Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
Uploaded by
Jason SonidoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
Uploaded by
Jason SonidoCopyright:
Available Formats
PROGRAMMABLE
LOGIC CONTROLLER
(PLC)
PLC = AUTOMATION
1.1 Three Factors of Automation
What is automation?
Moving the machine automatically in an Industrial Plant is automation.
Ex. Putting a cap (lid) on a bottle in a running conveyor
put a lid
Five Senses
Brain
Visual, feeling, taste,
hearing, smell
Judgment
Muscle
Action
1. Visual conforms that the bottle comes on the conveyor
INPUT
2. Judgment decides to put lid
CONTROL
3. Get a lid to put it on a bottle
OUTPUT
These are called 3 factors of automation
INPUT (X)
CONTROL
OUTPUT (Y)
Micro switch
Relay
Lamp
Limit switch
Sensors
Timer
Counter
Buzzer
Motors
Push button
switch
Thermostat
Cylinder
1.2 External Input / Output Signal and
Input / Output Number
-An input number is the number of
hexadecimal which begins from 0.
X indicates as the input signal
- (X01-X09 and XOA-X0F)
Y- indicates as the output signal
- (Y01-YO9 and Y0A-Y0F)
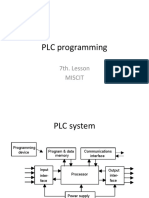
1.3 UNIT COMPOSITION OF A PLC MODULE
A block type example explains the composition of an actual sequencer.
Power
supply unit
CPU unit
Input /
output unit
Base
unit
Chapter 2 Components and functions of PLC
2.1 Components and functions of PLC
Input
Memory
CPU
Output
Power
Peripheral tool
Name
Power
Functions
Transforms the external
power supply to direct
power
Name
Functions
Input
Input devices were connected
here. It reads the signals from
the Photoelectric sensor devices
and transfer them to CPU.
Micro switch
Photoelectric sensor
CPU
Reads the signals from the
input part, judge them
according to the program
order, and sends the signal to
the output part.
program
Memory
memorize the program
Name
Functions
Lamp
Output
Peripheral
tool
Output devices are
connected here. It receive
the signals from CPU and
conveys them to output
devices.
Peripheral tool includes
programming console and
support software.
Buzzer
How the system works
Push the switch
to run the motor.
Memory
Push
the switch
Motor runs.
What is the next step after
the switch was pushed?
Program of the memory tells
me to move the motor.
The switch
has been pushed
Move the motor.
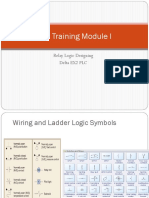
Chapter3: Ladder chart
Schematic/Ladder Diagram
Conventional
PLC Program
L1
L2
PB1
PB2
L1
L2
X1
M1
M1
M1
M1
L1
M1
X2
Y2
M1
All input Signals were assigned as X and
Output signal as Y
3.1 ON circuit or Normally Open (NO)
A contact
push
PB1
While the pushbutton is pushed,
the lamp shall keep on.
LAMP
PB1 or X1
LAMP or Y1
Y1
In this diagram, if you release the button the lamp will
return back to OFF mode.
3.2 OFF circuit or Normally Close (NC)
B contact
push
PB1
While the pushbutton is pushed,
the lamp shall keep off.
LAMP
PB2 or X2
LAMP or Y1
Y1
In this diagram, if you release the button the lamp will
return back to ON mode.
3.3 AND circuit (series)
PB1
AND
PB2
Turn on the lamp when both
PB1 and PB2 are pushed.
LAMP
<Ladder chart>
X1
X2
Y1
In this diagram, PB1 & PB2 shall push
together to turn the lamp ON.
3.4 OR circuit (parallel)
OR
X1
Y1
When either PB1 or PB2 is ON the
lamp shall be ON
PB1 (X1)
PB2 (X2)
LAMP (Y1)
X2
<Ladder chart>
Chapter 4. Programming and Time Chart
ON AND OFF TIME CHART
Common Symbols
Coil
M
Timer
T
Input
-X
Output - Y
Counter - C
Input A
Input B
Output Y
WHEN INPUT A IS ON, OUTPUT A WILL BE ON. WHEN INPUT B IS ON,
OUTPUT A WILL BE OFF.
