Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Communicative Language Teaching
Uploaded by
Jhong Floreta Montefalcon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views15 pagescommunicative
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentcommunicative
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views15 pagesCommunicative Language Teaching
Uploaded by
Jhong Floreta Montefalconcommunicative
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
Activity: The Telephone Game
■ Players must stand in a straight line. They need to be close enough
that whispering is possible but not so close that players can hear each
other.
■ The last person on the line will read the written phrase or sentence
and whisper it to the next person on the line.
■ Groupmates whisper the phrase or sentence to the person standing
next to him/her until it reaches the last person on the line.
■ The last person recites the phrase or sentence out loud so everyone
can hear.
COMMUNICATIVE
LANGUAGE
TEACHING
(CLT)
BRIEF HISTORY
■ CLT origins can be found in changes in the British Language teaching
tradition in the 1960’s.
■ Back then, the Situational Language teaching approach was a norm.
■ SLT consisted on internalizing the structures of a language.
■ Mostly, learning grammar rules without vocabulary development.
■ The SLT did not fill the need to develop language competence in
Language teaching.
■ A group of experts saw the need to focus in communicative proficiency
rather mastery of structures. (Richards, J.C. and Rodgers, T.S. p.64)
BRIEF HISTORY
■ Sandra J. Savignon , Christopher Candlin, D.A. Wilkins and Henry
Widdowson along with others promoted the CLT approach.
■ Along with the changes in Europe it helped to reform the language
teaching.
What is COMMUNICATIVE LANGUAGE
TEACHING?
■ Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) can be
understood as a set of principles about the goals of
language teaching, how the learners learn a
language, the kinds of classroom activities that best
facilitate learning, and the roles of teachers and
learners in the classroom (Jack C. Richards, 2006)
What is COMMUNICATIVE LANGUAGE
TEACHING?
■ An approach to the teaching of second and
foreign language, emphasizes interaction as
both the means and the ultimate goal of
learning a language. It is also referred to as
“Communicative Approach”.
What is COMMUNICATIVE LANGUAGE
TEACHING?
■ Cooperative Learning is a group learning activity
organized so that learning is dependent on the
socially structured exchange of information between
learners in groups and in which each learner is held
accountable for his or her own learning and is
motivated to increase the learning of others. (Olsen
and Kagan 1992.)
According to the communicative approach, in
order for learning to take place, emphasis must
be put on the importance of these variables:
■ Communication - activities that involves real communication
■ Tasks - activities in which language is used to carry out
meaningful tasks which supports the learning process.
■ Meaning - language that is meaningful and authentic to the
learner boosts learning.
OBJECTIVES
■ Use language as a means of communication,
object of learning and means of expressing
values.
■ Focus on Communication rather than structure.
■ Develop communicative competence through
socially structured interaction activities.
■ Focus on meaningful tasks.
■ Collaboration
ADVANTAGES
■ Increased frequency and variety in classroom
interaction.
■ Possibility for the development of language,
cognitive and language skills.
■ Integrating content-based instruction.
■ Variety of materials to be used for stimulation
and/or concept learning. Possibility for the
development of language, cognitive and language
skills.
■ Opportunity for students to be more active in their
learning and to use each other as live resources.
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
■ Raise of achievement of all students.
■ Positive relationships among students.
■ Experience on healthy social, psychological, and cognitive
development.
■ Replace competition for cooperation.
■ Replace teacher-fronted lessons for student-centered.
■ Interactive pair and group activities.
■ Development of learning and communication strategies.
■ Reduce learners stress and create a positive affective classroom
climate.
ROLES of the LEARNER
■ Work collaboratively on tasks with other group
members.
■ Must learn teamwork skills.
■ Be directors of their learning (plan, monitor and
evaluate their own learning)
■ Learning requires student’s direct and active
involvement and participation
■ Alternate roles involve partners in the role of tutors,
checkers, recorders and information shares.
ROLE OF THE TEACHERS
■ Create a highly structured and well-organized learning environment in
the classroom.
Setting goals, planning and structuring tasks, establishing the physical
arrangement of the classroom, assigning students to groups and
roles, and selecting materials and time.
Be a facilitator of learning.
Move around the class and help the group as needs arise:
During the time, the teacher interacts, teaches, reinforces, refocuses,
questions, clarifies, supports, expands, celebrate and empathizes.
