Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Practical 1
Uploaded by
harishpillai19940 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
180 views24 pagesThe document discusses different network topologies:
- Mesh, star, bus, ring, and tree are the most common topologies. Mesh provides the most redundancy but is most expensive. Star and bus are cheaper but a single point of failure can disable the whole network.
- Ring topology messages travel in a closed loop between nodes. Tree combines characteristics of bus and star, with groups of stars connected by a backbone.
- Hybrid topology combines two or more topologies to gain advantages while reducing weaknesses. It can isolate faults without disabling the whole network but requires complex design and expensive infrastructure.
Original Description:
network topologies - star, bus , tree,
Original Title
Practical-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different network topologies:
- Mesh, star, bus, ring, and tree are the most common topologies. Mesh provides the most redundancy but is most expensive. Star and bus are cheaper but a single point of failure can disable the whole network.
- Ring topology messages travel in a closed loop between nodes. Tree combines characteristics of bus and star, with groups of stars connected by a backbone.
- Hybrid topology combines two or more topologies to gain advantages while reducing weaknesses. It can isolate faults without disabling the whole network but requires complex design and expensive infrastructure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
180 views24 pagesPractical 1
Uploaded by
harishpillai1994The document discusses different network topologies:
- Mesh, star, bus, ring, and tree are the most common topologies. Mesh provides the most redundancy but is most expensive. Star and bus are cheaper but a single point of failure can disable the whole network.
- Ring topology messages travel in a closed loop between nodes. Tree combines characteristics of bus and star, with groups of stars connected by a backbone.
- Hybrid topology combines two or more topologies to gain advantages while reducing weaknesses. It can isolate faults without disabling the whole network but requires complex design and expensive infrastructure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 24
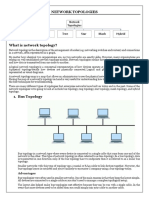
Network Topology refers to layout of a
network. How different nodes in a network
are connected to each other and how
they communicate is determined by the
network's topology.
Network Topology refers to layout of a
network and how different nodes in a
network are connected to each other and
how they communicate. This slideshow
describes five of the most common network
topologies.
MESH TOPOLOGY
STAR TOPOLOGY
BUS TOPOLOGY
RING TOPOLOGY
TREE TOPOLOGY
HYBRID TOPOLOGY
1. Mesh Topology
Mesh Network Topology: In a mesh network, devices are
connected with many redundant interconnections
between network nodes. In a true mesh topology every
node has a connection to every other node in the
network. There are two types of mesh topologies:
Full mesh topology: occurs when every node has a circuit
connecting it to every other node in a network. Full mesh is
very expensive to implement but yields the greatest
amount of redundancy, so in the event that one of those
nodes fails, network traffic can be directed to any of the
other nodes. Full mesh is usually reserved for backbone
networks.
Partial mesh topology: is less expensive to
implement and yields less redundancy than
full mesh topology. With partial mesh, some
nodes are organized in a full mesh scheme
but others are only connected to one or
two in the network. Partial mesh topology is
commonly found in peripheral networks
connected to a full meshed backbone.
Advantages:
No traffic problem as there are dedicated links.
Robust as failure of one link does not affect the entire system.
Security as data travels along a dedicated line.
Points to point links make fault identification easy.
Disadvantages:
The hardware is expansive as there is dedicated link for any two
nodes and each device should have (n-1) I/O ports.
There is mesh of wiring which can be difficult to manage.
Installation is complex as each node is connected to every
node.
2. Star Topology
Star Topology: In a star network
devices are connected to a central
computer, called a hub. Nodes
communicate across the network
by passing data through the hub.
Advantages:
Star topology is less expensive than a mesh topology
as there are no dedicated links between nodes and
each device needs only one link and one I/O ports to
connect it to any number of nodes.
Easy to install and make configurations.
Robust as failure of one link does not affect the entire
system. The remaining system will be active.
Disadvantage:
More cabling is required in a star than in other
topologies (except mesh). Entire network collapse if
central controller fails.
