Professional Documents
Culture Documents
History of The Atomic Model
Uploaded by
mrkhan95Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
History of The Atomic Model
Uploaded by
mrkhan95Copyright:
Available Formats
(From 400 BC to the Present)
By: Shabaz Khan
Atom(Noun) A unit of matter, the smallest unit of an element Consisting of a dense, central, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a system of electrons, equal in number to the number of nuclear protons
This Greek philosopher had an early atomic theory stating that
All matter is made up of atoms Atoms are eternal and invisible So small that they cant be divided, and they entirely fill up the space theyre in
An English chemist/physicist, formed the first modern atomic theory, stating that:
All elements are composed of tiny individual spheres Atoms of the same element have the same properties Atoms combine in whole number ratios to form compounds Atoms rearrange when undergoing chemical reactions
His atomic theory has been modified over the years especially with the discovery of subatomic particles, atoms in matter, and how atoms of one element differ from atoms of another
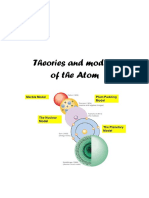
Daltons Model -Tiny, solid sphere
British physicist, who discovers the electron and developed the plum-pudding model of the atom
Pictures electrons embedded in a sphere of positive electrical charge
Japanese physicist, who suggested that an atom has a central nucleus
Electrons move in orbits like the rings of Saturn (Saturnian model) Pursued his theoretical model as a tool to account for the interactions of atoms, radioactivity, etc.
A New Zealand physicist, Ernest finds out that an atom has a small, dense, positively charged nucleus in a ball at the center of the atom
Used the results of his gold-foil experiment to formulate/back this discovery and his model Stated that the electrons orbited the nucleus in a manner like the solar system (Planets orbiting the Sun)
A Denmark physicist, who was working off Rutherfords concept of the atom, stated that the electrons moved around the nucleus at fixed distances
Bohr atomic model stated that atoms absorb or emit radiation only when the electrons abruptly jump between allowed, or stationary states
A French physicist, who hypothesized that the electrons in Bohrs model were confined to discrete orbits because they had properties of waves
Cornerstone of quantum mechanics He proposed a theory called the Principle of Complementarity (States that waves and particles represent complementary aspects of the same phenomenon)
An Austrian physicist, who introduced the Schrdinger Equation, a wave equation that describes the motion of electrons in atoms
His mathematical equations leads to his electron cloud model
An English physicist, who discovered the existence of neutrons, particles that have no charge
Atomic nuclei contains neutrons alongside with positive charged protons
Book:
Wilbraham, Staley, Matta, Waterman. Chemistry. Boston: Prentice Hall, 2008.
Web:
o www.cerritos.edu/ladkins/a106/abriefhistoryoftheato m o www.scientificweb.com/en/physics/biographies/hanta ronagaoka o www.hi.fi.tripod.com/timeline o www.nobeliefs.com/atom.htm o www.google.com
You might also like
- 3 Discovery of The Subatomic Particles - Atomic ModelsDocument41 pages3 Discovery of The Subatomic Particles - Atomic ModelsFranchesca De los SantosNo ratings yet
- As We All KnowDocument6 pagesAs We All KnowOmlean JairusNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document9 pagesLesson 2Mary Ann Elacion AballaNo ratings yet
- History of Atomic Theory NotesDocument22 pagesHistory of Atomic Theory Notesapi-281924829No ratings yet
- Atomic TheoryDocument5 pagesAtomic TheoryasharaqueenNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument17 pagesAtomic StructureVandana Khator100% (1)
- Material AssignmentDocument12 pagesMaterial AssignmentsteveNo ratings yet
- Chem ProjectDocument29 pagesChem ProjectMohammad Osama anasas aliNo ratings yet
- How The Ideas of The Atom, Along With The Idea of The Elements EvolvedDocument50 pagesHow The Ideas of The Atom, Along With The Idea of The Elements EvolvedChosen ExeNo ratings yet
- De Up of Three Particles: Protons, Neutrons and Electrons. ProtonsDocument5 pagesDe Up of Three Particles: Protons, Neutrons and Electrons. ProtonsAngelita13 ManaliliNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory: A Brief HistoryDocument61 pagesAtomic Theory: A Brief HistoryAbid Al RezaNo ratings yet