Ladder Diagram
L1
X1
L2
X2
M1
M1
Y1
M1
ON DELAY TIMER
Input A
Input B
t=5sec
Output Y
WHEN INPUT A IS ON, AFTER 5 SECS., OUTPUT A WILL BE ON. WHEN INPUT B IS
ON, OUTPUT Y WILL BE OFF.
Ladder Diagram
L1
X1
L2
X2
T1 k50
T1
M1
T1
Y1
M1
END
End
You might also like
- PLC Handbook PDFDocument119 pagesPLC Handbook PDFBudi100% (6)
- Hacks To Crush Plc Program Fast & Efficiently Everytime... : Coding, Simulating & Testing Programmable Logic Controller With ExamplesFrom EverandHacks To Crush Plc Program Fast & Efficiently Everytime... : Coding, Simulating & Testing Programmable Logic Controller With ExamplesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Basic PLCDocument77 pagesBasic PLCFirdaus Ali50% (2)
- Start Programming & Simulating PLC In Your Laptop from Scratch: A No BS, No Fluff, PLC Programming Volume 1: Volume, #1From EverandStart Programming & Simulating PLC In Your Laptop from Scratch: A No BS, No Fluff, PLC Programming Volume 1: Volume, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Basic PLC TrainingDocument114 pagesBasic PLC TrainingAffan Pringgo100% (12)
- PLC Programming from Novice to Professional: Learn PLC Programming with Training VideosFrom EverandPLC Programming from Novice to Professional: Learn PLC Programming with Training VideosRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Beginner - Guide PLC ControllerDocument255 pagesBeginner - Guide PLC ControllerLuís Ki-llahNo ratings yet
- PLC Basic Programme BookDocument45 pagesPLC Basic Programme Bookapi-384889275% (4)
- Ladder LogicDocument41 pagesLadder Logickmoorthy27100% (2)
- PLC Programming 2Document117 pagesPLC Programming 2tanmoy ghoshNo ratings yet
- PLC ExercisesDocument178 pagesPLC ExercisesJavier Fernando Cossío Calderón100% (3)
- PLC Training Course by AhmedelsisyDocument91 pagesPLC Training Course by Ahmedelsisymohamed_amri10067% (3)
- Start Programming, Simulating HMI and PLC in Your Laptop: A No Bs, No Fluff, HMI and PLC Programming & Simulating Volume 2: Volume, #2From EverandStart Programming, Simulating HMI and PLC in Your Laptop: A No Bs, No Fluff, HMI and PLC Programming & Simulating Volume 2: Volume, #2Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- PLC Full BookDocument112 pagesPLC Full BookDilip Patel100% (2)
- PLC Programming Examples PDFDocument132 pagesPLC Programming Examples PDFDeepak Nayak75% (12)
- A28-1146-059-03 SPZ-8000 PohDocument288 pagesA28-1146-059-03 SPZ-8000 PohMindaugas LetukasNo ratings yet
- PLC Programming Using RSLogix 500 & Industrial Applications: Learn ladder logic step by step with real-world applicationsFrom EverandPLC Programming Using RSLogix 500 & Industrial Applications: Learn ladder logic step by step with real-world applicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PLC Exam ProblemsDocument7 pagesPLC Exam ProblemsPriyanka Amazon100% (7)
- How To Become A PeeDocument38 pagesHow To Become A PeeKC MoralesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Fundamentals of LogicDocument64 pagesChapter 4 - Fundamentals of Logicbob100% (2)
- PLC ProgrammingDocument42 pagesPLC ProgrammingWily Ponce100% (1)
- PLC Lab ExercisesDocument33 pagesPLC Lab ExercisesShaheerLatif100% (5)
- Learn To Program, Simulate Plc & Hmi In Minutes with Real-World Examples from Scratch. A No Bs, No Fluff Practical Hands-On Project for Beginner to Intermediate: BoxsetFrom EverandLearn To Program, Simulate Plc & Hmi In Minutes with Real-World Examples from Scratch. A No Bs, No Fluff Practical Hands-On Project for Beginner to Intermediate: BoxsetNo ratings yet
- Electromechanical Relay GuideDocument19 pagesElectromechanical Relay GuideRajesh Naik Dharavath100% (1)
