Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Arch - Tech.III - ROOFS.Pitched Roofs - Flat Sheets & Corrugated R. Const.
Uploaded by
yasin100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
52 views39 pagesOriginal Title
Arch.Tech.III.ROOFS.Pitched Roofs.flat sheets & Corrugated R. Const.
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
52 views39 pagesArch - Tech.III - ROOFS.Pitched Roofs - Flat Sheets & Corrugated R. Const.
Uploaded by
yasinCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 39
Roofs
A roof is a part of external envelope of a building. A main function of
a roof enclosing space and to protect from the external factors to
space it covers. A roof may be flat or pitched has a supporting
component as roof structure and consists of roof finishing and ceiling.
The complexity of a roof structure is related to the span required for
the building. The larger the span more complex the structure will be.
Roof structures often determine the form and covering (finishing) of
roofs. According to the form of structures, the type of the roofs are
filet or pithed.
– Pitched roofs:
Their slope (or pitch) range between 18 – 173 % (60°)
Types are single pitched, double pithed and with hipped end
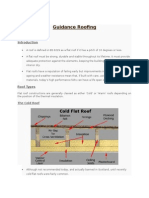
– Flat roofs
Their slope range between 01 – 10 %
Types are conventional-(warm) flat roofs, inverted roofs, cold roofs
– Curved roofs types are, barrel vaults, domes, hiperbolic paraboloids
Performance Requirements for Roofs (1)
Strength and stability
They are provided by the roof structure. The main considerations in the
design of roof structure is that of span. The wide variety of roof types in
different materials have been developped considering span of roofs as
the main criterion. The materials used are reinforced concrete, steel,
timber and reraly aluminum. The structural types generally imposed the
forms. The alternative roof structures are:
• Framed structures
– Reinforced concrete or steel framed structures with flat, ribbed or
grid roof deck
– Timber, steel and aluminum trusses and lattice girders
– Steel and timber space frames, and geodesic domes
• Form resistant structures as,
– Reinforced concrete folded plates and
– Reinforced concrete and steel shells as barrel vaults, domes and
hyperbolic paraboloids
• Suspension structures as tent, net and cable structures
In all types of structures, it is necessary to keep the dead weight to
a minimum, so that the imposed load can be carried with a greatest
economy of materials. Where spans are large, this weight factor is of
greatest importance.
Performance Requirements for Roofs (2)
Weather Resistance – Water Proofing
Roofings are required to prevent the entry of air togethet with water and
dust. To succed a satisfactory weather resistance – (water proofing)
certain materials are used. Suitable materials for waterproofing is selected
in accordance with slop (fall) of the roof. The following slops are used in
conjuction with the suitable materials:
– Suitable materials for flat roofs where the fall changes as 1.0 – 10.0 %
• Bituminous membranes with 1.5 – 4.0 mm thichness
• Plastics and rubber membranes with 1.0 – 2.0 mm thichness
• Mastic asphalt
– Suitable materials for the pitched roofs
• Lead, copper, zinc and Aluminum sheets - falls are 18 to 25 %
• Traditional clay tiles and concrete tiles – fall is 33 %
• Corrugated metal sheets as steel, Al., Zinc – falls are 18 - 40 %
• Corrugated plastics or cementeous materials – falls are 18 – 40 %
– Suitable materials for the curved roofs
• Bituminous and plastics membranes
• Leads coppers and Aluminum
Performance Requirements for Roofs (3)
Thermal Insulation
A roof transmittes heat through its body by conduction and also it
radiates heat from its surface to the clear sky where the temperature
is very low. Thus, an effective thermal insulation required to obtain
low enery loss as thermal transmittance (U-value) - 0.4 W/m2K.
Thermal insulation may be provided in a roof one of the four ways:
– A layer of insulation material is applied between roof structure and
impervious water proofing layer, as in the conventional warm roof.
– Layer of insulation material is applied between the rafters as in the high
pitched roof system, where attic rooms designed.
– Slabs of heavy insulation material placed externally to the whole roof
construction, which is reraly applied.
– Insulation may be obtained by mean of the resistance of the
construction of the roof substructure.
– An insulation is applied beneath the deck (as in the cold roof)
Most common method of thermal insulation is the first one for flat
roofs, and the second one for the high pitched roofs, if attic rooms is
designed as living space.
Pitched Roofs
A roof is a part of external envelope of a building. A main function of a roof
enclosing space and to protect from the external factors to space it covers. A
roof may be flat or pitched has a supporting component as roof structure and
consists of roof finishing and ceiling. The complexity of a roof structure is
related to the span required for the building. The larger the span more complex
the structure will be.
Roof structures often determine the form and covering (finishing) of roofs.
According to the form of structures, the type of the roofs are filet or pithed.
