Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IPV4 Addressing Fundamentals Explained
Uploaded by
Cha Dechavez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views20 pagesThis document discusses IP addressing and how IP addresses are used to identify devices on a network. It covers the basics of IPV4 addressing including the format of IP addresses as 32-bit numbers separated into four octets, how subnet masks distinguish the network and host portions of an IP address, and common methods for assigning IP addresses including DHCP, APIPA, and static addressing.
Original Description:
Ip Addressing
Original Title
Chapter 4 - IP Address
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses IP addressing and how IP addresses are used to identify devices on a network. It covers the basics of IPV4 addressing including the format of IP addresses as 32-bit numbers separated into four octets, how subnet masks distinguish the network and host portions of an IP address, and common methods for assigning IP addresses including DHCP, APIPA, and static addressing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views20 pagesIPV4 Addressing Fundamentals Explained
Uploaded by
Cha DechavezThis document discusses IP addressing and how IP addresses are used to identify devices on a network. It covers the basics of IPV4 addressing including the format of IP addresses as 32-bit numbers separated into four octets, how subnet masks distinguish the network and host portions of an IP address, and common methods for assigning IP addresses including DHCP, APIPA, and static addressing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
IPV ADDRESSING
ANNA CHARISMA F. DECHAVEZ, MIT
IP ADDRESS
• When two devices on a network
want to communicate, they need
logical addresses. Most modern
networks use Internet Protocol
(IP) addressing
IPV4 ADDRESSING
• A core function of IP is to provide
logical addressing for hosts.
• An IP address provides a
hierarchical structure to both
uniquely identify a host, and what
network that host exists on.
CHARACTERISTICS
• An IP address is most often represented in decimal, in the
following format:
158.80.164.3
• An IP address is comprised of four octets, separated by
periods:
First Octet Second Octet Third Octet Fourth
Octet
158 80 164 3
IN BINARY
• The above IP address represented in binary would look as
follows:
First Octet Second Octet Third Octet Fourth Octet
10011110 01010000 10100100 00000011
• Is a 32-bit binary number represented as four octets (four
8-bit numbers).
• Each octet is separated by a period.
• Known as IPV4
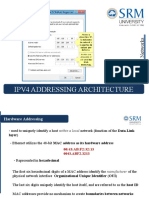
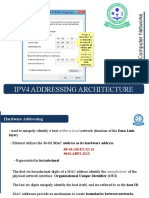
SUBNET MASK
• Part of an IP address identifies the
network. The other part of the address
identifies the host.
• A subnet mask is required to
provide this distinction:
158.80.164.3 255.255.0.0
REMEMBER:
• The above IP address has a subnet mask of
255.255.0.0.
• The subnet mask follows two rules:
• If a binary bit is set to a 1 (or on) in a subnet
mask, the corresponding bit in the address
identifies the network.
• If a binary bit is set to a 0 (or off) in a
subnet mask, the corresponding bit in the
address identifies the host.
IPV4 CLASSES
CLASS A
CLASS B
CLASS C
SUBNET AND BROADCAST
ADDRESS
• The subnet address is used to identify the
network itself.
• Subnet addresses contain all 0 bits in the
host portion of the address.
EXAMPLE OF SUBNET(NETWORK
ADDRESS)
BROADCAST ADDRESS
• identifies all hosts on a particular network.
• Broadcast addresses contain all 1 bits in
the host portion of the address.
PRIVATE VS PUBLIC IPV4
ADDRESSES
• A public address can be routed on the Internet.
• A private address is intended for internal use
within a home or organization, and can be freely used
by anyone.
ASSIGNING IP ADDRESS
IP ADDRESS
ASSIGNMENT
DHCP
• Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
• server is a special server configured to pass out IP address
and other IP configuration information to network clients.
• Use DHCP for small, medium, or large networks. DHCP
requires a DHCP server and minimal configuration.
APIPA
• Automatic Private IP Addressing
• is a Microsoft implementation of
automatic IP address assignment
without a DHCP server.
• hosts assign themselves an IP address
on the 169.254.0.0 network (mask of
255.255.0.0).
