Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Financial System Overview
Uploaded by
Swati Rathour0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views9 pagesIndian Financial Market
Original Title
Financial Market
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIndian Financial Market
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views9 pagesFinancial System Overview
Uploaded by
Swati RathourIndian Financial Market
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
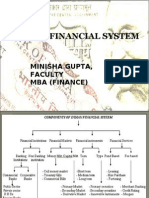
Financial System
An institutional framework existing in a
country to enable financial transactions
Three main parts
Financial assets (loans, deposits, bonds,
equities, etc.)
Financial institutions (banks, mutual funds,
insurance companies, etc.)
Financial markets (money market, capital
market, forex market, etc.)
Regulation is another aspect of the
financial system (RBI, SEBI, IRDA, FMC)
Financial assets/instruments
Enable channelising funds from surplus units
to deficit units
There are instruments for savers such as
deposits, equities, mutual fund units, etc.
There are instruments for borrowers such as
loans, overdrafts, etc.
Like businesses, governments too raise funds
through issuing of bonds, Treasury bills, etc.
Instruments like PPF, KVP, etc. are available
to savers who wish to lend money to the
government
Financial Institutions
Includes institutions and mechanisms which
Affect generation of savings by the community
Mobilisation of savings
Effective distribution of savings
Institutions are banks, insurance companies, mutual
funds- promote/mobilise savings
Individual investors, industrial and trading companiesborrowers
Financial Markets
Money Market- for short-term funds (less than a year)
Organised (Banks)
Unorganised (money lenders, chit funds, etc.)
Capital Market- for long-term funds
Primary Issues Market
Stock Market
Bond Market
Organised Money Market
Call money market
Bill Market
Treasury bills
Commercial bills
Bank loans (short-term)
Organised money market comprises RBI, banks
(commercial and co-operative)
Purpose of the money market
Banks borrow in the money market to:
Fill the gaps or temporary mismatch of funds
To meet the CRR and SLR mandatory requirements as
stipulated by the central bank
To meet sudden demand for funds arising out of large
outflows (like advance tax payments)
Call money market serves the role of equilibrating the
short-term liquidity position of the banks
Financial Intermediaries (1)
Mutual Funds- Promote savings and
mobilise funds which are invested in the
stock market and bond market
Indirect source of finance to companies
Pool funds of savers and invest in the
stock market/bond market
Their instruments at savers end are
called units
Offer many types of schemes: growth
fund, income fund, balanced fund
Regulated by SEBI
Financial Intermediaries (2)
Merchant banking- manage and underwrite
new issues, undertake syndication of credit,
advise corporate clients on fund raising
Subject to regulation by SEBI and RBI
SEBI regulates them on issue activity and
portfolio management of their business.
RBI supervises those merchant banks which
are subsidiaries or affiliates of commercial
banks
Have to adopt stipulated capital adequacy
norms and abide by a code of conduct
Thank you
You might also like
- Introduction To Statistics (Week 1)Document31 pagesIntroduction To Statistics (Week 1)Yvi BocaNo ratings yet
- Investment BanksDocument45 pagesInvestment BanksMuhammad Zeshan100% (1)
- Investment and Portfolio Management 5Document51 pagesInvestment and Portfolio Management 5madihashkh100% (1)
- TUA Income Tax Course SyllabusDocument5 pagesTUA Income Tax Course SyllabusFerdinand Caralde Narciso ImportadoNo ratings yet
- FM Syllabus for Financial ManagementDocument3 pagesFM Syllabus for Financial ManagementRio DhaniNo ratings yet
- Methods of DepreciationDocument12 pagesMethods of Depreciationamun din100% (1)
- Partnership: A Partnership Is An Association of Two or More Persons Who Own and Manage A Business For ProfitDocument34 pagesPartnership: A Partnership Is An Association of Two or More Persons Who Own and Manage A Business For ProfitRuthLimbongNo ratings yet
- PracticumDocument3 pagesPracticummataraiNo ratings yet
- Financial Markets and Services Syllabus PDFDocument2 pagesFinancial Markets and Services Syllabus PDFOberoi MalhOtra MeenakshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - The Financial Plan PDFDocument21 pagesChapter 10 - The Financial Plan PDFzulkifli alimuddinNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Comprehensive ExamDocument15 pagesFinancial Management Comprehensive ExamDetox FactorNo ratings yet
- Continuous Distributions and The Normal Distribution: Notation: Probability Density Function PDFDocument5 pagesContinuous Distributions and The Normal Distribution: Notation: Probability Density Function PDFPal AjayNo ratings yet
- Business Math Lesson Plan 6 2020Document2 pagesBusiness Math Lesson Plan 6 2020Daniel Jars100% (1)
- Financial StatementsDocument68 pagesFinancial StatementsEdmon Lopez100% (1)