Teacher speaks less than in a teacher fronted class.
ROLE OF THE TEACHERS
■ Provide broad questions to challenge critical
thinking,
Prepare the students for the task they will
carry out.
Assist students with the learning tasks.
Give few commands, imposing less disciplinary
control.
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Jack and John and The Month of MarchDocument2 pagesJack and John and The Month of MarchJhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Piaget SMAW Class OfficersDocument2 pagesGrade 11 Piaget SMAW Class OfficersJhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument1 pageResumeJhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- Republic of The PhilippinesDocument1 pageRepublic of The PhilippinesDevina RivasNo ratings yet
- School Data at a GlanceDocument17 pagesSchool Data at a GlanceJhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- How Hare Asked For WisdomDocument1 pageHow Hare Asked For WisdomJhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- Figurative Language Poem 1 Sketch by Carl SandburgDocument1 pageFigurative Language Poem 1 Sketch by Carl Sandburgtauki63No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Vowels and ConsonantsDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Vowels and ConsonantsElizabeth Strings100% (6)
- Board Game Snakes Ladders With English Game Questi Fun Activities Games Games - 9951Document10 pagesBoard Game Snakes Ladders With English Game Questi Fun Activities Games Games - 9951Jhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- History of Las NievesDocument1 pageHistory of Las NievesJhong Floreta Montefalcon100% (1)
- Classroom Evaluation SheetDocument1 pageClassroom Evaluation SheetJhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- ProficientDocument12 pagesProficientOdie PenafloridaNo ratings yet
- Classroom Evaluation SheetDocument1 pageClassroom Evaluation SheetJhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- Paragraph Organization QuizDocument3 pagesParagraph Organization QuizJhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- Las Nieves HS Midterm ExamDocument1 pageLas Nieves HS Midterm ExamJhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- Attendance Sheet 2019Document24 pagesAttendance Sheet 2019Jhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- Ethical RealismDocument17 pagesEthical RealismJhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- ResearchDocument3 pagesResearchJhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing PresentationDocument8 pagesAcademic Writing PresentationJhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Management TheoriesDocument19 pagesEvolution of Management TheoriesJhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- Ethical Realism: SocratesDocument5 pagesEthical Realism: SocratesJhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- DO s2019 027 PDFDocument258 pagesDO s2019 027 PDFFharzaydpaul Langgal HassanNo ratings yet
- Purpose and Objectives of a BusinessDocument4 pagesPurpose and Objectives of a BusinessJhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- DoE Agusan del Norte Division Promotion RequirementsDocument2 pagesDoE Agusan del Norte Division Promotion RequirementsJhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- ProficientDocument12 pagesProficientOdie PenafloridaNo ratings yet
- Brigada Eskwela Slip 2018 Libertad National High SchoolDocument1 pageBrigada Eskwela Slip 2018 Libertad National High SchoolJhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- 1St Quarter Exam EAAPDocument8 pages1St Quarter Exam EAAPJhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- 4A of Lesson Planning PDFDocument1 page4A of Lesson Planning PDFMhaye CendanaNo ratings yet
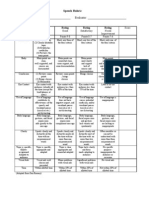
- Speech Rubric RevisedDocument1 pageSpeech Rubric RevisedVenoritaNo ratings yet
- 0995 - Division Memorandum No. 06, S. 2019Document4 pages0995 - Division Memorandum No. 06, S. 2019Jhong Floreta MontefalconNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Capitol University Medical Center PoliciesDocument5 pagesCapitol University Medical Center PoliciesCharles CagaananNo ratings yet