- INSTANT PLC Programming with RSLogix 5000From EverandINSTANT PLC Programming with RSLogix 5000Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Chapter 6 Developing Fundamental PLC Wiring Diagrams and Ladder Logic ProgramsDocument86 pagesChapter 6 Developing Fundamental PLC Wiring Diagrams and Ladder Logic Programsbob88% (8)
- PLC Lab ManualDocument34 pagesPLC Lab ManualDhiraj maliNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Controllers A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandProgrammable Logic Controllers A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- ACCA Manual S Master FormDocument1 pageACCA Manual S Master Formfirstclassac100% (2)
- Introduction To PLC PresentationDocument214 pagesIntroduction To PLC Presentationtharindu100% (3)
- PLC ProgrammingDocument116 pagesPLC ProgrammingVali Ene100% (4)
- Chapter 3 - Number Systems and CodesDocument58 pagesChapter 3 - Number Systems and Codesbob100% (5)
- PLC For Motor ControlDocument8 pagesPLC For Motor Controlsunil8080No ratings yet
- PLC Controls with Structured Text (ST): IEC 61131-3 and best practice ST programmingFrom EverandPLC Controls with Structured Text (ST): IEC 61131-3 and best practice ST programmingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Sample PLC Exam ProblemsDocument5 pagesSample PLC Exam Problemsknbaluvlsi90% (10)
- OMRON PLC TrainingDocument169 pagesOMRON PLC TrainingBehnam Rezaei100% (10)
- PLCDocument113 pagesPLCpfalencar0% (1)
- PLC ExamplesDocument78 pagesPLC ExamplesMuhammad Mahfud RosyidiNo ratings yet
- PLC TutorialDocument48 pagesPLC Tutorialaaaguilar90% (10)
- PLC Solution BookDocument49 pagesPLC Solution BookJagadeesh Rajamanickam71% (14)
- PLC Excercises (Module 1-3) PDFDocument101 pagesPLC Excercises (Module 1-3) PDFAnonymous 324QXtcuxoNo ratings yet
- PLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsFrom EverandPLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1:-: Assignments On No/NcDocument3 pagesAssignment 1:-: Assignments On No/NcsalonyNo ratings yet
- Selecting Arrester MCOV-UcDocument9 pagesSelecting Arrester MCOV-Ucjose GonzalezNo ratings yet
- PLC programmable logic controller A Clear and Concise ReferenceFrom EverandPLC programmable logic controller A Clear and Concise ReferenceNo ratings yet
- PLC Programming ExampleDocument26 pagesPLC Programming ExampleManu R Krishnan50% (2)
- PLCDocument62 pagesPLCASHISH BHARAMBENo ratings yet
- Workbook PLCDocument16 pagesWorkbook PLCkhairul fahmiNo ratings yet
- PLC NotesDocument170 pagesPLC NotesBikasita Talukdar100% (2)
- OMRON PLC ProgrammingDocument253 pagesOMRON PLC ProgrammingŞaban Şeker100% (1)
- Lecture Notes PLC - Unit IIDocument82 pagesLecture Notes PLC - Unit IIMo Imran100% (1)
- Automatic Car Wash PLC ProgramDocument105 pagesAutomatic Car Wash PLC Programtechknow leader50% (2)
- PLC Connection Guide (Unlockplc - Com)Document1,163 pagesPLC Connection Guide (Unlockplc - Com)Unlock PLC88% (8)
- PLC Programming Using SIMATIC MANAGER for Beginners: With Basic Concepts of Ladder Logic ProgrammingFrom EverandPLC Programming Using SIMATIC MANAGER for Beginners: With Basic Concepts of Ladder Logic ProgrammingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Chapter 8: PLC Programming Language - Basic InstructionsDocument57 pagesChapter 8: PLC Programming Language - Basic InstructionsNguyễn Tuấn HòaNo ratings yet
- ALLEN-BRADLEY'S POWER SYSTEM HARMONICS (A Reference Guide To Causes, Effects and Corrective Measures)Document14 pagesALLEN-BRADLEY'S POWER SYSTEM HARMONICS (A Reference Guide To Causes, Effects and Corrective Measures)Alda EnglandNo ratings yet