- 12 Chem Structures NotesDocument27 pages12 Chem Structures Notes34253647564No ratings yet
- History of The Atom - With TimelineDocument24 pagesHistory of The Atom - With Timelineapi-271621209100% (1)
- Atomic StructureDocument91 pagesAtomic StructureUmmu juraijNo ratings yet
- Atoms 3rd TopicDocument36 pagesAtoms 3rd TopicReynalie BotonNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 4Document4 pagesPhysical Science Week 4Alona Cello ParagesNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Review: Chemistry Unit 2 Mr. PaskowitzDocument14 pagesAtomic Structure Review: Chemistry Unit 2 Mr. Paskowitzapasko1No ratings yet
- Atomic SructuresDocument2 pagesAtomic SructuresChinee FloresNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS ReviewerDocument29 pagesPHYSICS ReviewerKarla YasaNo ratings yet
- Theories and Models of The AtomDocument13 pagesTheories and Models of The AtomAlex Omunga100% (2)
- Module 4 - Ict 1 11 6 1Document3 pagesModule 4 - Ict 1 11 6 1JHED HULAR CONDENo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 2nd QTRDocument23 pagesScience Reviewer 2nd QTREl GamezNo ratings yet
- ATOMIC HISTORY AND MODEL LlectureDocument2 pagesATOMIC HISTORY AND MODEL LlectureSherchen Antonio-CortesNo ratings yet
- Atomic Models and TheoryDocument23 pagesAtomic Models and TheoryKhair TaupNo ratings yet
- Q2-W1 Quantum ModelDocument22 pagesQ2-W1 Quantum Model渡辺正平No ratings yet
- Dalton's Atomic TheoryDocument5 pagesDalton's Atomic TheoryKeanneMarieJandusayNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelsDocument26 pagesAtomic ModelsFlitcher Diane PilotonNo ratings yet
- Contributions of Philosopher Sin Relation To Atom.Document23 pagesContributions of Philosopher Sin Relation To Atom.Moriel Barrogo BequilloNo ratings yet
- Name: Frances John Salo 9-Aguho ScienceDocument5 pagesName: Frances John Salo 9-Aguho ScienceHelloItsXp TiongsonNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelsDocument10 pagesAtomic ModelsMuhammad SamyNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelsDocument35 pagesAtomic Modelsrinlacer100% (1)
- Science Lesson: Ms. Ellaine Jennica B. FantilananDocument17 pagesScience Lesson: Ms. Ellaine Jennica B. FantilananRuger FloresNo ratings yet
- 1 Atomic IntroDocument34 pages1 Atomic Introapi-273966469No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Lecture1Document82 pagesAtomic Structure Lecture1JUDITH TEMBONo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanical Model of The Atom C12-2-04Document11 pagesQuantum Mechanical Model of The Atom C12-2-04Lisabel FactorNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atoms 3and4Document18 pagesStructure of Atoms 3and4Emperical FlameNo ratings yet
- Physical Science ReviewerDocument8 pagesPhysical Science ReviewerAliana FemiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document23 pagesChapter 1Alemayehu MamoNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesAtomic StructureAl MubarakNo ratings yet
- CHM 101 (Electronic Configuration)Document22 pagesCHM 101 (Electronic Configuration)ogedengbed28No ratings yet
- (De Dios) Science ProjectDocument22 pages(De Dios) Science ProjectRoucyzle Ynnah AcidoNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Atom 5. Electrons in AtomsDocument20 pagesThe Structure of The Atom 5. Electrons in AtomsLore WheelockNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 y 5Document20 pagesChap 4 y 5Lore WheelockNo ratings yet
- SCH 100 L1Document7 pagesSCH 100 L1nickmcklin7No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure 1695 Converted 1 77Document9 pagesAtomic Structure 1695 Converted 1 77Sanjana DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules and IonsDocument3 pagesAtoms, Molecules and IonsHayaNo ratings yet