3.Bus Topology
Bus Topology: In networking a bus is the
central cable -- the main wire -- that
connects all devices on a local-area
network (LAN).
It is also called the backbone. This is
often used to describe the main network
connections composing the Internet.
Bus networks are relatively inexpensive
and easy to install for small networks.
Ethernet systems use a bus topology.
Advantages:
Requires less cabling compared to mesh, star and
tree topologies.
Easy to install.
Disadvantages:
It's Difficult to add new devices.
Difficult reconfiguration and fault isolation.
A fault in Backbone stops all transmission, even
between devices on the same side of the problem
because of noise generated by faulty point.
4. Ring Topology
Ring Topology: A local-area network (LAN)
whose topology is a ring. That is, all of the
nodes are connected in a closed loop.
Messages travel around the ring, with each
node reading those messages addressed to it.
One main advantage to a ring network is that
it can span larger distances than other types of
networks, such as bus networks, because each
node regenerates messages as they pass
through it.
Advantages:
Relatively easy to install and reconfigure.
Easy to add new node as only two
connections need changes.
Disadvantages:
A fault in the ring can disable the entire
network. This weakness can be solved by
using a dual ring.
5. Tree Topology
Tree Topology: This is a "hybrid" topology
that combines characteristics of linear
bus and star topologies.
In a tree network, groups of star-
configured networks are connected to a
linear bus backbone cable.
Advantages:
Central hub (repeater) increases the
distance a signal can travel between
devices.
Disadvantages:
More cabling is required in a tree than in
other topologies (except mesh).
Entire network collapse if central Hub fails.
6.Hybrid Topology
Hybrid, as the name suggests, is mixture of two different things.
Similarly in this type of topology we integrate two or more
different topologies to form a resultant topology which has
good points(as well as weaknesses) of all the constituent basic
topologies rather than having characteristics of one specific
topology. This combination of topologies is done according to
the requirements of the organization.
For example, if there exists a ring topology in one office
department while a bus topology in another department,
connecting these two will result in Hybrid topology.
Remember connecting two similar topologies cannot be
termed as Hybrid topology. Star-Ring and Star-Bus networks
are most common examples of hybrid network.
Advantages of Hybrid Network Topology
1) Reliable : Unlike other networks, fault detection and troubleshooting is
easy in this type of topology. The part in which fault is detected can be
isolated from the rest of network and required corrective measures can be
taken, WITHOUT affecting the functioning of rest of the network.
2) Scalable: Its easy to increase the size of network by adding new
components, without disturbing existing architecture.
3) Flexible: Hybrid Network can be designed according to the requirements
of the organization and by optimizing the available resources. Special care
can be given to nodes where traffic is high as well as where chances of fault
are high.
4) Effective: Hybrid topology is the combination of two or more topologies, so
we can design it in such a way that strengths of constituent topologies are
maximized while there weaknesses are neutralized. For example we saw Ring
Topology has good data reliability (achieved by use of tokens) and Star
topology has high tolerance capability (as each node is not directly
connected to other but through central device), so these two can be used
effectively in hybrid star-ring topology.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology
1) Complexity of Design: One of the biggest
drawback of hybrid topology is its design. Its not easy
to design this type of architecture and its a tough job
for designers. Configuration and installation process
needs to be very efficient.
2) Costly Hub: The hubs used to connect two distinct
networks, are very expensive. These hubs are
different from usual hubs as they need to be
intelligent enough to work with different architectures
and should be function even if a part of network is
down.
3) Costly Infrastructure: As hybrid architectures are
usually larger in scale, they require a lot of cables,
cooling systems, sophisticate network devices, etc.