- ALLEN-BRADLEY'S POWER SYSTEM HARMONICS (A Reference Guide To Causes, Effects and Corrective Measures)Document14 pagesALLEN-BRADLEY'S POWER SYSTEM HARMONICS (A Reference Guide To Causes, Effects and Corrective Measures)Alda EnglandNo ratings yet
- Earthing System - Schneider ElectricDocument8 pagesEarthing System - Schneider ElectricAnne Kelley100% (1)
- PLCDocument54 pagesPLCEmmanuel Molina100% (2)
- Plc-Driver Siemens Simotion - Mpi Profibus Industrial Ethernet Tcp-IpDocument8 pagesPlc-Driver Siemens Simotion - Mpi Profibus Industrial Ethernet Tcp-IpAsian SinabutarNo ratings yet
- DATACENTERS Electrical DesignDocument46 pagesDATACENTERS Electrical Designhunterhead2100% (3)
- DATACENTERS Electrical DesignDocument46 pagesDATACENTERS Electrical Designhunterhead2100% (3)
- Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) : Block Diagram of PLCDocument62 pagesProgrammable Logic Controller (PLC) : Block Diagram of PLCASHISH BHARAMBENo ratings yet
- PLC Exercises: Ladder Diagram ProgrammingDocument27 pagesPLC Exercises: Ladder Diagram Programmingganeshrudra100% (4)
- Hvac PM Service Checklist ContractorDocument1 pageHvac PM Service Checklist Contractorudupiganesh3069100% (1)
- Bonaire Multi Appliance Comfort ControlDocument52 pagesBonaire Multi Appliance Comfort ControlMartin huntNo ratings yet
- Example of PLC Program PDFDocument2 pagesExample of PLC Program PDFMia0% (1)
- Simatic Converting Toolbox enDocument163 pagesSimatic Converting Toolbox enasolelpanchoNo ratings yet
- Discovering Control, An Intermediate Guide To Learning PLCs (JY997D26101-A)Document206 pagesDiscovering Control, An Intermediate Guide To Learning PLCs (JY997D26101-A)Wallie Billingsley0% (1)
- NO - 1 Objective 2 List of Equipments 3 Theory 4 Result 5 Discussion 6 Conclusion 7 ReferencesDocument4 pagesNO - 1 Objective 2 List of Equipments 3 Theory 4 Result 5 Discussion 6 Conclusion 7 ReferencesHafezulAfiqNo ratings yet
- Project 3 MotorDocument22 pagesProject 3 MotorJagadeesh k v JagadeeshNo ratings yet
- Basic Automation 2020Document5 pagesBasic Automation 2020Biodence NasaliNo ratings yet
- Himel International Catalogue 2023Document454 pagesHimel International Catalogue 2023Jason SonidoNo ratings yet
- Power - Factor 2023Document17 pagesPower - Factor 2023Jason SonidoNo ratings yet
- Auto Transformer ModuleDocument10 pagesAuto Transformer ModuleIkhwanJackNo ratings yet
- Reducing Fault Stress With Zone-Selective Interlocking: Data BulletinDocument28 pagesReducing Fault Stress With Zone-Selective Interlocking: Data BulletinJason SonidoNo ratings yet
- Symmetra™ PX: Earthing PrinciplesDocument20 pagesSymmetra™ PX: Earthing PrinciplesJason SonidoNo ratings yet
- Flash Hazard Category PDFDocument1 pageFlash Hazard Category PDFJason SonidoNo ratings yet
- Contactor by EE Controls PDFDocument10 pagesContactor by EE Controls PDFPaul MendozaNo ratings yet
- ANSI MV TechTopics55 EN PDFDocument2 pagesANSI MV TechTopics55 EN PDFJason SonidoNo ratings yet
- Effects of Imbalances and Non Linear Loads in Electricity Distribution System PDFDocument104 pagesEffects of Imbalances and Non Linear Loads in Electricity Distribution System PDFwalet1No ratings yet
- Contactor by EE Controls PDFDocument10 pagesContactor by EE Controls PDFPaul MendozaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Book PDFDocument36 pagesElectrical Safety Book PDFhoaithuat100% (1)
- Safety Manual: Updated: July 2013Document26 pagesSafety Manual: Updated: July 2013Jason SonidoNo ratings yet
- Safety Manual: Updated: July 2013Document26 pagesSafety Manual: Updated: July 2013Jason SonidoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Book PDFDocument36 pagesElectrical Safety Book PDFhoaithuat100% (1)
