross section onto
which nut is threaded in clockwise direction
When cut on lathe, toolbit
advanced from right to left
Thread Terminology
19
Left-hand thread
Helical ridge of uniform cross section onto
which nut is threaded in counterclockwise
direction
When cut on lathe, toolbit advanced from
left to right
Thread Terminology
20
Thread Forms
ISO Metric
American National Standard Thread
British Standard Whitworth (BSW) Thread
Unified Thread
American National Acme Thread
Square Thread
Brown & Sharpe Worm Thread
International Metric thread
21
ISO Metric Thread
60 included angle
D (Internal) = 0.6143 x pitch
Crest = .125 x pitch
Root = .250 x pitch
22
ISO Metric Thread
x .250
x .125
x . (external)
P FR
P FC
P D
54127 0
23
ISO metric pitch and diameter
combinations
Nominal Thread Nominal Thread
Diameter Pitch Diameter Pitch
(mm) (mm) (mm) (mm)
1.6 0.35 20 2.5
2 0.4 24 3
2.5 0.45 30 3.5
3 0.5 36 4
3.5 0.6 42 4.5
4 0.7 48 5
5 0.8 56 5.5
Portion of table taken
from textbook
24
American National Standard
Thread
Divided into four main series, all having
same shape and proportions
National Coarse (NC)
National Fine (NF)
National Special (NS)
National Pipe (NPT)
25
Common Thread Forms
Coarse Thread Series UNC
The one most commonly used in the mass
production of bolts, screws, nuts and other
general fastening applications.
Less of a tendency for cross-threading
than fine threads.
It is also used on quick assembly or
disassembly, or if corrosion or slight damage
is possible.
26
Common Thread Forms
Fine Thread Series UNF
When used on external threads have greater
tensile stress area than coarse threads of the
same size.
Resists stripping out better than coarse threads
in areas where the external and mating internal
threads are subjected to loads equal to or
greater than the capacity of the screw or bolt.
Used were the length of engagement is
limited
27
Common Thread Forms
28
Common Thread Forms
Taper Pipe Series NPT
When used with a sealer (such as pipe dope or
teflon tape) will produce a pressure tight joint.
The taper of the external thread forms a joint
with the taper of the internal thread.
29
American National
Standard Thread
N
P F
N
P D
.125
or x .125
.6134
or x .
6134
30
British Standard Whitworth
(BSW) Thread
Application is same
as for American
National form
thread
N
P R
N
P D
.1373
or x .1373
.6403
or x .
6403
31
Unified Thread
Developed by U.S., Britain, and Canada for
standardized thread system
Combination of British Standard Whitworth
and American National Standard Thread
32
N
P F
N
P F
N
P D
N
P D
.250
or x .250 thread) (internal
.125
or x .125 thread) (external
.5413
or x . thread) (internal
.6134
or x . thread) (external
5413
6134
Unified Thread
33
Acme Screw Thread
Replacing square thread in many cases
Used for feed screws, jacks, and vises
D = minimum .500P
= maximum .500P + 0.010
F = .3707P
C = .3707P - .0052
(for maximum depth)
34
Brown & Sharpe Worm
Thread
Used to mesh worm gears and transmit motion
between two shafts at right angles to each other
but not in same plane
D = .6866P
F = .335P
C = .310P
35
Square Thread
Being replaced by Acme thread because
of difficulty in cutting it
Often found on vises
and jack screws
D = .500P
F = .500P
C = .500P + .002
36
International Metric thread
Standardized thread used in Europe
F = 0.125P
R = 0.0633P (maximum)
= 0.054P (minimum)
D = 0.7035P (maximum)
= 0.6855P (minimum)
37
Thread Fits and
Classifications
Fit
Relationship between two mating parts
Determined by amount of clearance or
interference when they are assembled
Nominal size
Designation used to identify size of part
Actual size
Measured size of thread or part
Basic size: size from which tolerances are
set
38
Allowance
Permissible difference between largest
external thread and smallest internal
thread
Difference produces tightest fit
acceptable for any given classification
The allowance for a 1- 8 UNC Class 2A and 2B
Minimum pitch diameter of the
internal thread (2B) = .9188 in.