S TAT I C
•Using static addressing,
IP configuration
information must be
manually configured on
each host
You might also like
- Introduction To Ip AddressDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Ip AddressMetsi KinNo ratings yet
- 98-366 MVA Slides Lesson 4Document31 pages98-366 MVA Slides Lesson 4cvigaNo ratings yet
- Mod 03Document56 pagesMod 03michael.santiago15No ratings yet
- IPv4 Addressing and ProtocolsDocument9 pagesIPv4 Addressing and ProtocolsGavin MudyiwaNo ratings yet
- Networking Fundamentals Final 2Document32 pagesNetworking Fundamentals Final 2pranjalNo ratings yet
- Ccna1 m9 TCP Ip and Ip Addressing PDFDocument25 pagesCcna1 m9 TCP Ip and Ip Addressing PDFTurkishExplorer AhmetNo ratings yet
- Unit 4. NetworkingDocument31 pagesUnit 4. Networkingbca2022jagranNo ratings yet
- IPv4 OverviewDocument65 pagesIPv4 OverviewNguyễn Tiến HoàiNo ratings yet
- Addressing & SubnettingDocument80 pagesAddressing & SubnettingboybkaNo ratings yet
- Network Strategies CH#2 Internet Protocol (IPV4)Document31 pagesNetwork Strategies CH#2 Internet Protocol (IPV4)Arezo HalimiNo ratings yet
- 08.MAC and IP FundamentalsDocument37 pages08.MAC and IP Fundamentalsksav yadavNo ratings yet
- 6.0 IP Addressing: 6.1 IP Address Class 6.2 IP V4, IPV6Document19 pages6.0 IP Addressing: 6.1 IP Address Class 6.2 IP V4, IPV6Samuel ZodinglianaNo ratings yet
- 3 IPv4 Part2Document38 pages3 IPv4 Part2Easha AsifNo ratings yet
- IPAddressesSubnettingandNATLessonPresentation 1Document10 pagesIPAddressesSubnettingandNATLessonPresentation 1Tiffany JonesNo ratings yet
- IP Address Fundamentals ExplainedDocument25 pagesIP Address Fundamentals ExplainedZulkernain Omer TariqNo ratings yet
- Ipv4 Con GurationDocument5 pagesIpv4 Con GurationLaura DeeNo ratings yet
- CN - Chapter 5 - The Network Layer - Class 3, 4Document24 pagesCN - Chapter 5 - The Network Layer - Class 3, 4himanshuajaypandeyNo ratings yet
- Tcp/Ip and Ipv4 - Address ClassesDocument33 pagesTcp/Ip and Ipv4 - Address ClassesjayshreeNo ratings yet
- IP Addressing: Pengalamatan Host Pada Jaringan Tcp/IpDocument15 pagesIP Addressing: Pengalamatan Host Pada Jaringan Tcp/Iperico septiahariNo ratings yet
- CCNA Semester 1: Routing & AddressingDocument88 pagesCCNA Semester 1: Routing & AddressingTung HoangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Part 1Document25 pagesChapter 4 Part 1FantaNo ratings yet
- Network: - Connectivity and Communication - Intranet - Extranet - InternetDocument18 pagesNetwork: - Connectivity and Communication - Intranet - Extranet - Internetmirubaig2659No ratings yet
- IPV4 and Subnetting StrategyDocument39 pagesIPV4 and Subnetting StrategyrolandsabitNo ratings yet
- CHP 4 CNFDocument16 pagesCHP 4 CNFWilfried MonkamNo ratings yet
- IP AddressingDocument29 pagesIP AddressingcsebitannaNo ratings yet
- TCP IP FundamentalsDocument11 pagesTCP IP FundamentalsMadhav ReddyNo ratings yet
- ch4 Ip AddressingDocument73 pagesch4 Ip AddressinggargiwawreNo ratings yet
- DC and CN Chapter-7Document31 pagesDC and CN Chapter-7habtamud655No ratings yet
- Unit II Basic InternetworkingDocument73 pagesUnit II Basic InternetworkingRahavi SelvarajanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - The InternetDocument46 pagesChapter 3 - The Internetfnata AiNo ratings yet
- CN Unit 2Document49 pagesCN Unit 2Prakhar MishraNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks IP Addressing - UNIT IIDocument49 pagesComputer Networks IP Addressing - UNIT IISayeeKumar MadheshNo ratings yet
- Unit 3.2-IP AddressingDocument21 pagesUnit 3.2-IP AddressingYuvaraj TankalaNo ratings yet
- Instructor Materials Chapter 7: IP Addressing: CCNA Routing and Switching Introduction To Networks v6.0Document28 pagesInstructor Materials Chapter 7: IP Addressing: CCNA Routing and Switching Introduction To Networks v6.0Nuhamin BirhanuNo ratings yet
- RailnetDocument55 pagesRailnetHarshit DhakadNo ratings yet
- Network Addressing, Subnetting and Masking ExplainedDocument42 pagesNetwork Addressing, Subnetting and Masking ExplainedDaniel AshagrieNo ratings yet
- 70-410 r2 Lecture Slides Lesson 10Document47 pages70-410 r2 Lecture Slides Lesson 10hhhhhNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Chapter SummaryDocument50 pagesTCP/IP Chapter SummaryEchezona Uzochukwu AzubikeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document15 pagesChapter 10Ethio DotNetDeveloperNo ratings yet