- Colegio de Los Baños: Master in ManagementDocument6 pagesColegio de Los Baños: Master in ManagementRainiel Victor M. CrisologoNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Capital Budgeting 2015Document57 pagesThe Basics of Capital Budgeting 2015AJNo ratings yet
- GE203-Probability and StatisticsDocument2 pagesGE203-Probability and StatisticsMarlon Marcaida100% (1)
- How a Financial System Works to Facilitate Economic GrowthDocument25 pagesHow a Financial System Works to Facilitate Economic GrowthArpitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Using Discounted Cash Flow Analysis To Make Investment DecisionsDocument14 pagesChapter 6 - Using Discounted Cash Flow Analysis To Make Investment DecisionsSheena Rhei Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Role of Financial Institutions and MarketsDocument11 pagesUnit 1 Role of Financial Institutions and MarketsGalijang ShampangNo ratings yet
- Financial Literacy Among Eight European CountriesDocument14 pagesFinancial Literacy Among Eight European CountriesadamNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic University of The Philippines: City of Santa Rosa LagunaDocument8 pagesPolytechnic University of The Philippines: City of Santa Rosa LagunaChristel OrugaNo ratings yet
- T1 Introduction (Answer)Document5 pagesT1 Introduction (Answer)Wen Kai YeamNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions and MarketsDocument20 pagesFinancial Institutions and MarketsCome-all NathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Cash Flow Analysis - SVDocument26 pagesChapter 3 - Cash Flow Analysis - SVNguyen LienNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument4 pagesRatio AnalysisdattacuriousNo ratings yet
- Ched-Dbm Joint Memorandum Circular No. 2017-1Document13 pagesChed-Dbm Joint Memorandum Circular No. 2017-1John Ceasar PascoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Overview of Financial ManagementDocument14 pagesChapter 1 Overview of Financial ManagementMarylou De MelloNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 (Data Collection Methods)Document28 pagesLecture 7 (Data Collection Methods)Adnan AzizNo ratings yet
- Aims and Functions of Finance ExplainedDocument17 pagesAims and Functions of Finance ExplainedMahesh HadapadNo ratings yet
- Laerd Statistics 2013Document3 pagesLaerd Statistics 2013Rene John Bulalaque Escal100% (1)
- Sources of Finance: Neeta Asnani Alpana Garg Pratibha Arora Kalpana TewaniDocument23 pagesSources of Finance: Neeta Asnani Alpana Garg Pratibha Arora Kalpana TewaniMahima LounganiNo ratings yet
- Article V: Suffrage: Prepared by Raizza CorpuzDocument16 pagesArticle V: Suffrage: Prepared by Raizza CorpuzBeverly A. CannuNo ratings yet
- Financial Market, Instrument and InstitutionDocument43 pagesFinancial Market, Instrument and InstitutionMarkus Bernabe DaviraNo ratings yet
- Venture Capital MarshallDocument9 pagesVenture Capital Marshallveda20No ratings yet
- GE1 (Mathematic in The Modern World) SyllabusDocument8 pagesGE1 (Mathematic in The Modern World) SyllabusTrish LaguitanNo ratings yet
- Financial Ratio AnalysisDocument85 pagesFinancial Ratio AnalysisSarah PontinesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To InvestmentDocument30 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To InvestmentAnh ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow StatementDocument19 pagesCash Flow Statementasherjoe67% (3)
- Simple Interest ExampleDocument3 pagesSimple Interest ExampleRayarch Wu0% (1)
- Introduction To Financial ManagemntDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Financial ManagemntibsNo ratings yet
- Money MarketDocument25 pagesMoney MarketJogendra Behera100% (1)
- Simple InterestDocument12 pagesSimple Interestaaaaddddyyyy0% (1)
- Lecture in Finance 105 0n Investment Laws, Rules, and RegulationsDocument30 pagesLecture in Finance 105 0n Investment Laws, Rules, and RegulationsJoy ZeeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.2 Quantitative Data-Collection TechniquesDocument27 pagesLesson 2.2 Quantitative Data-Collection TechniquesSilang MatthewNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation - The Filipino Concept of ArtDocument25 pagesArt Appreciation - The Filipino Concept of ArtRex GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Lending Functions of A BankDocument15 pagesLending Functions of A BankJhalak MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- URS OBE Syllabus FormatDocument3 pagesURS OBE Syllabus FormatGian Paolo Ramirez Francisco100% (1)
- Viney7e SM Ch01Document9 pagesViney7e SM Ch01Tofuu PowerNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting Decision Is An Important, Crucial and Critical Business Decision Due ToDocument7 pagesCapital Budgeting Decision Is An Important, Crucial and Critical Business Decision Due ToGaganNo ratings yet
- Day 01-Basic Statistics - Part (I)Document29 pagesDay 01-Basic Statistics - Part (I)Sparsh VijayvargiaNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Practicum IIDocument28 pagesPortfolio Practicum IIAnna Mae TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Identification of Target MarketsDocument21 pagesIdentification of Target MarketsfuckwitNo ratings yet