Maximum pitch diameter of the
external thread (2A) = .9168 in.
Allowance = .002 in.
39
Tolerance
Variation permitted in part size
Total tolerance is sum of plus and minus
tolerances
In Unified and National systems, tolerance is
plus on external threads and minus on internal
threads
Maximum pitch diameter of the
external thread (2A) = .9168 in.
Minimum pitch diameter of the
external thread (2A) = .9100 in.
Tolerance = .0068 in.
The tolerance for a 1 in.8 UNC Class 2A thread is:
40
Limits
Maximum and minimum dimensions of part
Maximum pitch diameter of the
external thread (2A) = .9168 in..
Minimum pitch diameter of the
external thread (2A) = .9100 in.
The limits for a 1 in.8 UNC Class 2A thread are:
41
ISO Metric Tolerances and
Allowances
ISO metric screw thread tolerance
system provides for allowances and
tolerances defined by tolerance grades,
tolerance positions, and tolerance
classes
Tolerance grades specified numerically
Medium tolerance indicated by number 6,
number below 6 indicates finer tolerance
and number above 6 indicates greater
tolerance
42
Tolerance Example:
An external metric thread may be
designated as follows:
Pitch Outside
Nominal Diameter Diameter
Metric Size Pitch Tolerance Tolerance
M 6 X 0.75 - 5g 6g
The thread fit between mating parts is indicated by
internal thread designation followed by the external
thread tolerance:
M 20 X 2 - 6H/5g 6g
43
Allowance Symbols
For external threads:
e indicates a large allowance
g indicates a small allowance
h indicates no allowance
For internal threads:
G indicates a small allowance
H indicates no allowance
44
Classes of Unified Thread
Fits
External threads classified as 1A, 2A, and
3A and internal threads as 1B, 2B, 3B
Classes 1A and 1B
Threads for work that must be assembled
Loosest fit
Classes 2A and 2B
Used for most commercial fasteners
Medium or free fit
Classes 3A and 3B
Used where more accurate fit and lead required
No allowance provided
45
Classes Of Thread Fits
-20 UNC 2A
In this particular case the class of fit
would be a 2. The symbol A indicates an
external thread.
-28 UNF 3B
In this particular case the class of fit
would be a 3. The symbol B indicates
an internal thread.
46
Thread Calculations
D = single depth of thread
P = pitch
in. .061 .100 x .61343
x .
in. .
P D
tpi
P
61343
100
10
1 1
Calculate pitch, depth, minor diameter, and
width of flat for a -10 UNC thread.
in. 0125 .
10
1
x
8
1
8
flat of Width
in. 628 .
.061) (.061 - .75
) ( - dia Major dia Minor
P
D D
47
Thread Calculations
P = pitch = 1 mm
D = 0.54127 x 1
= 0.54 mm
What is the depth, minor diameter, crest
and root for an M 6.3 X 1 thread?
mm .
1 x .
x .125 crest of Width
mm .
.54) (.54 - 6.3
) ( - dia Major dia Minor
125 0
125 0
0
22 5
P
D D
mm .
1 x 0.25
x . root of Width
25 0
25 0
P
48
Thread-Chasing dial
Lathe spindle and
lead screw must be
in same relative
position for each cut
Thread-chasing dial
attached to carriage for
this purpose
Dial has eight divisions
Even threads use any
division
Odd threads either
numbered
or unnumbered: not both
49
Measuring Threads
1. Three-wire method
2. Thread ring gage
3. Thread plug gage
4. Thread snap gage
5. Screw thread micrometer
6. Optical comparator
50
Three-Wire Measuring
Three wires of equal diameter placed
in thread, two on one side and one on
other side
Standard micrometer used to measure
distance over wires (M)
Different sizes and pitches of threads
require different sizes of wires
51
The Three-Wire Method of
Measuring 60 Threads
52
Measurement with Wires
N
G D M
5155 1
3
.