- Chapter VI Computer Network and CommunicationDocument29 pagesChapter VI Computer Network and CommunicationAbinet KassahunNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Network ManagmentDocument96 pagesChapter Three: Network ManagmentNuraddin IdrisNo ratings yet
- Internet Protocol Version4 (Ipv4) & Subnetting StrategyDocument50 pagesInternet Protocol Version4 (Ipv4) & Subnetting StrategyMahmood Al SisanNo ratings yet
- CCNA ICND1 100-101 Official Cert Guide FundamentalsDocument29 pagesCCNA ICND1 100-101 Official Cert Guide FundamentalsKushalNo ratings yet
- CN U4 Network LayerDocument47 pagesCN U4 Network LayerAravind SNo ratings yet
- MIT3030 IP Addressing: Structure, Classes, Subnetting & CIDRDocument43 pagesMIT3030 IP Addressing: Structure, Classes, Subnetting & CIDRMalinda LakmalNo ratings yet
- IP AddressDocument22 pagesIP AddressVedant AggrawalNo ratings yet
- T2 MAC and IP Addresses UpdatedDocument20 pagesT2 MAC and IP Addresses UpdatedJake JakeNo ratings yet
- IPv4 Addressing and Routing AnalysisDocument61 pagesIPv4 Addressing and Routing AnalysisRobi BrownNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of IP AddressingDocument13 pagesFundamentals of IP AddressingMuhammad AsharNo ratings yet
- Ip 4Document69 pagesIp 4SwatiNo ratings yet
- ITN - Module - 11IPv4y SUBNETDocument58 pagesITN - Module - 11IPv4y SUBNETCuero YeiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Eight NewDocument27 pagesChapter Eight NewEthio DotNetDeveloperNo ratings yet
- Data Comm Part 2.ppt NewDocument48 pagesData Comm Part 2.ppt Newmuhabamohamed21No ratings yet
- 5-IP Address and Subnetting Subnet MaskDocument36 pages5-IP Address and Subnetting Subnet MaskAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- Instructor Materials Chapter 4: Network Protocols and ServicesDocument43 pagesInstructor Materials Chapter 4: Network Protocols and ServicesmfhamzeNo ratings yet
- IP AddressingDocument6 pagesIP AddressingLawrence RolluquiNo ratings yet
- chapter3-IP AddressingDocument47 pageschapter3-IP AddressingmulugetaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word Ribbon GuideDocument1 pageMicrosoft Word Ribbon GuideCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Defense Rating Sheet (CNA)Document2 pagesDefense Rating Sheet (CNA)Cha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Logic DiagramDocument51 pagesLogic DiagramCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Batch File - Arithmetic CommandsDocument26 pagesBatch File - Arithmetic CommandsCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Chaper 5 - SubnettingDocument62 pagesChaper 5 - SubnettingCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Importance of Number System in ElectronicsDocument9 pagesImportance of Number System in ElectronicsCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Activity - Network ManagementDocument1 pageActivity - Network ManagementCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Creating Gpo (Group Policy Object)Document13 pagesCreating Gpo (Group Policy Object)Cha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Folder RedirectionDocument22 pagesFolder RedirectionCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- AdvertisingDocument48 pagesAdvertisingCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Technological Research: University of Makati Scope, Mis - ItemDocument33 pagesTechnological Research: University of Makati Scope, Mis - ItemCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Frame RelayDocument11 pagesFrame RelayCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Understanding Devices and InfrastructureDocument36 pagesUnderstanding Devices and InfrastructureCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Network MediaDocument61 pagesChapter 2 - Network MediaCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 - Empowerment TechnologiesDocument18 pagesChapter1 - Empowerment TechnologiesCha Dechavez100% (1)