- Effects of Imbalances and Non Linear Loads in Electricity Distribution System PDFDocument104 pagesEffects of Imbalances and Non Linear Loads in Electricity Distribution System PDFwalet1No ratings yet
- Basic Specification of Work Piece Detect SensorDocument3 pagesBasic Specification of Work Piece Detect SensorJason SonidoNo ratings yet
- Flash Hazard Category PDFDocument1 pageFlash Hazard Category PDFJason SonidoNo ratings yet
- A Guide To ControlDocument18 pagesA Guide To ControlJason SonidoNo ratings yet
- PLC or DCS PDFDocument12 pagesPLC or DCS PDFsafvanshaikhNo ratings yet
- Vector AnalysisDocument77 pagesVector Analysisalenair888100% (1)
- Electric Motors: Jason Sonido - ReeDocument19 pagesElectric Motors: Jason Sonido - ReeJason SonidoNo ratings yet
- Servo Controller 3.00 GuideDocument13 pagesServo Controller 3.00 GuidederbalijalelNo ratings yet
- Electromechanical EngDocument18 pagesElectromechanical EngAnonymous gsu1cFNo ratings yet
- Smart Port: Design and PerspectivesDocument6 pagesSmart Port: Design and Perspectivesjoshua medranoNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Compresores Hermeticos Piston MT MTZ NTZ Danfoss PDFDocument8 pagesCatalogo Compresores Hermeticos Piston MT MTZ NTZ Danfoss PDFPablo Angel ToiaNo ratings yet
- Internet Cafe Timer ThesisDocument6 pagesInternet Cafe Timer Thesisglasunvema1980100% (2)
- Implications of Increasing Grade of AutomationDocument36 pagesImplications of Increasing Grade of AutomationRudy IndrawanNo ratings yet
- Automated Programming SystemDocument8 pagesAutomated Programming SystemXeltekNo ratings yet
- D 101801Document982 pagesD 101801Bhanu Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- A Guide To PLC and SCADA Automation in Steam Boilers - Boilers and Steam Boiler Manufacturer in Maharashtra, PuneDocument4 pagesA Guide To PLC and SCADA Automation in Steam Boilers - Boilers and Steam Boiler Manufacturer in Maharashtra, PuneOsama AlgueferNo ratings yet
- EN 44-3 Dual-Temperature Chillers PlantsDocument12 pagesEN 44-3 Dual-Temperature Chillers PlantsJose Pedro CostaNo ratings yet
- How To Smart Home - A Step by Step Guide To Your Personal Internet of Things - 3rd Edition (2015) PDFDocument322 pagesHow To Smart Home - A Step by Step Guide To Your Personal Internet of Things - 3rd Edition (2015) PDFRicardo HaroNo ratings yet
- SN - Gorilla Guide It Asset ManagementDocument97 pagesSN - Gorilla Guide It Asset ManagementAlain TernetNo ratings yet
- Ashrae Journal On Reheat: Dan Int-HoutDocument7 pagesAshrae Journal On Reheat: Dan Int-HoutSergio GarroNo ratings yet
- M-Lance: The Missing Link in Tubular Catalyst HandlingDocument2 pagesM-Lance: The Missing Link in Tubular Catalyst HandlingСергей КNo ratings yet
- Introduction1989 Reprint PDFDocument15 pagesIntroduction1989 Reprint PDFvniranjanNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Basic Elements of AutomationDocument18 pagesUNIT-1 Basic Elements of AutomationSudhanshu PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 HeraguDocument26 pagesChapter 1 HeraguRahvany Celsia NingrumNo ratings yet
- Applications of MicroprocessorsDocument10 pagesApplications of MicroprocessorsTECHNOLOGY UPDATESNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Submittal 4TTA3060Document2 pages3.4 Submittal 4TTA3060Deison F. Arango A.No ratings yet
- HVACDocument58 pagesHVACAnonymous 6V5QyM1M3LNo ratings yet
- SAP Business ByDesign Road MapDocument17 pagesSAP Business ByDesign Road MapSarras InfoNo ratings yet
- The Potential of Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing IndustryDocument3 pagesThe Potential of Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing IndustryLucille J. SnellingNo ratings yet
- Aom Chapter IDocument18 pagesAom Chapter IMay Claire M. GalangcoNo ratings yet