- Anna University Literature Review FormatDocument4 pagesAnna University Literature Review Formatea844bbv100% (1)
- Grade 12 Class Achievements for 2018-2019 School YearDocument3 pagesGrade 12 Class Achievements for 2018-2019 School YearRhaedenNarababYalanibNo ratings yet
- NLRB DocumentDocument55 pagesNLRB DocumentZoe GallandNo ratings yet
- The Big Five Personality Traits ExplainedDocument19 pagesThe Big Five Personality Traits Explainedashraul islamNo ratings yet
- SDG Primer Companion Textbook PDFDocument68 pagesSDG Primer Companion Textbook PDFAaron BareNo ratings yet
- Digital Transformation For A Sustainable Society in The 21st CenturyDocument186 pagesDigital Transformation For A Sustainable Society in The 21st Centuryhadjar khalNo ratings yet
- Statements of Purpose Guidelines and Sample EssaysDocument51 pagesStatements of Purpose Guidelines and Sample Essaysyawnbot botNo ratings yet
- Trends, Networks and Critical Thinking Skills in The 21st Century - TOPIC OUTLINEDocument3 pagesTrends, Networks and Critical Thinking Skills in The 21st Century - TOPIC OUTLINERodrick Sonajo Ramos100% (1)
- Cambridge O'level Principle of Accounts SyllabusDocument23 pagesCambridge O'level Principle of Accounts SyllabusTalhaRehman100% (1)
- Walled City of Lahore Authority - Wcla: S T NS T NDocument4 pagesWalled City of Lahore Authority - Wcla: S T NS T NSajidComsatsNo ratings yet
- Social Justice EducationDocument20 pagesSocial Justice EducationSean100% (1)
- The Snowy Day - Lesson Plan EditedDocument5 pagesThe Snowy Day - Lesson Plan Editedapi-242586984No ratings yet
- Basic Triangle Congruence Lesson PlanDocument1 pageBasic Triangle Congruence Lesson Planapi-219434647No ratings yet
- Management Traineeship Scheme Brochure PDFDocument6 pagesManagement Traineeship Scheme Brochure PDFShueab MujawarNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Entrepreneurial Background, Trait and Motivation 2.1 The Entrepreneurial BackgroundDocument13 pagesChapter Two: Entrepreneurial Background, Trait and Motivation 2.1 The Entrepreneurial Backgroundsami damtewNo ratings yet
- Berkeley Side: Magnes Collections Get New Downtown Berkeley Home, by Frances Dinkelspiel - 10.13.2010Document3 pagesBerkeley Side: Magnes Collections Get New Downtown Berkeley Home, by Frances Dinkelspiel - 10.13.2010magnesmuseumNo ratings yet
- Resume - CarlyDocument1 pageResume - Carlyapi-317491156No ratings yet
- UNIT-4 Performance ManagenmentDocument17 pagesUNIT-4 Performance Managenmentsahoo_pradipkumarNo ratings yet
- Holistic Teacher Development LAC SessionDocument2 pagesHolistic Teacher Development LAC SessionfrancisNo ratings yet
- Social Justice: Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Other Backward Classes, Minorities, and Other Vulnerable GroupsDocument36 pagesSocial Justice: Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Other Backward Classes, Minorities, and Other Vulnerable GroupsthegemishereNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 MAED 213Document1 pageQuiz 2 MAED 213Ramoj Reveche PalmaNo ratings yet
- 0452 s07 Ms 3 PDFDocument10 pages0452 s07 Ms 3 PDFAbirHudaNo ratings yet
- Menulis Paper Jurnal Ilmiah - M. Zaini MiftahDocument44 pagesMenulis Paper Jurnal Ilmiah - M. Zaini MiftahlinearsjournalNo ratings yet
- CUET Maths Domain Chapter Wise: MixedDocument19 pagesCUET Maths Domain Chapter Wise: MixedDivyansh Singh BaghelNo ratings yet
- The War That Never Was: Exploding The Myth of The Historical Conflict Between Christianity and ScienceDocument12 pagesThe War That Never Was: Exploding The Myth of The Historical Conflict Between Christianity and ScienceEduardo CruzNo ratings yet
- Arnis Traning Matrix 2023Document6 pagesArnis Traning Matrix 2023RA CastroNo ratings yet
- Problems Encountered by Teachers in The Teaching-Learning Process: A Basis of An Action PlanDocument20 pagesProblems Encountered by Teachers in The Teaching-Learning Process: A Basis of An Action PlanERIKA O. FADEROGAONo ratings yet
- Weiss Functional Impairment Rating Scale (Wfirs) InstructionsDocument3 pagesWeiss Functional Impairment Rating Scale (Wfirs) InstructionsMariana LópezNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report On The Division SeminarDocument3 pagesNarrative Report On The Division Seminarvincevillamora2k11No ratings yet