- History of Atomic TheoryDocument38 pagesHistory of Atomic TheorylovelyshaneibrahimNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelsDocument13 pagesAtomic Modelsmax mishraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 AtomsDocument98 pagesChapter 3 AtomsAriana cruzNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesAtomic StructureDileep KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note - Atomic StructureDocument10 pagesLecture Note - Atomic StructureJojimar JulianNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - Discovery of Subatomic ParticlesDocument6 pagesAtomic Structure - Discovery of Subatomic ParticlesDivyansh DangiNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Atomic Theory: ObjectivesDocument19 pages1.1 Atomic Theory: ObjectivesEyad AymanNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom ProjectDocument21 pagesStructure of Atom ProjectJaisam JNo ratings yet
- ATOMS: Development of The Atomic Theory DemocritusDocument3 pagesATOMS: Development of The Atomic Theory DemocritusEros ErosNo ratings yet
- Not Indivisible (The Structure of Atom)Document15 pagesNot Indivisible (The Structure of Atom)Sheena DalguntasNo ratings yet
- Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesAtomic Theorybinaroth03No ratings yet
- Atoms and PeriodiciDocument19 pagesAtoms and PeriodiciAbhishek SivanNo ratings yet
- Elementary Particles : The Building Blocks of the Universe - Physics and the Universe | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandElementary Particles : The Building Blocks of the Universe - Physics and the Universe | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- OnTownsends Discharge in GasesDocument10 pagesOnTownsends Discharge in Gaseshodeegits9526No ratings yet
- Conservation of MomentumDocument23 pagesConservation of MomentumPauling ChiaNo ratings yet
- Wärtsilä Development & Financial ServicesDocument6 pagesWärtsilä Development & Financial ServicesdivyeshbalarNo ratings yet
- Small Scale Biogas DigesterDocument56 pagesSmall Scale Biogas DigesterCODE0303456No ratings yet
- Physics Ss3 MockDocument2 pagesPhysics Ss3 MockOba Fred AjubolakaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document14 pagesUnit 4amsk24_24No ratings yet
- Topic 1 The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument24 pagesTopic 1 The Particulate Nature of MatterNorazian Binti TaatNo ratings yet
- 1-S2.0-S0360128515300149-Main Imp PDFDocument40 pages1-S2.0-S0360128515300149-Main Imp PDFSuresh ChinniNo ratings yet
- Zero Energy Building Project in IndonesiaDocument6 pagesZero Energy Building Project in IndonesiaIkki VqNo ratings yet
- AP Physics: Algebra Based - Study GuideDocument67 pagesAP Physics: Algebra Based - Study GuideThomas LaiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Bohrs ModelDocument2 pagesAtomic Bohrs ModelUday Prakash SahuNo ratings yet
- Powermag201004 2 DLDocument76 pagesPowermag201004 2 DL3319826No ratings yet
- Atom Project With RubricDocument7 pagesAtom Project With Rubricapi-249777358No ratings yet
- Status of Small Hydro and Micro Hydro - Country Presentation NepalDocument43 pagesStatus of Small Hydro and Micro Hydro - Country Presentation Nepalpashupati814848No ratings yet
- ABB PMS SolutionsDocument5 pagesABB PMS Solutionsdennisraj1No ratings yet
- Phy400 Lab 3Document7 pagesPhy400 Lab 3Anonymous 5LtOddNo ratings yet
- Green Smith BrochureDocument5 pagesGreen Smith BrochureBharadwaj_Vasu_7233No ratings yet
- HK I TermodinamikaDocument21 pagesHK I TermodinamikaPutri Desty AmeliaNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat To Power ApplicationsDocument10 pagesWaste Heat To Power ApplicationsArul PrakashNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Work & EnergyDocument83 pagesCH 4 Work & EnergyAadil KhanNo ratings yet
- Particle PhysicsDocument6 pagesParticle PhysicsTeka KamNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Weight and MassDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Weight and MassDeep DebnathNo ratings yet
- Flamingo ChillersDocument1 pageFlamingo Chillerssaurabhkumar0664No ratings yet
- Eeg 1 en Forweb PDocument56 pagesEeg 1 en Forweb PBudihardjo Sarwo SastrosudiroNo ratings yet
- Power and Industrial Plant Engineering By:AlcorconDocument126 pagesPower and Industrial Plant Engineering By:AlcorconNelson Naval Cabingas77% (13)
- Trends in The Periodic TableDocument41 pagesTrends in The Periodic TableLachlan EllisonNo ratings yet
- Summary of Blended Coal FeedingDocument3 pagesSummary of Blended Coal FeedingS V NAGESHNo ratings yet
- Profile of Albert EinsteinDocument4 pagesProfile of Albert Einsteinfirstman31No ratings yet
- Lab 1 CalorimeterDocument4 pagesLab 1 CalorimeterAndrian NasirNo ratings yet
- Sunny Island Off GridDocument32 pagesSunny Island Off Gridmat_pranNo ratings yet