You might also like
- CN LAB FileDocument58 pagesCN LAB FileHEERAJNo ratings yet
- What Is Network TopologyDocument5 pagesWhat Is Network TopologyRohit JainNo ratings yet
- Star TopologyDocument7 pagesStar TopologyadelenyamhuriNo ratings yet
- Network Topology 1Document10 pagesNetwork Topology 1anonymousNo ratings yet
- Cn-Lab ManualDocument44 pagesCn-Lab ManualRohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Network Topologies: and Its TypesDocument19 pagesNetwork Topologies: and Its TypesJeff Clifford LuyahanNo ratings yet
- Network TopologiesDocument6 pagesNetwork TopologiesTaimoor ZubairNo ratings yet
- Understanding Network Topology Types and Their UsesDocument25 pagesUnderstanding Network Topology Types and Their UsesMimi Rubia AvilaNo ratings yet
- 89492NW TopologiesDocument25 pages89492NW TopologiesAbdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Network Basics: Network Topology: Node: A NodeDocument3 pagesNetwork Basics: Network Topology: Node: A Nodemanohar reddyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Network TopologyDocument3 pagesLesson 4 - Network TopologyGeorgia Andales TaganahanNo ratings yet
- Topology in Network Design: BackboneDocument9 pagesTopology in Network Design: BackboneSandeep ChNo ratings yet
- Topology in Network Design: BackboneDocument9 pagesTopology in Network Design: BackboneSandeep ChNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument12 pagesNetwork TopologyShakeel MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument2 pagesNetwork TopologyDiom ShresthaNo ratings yet
- TopologyDocument10 pagesTopologyAmeliaNo ratings yet
- Core 2Document30 pagesCore 2keanee simbajonNo ratings yet
- What Is Network TopologyDocument4 pagesWhat Is Network TopologyGoldy BatraNo ratings yet
- Types of Computer Network TopologiesDocument9 pagesTypes of Computer Network TopologiesAamna humayunNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument2 pagesNetwork TopologyJason CuarentaNo ratings yet
- Network TopologiesDocument9 pagesNetwork TopologiesshijinbgopalNo ratings yet
- 02 TopologyDocument4 pages02 TopologyHailay HadushNo ratings yet
- Types of Network Topology: Name: Neel Patel School: DCPEMS Class: 11 Sub: IT Guided: Roshni Sundrani MamDocument16 pagesTypes of Network Topology: Name: Neel Patel School: DCPEMS Class: 11 Sub: IT Guided: Roshni Sundrani MamNeel PatelNo ratings yet
- CN - Assignment2Document14 pagesCN - Assignment2WhatsApp statusNo ratings yet
- Network Topology ReportDocument11 pagesNetwork Topology ReportAdilet KenesovNo ratings yet
- BUS TopologyDocument9 pagesBUS TopologyObby-GiftMwambaKachecheNo ratings yet
- Topology 3Document3 pagesTopology 3mcsm-f18-055No ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument7 pagesNetwork TopologyJayvee Puntalba CalinogNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture FileDocument49 pagesComputer Architecture FileFunsuk VangduNo ratings yet
- Study About Basic of Network (Topologies) and Types of network-LAN, Man, WanDocument11 pagesStudy About Basic of Network (Topologies) and Types of network-LAN, Man, WanAnonymous aQxekTRNo ratings yet
- Network Topologies ExplainedDocument5 pagesNetwork Topologies ExplainedSaurav PooniaNo ratings yet
- Network Topology DiagramDocument7 pagesNetwork Topology DiagramSatvik SalatNo ratings yet
- Exercises 2017-2018Document6 pagesExercises 2017-2018tuyambaze jean claudeNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Network TypologiesDocument6 pagesDifference Between Network Typologiesشمیم نازNo ratings yet
- Home Ccatcracker Pyapps Ccatcracker Ccatcracker Networking PDFDocument92 pagesHome Ccatcracker Pyapps Ccatcracker Ccatcracker Networking PDFTejas RaneNo ratings yet