Pitched roofs:
Their slope (or pitch) range between 18 – 100 %
Types are single pitched, double pithed and double pitched with hipped end
fall
fall fall
Single pitched roof Double pitched roof Double pitched roof
with hipped end
Performance Requirements for Pitched Roofs
The complexity of a roof structure is related to the span required for the
building. A roof should meet the following performance requirements:
Performance Measures to meet performance requirements
requirements for Pitched Roofs
Strength and stability To have a high level of slop (pitch), either a truss or a
inclined concrete roof slab is required so the roof pithes
can be constructed from reinfoeced concrete slabs
Weather exclusion, Roof tiles are applied to drain about 95 % of rain water.
Avoid air penetration To remove the surplus water and avoiding air penetration
into the roof, water proofing membrane is applied over
timber boarding.
Thermal Insulation • Thermal insulation mats or boards are applied under
Avoid convective heat timber boarding, between the roof rafters, or
loos & air leakage • the thermal insulation is layed on the roof deck.
Avoiding the solar Seramic tiles, metals, bitumen membranes or aggregate
radiation effect, and applied as a roofing should be finished and colored to
Durability avoid color change, physical deterioration and keeping
quality during intended life span of roofing.
Weather Exclusion from Pitched Roofs
The rain penetration depends both on rain amount and wind
speed and is directly effected by rain intensity rather than total
duration of rain. This is of particular importance where the roof
coveing is tiles. This tipe of covering depends upon the
adequacy of the overlap of the units and the pitch of the roof.
When the angle is more than 30°, pressure occure in winward
side of the pitched roof and suction occures in leaward and
furthermore, if the pitche is less than 20° suction occures in
two side of the pitch.
Due to these facts, about 5 % of the rain water penetrates in
between the overlapped roof tiles. To avoid leakage of water
into the roof water proofing membranes should be applied on
the timber bording beneth the tiles.
You might also like
- Buildings' Envelope ElementsDocument17 pagesBuildings' Envelope ElementsAnnisyah Novitasari100% (1)
- Roof Design Principles: GenerallyDocument55 pagesRoof Design Principles: Generallyrcxy98No ratings yet
- Building Materials and Roofing GuideDocument51 pagesBuilding Materials and Roofing GuideRemya R Kumar100% (1)
- Building Roof and Its Functions (Psychological, Climatic and Structural) - Flat Roof and Pitched RoofDocument15 pagesBuilding Roof and Its Functions (Psychological, Climatic and Structural) - Flat Roof and Pitched RoofAnqa Parvez100% (1)
- Buildingmaterials 161105084923Document17 pagesBuildingmaterials 161105084923Glistering Dhar100% (1)
- 4 TYPES PITCHED ROOFSDocument38 pages4 TYPES PITCHED ROOFSisaacwabbi100% (3)
- Roof - Functional Purpose: BE - 1105 Building Design and Construction Lecture Note - 06Document11 pagesRoof - Functional Purpose: BE - 1105 Building Design and Construction Lecture Note - 06Ken Ingram100% (1)
- ROOFSDocument4 pagesROOFSRoshan Ram100% (1)
- Design Elements RoofDocument2 pagesDesign Elements Roofcrizel100% (1)
- Roofing Technology: Arch 173: Building Construction 2Document129 pagesRoofing Technology: Arch 173: Building Construction 2Shaheed Faruk100% (1)
- Flat Roof Types Guide - 40 CharacterDocument42 pagesFlat Roof Types Guide - 40 CharacterMujjo SahbNo ratings yet
- Roofs: Design ElementsDocument6 pagesRoofs: Design ElementsThe Ultimate Fun & Entertainment100% (1)
- AK RoofingDocument25 pagesAK RoofingSampat Kumar100% (1)
- Building Weather Cathedral Stadium Dwellings Rain Heat Sunlight Wind Conservatory VerandahDocument24 pagesBuilding Weather Cathedral Stadium Dwellings Rain Heat Sunlight Wind Conservatory Verandahdudynayn100% (1)
- BMC V - Unit-4-Advanced Construction Techniques and MaterialsDocument13 pagesBMC V - Unit-4-Advanced Construction Techniques and Materialsaurora krishreddyNo ratings yet
- 3.1.1 ROOFS: Unctional EquirementsDocument16 pages3.1.1 ROOFS: Unctional EquirementsSAMSON WERESON100% (1)