- 04 The Full Syllabus - Management Level Continued: Paper F2 Assessment StrategyDocument3 pages04 The Full Syllabus - Management Level Continued: Paper F2 Assessment StrategyRehman MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framew Ork and Accountin G Standards: Justiniano L. Santos, CPA, MBADocument46 pagesConceptual Framew Ork and Accountin G Standards: Justiniano L. Santos, CPA, MBACarmela BuluranNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate Management SystemsDocument3 pagesExchange Rate Management SystemsMonalisa PadhyNo ratings yet
- 02 Entrepreneurship and Economic DevelopmentDocument11 pages02 Entrepreneurship and Economic DevelopmentJan MezoNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus in Fundamentals of Accounting 2Document8 pagesCourse Syllabus in Fundamentals of Accounting 2Edrin Roy Cachero SyNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BACC 8.2Document12 pagesSyllabus BACC 8.2ROMEO DE GUZMAN, JR.100% (1)
- Indian Financial System: Minisha Gupta, Faculty Mba (Finance)Document27 pagesIndian Financial System: Minisha Gupta, Faculty Mba (Finance)Minisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Maha Kaushal SeDocument32 pagesMaha Kaushal SeSwati RathourNo ratings yet
- Activity Based CostingDocument3 pagesActivity Based CostingSwati RathourNo ratings yet
- Narasimham CommitteeDocument9 pagesNarasimham CommitteeSwati RathourNo ratings yet
- Role of BankingDocument15 pagesRole of BankingSwati RathourNo ratings yet
- BCSBIDocument3 pagesBCSBISwati RathourNo ratings yet
- Depreciation AccountingDocument17 pagesDepreciation AccountingSwati Rathour100% (1)
- BudgetingDocument3 pagesBudgetingSwati RathourNo ratings yet
- Banking and Financial Institution MOST IMPORTANT MCQ by AKASHDocument100 pagesBanking and Financial Institution MOST IMPORTANT MCQ by AKASHAkash YadavNo ratings yet
- Finc3014 Major Assignment FinalDocument17 pagesFinc3014 Major Assignment FinalLliam Clayton-JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Cecocafen Case Grupo 2Document24 pagesCecocafen Case Grupo 2Amigos Al CougarNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Why Study Money, BankingDocument15 pagesCH 1 Why Study Money, BankingLoving GamesNo ratings yet
- HDFC Children's Gift Fund - Savings Plan - : Nature of Scheme Inception Date Option/PlanDocument5 pagesHDFC Children's Gift Fund - Savings Plan - : Nature of Scheme Inception Date Option/Plansandeepkumar404No ratings yet
- Call Money Market in IndiaDocument37 pagesCall Money Market in IndiaDivya71% (7)
- Bazi - 5 Element Bazi Missing Element, Use Your BackupDocument12 pagesBazi - 5 Element Bazi Missing Element, Use Your BackupPawan100% (2)
- Risk ManagementDocument5 pagesRisk ManagementAlejandra CastillaNo ratings yet
- Debt Instrument Project PDFDocument50 pagesDebt Instrument Project PDFRohit VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Vaishu Final ProjectDocument96 pagesVaishu Final ProjectShravan SinghNo ratings yet
- Nism Series VIIDocument117 pagesNism Series VIIShalini Kamalia100% (1)
- Financialization and Global EconomyDocument18 pagesFinancialization and Global EconomyFranco AcebeyNo ratings yet
- Sample Issue Only For The Purpose of Authors ConfirmationDocument156 pagesSample Issue Only For The Purpose of Authors ConfirmationSunita SharmaNo ratings yet
- CMFAS M6 v2.8 PDFDocument220 pagesCMFAS M6 v2.8 PDFLim Shi Hui0% (1)
- John Keppler - Profit With The Market ProfileDocument305 pagesJohn Keppler - Profit With The Market ProfileRicardo_Semog91% (11)
- About The IMF2Document10 pagesAbout The IMF2Subhobrata MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- What Are Financial MktsDocument2 pagesWhat Are Financial MktsnaziaNo ratings yet
- Risk Management OverviewDocument35 pagesRisk Management OverviewSrinivas AcharNo ratings yet
- Introductory Econometrics For Finance © Chris Brooks 2008 1Document17 pagesIntroductory Econometrics For Finance © Chris Brooks 2008 1Ana MariaNo ratings yet
- 5-8 Financial Markets McqsDocument26 pages5-8 Financial Markets McqsdmangiginNo ratings yet
- Recent Trends in Financial InnovationDocument5 pagesRecent Trends in Financial InnovationAdeem AshrafiNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Overview of Financial SystemsDocument23 pagesTopic 1 - Overview of Financial SystemsĐinh PhươngNo ratings yet
- Money and BankingDocument531 pagesMoney and BankingKofi Appiah-DanquahNo ratings yet
- MGT 3062 Test 4Document5 pagesMGT 3062 Test 4Jesus Colin CampuzanoNo ratings yet
- Content: No Particular Page No 1 2 2 3Document68 pagesContent: No Particular Page No 1 2 2 3amitnpatel1No ratings yet
- Conda CheatsheetDocument22 pagesConda CheatsheetKaushik Hazarika100% (1)
- Uralsib CSR Report 2009Document119 pagesUralsib CSR Report 2009api-115711968No ratings yet
- Project Report on IPO in IndiaDocument7 pagesProject Report on IPO in IndianeetliNo ratings yet
- Vault Guide To Investment ManagementDocument125 pagesVault Guide To Investment Management0123456789ra100% (2)