- Ict DatabaseDocument5 pagesIct DatabasebasitNo ratings yet
- Xavier University - Ateneo de Cagayan University College of Engineering Electronics Engineering DepartmentDocument6 pagesXavier University - Ateneo de Cagayan University College of Engineering Electronics Engineering DepartmentMor DepRzNo ratings yet
- Basic NetworkingDocument8 pagesBasic NetworkingDavid Atoroyo SikaNo ratings yet
- Network TopologiesDocument23 pagesNetwork TopologiesdendenliberoNo ratings yet
- Network Topology Types GuideDocument9 pagesNetwork Topology Types GuidePriyam TripathiNo ratings yet
- MemunaDocument6 pagesMemunajallohadrahNo ratings yet
- Network TopologiesDocument5 pagesNetwork TopologiesSanjiv Kumar SorahiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document22 pagesLesson 2Queen M SANo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document9 pagesLab 4Haidar MalikNo ratings yet
- Types of Network TopologyDocument10 pagesTypes of Network TopologySalman TahirNo ratings yet
- Ecommerce 1-5QNS FinalDocument20 pagesEcommerce 1-5QNS FinalMAGOMU DAN DAVIDNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Practical - 4Document8 pagesComputer Networks: Practical - 4JeetNo ratings yet
- Bus TopologyDocument6 pagesBus Topologylea_eazeNo ratings yet
- Network Topology Types ExplainedDocument5 pagesNetwork Topology Types Explainedmd.jewel ranaNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Bus TopologyDocument4 pagesAdvantages of Bus TopologyUsAmaImtiAzNo ratings yet
- Types of Network TopologyDocument7 pagesTypes of Network TopologyMarvin OrbigoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4-Network TopologyDocument32 pagesLecture 4-Network Topologyjasmhmyd205No ratings yet
- Assignment - Ii: Computer NetworksDocument8 pagesAssignment - Ii: Computer NetworksAashish RaghunathNo ratings yet
- Network Topologies: Lecture # 2Document21 pagesNetwork Topologies: Lecture # 2Monika RehmanNo ratings yet
- A Computer Network Is A Group of Computer Systems and Other Computing Hardware Devices That Are Linked Together Through Communication Channels To Facilitate Communication and ResourceDocument7 pagesA Computer Network Is A Group of Computer Systems and Other Computing Hardware Devices That Are Linked Together Through Communication Channels To Facilitate Communication and Resource2nablsNo ratings yet
- Types of Network Topology: BSCS-2Document7 pagesTypes of Network Topology: BSCS-2JAYROLD LLAVANNo ratings yet
- Network Topology Is The Arrangement of The Various Elements (Document8 pagesNetwork Topology Is The Arrangement of The Various Elements (shayan sohailNo ratings yet
- Network Lab ManualDocument7 pagesNetwork Lab ManualANKIT67% (3)
- Computer Networks Toplogys1Document9 pagesComputer Networks Toplogys1ammapetNo ratings yet
- Basic Terminal Directory CommandsDocument2 pagesBasic Terminal Directory Commandsharishpillai1994No ratings yet
- Darshan Sem7 170701 CD 2014Document81 pagesDarshan Sem7 170701 CD 2014harishpillai1994No ratings yet
- New Doc 2017-10-20 22.26.09 - 20171020223432Document6 pagesNew Doc 2017-10-20 22.26.09 - 20171020223432harishpillai1994No ratings yet
- Deepa Network SecurityDocument69 pagesDeepa Network Securityharishpillai1994No ratings yet
- Final CN Lab ManualDocument49 pagesFinal CN Lab Manualharishpillai1994No ratings yet
- SRS FormatDocument9 pagesSRS Formatharishpillai1994No ratings yet
- DAA Lab ProgramsDocument9 pagesDAA Lab Programsharishpillai1994No ratings yet
- DAA Lab ProgramsDocument9 pagesDAA Lab Programsharishpillai1994No ratings yet
- DAA Lab ProgramsDocument9 pagesDAA Lab Programsharishpillai1994No ratings yet
- ASTM Reference RadiographsDocument3 pagesASTM Reference RadiographsAkbar ShaikNo ratings yet