- Importance Computer Hardware ElectiveDocument7 pagesImportance Computer Hardware ElectiveCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Analyzing The Existing IT InfrastructureDocument6 pagesAnalyzing The Existing IT InfrastructureCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- MOTHERBOARDDocument70 pagesMOTHERBOARDCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- ComputerDocument12 pagesComputerCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Geographical AnalysisDocument7 pagesGeographical AnalysisCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Project Network Implementation PlanDocument15 pagesProject Network Implementation PlanCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Purpose and Value of Is Audit and ITDocument15 pagesPurpose and Value of Is Audit and ITCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Re DistDocument4 pagesRe DistAshley Gabriela Rodríguez RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Documenting The ProjectDocument11 pagesDocumenting The ProjectCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NetworkingDocument29 pagesIntroduction To NetworkingCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Os JCDocument8 pagesOs JCCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- CIS262-12b Fall - SyllabusDocument4 pagesCIS262-12b Fall - SyllabusCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Syllabus GE CourseDocument4 pagesSyllabus GE CourseCha DechavezNo ratings yet
- Journal entries from early 2011Document14 pagesJournal entries from early 2011Cha DechavezNo ratings yet
- CP R80.20.15 1500 Appliance Series AdminGuide Locally ManagedDocument281 pagesCP R80.20.15 1500 Appliance Series AdminGuide Locally ManagedJoseph JosefNo ratings yet
- Full Form of Hardware and Networking DevicesDocument11 pagesFull Form of Hardware and Networking DevicesSuprabhat05No ratings yet
- Afdx PDFDocument31 pagesAfdx PDFmeeraNo ratings yet
- Yateucn DatasheetDocument3 pagesYateucn DatasheetajdCruiseNo ratings yet
- 10.1.5 Packet Tracer - Use CDP To Map A NetworkDocument4 pages10.1.5 Packet Tracer - Use CDP To Map A NetworkMubba AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mtcre Example Test PDFDocument4 pagesMtcre Example Test PDFFlava0% (1)
- Ccna1 V7 Cap 1-3Document6 pagesCcna1 V7 Cap 1-3ask_gaby100% (1)
- Telstra Smart Modem Gen 2 DJA0231Document52 pagesTelstra Smart Modem Gen 2 DJA0231Vincent HardyNo ratings yet
- NET102 Chapter3NetworkProtocolsandCommunicationDocument42 pagesNET102 Chapter3NetworkProtocolsandCommunicationsteven EstevanNo ratings yet
- Install VoucherboxDocument3 pagesInstall VoucherboxAsrofiNo ratings yet
- ASA5500 - Configuration - Guide - 8.4 and 8.6 - VPN - Configuring LAN-to-LAN VPNsDocument1 pageASA5500 - Configuration - Guide - 8.4 and 8.6 - VPN - Configuring LAN-to-LAN VPNschassisdNo ratings yet
- CSS - Info Sheet 3.2-5 - Respond To Unplanned Events or Conditions - DNSDocument9 pagesCSS - Info Sheet 3.2-5 - Respond To Unplanned Events or Conditions - DNSomarNo ratings yet
- Veeam PN 2 1 User GuideDocument137 pagesVeeam PN 2 1 User GuideMohamed TarsafiNo ratings yet
- Internet and Distributed Systems PDFDocument258 pagesInternet and Distributed Systems PDFMichael OrtizNo ratings yet
- Internet Gateway Router Design Using Cisco ASR 1000 Series RoutersDocument8 pagesInternet Gateway Router Design Using Cisco ASR 1000 Series RoutersAnonymous SmYjg7gNo ratings yet
- Overview of Data Communications and Networking: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Document25 pagesOverview of Data Communications and Networking: Mcgraw-Hill ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Tanveer SardarNo ratings yet
- Cisco Aironet1200 DatasheetDocument8 pagesCisco Aironet1200 DatasheetAbdirisaq MohamudNo ratings yet
- FTD GuideDocument40 pagesFTD GuideDevikaNo ratings yet
- Practical 07 - Java Socket ProgrammingDocument5 pagesPractical 07 - Java Socket ProgrammingJust BleachNo ratings yet
- Configuración de Rip V2 HuaweiDocument4 pagesConfiguración de Rip V2 HuaweiIvan Leonardo Aguasaco GonzalezNo ratings yet
- 4G Protoclos PDFDocument19 pages4G Protoclos PDFYou ChackNo ratings yet
- API Umbrella Documentation: Release 0.15.1Document33 pagesAPI Umbrella Documentation: Release 0.15.1kikweteNo ratings yet
- (Join Files) 3 Arquivos.0009Document28 pages(Join Files) 3 Arquivos.0009Alita Laiana GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- NTLM Is Dead - DefCon 16Document52 pagesNTLM Is Dead - DefCon 16zboubiNo ratings yet
- MikroTik Monitoring Made EasyDocument34 pagesMikroTik Monitoring Made Easymona_mi8202No ratings yet
- Subnetting Assignment #1Document3 pagesSubnetting Assignment #1sugapriyaNo ratings yet
- Network Security Protocols AnalysisDocument40 pagesNetwork Security Protocols AnalysisNaresh MunrejaNo ratings yet
- ASSA ABLOY Global Solutions Web APIDocument102 pagesASSA ABLOY Global Solutions Web APIDavid MachadoNo ratings yet
- NetEngine 8000 X4 Router DatasheetDocument4 pagesNetEngine 8000 X4 Router DatasheetAnataTumongloNo ratings yet
- ECM 4002 PHYSICAL & LOGICAL DESIGN OF IOTDocument45 pagesECM 4002 PHYSICAL & LOGICAL DESIGN OF IOTVydeki Vijayakumar40% (5)