where M = measurement over the wires
D = major diameter of the thread
G = diameter of the wire size used
N = number of tpi
Any of the
following
formulas can
be used to
calculate G:
P
N
P
N
P
N
.505 or
.505
wire Smallest
.57735 or
.57735
wire size - Best
1.010 or
.
wire Largest
010 1
53
Multiple Threads
May be double, triple or quadruple,
depending on number of starts around
periphery of work
Pitch: distance from point on one thread to
corresponding point on next thread
Lead: distance nut advances lengthwise in
one complete revolution
Single-start: pitch and lead equal
Double-start: lead twice the pitch
Triple-start: lead three times pitch
54
Single
Double
Triple
55
Internal Threads
Cutting threads in a hole
Operation performed on work held in
chuck or collet or mounted on faceplate
Threading tool similar to boring toolbit
except shape ground to form of thread to
be cut
56
The compound rest is set at 29 to the left
for cutting right-hand internal threads.
Internal Threads
You might also like
- A PresentationDocument57 pagesA Presentationmadan023No ratings yet
- Threads and Threaded FastenersDocument12 pagesThreads and Threaded FastenersPalaNo ratings yet
- BoltsDocument18 pagesBoltsSatyaKrishna Palla100% (1)
- Threads and FastenersDocument89 pagesThreads and Fastenerstheleovn0% (1)
- Screw Thread PDFDocument45 pagesScrew Thread PDFPandurang Nalawade67% (3)
- ThreadsDocument50 pagesThreadsSagar JathanNo ratings yet
- Threads and Thread CuttingDocument56 pagesThreads and Thread CuttingkoshkadaNo ratings yet
- Bolts TheoryDocument30 pagesBolts TheoryIbrahim Mesfin100% (1)
- Thread DetailsDocument27 pagesThread DetailsN.PalaniappanNo ratings yet
- ThreadsDocument62 pagesThreadsAyush SinghNo ratings yet
- Screw Threads: ME354 Albert ClaypoolDocument13 pagesScrew Threads: ME354 Albert ClaypoolfotickNo ratings yet
- Design Bolts and ScrewsDocument42 pagesDesign Bolts and ScrewsBirondo100% (1)
- Screw Thread FundamentalsDocument56 pagesScrew Thread FundamentalsAbhishek Kumar100% (1)
- 07 Power Screws and Threaded Fasteners (Handout)Document16 pages07 Power Screws and Threaded Fasteners (Handout)tnvsaikiran3100% (3)
- Problems s8Document4 pagesProblems s8zangue billy jamesNo ratings yet
- Machine DesignDocument26 pagesMachine Designrajasekar21No ratings yet
- Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing: Procedure / Drafting FNHA-3-B-072.00Document69 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing: Procedure / Drafting FNHA-3-B-072.00003689% (9)
- M6 Hardware (Phase B)Document88 pagesM6 Hardware (Phase B)Moin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Bolted JointsDocument3 pagesBolted JointsGiuseppe GiuseppeNo ratings yet
- Belt Drive SystemsDocument8 pagesBelt Drive SystemsYavuz KeskinNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Notes BDocument50 pagesEngineering Drawing Notes BAchinNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Assembly - Chapter 33Document67 pagesMechanical Assembly - Chapter 33xharpreetxNo ratings yet
- Screw Threads and Assembly Drawing Class NotesNotesDocument17 pagesScrew Threads and Assembly Drawing Class NotesNotesRay NjorogeNo ratings yet
- Knuckle Joints DesignDocument10 pagesKnuckle Joints DesignKvrd Prasad100% (1)
- Power ScrewsDocument10 pagesPower ScrewsamanggayamNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation CH3Document84 pagesInstrumentation CH3muru0105No ratings yet