- Pitched RoofingDocument60 pagesPitched RoofingOmaidTanhaNo ratings yet
- Flat Roof - GFFDocument19 pagesFlat Roof - GFFwindyNo ratings yet
- Kle Institute of Technology, Hubli: Team MembersDocument12 pagesKle Institute of Technology, Hubli: Team MembersVijayanand PrajwalNo ratings yet
- Building SuperstructureDocument76 pagesBuilding Superstructurehamnahrico100% (20)
- IKO BUFR Design Guide Feb 2012Document40 pagesIKO BUFR Design Guide Feb 2012Deana WhiteNo ratings yet
- Construction Technology. 4th Sem CivilDocument12 pagesConstruction Technology. 4th Sem CivilZerro erANo ratings yet
- Roof Type and Treatments in High RiseDocument26 pagesRoof Type and Treatments in High RiseUzair SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- 12 Pitched RoofsDocument3 pages12 Pitched Roofshkalloli@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Roofs and Roofs TrussesDocument5 pagesRoofs and Roofs TrussesKatyayini Nelli100% (1)
- 2 - 3 Flat RoofsDocument20 pages2 - 3 Flat RoofsRohana MamatNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Roofing MaterialsDocument32 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Roofing MaterialsGerald PrimaveraNo ratings yet
- Dcq40172: Construction Economics (Report) : Dub4B December 2020 Puan Asmawati Bin Mohd YusopDocument13 pagesDcq40172: Construction Economics (Report) : Dub4B December 2020 Puan Asmawati Bin Mohd YusopMukhlis AR100% (1)
- 5.CE 315 - Chapter 2C - Roof Plan 3CE-2Document8 pages5.CE 315 - Chapter 2C - Roof Plan 3CE-2Mt KulisNo ratings yet
- The Functions and Classification of RoofsDocument6 pagesThe Functions and Classification of RoofsKevin De Silva86% (7)
- Roof Types & MaterialsDocument6 pagesRoof Types & MaterialsPratik Ghimire100% (1)
- Roofing SystemsDocument13 pagesRoofing SystemsMohamed Hisham100% (1)
- Flat RoofDocument9 pagesFlat RoofAdrian Mosquisa100% (1)
- Roof Slab SystemDocument42 pagesRoof Slab SystemGelyn Macasieb100% (1)
- TsehayDocument21 pagesTsehayMekuannint Demeke100% (1)
- Roof CoveringsDocument24 pagesRoof Coveringsdavid adawo100% (1)
- GFF - Flat Roof PDFDocument19 pagesGFF - Flat Roof PDFSêlva AvlêsNo ratings yet
- Exterior Walling System - Group No. - 04Document27 pagesExterior Walling System - Group No. - 04latika100% (1)
- Building Enclosures Exterior Building Materials: Madhav Institute of Technology and Science GwaliorDocument18 pagesBuilding Enclosures Exterior Building Materials: Madhav Institute of Technology and Science Gwalioratharvasaxena93No ratings yet
- Flat Roof:: The Construction Cost For RCC Roof Slab of Area 25 X 20 Is Approx. 20,000 RsDocument4 pagesFlat Roof:: The Construction Cost For RCC Roof Slab of Area 25 X 20 Is Approx. 20,000 RsSAURABH KUMAR SINGH100% (1)
- Construction TechniquesDocument8 pagesConstruction Techniquesarshi_raushan3427No ratings yet
- Heat Insulation: Submitted byDocument31 pagesHeat Insulation: Submitted byamishaNo ratings yet
- BCM 1 - Week 13 Roof SystemDocument57 pagesBCM 1 - Week 13 Roof SystemZEENAT YUSOF100% (1)
- RoofDocument55 pagesRoofRosele LabarreteNo ratings yet
- External Walls and RoofDocument101 pagesExternal Walls and Roofmmae64100% (1)
- Ventilated Facades Brochure LoRes2Document32 pagesVentilated Facades Brochure LoRes2Stroescu SilviuNo ratings yet
- Roof Coverings: Building MaterialsDocument38 pagesRoof Coverings: Building Materialssoniya bhandariNo ratings yet
- Industrial Building Architectural and Structural Design 1Document6 pagesIndustrial Building Architectural and Structural Design 1api-655156856No ratings yet
- Report On Structural System: Building Construction 1751 - Aparna PardhiDocument17 pagesReport On Structural System: Building Construction 1751 - Aparna PardhiVaishali PardhiNo ratings yet
- Roof Decks: Santiago, Gian Kennette HDocument21 pagesRoof Decks: Santiago, Gian Kennette HAnonymous pTZCrF7No ratings yet
- RoofsDocument17 pagesRoofsMUKABWA DEONE LUKASINo ratings yet
- Building Construction-V: Types of Metal CladdingDocument6 pagesBuilding Construction-V: Types of Metal CladdingShrish BaglaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Structural Systems Curtain Walls and Aluminium PanelsDocument89 pagesAdvanced Structural Systems Curtain Walls and Aluminium PanelssindhuraNo ratings yet