- Coca Cola Concept-1Document7 pagesCoca Cola Concept-1srinivas250No ratings yet
- 2014 Chevrolet Cruze maintenance schedule guideDocument2 pages2014 Chevrolet Cruze maintenance schedule guidericardo rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Carbon Trust Certification OverviewDocument2 pagesCarbon Trust Certification OverviewMatt MaceNo ratings yet
- MCQs on Defence Audit Code Chapter 9 and 10Document2 pagesMCQs on Defence Audit Code Chapter 9 and 10Rustam SalamNo ratings yet
- Webpage citation guideDocument4 pagesWebpage citation guiderogelyn samilinNo ratings yet
- The New Breed of Rally BDA: Motor SportDocument8 pagesThe New Breed of Rally BDA: Motor SportHarold MorleyNo ratings yet
- Accounts - User Guide: Release R15.000Document207 pagesAccounts - User Guide: Release R15.000lolitaferozNo ratings yet
- UE Capability Information (UL-DCCH) - Part2Document51 pagesUE Capability Information (UL-DCCH) - Part2AhmedNo ratings yet
- FFTW Installation On WindowsDocument6 pagesFFTW Installation On WindowsDebora SchwarzNo ratings yet
- Wyckoff e BookDocument43 pagesWyckoff e BookIan Moncrieffe95% (22)
- Design of A Double Corbel Using CAST Per ACI 318-02 Appendix A, SI UnitDocument41 pagesDesign of A Double Corbel Using CAST Per ACI 318-02 Appendix A, SI Unityoga arkanNo ratings yet
- Depressurization LED Solar Charge Controller with Constant Current Source SR-DL100/SR-DL50Document4 pagesDepressurization LED Solar Charge Controller with Constant Current Source SR-DL100/SR-DL50Ria IndahNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Fluid-Conveying Beams: Governing Equations and Finite Element ModelsDocument22 pagesDynamics of Fluid-Conveying Beams: Governing Equations and Finite Element ModelsDario AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Agro Chems MrRGAgarwalDocument17 pagesAgro Chems MrRGAgarwalapi-3833893No ratings yet
- Product Models Comparison: Fortigate 1100E Fortigate 1800FDocument1 pageProduct Models Comparison: Fortigate 1100E Fortigate 1800FAbdullah AmerNo ratings yet
- Node NO Slot NO CH No. Tag Name Address Signal Description: All Valve Fault Take From LogicDocument103 pagesNode NO Slot NO CH No. Tag Name Address Signal Description: All Valve Fault Take From Logicash_captchajobsNo ratings yet
- Supply AnalysisDocument5 pagesSupply AnalysisCherie DiazNo ratings yet
- SolidEdge MachineryLibrary V15.00Document139 pagesSolidEdge MachineryLibrary V15.00ttNo ratings yet
- ME6019 - NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTING AND MATERIALS MCQ PadeepzDocument13 pagesME6019 - NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTING AND MATERIALS MCQ PadeepzAjithNo ratings yet
- Earth Planet - Google SearchDocument1 pageEarth Planet - Google SearchDaivik Lakkol Eswara PrasadNo ratings yet
- ENY1-03-0203-M UserDocument101 pagesENY1-03-0203-M UserAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Socomec EN61439 PDFDocument8 pagesSocomec EN61439 PDFdesportista_luisNo ratings yet
- 7 - Lakhs Bank EstimateDocument8 pages7 - Lakhs Bank Estimatevikram Bargur67% (3)
- Ibad Rehman CV NewDocument4 pagesIbad Rehman CV NewAnonymous ECcVsLNo ratings yet
- Dues+&+Bylaws+Committee+Packet ICPI John@bestadmix Com Tholyfield@Document52 pagesDues+&+Bylaws+Committee+Packet ICPI John@bestadmix Com Tholyfield@Greefield JasonNo ratings yet
- Ermac vs. MedeloDocument1 pageErmac vs. MedeloJessa F. Austria-CalderonNo ratings yet
- ZirakDocument4 pagesZiraktaibzirakchamkani81No ratings yet
- Ey Blockchain Innovation Wealth Asset ManagementDocument16 pagesEy Blockchain Innovation Wealth Asset ManagementmichaeleslamiNo ratings yet
- Guideline 3 Building ActivitiesDocument25 pagesGuideline 3 Building ActivitiesCesarMartinezNo ratings yet