- Thread Fasteners Loosening TribologyDocument179 pagesThread Fasteners Loosening TribologysasunNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Fasteners - Part IIDocument24 pagesMechanical Fasteners - Part IIsaded05No ratings yet
- Aircraft Materials and Hardware: BoltsDocument27 pagesAircraft Materials and Hardware: BoltsPakistaniTalent cover songsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power Screw AssingmentDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Power Screw AssingmentZohaibShoukatBalochNo ratings yet
- Primary Functions of A ThreadDocument10 pagesPrimary Functions of A ThreadEng-Mohammed Abu NuktaNo ratings yet
- A Bearing Is A Device To Permit Constrained Relative Motion Between Two Parts, Typically Rotation or Linear MovementDocument18 pagesA Bearing Is A Device To Permit Constrained Relative Motion Between Two Parts, Typically Rotation or Linear MovementSreedhar Madhana100% (1)
- Screws Nuts Washer SizesDocument5 pagesScrews Nuts Washer SizesHEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Solution: Fig. 6.27 Differential Screw JackDocument6 pagesSolution: Fig. 6.27 Differential Screw JackWahyu AwaludinNo ratings yet
- Ansys Report of Knuckle JointDocument27 pagesAnsys Report of Knuckle JointNíthìsh GøwdåNo ratings yet
- Surface Finish ChartsDocument5 pagesSurface Finish ChartsagssugaNo ratings yet
- Motor Quality Guide: Reliability, Life Cycle Costs, and Choosing the Right SupplierDocument12 pagesMotor Quality Guide: Reliability, Life Cycle Costs, and Choosing the Right SupplierRyan Jay100% (1)
- Gear Cutting Operations GuideDocument23 pagesGear Cutting Operations GuideHossam AliNo ratings yet
- Power Screws - Types and Uses ExplainedDocument6 pagesPower Screws - Types and Uses ExplainedDeepak KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Bevel GearsDocument1 pageBevel GearsBalasoobramaniam CarooppunnenNo ratings yet
- Wire Rope BookletDocument27 pagesWire Rope BookletVasanth RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5, CH 6, Tolerances, FitsDocument55 pagesChapter 5, CH 6, Tolerances, Fitssamuel mekuriawNo ratings yet
- Dte - Rolling Contact BearingsDocument32 pagesDte - Rolling Contact Bearingspotnuru Jaivanth100% (1)
- SpringDocument30 pagesSpringlin_meckylogiNo ratings yet
- Threads and Thread CuttingDocument56 pagesThreads and Thread CuttingVenugopal MahalingamNo ratings yet
- Threads and Thread CuttingDocument56 pagesThreads and Thread Cuttingcpojha100% (1)
- Thread Cutting GuideDocument111 pagesThread Cutting GuideKundan Patil100% (1)
- Threads and Thread CuttingDocument21 pagesThreads and Thread CuttingravijecrcNo ratings yet
- Thread and Thread CuttingDocument9 pagesThread and Thread Cuttinglyk zNo ratings yet
- Threads and FastenersDocument25 pagesThreads and FastenersMuhammed UmarNo ratings yet
- Threaded & Riveted JointsDocument43 pagesThreaded & Riveted JointsMadhurima BhandariNo ratings yet
- Metric STD ThreadDocument4 pagesMetric STD ThreadmayurNo ratings yet
- Material Removal Manufacturing Processes: MACH71685 Dr. Liviu Radulescu, P.EngDocument30 pagesMaterial Removal Manufacturing Processes: MACH71685 Dr. Liviu Radulescu, P.EngEthan StoneNo ratings yet
- Understanding Thread Forms and Lathe SetupDocument30 pagesUnderstanding Thread Forms and Lathe SetupAkulNo ratings yet
- 10-1 Threaded FastenersDocument23 pages10-1 Threaded FastenersDeepak Ranjan BholaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Strength Calculation of JointsDocument76 pagesChapter 3 Strength Calculation of Jointsrobel metiku100% (1)
- Threads and FastenersDocument21 pagesThreads and FastenersSunil DeoNo ratings yet