- Types of Roof Coverings and ElementsDocument10 pagesTypes of Roof Coverings and Elementsashenafi zerihunNo ratings yet
- Cladding For BuildingsDocument8 pagesCladding For BuildingsCaryl Louise ObcianaNo ratings yet
- Your Home Inspected: An Addendum for Residential Home Inspection ReportsFrom EverandYour Home Inspected: An Addendum for Residential Home Inspection ReportsNo ratings yet
- Reagentless Iron Detection in Water Based On Unclad Fiber Optical SensorDocument9 pagesReagentless Iron Detection in Water Based On Unclad Fiber Optical SensorTELKOMNIKANo ratings yet
- Pressure For Different Temperatures For Dimensions of Stainless Steel Welded Pipe and Seamless PipesDocument7 pagesPressure For Different Temperatures For Dimensions of Stainless Steel Welded Pipe and Seamless PipeswenigmaNo ratings yet
- CementDocument11 pagesCementAbubakar Musa100% (1)
- Fin Irjmets1658324268Document7 pagesFin Irjmets1658324268Raja MalluNo ratings yet
- Gaylee Saws / Bitner Tooling TechnologiesDocument36 pagesGaylee Saws / Bitner Tooling TechnologiesPuneeth KumarNo ratings yet
- Stas Week 16-17 Nano WorldDocument4 pagesStas Week 16-17 Nano WorldZyra PascualNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics - A-Level Physics Revision - XtremePapers - Com - The Best Place For Your Educational Needs.Document2 pagesThermal Physics - A-Level Physics Revision - XtremePapers - Com - The Best Place For Your Educational Needs.Sùpêr Stùd HämxãNo ratings yet
- en 13445 1Document9 pagesen 13445 1Saúl Domínguez NegreiraNo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry 1mark TestDocument6 pages12th Chemistry 1mark TestPons RathiNo ratings yet
- Application of Composites in InfrastructureDocument4 pagesApplication of Composites in InfrastructurekamranNo ratings yet
- H - M Guess Paper Chemistry 9TH 2024Document2 pagesH - M Guess Paper Chemistry 9TH 2024zianali2005No ratings yet
- Prepared by R. Sendil KumarDocument73 pagesPrepared by R. Sendil KumarRGNo ratings yet
- Titanvene Lldpe-LctnDocument4 pagesTitanvene Lldpe-LctnRifan HarfaniNo ratings yet
- Boq For The WarehouseDocument19 pagesBoq For The Warehousessembatya reagan100% (2)
- Clear Edge Solid Reduction Final LetterDocument3 pagesClear Edge Solid Reduction Final Letterbalachandar thavamaniNo ratings yet
- REINFORCED CONCRETE DESIGN FEU CORRELATION COURSEDocument4 pagesREINFORCED CONCRETE DESIGN FEU CORRELATION COURSEJosephbraken Balderama Labacanacruz100% (1)
- 29 IM 240DNE XNE Service ManualDocument83 pages29 IM 240DNE XNE Service ManualSenen Geraldino JrNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends AssignmentDocument4 pagesPeriodic Trends AssignmentFarhan HabibzaiNo ratings yet
- Delegate List - 10th IMRC With Contact Details (2) - Removed - RemovedDocument134 pagesDelegate List - 10th IMRC With Contact Details (2) - Removed - RemovedSharon SusmithaNo ratings yet
- Shigley Mechanical Engineering DesignDocument18 pagesShigley Mechanical Engineering DesignNishanth MudkeNo ratings yet
- BS 5500 Appendix K and DDocument14 pagesBS 5500 Appendix K and DCRISTIAN SILVIU IANUCNo ratings yet
- From Feedstocks To Final Products: Biomass ConversionDocument4 pagesFrom Feedstocks To Final Products: Biomass ConversionJoshi kartikNo ratings yet
- 3M 6000 Full Face Mask-Data SheetDocument5 pages3M 6000 Full Face Mask-Data SheetMichael TadrosNo ratings yet
- Lame ConstantsDocument2 pagesLame ConstantsAldi NurseptaNo ratings yet
- Polypropylene - Chemistry and Production ProcessesDocument45 pagesPolypropylene - Chemistry and Production Processeschiuchan888No ratings yet
- Pre Heat & PWHT of PipingDocument2 pagesPre Heat & PWHT of PipingHarish GandhiNo ratings yet
- 2 Caterpillar Drive Chain PDFDocument1 page2 Caterpillar Drive Chain PDFwaseemNo ratings yet
- Leaching and Solid-Liquid SeparationDocument5 pagesLeaching and Solid-Liquid SeparationJackNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Imperfection in SolidDocument50 pagesChapter 4 Imperfection in SolidNik AthikahNo ratings yet
- WorkoutDocument2 pagesWorkoutWei Shen100% (1)