- 7 Bolted Connections-T8 T9Document24 pages7 Bolted Connections-T8 T9Bernardine BenedictNo ratings yet
- Threads FastenersDocument81 pagesThreads FastenersДмитрий РыбаковNo ratings yet
- Adobe Acrobat XI Pro 10116 Multilingual Crack Serial Key PDFDocument4 pagesAdobe Acrobat XI Pro 10116 Multilingual Crack Serial Key PDFNicoleNo ratings yet
- Seizing the Light A Social Aesthetic History of Photography Robert HirschDocument26 pagesSeizing the Light A Social Aesthetic History of Photography Robert HirschSvetlana DograNo ratings yet
- Tele Immersion: Aman BabberDocument16 pagesTele Immersion: Aman Babberbabbar_amanNo ratings yet
- Jordan Vs LebronDocument6 pagesJordan Vs Lebronapi-719540801No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument5 pagesDocumentKaran KirubajkNo ratings yet
- WL100-GA - Rev 01Document1 pageWL100-GA - Rev 01affendy roynNo ratings yet
- Class and Race OptionsDocument4 pagesClass and Race OptionsGeorge50% (2)
- Troop Meeting Plan FormDocument1 pageTroop Meeting Plan FormSTARTTOLOOKNo ratings yet
- Latian Soal XIDocument5 pagesLatian Soal XIHenny KusumaNo ratings yet
- Hospitality Review MooreDocument4 pagesHospitality Review Mooremarina partsvaniaNo ratings yet
- T1X User Manual 1.0 v5.0 - EditableDocument36 pagesT1X User Manual 1.0 v5.0 - EditableRifanto Bin SatariNo ratings yet
- Executive+Committee+Roster+ +february+2014Document6 pagesExecutive+Committee+Roster+ +february+2014George SkinnerNo ratings yet
- National Artists of The PhilippinesDocument17 pagesNational Artists of The PhilippinesDeniseNo ratings yet
- Structuralist Analysis of Stage FX's The MousetrapDocument2 pagesStructuralist Analysis of Stage FX's The Mousetrapsuperwee100No ratings yet
- Gateway B1+ (1st Edition) Test Unit 8Document8 pagesGateway B1+ (1st Edition) Test Unit 8Semir Omerdić75% (20)
- Modul Bahasa Inggris SDDocument9 pagesModul Bahasa Inggris SDitsmeupkNo ratings yet
- Packexpo18 PressDocument4 pagesPackexpo18 PressarunNo ratings yet
- 4th Periodical Test g12 P.EDocument8 pages4th Periodical Test g12 P.EYram LemNo ratings yet
- Passive Sentences Matched PicturesDocument2 pagesPassive Sentences Matched PicturessorinadanNo ratings yet
- Egypt and PersiaDocument4 pagesEgypt and PersiaDominique John JuanilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Probability II Sample Space and EventsDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Probability II Sample Space and Eventsleelee1127No ratings yet
- The Digital Matrix in The Automotive Sector - Venkat VenkatramanDocument30 pagesThe Digital Matrix in The Automotive Sector - Venkat VenkatramanIvan Martinez100% (2)
- the-QuertDell-XPS-9360-Hackintosh Dell XPS 13 (9360) For macOS MojaveDocument7 pagesthe-QuertDell-XPS-9360-Hackintosh Dell XPS 13 (9360) For macOS MojaversuchwaniNo ratings yet
- Preview of SweetDocument20 pagesPreview of SweetMisha MK25% (4)
- x5 CatalogueDocument18 pagesx5 CatalogueKmt_AeNo ratings yet
- Soalan Sains - Year 5 (Module 1)Document19 pagesSoalan Sains - Year 5 (Module 1)ZAZOLNIZAM BIN ZAKARIA67% (3)
- Last ExceptionDocument7 pagesLast ExceptionAnindhita Mega PNo ratings yet
- Iron Kingdoms - Adventure - Fool's Errand (LVL 3-5) PDFDocument29 pagesIron Kingdoms - Adventure - Fool's Errand (LVL 3-5) PDFnomad79No ratings yet
- Beating The Caro-Kann - Kotronias PDFDocument115 pagesBeating The Caro-Kann - Kotronias PDFNamrah Zubair0% (1)
- 1st Quarter Summative Test in English 9Document4 pages1st Quarter Summative Test in English 9MA. GELINA DEPONENo ratings yet